BCH LE2 (3) Mito. Oxidation
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What are the two enzymes found on the Outer mitochondrial membrane?
1) Acyl-CoA synthetase (ACS)
Use ATP to convert Fatty Acids into Acetyl CoA.
Acetyl CoA can then enter inside mitochondria via carnitine shuttle.
2) Glycerol Phosphate Acyl transferase (GPAT)
Adds Fatty Acids + Glycerol 3 phosphate → Lysophosphatidic acid
Lysophosphatidic acid is used as a precursor for Phospholipid and TAG generation.
T or F? Enzymes found in the outer mitochondrial membrane needs a transporter.
True!
What are the enzymes found on the INNER mitochondrial MEMBRANE
Electron carriers
ATP synthase (aka Complex V or 5)
Membrane transporters.
What are the enzymes found in the INNER mitochodrial MATRIX
1) Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)
2) B-oxidation Enzymes
What enzyme bridges Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle through the conversion of Pyruvate → Acetyl CoA.
+++ is found in the inner mitochondrial matrix.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH complex)
The Electron Transport Chain is embeded in which cell layer?
The Inner Mitochondrial Membrane.
What does the ETC or respiratory transport chain aim to do?
Transfer electrons from reducing equivalents (NADH and FADH) to Oxygen.
This generates a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
What will be formed from the ETC oxidation of the reducing equivalents?
WATERRRR
The redox potential or Free energy of reactants is directly or indirectly proportional to their ability to donate or accept electrons?
Directly proportional.
What are the 5 Complexes found on the Inner Mitochondrial matrix?
Complex 1
Complex 2
Complex 3
Complex 4
Complex 5 // ATP Synthase
what are the 2 additional molecules that are also embeded in the Inner mito. matrix?
Co-enzyme Q
Cytochrome C
What does complex 5 or ATP synthase do?
