Hit to lead activities
What are hit to lead activities used for?
- Activity on other species
- Secondary phenotypic assays
- In-vitro DMPK, P450
- Lead selection
- Reiterative chemistry and in-vitro assays
- P450, Cli, liability assays
What are the key properties to consider when conducting hit to lead activities?
o Aqueous solubility – target value is >100µM
§ This is important for running in-vitro assays and for in-vivo delivery of the drug
§ Drug needs to be able to reach the minimum effective plasma concentration
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are hit to lead activities used for?
- Activity on other species
- Secondary phenotypic assays
- In-vitro DMPK, P450
- Lead selection
- Reiterative chemistry and in-vitro assays
- P450, Cli, liability assays
What are the key properties to consider when conducting hit to lead activities?
o Aqueous solubility – target value is >100µM
§ This is important for running in-vitro assays and for in-vivo delivery of the drug
§ Drug needs to be able to reach the minimum effective plasma concentration

What are the different solubility levels
Higher the ml/g, the less soluble
What is the target lipophilicity in hit to lead activities?
o LogD) – target value is 0-3 (lower means more likely to cross BBB)
§ Measures the movement of a compound across membranes
If lipophilicity is too high, it will not be soluble enough
What is the microsomal stability target in hit to lead activities?
o target value <30 µL/min/mg protein
§ This measures the compound clearance via liver in-vivo
What is the target CYP450 inhibition target for hit to lead activities?
o target value >10µM
§ This is the main enzyme which metabolises drugs, and its inhibition can cause toxicity via accumulation of the drug tested and other drugs
What is the Caco-2 permeability (Papp) target in hit to lead activities?
o target value >1x10^-6 cm-1 (asymmetry <2)
§ Caco-2 colon carcinoma cell line is used to estimate the permeability across the intestinal epithelium
§ Important for measuring drug absorption from the gut
What is the MDR-1MDCK permeability (Papp) target in hit to lead activities?
o target value >10x10_6cm-1 (asymmetry <2)
§ MDCK cells transfected with the MDR1 gene encodes the efflux protein P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which can be found in the intestine, kidney and brain
§ P-gp presence can be used to predict intestinal and brain permability
What is the G2 hepatoxicity target in hit to lead activities?
o target value : no effect at 50 x IC50 or EC50
Human HepG2 cells can be the cause for effects of toxicity on human liver, which can be the cause of drug failure in the clinic
What is the cytotoxicity in suitable cell line target in hit to lead activities?
o target value : no effect at 50 x IC50 or EC50B
§ Reduces the likelihood of cellular toxicity in-vivo
What do hit compounds look like?
- Functional groups are arranged around a central core or scaffold
- The core will usually be flat, rigid and heteroaromatic
What is the importance of a heterocyclic core?
o Related to the rapid synthesis of analogues
o Allows for easy alterations of R groups, which can be used to fine-tune the properties of the drugs
o If a certain chemical space has been patented, the pharmacophore can be slightly modified to work around it (regardless of indication
�
What is the criteria for hits?
- Reproducible in-vitro affinity/efficacy
- Favourable properties (cLogP, pKa, aqueous solubility, molecular weight etc)
- Chemical tractability – relatively easy to synthesise
- Evidence that related compounds retain activity (not a false positive)
- Patentable structures or a strategy to enhance chemical novelty
No significant toxicity alerts from the compound or known metabolite
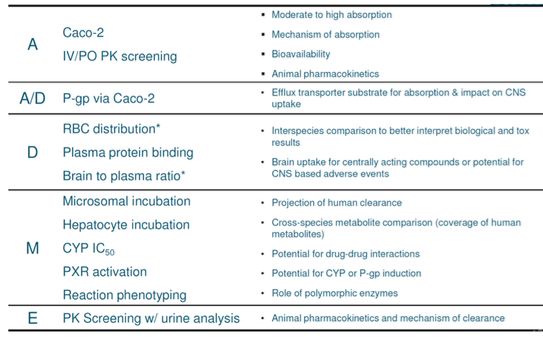
Describe how to assess druggability in hits (DMPK properties)
What is a measure of intestinal absorption. Describe it
- Caco-2 is an evaluation of intestinal absorption
o Most absorption occurs in small intestine, although some may occur in the small intestine
o In Caco-2, compounds are incubated on the apical side of the monolayer of Caco-2 cells in the gut
o After a set amount of time, the basolateral side is sampled and analysed
o Permeability is expressed as Papp
o Papp>10^-6cms-1 should correspond to good in-vivo absorption (higher means more permeable)
What is plasma protein binding?
- high binding will affect the dose, drug half-life and have safety implications
o PPB is expressed as fu (fraction unbound)
o If the fu is too high, it will limit diffusion to the site of action (good thing)
o Fu>90% is preferred
o If the drug is safe, the dose can be increased so that more unbound drug is available to be used
What is the criteria for the hit to lead phase?
- Improved affinity/efficacy
- Selective over related target by over 100-fold
- PPB, CYP inhibitor induction and hERG profiles are acceptable
- Selectivity over non-related targets
- Efficacy in an animal model shows dose-response relationship
- No toxicity or mutagenicity at an efficacious dose
- Patent strategy determined for lead compounds
What is lead optimisation?
- refining the chemical structure of a confirmed hit to improve its drug like characteristics
What factors should be considered for lead optimisation?
- distribution; affinity; intrinsic activity; intrinsic stability; solubility; permeability
Is lead optimisation used to alter affinity?
No
Used to maintain and improve efficacy
What is analogue synthesis?
