executive branch & bureaucracy
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
list all articles
lazy elephants jump slowly and sleep regularly - legislative, executive, judicial, states reserved powers, amendments/amending the constitution, supremacy, ratification
which article is about the executive branch?
article 2
requirements to become president
Natural-born citizen
at least 35 years old
Resident for at least 14 years prior to taking office
formal powers of the president (+ define “formal powers”)
= explicitly given in Constitution
Commander-in-Chief
Issue pardons (legal forgiveness for a federal crime) & reprieves (temporary postponement or delay in implementing a criminal sentence) - ex. Nixon given pardon by Ford
Appoints ambassadors, cabinet members, judges (SCOTUS & lower court), etc
Veto or approve bills (SVDp²)
Convenes congress meetings
informal powers of the president (+ define “informal powers”)
= inherent (not stated in const.) or given by Congress and/or Courts over time
negotiating treaties
running federal bureaucracy (implements/enforces laws passed by Congress & signed by Pres)
signing statements
Bully Pulpit
executive orders
Define Bully Pulpit
president's use of their highly well known position/platform to influence public opinion to apply pressure other branches of government and/or shape national conversation - key concept in presidential communication, showing how the president leverages the prestige of their position to advocate for policy and rally public support
4 presidential roles
Chief Legislator
Commander-in-Chief
Chief Diplomat
Chief Executive & Administrator
Chief Legislator
Recommends legislation (ex. at SOTU address)
Power of Persuasion —> Bully pulpit
Veto power (pocket veto)
pocket veto
line-item veto
Power of Persuasion (+ what pres role does this come from?)
as Chief Legislator — Pres can address AM citizens directly to influence policy, secure public support, and achieve legislative goal/policy (if passing smtn through Congress will be difficult; aka Bully Pulpit w/ applying pressure on another branch)
Pocket Veto
an indirect veto of a legislative bill by the president by not acting on the bill for more than 10 days and Congress is not in session — done to not be associated w/ bill
Line-Item Veto
Pres are able to veto a specific line, part, or section of budget spending from an appropriations bill —declared unconst. after Clinton v. NYC —> only gov can do now
Commander-in-Chief (+what act relates to this role?)
some discretion in using military force
only Congress can declare war
changing world led to expansion of this power
ex. wars w/o declaration like Cold War, War on Terror, Iraq Wars, Vietnam War attacks
War Powers Act of 1973
War Powers Act of 1973 (+ what pres role did this affect?)
enforced after Pentagon Papers — limited Pres ability to use military force w/o Congress’s consent
60-day window of military force allowed w/o declaration
must notify Congress 48 hrs after deploying forces for approval & continuation
Chief Diplomat
guides foreign policy & negotiates treaties (not legally binding until 2/3 senate approves though)
Treaty of Versailles 1919
Executive Agreement: non-binding agreement w/ foreign officials
Executive Agreement
Pres as Chief Diplomat — a non-binding, international agreement b/w the US Pres & foreign official that does not require Senate approval
exists to overcome difficulties of Senate oversight —> made more quickly & flexible
ex. Limited Test Ban Treaty of 1963 by Kennedy & Nikita Khrushchev during Cuban Missile Crisis
Can be overturned by future Pres
ex. Iran Nuclear Deal 2015 (limit Iran's nuclear program in exchange for sanctions relief)
Chief Executive & Administrator
President & their cabinet appointees (can be fired by only executive) are responsible of enforcing or implementing new laws to help shape their policy agenda (interpretation)
Executive Orders
Administrator powers
Signing Statements
Executive Privilege
Define Executive Orders
kinda legislative power that allows Pres direct policy implementation or action w/o consulting w/ Congress
Ex. Executive Order 9066 w/ mass incarceration of Japanese-Americans
Cannot be used to address Congress’s enumerated powers (stated in const.)
Ex. change tax policy, interstate commerce clause laws
Signing Statements
written comments issued by a President when signing legislation into law used to state their interpretation of it —> how they intend to enforce it
gives some freedom to Pres
Executive Privilege
Pres’s right to withhold certain info from other branches or public to protect confidentiality
ex. discussions or conversations they have had
doesn’t count when Pres is charged w/ crime —> ex. US v. Nixon w/ Watergate
causes of the rise of imperial presidency (centralization of pres power)
personalities & popularity (ex. jackson)
national crisis (civil war, vietnam, cold war/fear of communism, war on terror, world wars)
the US emerging as a world power (enhancing power in foreign affairs) —> imperialism
increased executive control over the legislative process
which president did the most to expand the power of the pres (and how?)