It pumps proton gradient which generates ATP.
This process is also known as Chemi osmosis
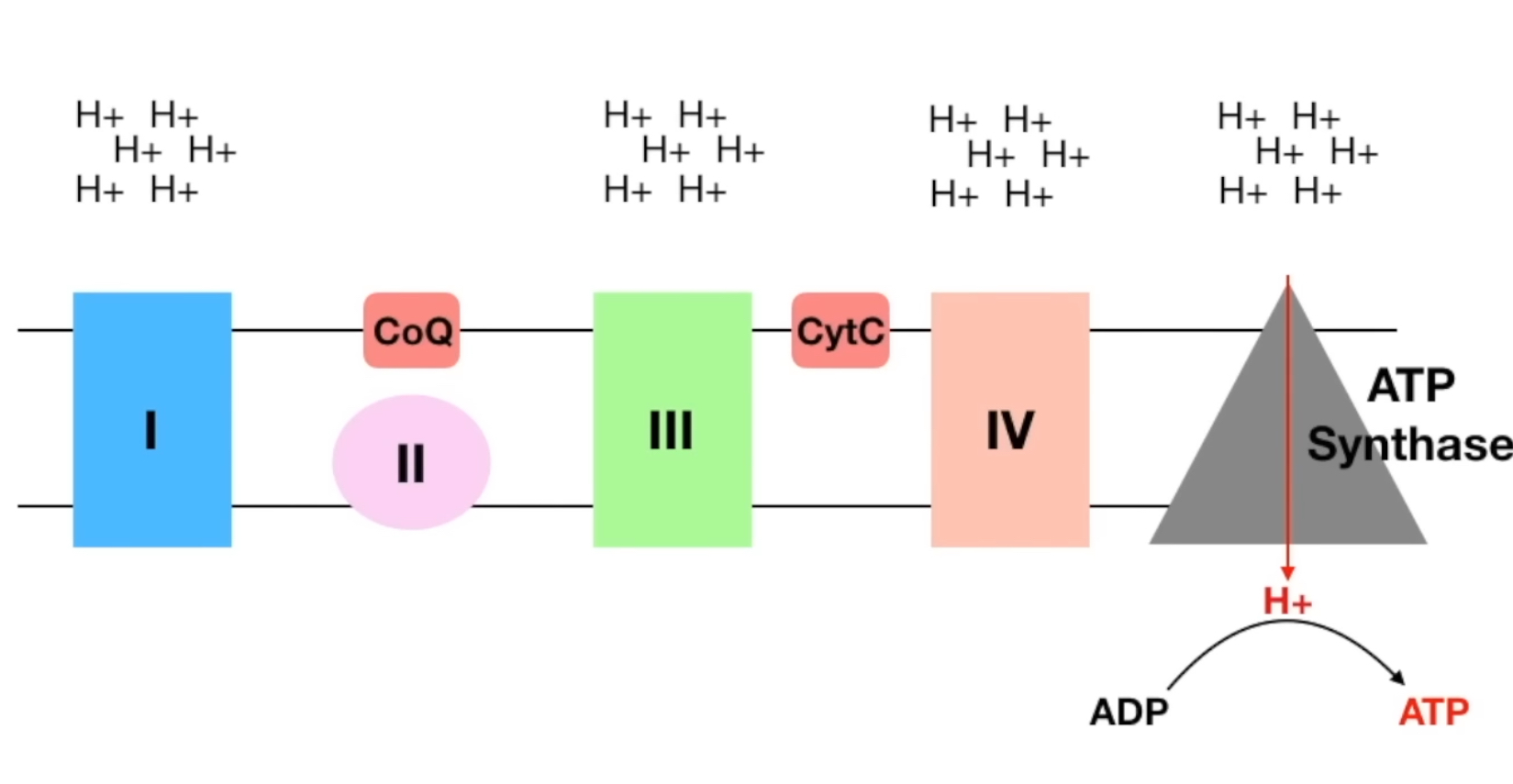
Overview of Mito. Ox!
NADH (from TCA) found inside the Mitochondrial matrix donates [e- ] to complex 1 ( NADH→ NAD+).
This charges up complex 1.
The charged up Complex 1 can now pump protons [H+] found inside the mito matrix → Intermembrane space.
[H+] now accumulates outside in the Intermembrane space.
Complex 1 will pass the [e-] to Coenzyme Q.
FADH2 (from TCA) donates [e- ] to Complex 2 (FADH2 → FAD)
[e- ] from Complex 2 is passed to Coenzyme Q.
dalawa na yung [e- ]!
Coenzyme Q passes [e- ] to Complex 3.
This charges Complex 3.
Charged up Complex 3 can pump [H+] found inside the mito matrix → Intermembrane space.
Complex 3 passed [e-] to Cytochrome C.
Cytochrome C passes [e-] to Complex 4.
This charges Complex 4.
Charged up Complex 4 can pump [H+] found inside the mito matrix → Intermembrane space.
NOW THE INTERMEMBRANE SPACE IS SUUUUPER FILLED WITH PROTONS compared to the Mito. Matrix.
Complex 4 passes its [e-] to Oxygen!
Oxygen is the Final Electron Acceptor.
When O2 accepts the [e-] it splits into two.
This forms 2 water molecules: H2O + H2O.
Can complex 2 pump out H+ into the intermembrane space?
NO
NADH will only work with which Complex?
FADH2 will only work with which Complex?
NADH - Complex 1
FADH2 - Complex 2
What is the common electron acceptor from Complex 1 and 2?
Coenzyme Q
Who does complex 4 pass its electron to?
Oxygen!
O2 is the FINAL ELECTRON ACCEPTOR
Complex 5 or ATP synthase ‘s job is to help convert ADP → ATP. How does ATP synthase do this?
It makes use of the Proton gradient.
Since protons will ALWAYS want to flow DOWN THE GRADIENT.
Protons will flow down THROUGH ATP synthase (Intermembrane space → Mitochondrial matrix)
This [H+] catalyzes the conversion of ADP → ATP
Which complex inhibitors are known to be most fatal? E.g. Cyanide and Carbon Monoxide.
