C2 - Modeling quality change along the chain
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
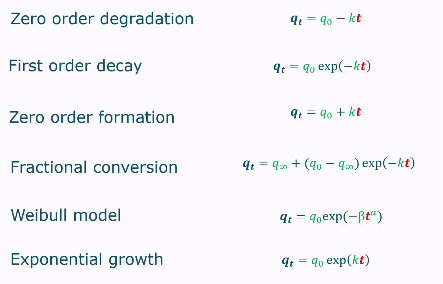
Zero order degradation model
zero order kinetics
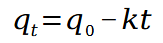
The different variables in the kinetic models
Dependent variable: quality performance indicator
independent variable: always time (red)
parameters: relate dependent to independent variables. (green)
rate constant (k)
shows how fast the dependent variables is changing.
except with beta, it relates to k.
is constant
Graph zero-order kinetics
intercept = q0
slope = k
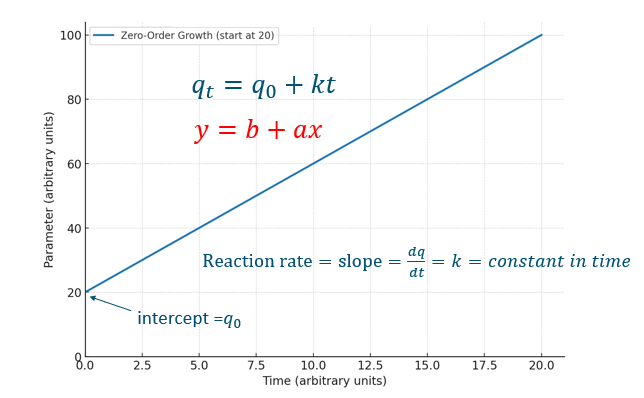
Example of zero order kinetics (decrease)
Normally is very rare
But an example is a biochemical reaction, catalyzed by enzymes
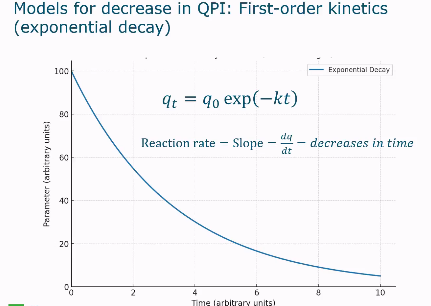
First order decay
Exponential decay
Example: thermal degradation of betalain
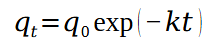
First order exponential decay graph
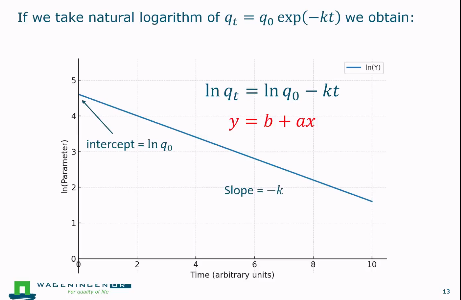
What happens when you take the logarithm of first order exponential decay equation?
The ln version as shown in the picture will form a straight line.
If the points do not follow a straight line, the model is not exponential first order decay
half-life
time needed to half dependent variable
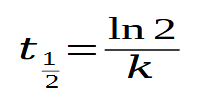
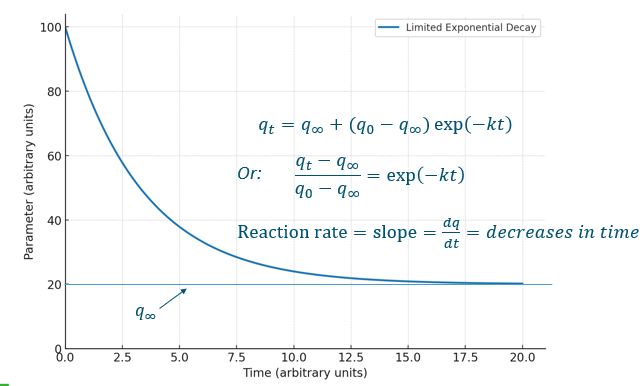
Fractional conversion equation
Used when graph is basically an exponential decay, except the line does not have an asymptote at y = 0.
Then a fractional conversion model is used.