- Working with all available information to develop the pharmacophore to lead to more active compounds (via minimal active fragment, x-ray crystallography etc)
Describe the lead optimisation. For ziprasidone for schz
o A dual D2/5-HT2 antagonist
o You would already have a hit/lead
o Then you would optimise the groups to improve the drug properties
o Eg increasing solubility whilst maintaining the pharmacophore
o Ziprasidone had good in-vitro efficacy and affinity but had poor solubility so, in-vivo had poor results
What are lead optimisation cycles
o A number of optimisation cycles might need to go through
o After adjusting the properties, you have to test the target activity again
Why are heteronormative groups preferred over aromatic groups in lead optimisation?
Polar interactions are often key to activity in lead optimisation
What are bio isotopes and why are they relevant?
functional groups that behave similarly within the biological system (may have similar electronic, lipophilicity, size, shape)
These solve many problems in lead optimisation
how do H bond donors and acceptors affect lead optimisation?
o Too many H-bond donors and acceptors makes desolvation difficult (no more than 5 donors and 10 acceptors)
§ Also affects absorption across the gut membrane
§ Donors have more influence than acceptors
§ Bonds too strongly to water
How does logP affect lead optimisation?
o Lipophilic compounds have poor aqueous solubility, meaning they have poor absorption (LogP less than 5)
§ Lipophilic compounds also have more interactions with the CYP enzyme system (CYP proteins job is to make compounds more soluble for excretion)
§ Lipophilicity can increase affinity to the target but can also increase off-target interaction
How do hydrophobic interactions affect lead optimisation?
§ Hydrophobic interactions are less specific than polar interactions
§ If it is more than 5, the compound may partition into the cellular environment but may not partition back
§ If a compound has a high logP, it is likely to stay in the non-polar phase (lipid membrane) and will not want to partition back into the aqueous phase (cellular environment)
How does molecular weight affect lead optimisation?
o Molecular weight over 500 means modifications are hard to make
§ Selectivity issue and off-target toxicity can kill a project
§ Can also affect absorption
Can you use lipinskis rule of 5 for anti microbial?
No because they target bacteria
How does olanzapine show the importance of balancing lipophilicity?
- The phenyl ring in chlozapine has been made into a thiazole, which improved the polarity of the compound and hence the bioavailability (~100% vs 55%)
- This shows that changing the lipophilicity alters the drug activity and we should start off with a compound with the lowest possible lipophilicity
What are the assumptions of in vitro assays?
o In-vitro assays predict in-vivo effects
o The effects of chemicals in laboratory animals apply to humans
o The use of high doses in animals is valid for predicting possible toxicity in humans
What are the types of toxic effects that can occur in-vivo during clinical trials that may not be predicted in vitro?
o Mechanism based pharmacology – caused when the activation of the target causes unwanted effects as well as the desired therapeutic effect
o Formation of reactive metabolites – forming a reactive electrophile
o Activation of other receptors including hERG – aka off-target toxicityInteractions with other substances
How can formation of reactive metabolites be avoided!
§ functional groups known to create reactive metabolites can be avoided
§ The presence of reactive groups can be tested for (Eg in the case of paracetamol, mass spectroscopy can be used to look for proteins that bind to glutathione)
What is the ames test and what is it used for?
§ used to detect mutagenicity:
· A genetically modified bacterium, which cannot grow in the absence of histidine is used
· This bacterium is exposed to a chemical that
· If the chemical can cause mutations, the genetic modification can be reversed and the bacteria will grow
· This can be carried out in the presence of liver enzymes to look for mutagenic metabolites
· So, the bacteria won’t grow if a mutation is not caused
How can activation of other receptors be avoided?
§ Screen the compound against other systems – same compound will be tested in other assays to test for activity
§ The absolute potency at another receptor is less important than how much less the potency at the primary receptor is
What does activation of hERG cause?
§ causes prolongation of electrical impulses that regulate heartbeat via K+ channels (hyperpolarisation), which can lead to QT prolongation
§ This can lead to fatal arrythmias
§ Eg drugs with an aromatic ring, with an alkyl spacer and a basic centre are likely to cause QT prolongation (eg terfenadine, astemizole, grepafloxacin, sertindole)
How can activation of hERG be avoided?
§ Changing the lipophilic aromatic ring to a polar one reduces the hERG activity by >10x
How can off target based toxicity be avoided?
- making a very potent compound
o Normally a lower dose is given, which reduces toxicity unless the drug target is what causes the toxicity
What happens if CYP450 is induced?
- By inducing CYP450, there will be increased expression of CYP450, which will in turn increase the metabolism of it
- This would then lower the effective concentration of the drug in the blood (could fall into the subtherapeutic levels – drug may not work as well at the same dose)
Provide a fatal example of when CYP450 was induced
- Terfenadine – antihistamine
- Found to cause life-threatening arrythmias when co-administered with medicines such as erythromycin or ketoconazole
- This occurs via the inhibition of hepatic P450 enzymes
- This prevented the metabolism of ketoconazole, increasing it’s plasma concentration, making it more likely to bind to hERG channels, causing QT prolongation
What pk properties are measured in animals during lead optimisation?
- Cmax, Tmax, half-life, Vd and clearance are measured
- These help to identify the onset of action, duration of action and bioavailability
What is the criteria for a preclinical candidate?
- Preferred crystalline form identified
- Compound is sufficiently stable to allow a shelf-life >2 years
- Scale up lead compound to 100g
- Full PK and metabolite profiling in 2 species
- Predicted human half-life and dose
- No toxicity in extended animal study