W1 - conduction system
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
neuromuscular system
somatic motor and autonomic control at the level of the brain
AP are generated
travel down neuron to neuromuscular junction
AP initiate chain of events that lead to msucle contraction
activity can be modified by the autonomic nervous system (extrinsic innervation)
contraction of cardiac cells is predominantly self regulated
doesn’t need commands form the brain
contractions
heart beat is dependent on electrical activity that the heart generates via the intrinsic conduction system
myocardium includes cardiac pacemaker cells (autorhythmic cells)
unstable resting membrane potential (changing)
continually depolarise to generate APs → action potentials in one muscle cell can be connected to the neck muscle cell → allows coordinated activity
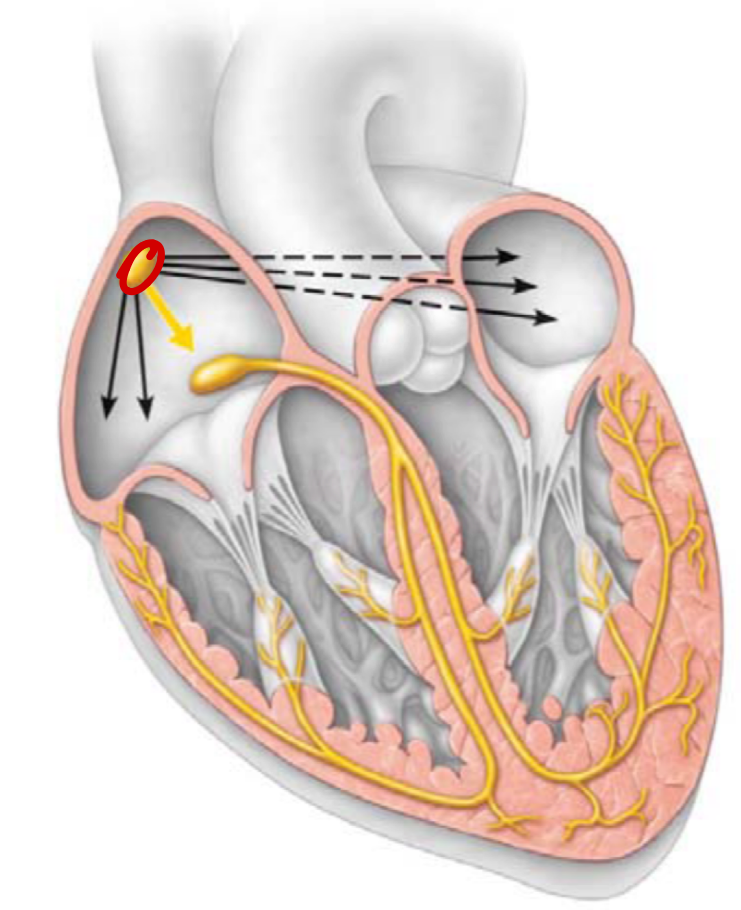
Sinoatrial (SA) node (1)
the pacemaker, generate impulses
right atrial wall
depolarises 80-100x per minute
ANS modifies this to 75x per minute