FDR
broke washington’s term precedent —> 22nd amdt
attempt to pack the court for his New Deal
Executive Order 9066 (internment of japanese americans)
wars powers act of 1973
limited pres power to send forces internationally and declare war w/o senate consent
48 hrs to notify Congress of sending troops
60 day window for congress to vote on whether to continue or remove military deployment
how is the pres the “Communicator-In-Chief”? (+ examples)
he is more well known and can communicate easier with the US people compared to other branches
State of the union addresss
TR & bully pulpit
FDR & Fireside Chats
Press secretary
Social media
3 parts of the white house staff
Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
Chief of Staff — access to Pres “gatekeeper,” close advisor on policy & politics managing the Pres’ schedule
National Security Council — CIA + other intelligence chiefs, sec of state & def, & top officers of the military
Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
creates budget each year to be passed by Congress
the cabinet
total of 15 principal secretaries that advice the Pres & run the executive departments—appointed by pres to carry out policy agenda
state department
oldest; focuses on US foreign policy & international relations
ex. negotiates treaties; represents the U.S. in international organizations like the United Nations; protects American interests and citizens abroad; issuing passports and visas
ambassadors for each country (appointed by pres)
2/3 are professional diplomats (worked their way up)
1/3 are political appointees (political connections or aided pres)
defense department
responsible of military force & national security; civilian overseers of the military section/aren’t active in military (prevent dictatorship, bias, risk of capture)
federal agencies
subcabinet organizations that carry out specific govt functions
often part of larger department
except independent agencies
ex. FBI (Justice Dept), Coast Guard (Homeland Sec)
federal bureaucracy tasks & duties
vast hierarchical organizations of executive branch employees
“Discretionary Rule Making” — power to interpret and create laws & binding regulations to enforce public policy; ex. EPA’s Clean Water Act
Enforcing & Fines — can impose fines and other punishments to industries or companies that violate policies; ex. Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill
Testifying before Congress — make sure they’re doing their job
independent agencies
has unique but evolving powers to enforce or regulate industry; not under a cabinet department; board of 5-7 ppl (compared to 1 person); staggered terms to prevent presidential control; ex. CIA, EPA, NASA
ways federal bureaucracy implements the law
creating agencies to pay subsidies (sum of money granted by the government to assist an industry or business so that the price of a commodity or service may remain low or competitive)
grant system for giving $ to states (grants)
regulatory authority — ex. EPA define emission standards or Compliance Monitoring
Delegated Discretion Authority
Congress allows agencies the power to interpret legislation, create specific rules/policies, and implement them immediately — ex. EPA & Clean Air Act
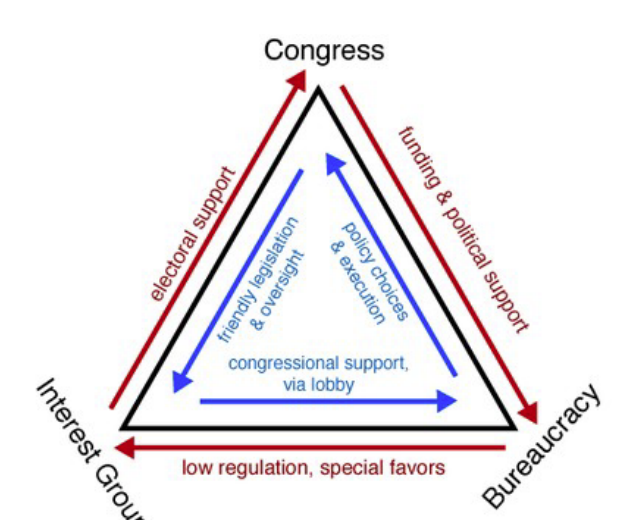
Iron Triangles
mutually beneficial relationship b/w agencies, Congress, & interest groups who work tgtr to create policies
most influential VP?
Dick Cheney for Pres George W Bush
National Security Council (NSC)
advises the Pres on national security and foreign policy
are bureaucrats appointed by pres?
no
departments vs. independent agencies
departments
led by 1 cabinet secretary
more politically influenced
broad control & mandates
independent agencies
more autonomy (free from political pressure w/ staggered terms)
led by 5-7 member board
specialized functions
iron triangles v. issue networks
two models of policymaking relationships, but differ in structure and stability
iron triangle — long-term, stable alliance for mutual benefit
issue network — looser, more temporary coalition of various actors (including academics, lobbyists, think tanks, media, and government officials) who form around a specific policy issue
often competing/opposing interests
What caused the change from spoils system & patronage —> merit system? (what act resulted)
Death of Pres Garfield after guy wasn’t hired for supporting his presidency —> Pendleton Civil Service Act of 1883
set up modern federal bureaucracy w/ civil service commission
Pendleton Civil Service Act of 1883
replaced the patronage-based "spoils system" w/ a merit-based system for government jobs, requiring candidates to pass open, competitive examinations and be qualified
Civil Service Reform Act 1978
diversified government (not like Wilson), set merit-based hiring, changed firing practices, & greater oversight to prevent political influence & patronage
Congressional Oversight
Congress's power to review, monitor, and supervise the implementation of public policy by the executive branch (bureaucracy) to ensure laws are faithfully executed, public interests are served, and to prevent waste, fraud, or abuse.
ex. Committee Hearings, conducting investigations, reviewing agency reports
House’s Power of Purse authorizes and checks spending
Presidential oversight (how does the Pres do this & what agency does this too?)
power of the Pres to supervise executive agencies and ensure that laws are being faithfully implemented and carry out agenda
Office of Information & Regulatory Affairs (OIRA)
appoints officials & issues orders to the bureaucracy to fulfill agenda
Office of Information & Regulatory Affairs (OIRA)
part of OMB (office of management & budget) reviews proposed federal regulations from agencies/departments to ensure they align with the president's priorities/agenda
how does Congress maintain oversight/keep the bureaucracy in check?
Final say through Committee Clearance (background check, action approval, establishments)
prior: legislative veto (struck down by SC decision in INS v. Chadha)
how do the Courts maintain oversight/keep the bureaucracy in check?
sometimes overlap in prosecution of offenders in criminal trials
challenges to agency actions carried out in federal court from court decisions — "US Circuit Court of Appeals”
courts used to support independent agency decisions
whistleblower protection act of 1989
protects government employees from retaliation when they report wrongdoing, such as fraud, waste, and abuse, within their agencies; excludes when national — ex. watergate