Bio eye parts
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO HNS EYE FLASH CARDS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
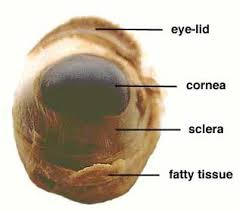
Cornea
Clear curved front layer of the eye that protects it and helps focus light.
Cornea function
Refracts (bends) incoming light
What’s special about the cornea in a sheep eye?
Cloudy in preserved specimens (non-living); transparent in living eyes.
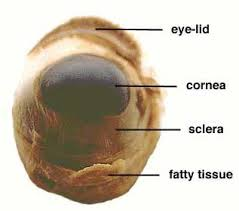
Sclera
The tough, white outer layer of the eye (“white of the eye”).
What’s the sclera’s function?
Protects the inner eye and maintains its shape.
Sheep eye note for sclera?
Very tough and hard to cut; helps identify the outside layer.
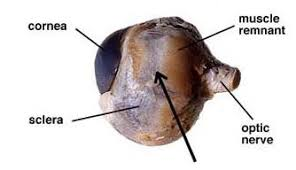
Optic Nerve
The bundle of nerve fibers that carries visual information from the retina to the brain.
Function of the optic nerve?
Transmits electrical signals from photoreceptors to the visual cortex.
What’s at the start of the optic nerve?
The optic disc (blind spot), where there are no photoreceptors.
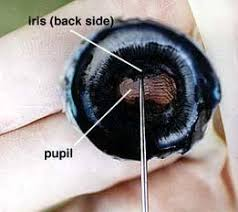
Iris
The colored part of the eye that controls pupil size.
Function of the iris?
Muscles adjust the pupil to regulate how much light enters the eye.
Sheep vs human iris?
Sheep iris surrounds an oblong pupil; human iris surrounds a circular pupil.
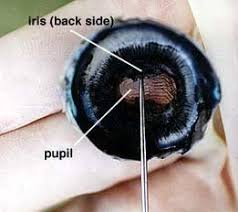
Pupil
The black opening in the center of the iris that lets light enter the eye.
Function of the pupil?
Expands or contracts to control light intake.
Sheep vs human pupil?
Sheep pupil is oblong (horizontal); human pupil is round.
Suspensory Ligament
Fibers that hold the lens in place and connect it to the ciliary body.
Function of suspensory ligaments?
Adjust the lens shape for focusing (tighten or loosen as muscles contract).
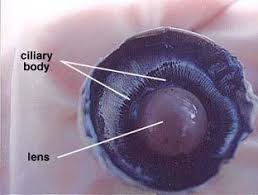
Ciliary Body
A ring of smooth muscle and tissue behind the iris.
Function of the ciliary body?
Controls the lens shape (focus) and produces aqueous humor.
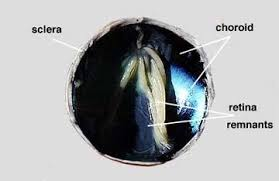
Choroid
The dark, middle layer of the eye between the sclera and retina.
Function of the choroid?
Contains blood vessels that nourish the retina; absorbs stray light.
Special feature in sheep?
Contains the tapetum lucidum, a shiny reflective layer for night vision.
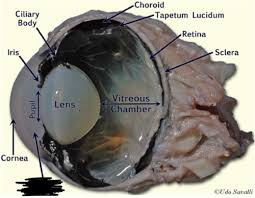
Tapetum Lucidum
Iridescent reflective layer in the choroid of nocturnal animals.
Function of tapetum lucidum?
Reflects light back through the retina to improve night vision.
Human vs sheep?
Humans do NOT have a tapetum lucidum; sheep do.
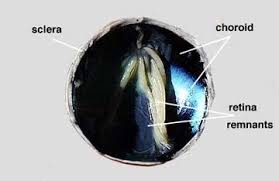
Retina
The thin inner layer at the back of the eye containing photoreceptor cells.
Function of the retina?
Converts light into electrical signals sent to the brain via the optic nerve.
What are the two types of photoreceptors?
Rods (light/dark) and cones (color).
Where is the retina attached?
Firmly attached only at the optic disc (blind spot).
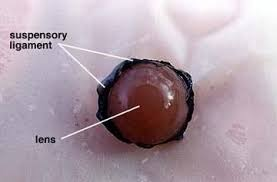
Lens
A clear, flexible, convex structure behind the iris and pupil.
Function of the lens?
Focuses light onto the retina by changing shape.
What happens when the lens becomes cloudy?
Cataract forms, blocking or reducing light to the retina.
Shape and feel in sheep eye?
Hard, marble-like or bean-shaped.
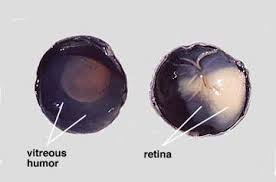
Vitreous humor?
The clear, gel-like fluid filling the space between lens and retina.
Function of the vitreous humor?
Maintains eye shape and holds the retina in place.
Difference from aqueous humor?
Aqueous humor is watery and in front of the lens; vitreous humor is gel-like and behind the lens.