electrical activity from SA node penetrates to LA
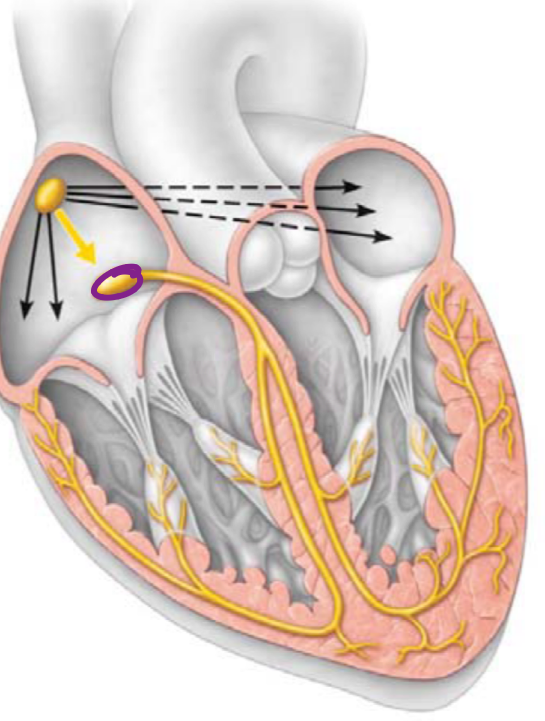
Atrioventricular (AV) node (2)
the impulses pause at the atrioventricular (AV) node
delays impulse for 0.1 sec while atria complete contraction
generates impulses 40-60x per min
delay of 0.1 se allows for atrium to fully contract, propelling blood into ventricles
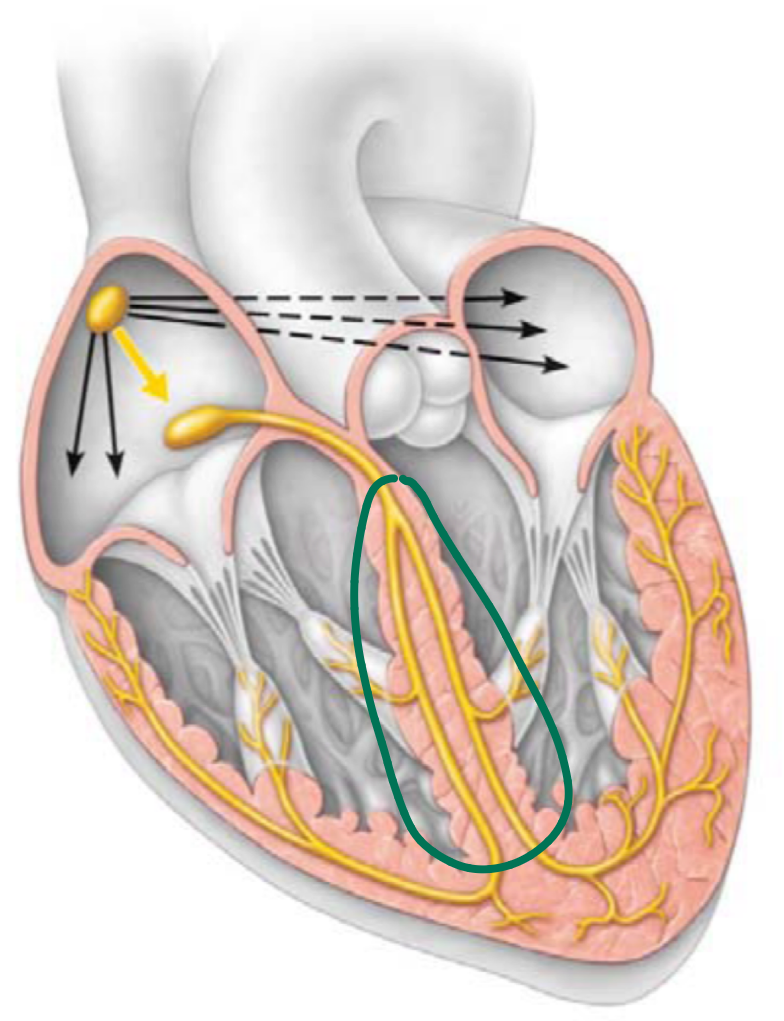
Atrioventricular bundle (bundle of his) (3)
connects the atria to the ventricles
bundle branches (4)
conducts impulses through the interventricular septum
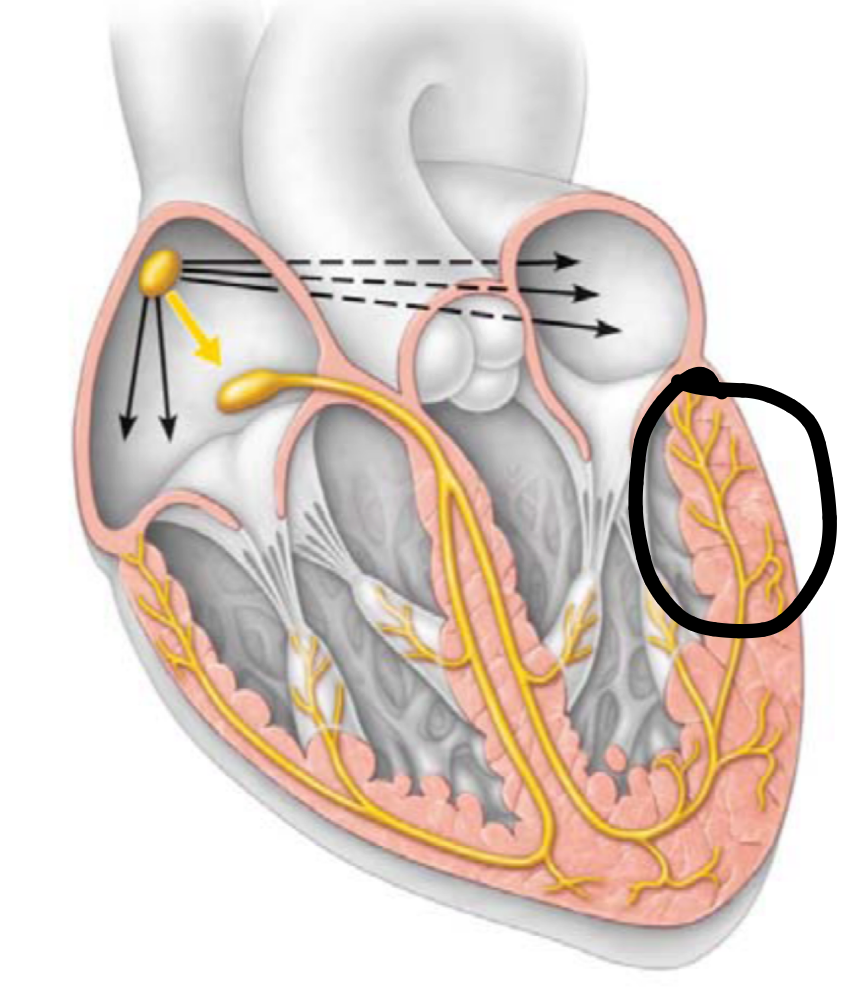
purkinje fibers (5)
depolarize the contractile cells of both ventricles
extrinsic innervation
autonomic nervous system modifies heart activity
cardiac centres in the medulla oblongata
carioaccelerayory centre increases heart eate and force of contraction
sympathetic input via the thoracic spinal cord to the SA node, AV node, myocardium, coronary arteries
cardioinhibitory centre decreases heart rate
parasympathetic input via the vagus nerve to the SA and AV nodes