Complex 4 Inhibitors!
Amorbartibal is a Barbituate that blocks the transfer of electronns from Fe-S to Q. This is known to inhibit which complex?
Complex 1 Amorbartibal
Antimycin A is a _ complex inhibitor
Complex 3 Inhibitor.
Mechanism of action of Antimycin A?
Inhibits complex 3.
Binds to Qi site of Cytochrome C reductdase → inhibits Ubiquinol Oxidation.
Thus NO ATP is formed!
What are Iron Sulfur Clusters? (Fe-S)
Serve as ELECTRON CARIERS.
Which complexes can Fe-S be found?
Complex 1 2 and 3
Fe-S in complex 1 and 2 contain Fe atoms via Cysteine SH groups.
Fe-S in complex 3 contain Fe atoms via
Histidine- SH groups
aka Rieske F-S
What happens in complex 1?
NADH gives electrons → flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
FMN gives electrons via Fe-S → CoQ
Complex 1 pumps out 4 [H+] into intermembrane space.
What happens in Complex 2?
Complex 2 is aka Succinate Dehydrogenase.
Succinate → Furmarate!!
FADH2 gives electrons → CoQ via FE-S
Remember NO PUMPING OF PROTONS OUT!
CoQ accepts electrons from Complex 1 and 2. It is reduced to Ubiquinol (CoQH2). What happens to Ubiquinol?
Ubiquinol diffuses inside the inner mitochondrial membrane → Complex 3
Transfer of electrons from Ubiquinol to Complex 3
What happens in complex 3?
Complex 3 pumps out FOUR protons out into the intermembrane space.
Cytochrome C function?
Move electrons from Complex 3 into Complex 4
What happens in Complex 4?
Electrons from Complex 4 are transfered via:
Cytochrome a
Cytochrom a3
Copper centers (Cu-A and Cu-B)
To OXYGEN!
Oxygen is reduced to water.
Complex 4 Pumps OUT TWO protons.
Protons from the Intermembrane space flow back into the Mito. matrix through which subunit of ATP synthase?
F0
The flow of protons back through F0 drives the rotation of?
F1 subunit thus catalyzing the synthesis of ATP
Respiratory Chain (Mito ox) and Oxidative Phosphorylation is coupled to each other by?
ATP synthase.
Most of the energy used by cells comes from?
Respiratory chain or Oxidative Phosphorylation
Respiratory Chain
Which complex is a major source of ROS which cause damage to mitochodrial DNA and Aging?
Complex 1
Ubiquinone is oxidized or Reduced?
Oxidized.
Think of the "-one" at the end as sounding like "quinone," which is an oxidized molecule. It's ready to accept electrons.
Is ubiquinol oxidized or reduced?
Ubiquinol is the reduced form. The "-ol" at the end is a suffix for an alcohol, which is a reduced molecule.
Which component of ATP synthase is responsible for the conformational change in the catalytic subunits that drives ATP synthesis?
A. The γ subunit
B. The α subunits
C. The c ring
D. The β subunits
The γ subunit.
Rotation of the Y subunit, driven by proton flow through the Fₒ component, directly interacts with the β subunits, forcing them to change shape and synthesize ATP.
A toxin blocks the transfer of electrons from Complex I to Coenzyme Q. Which of the following toxins acts in this manner?
A. Rotenone
B.Cyanide
C.Oligomycin
D. Malonate
Rotenone
What is the primary function of the malate-aspartate shuttle?
A.
To move FADH₂ from the cytosol into the mitochondria.
B.
To generate ATP directly in the intermembrane space.
C.
To transport high-energy electrons from cytosolic NADH into the mitochondria.
D.
To transport pyruvate into the mitochondrial matrix.
To transport high-energy electrons from cytosolic NADH into the mitochondria.
Which state of respiratory control is characterized by high levels of ADP and substrate, leading to the maximum rate of oxygen consumption?