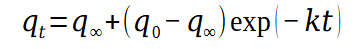
Fractional conversion graph
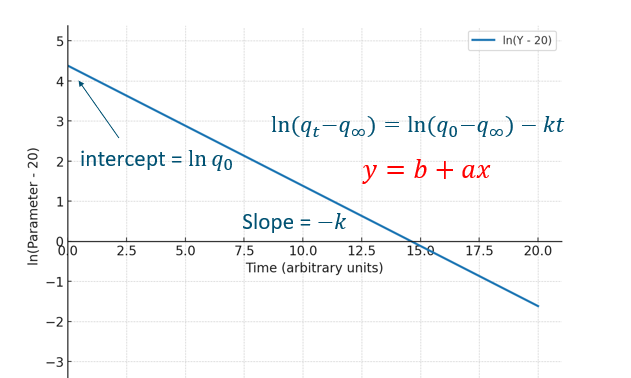
Fractional conversion in logarithmic form
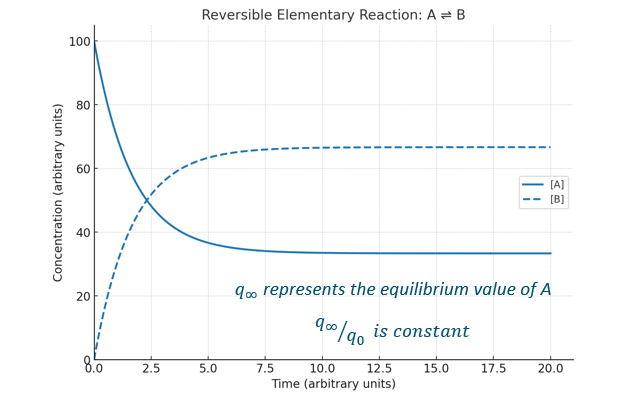
Example fractional conversion kinetics reversible reaction
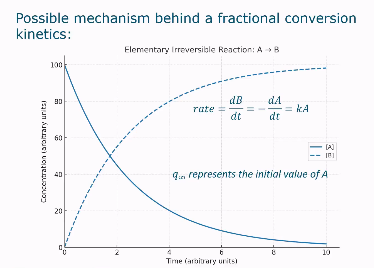
Example fractional conversion kinetics irreversible reaction
Weibull model
Similar to first order exponential decay
B = scale parameter (reciprocal of rate constant)
B<1 = decelerating rate
B>1 = Accelerating rate
a = shape parameter
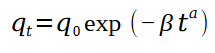
How does the a variable in the weibull model change the shape of the graph?
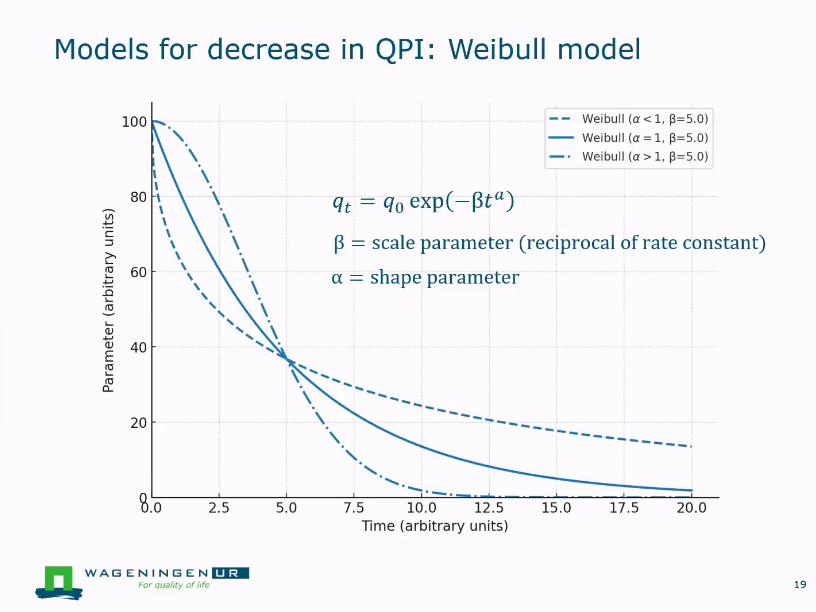
Example weibull model
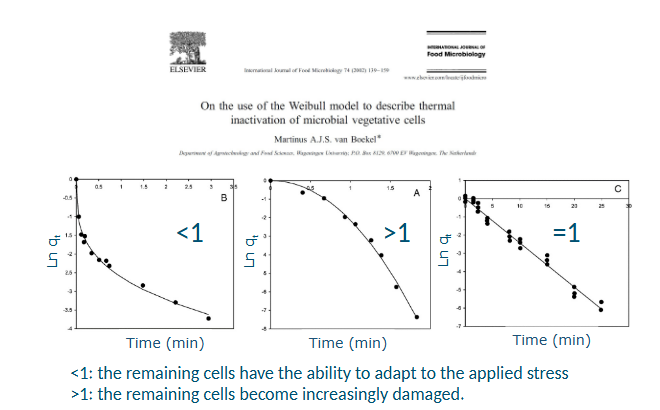
Exponential growth
Exponential growth graph
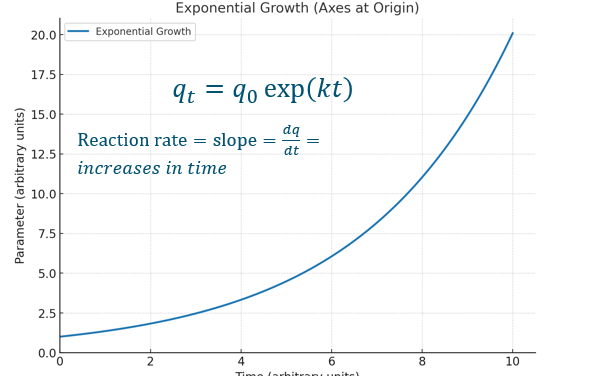
What is good to know about rate constant?
Doesnt change, because it is a CONSTANT