A. State 2
B. State 1
C. State 4
D. State 3
State 3
substrates and ADP are abundant, allowing the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation to proceed at their maximum capacity
Remember:
State 4
'resting' state where substrate is available, but ADP has been mostly converted to ATP, so respiration slows down due to the lack of an acceptor for phosphorylation.
How does 2,4-Dinitrophenol (DNP) affect the relationship between electron transport and ATP synthesis?
A.
It allows electron transport to continue but stops ATP synthesis.
B.
It inhibits both processes by blocking Complex III.
C.
It blocks the Fₒ proton channel of ATP synthase.
D.
It enhances ATP synthesis by increasing the proton gradient.
DNP is an uncoupler.
It dissipates the proton gradient by carrying protons across the inner membrane
so the energy is released as heat instead of being used by ATP synthase to make ATP.
The ETC continues, and may even speed up.
Therefore Correct Ans: A. It allows electron transport to continue but stops ATP synthesis.
The glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle transfers electrons from cytosolic NADH to which molecule in the inner mitochondrial membrane?
A.
Complex I
B.
ATP synthase
C.
Cytochrome c
D.
Mitochondrial FAD
Mitochondrial FAD
Electrons are transferred to mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, which uses FAD as a cofactor. This FAD is reduced to FADH₂, which then donates electrons to Coenzyme Q (Complex II).
Common sense q.
A,B and C are found in the Inner Mitrochondrial Membrane. (this is between the Intermembrane space and Mitochondrial Matrix)
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy is associated with a mutation in a gene encoding a component of which respiratory complex?
A.
Complex II
B.
Complex I
C.
Complex III
D.
Complex IV
Complex I!
This disease is due to a single base mutation in mitochondrial DNA that encodes a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I).
What is the function of the Creatine Phosphate Shuttle?
A.
To transport creatine into the mitochondria for breakdown.
B.
To move electrons from the cytosol to the ETC.
C.
To transport high-energy phosphate from mitochondria to the cytosol.
D.
To uncouple ATP synthesis from electron transport.
To transport high-energy phosphate from mitochondria to the cytosol.
Atractyloside inhibits oxidative phosphorylation by what mechanism?
A.
Inhibiting the adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT).
B.
Blocking the flow of protons through the Fₒ subunit of ATP synthase.
C.
Acting as a competitive inhibitor for succinate dehydrogenase.
D.
Binding to Complex IV and preventing the reduction of oxygen.
Inhibiting the adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT).
preventing the exchange of ATP (out) for ADP (in), thus starving ATP synthase of its substrate.
Uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), or thermogenin, is crucial for non-shivering thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue. How does it generate heat?
A.
It directly inhibits the electron transport chain to release heat.
B.
It provides a channel for protons to re-enter the matrix, bypassing ATP synthase.
C.
It speeds up the reactions within the Krebs cycle.
D.
It forces ATP synthase to run in reverse, hydrolyzing ATP.
It provides a channel for protons to re-enter the matrix, bypassing ATP synthase.
The F0 subunit of ATP synthase is embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. What is its primary function?
A.
It synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
B.
It transmits rotational motion from the F0subunit to the F1 subunit.
C.
It contains the binding sites for ADP and ATP.
D.
It provides a channel for protons (H+) to pass into the mitochondrial matrix.
provides a channel for protons (H+) to pass into the mitochondrial matrix.
What best describes the condition of State 4 respiration?
The rate of respiration is limited by a lack of available ADP.
A severe deficiency in the oxidoreductase enzymes of Complex I and III is a characteristic of which clinical condition?
A. Brown adipose tissue thermogenesis
B.Leber hereditary optic neuropathy
C.MELAS
D.Fatal infantile mitochondrial myopathy and renal dysfunction
Fatal infantile mitochondrial myopathy and renal dysfunction
How does Oligomycin inhibit oxidative phosphorylation?
A.
It prevents the exchange of ADP and ATP across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
B.
It acts as a competitive inhibitor for succinate dehydrogenase.
C.
It blocks the transfer of electrons from Complex I to Coenzyme Q.
D.
It blocks the flow of protons (H+) through the F0 subunit of ATP synthase.
It blocks the flow of protons (H+) through the F0 subunit of ATP synthase.
Which of the following best describes the function of the β subunits within the F1 component of ATP synthase?
A.
They form the rotor that spins in response to proton flow.
B.
They translocate ADP and ATP across the mitochondrial membrane.
C.
They contain the binding sites for ADP and inorganic phosphate and are responsible for synthesizing ATP.
D.
They serve as a stator, holding the catalytic subunits in place while the rotor spins.
They contain the binding sites for ADP and inorganic phosphate and are responsible for synthesizing ATP.
What is the primary role of the Pyruvate transporter?
A.
To move pyruvate from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix.
B.
To transport pyruvate into the cytosol for gluconeogenesis.
C.
To move pyruvate out of the mitochondria in exchange for malate.
D.
To move pyruvate into the mitochondria in exchange for a phosphate group.
To move pyruvate from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix.
The Malate-Aspartate Shuttle and the Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle both transfer electrons from cytosolic NADH to the mitochondrial electron transport chain. What is the main difference in their ATP yield?
A.
Both shuttles yield 2.5 ATP per mole of NADH.
B.
The Malate-Aspartate Shuttle yields 2.5 ATP per mole of NADH, while the Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle yields 1.5 ATP.
C.
Both shuttles yield 1.5 ATP per mole of NADH.
D.
The Malate-Aspartate Shuttle yields 1.5 ATP per mole of NADH, while the Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle yields 2.5 ATP.
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle = 2.5 ATP per mole of NADH
Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle = 1.5 ATP.
What is the mechanism of action of Cyanide and Carbon Monoxide?
They inhibit Complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase) by binding to its iron-copper center.
In which state of respiratory control is the mitochondrial respiratory rate limited by the availability of ADP?
A.
State 3
B.
State 1
C.
State 4
D.
State 2
State 2
(-) ADP (+) Substrate
substrate is available but the mitochondria are in a standby mode due to a lack of ADP.
State 1
(?) ADP (?) Substrate
State 1
(+) ADP (+) Substrate
State 2
(?) ADP (?) Substrate
State 2
(-) ADP (+) Substrate
State 3
(?) ADP (?) Substrate
State 3
(+) ADP (-) Substrate
State 4
(?) ADP (?) Substrate
State 3
(-) ADP → ATP (-) Substrate
Uncouplers, such as 2,4-Dinitrophenol (DNP), have what effect on the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis?
A.
They block the electron transport chain, which in turn stops ATP synthesis.
B.
They stop ATP synthesis by dissipating the proton gradient, but allow the electron transport chain to continue.
C.
They increase the efficiency of ATP synthesis by creating a stronger proton gradient.
D.
They inhibit ATP synthase, which then causes the electron transport chain to slow down.
They stop ATP synthesis by dissipating the proton gradient, but allow the electron transport chain to continue.
The rotation of the γ subunit causes the β subunits of ATP synthase to transition through three distinct conformations. What are these three states?
A.
Open, Closed, and Tight
B.
Open, Loose, and Tight
C.
Loose, Neutral, and Capped
D.
Active, Inactive, and Stabilized
Open, Loose, and Tight
Which of the following is a competitive inhibitor of Complex II, acting similarly to succinate?
A.
Rotenone
B.
Oligomycin
C.
Malonate
D.
Antimycin A
Malonate
Why does the Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle yield less ATP per mole of cytosolic NADH compared to the Malate-Aspartate Shuttle?
A.
The Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle requires more energy to transport NADH into the mitochondria.
B.
The Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle bypasses Complex I, entering the chain later at Complex II.
C.
The Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle transfers electrons directly to oxygen, bypassing the entire ETC.
D.
The Malate-Aspartate Shuttle uses FADH$_{2}$ instead of NADH.
The Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle bypasses Complex I, entering the chain later at Complex II.
What is the key difference between State 3 and State 4 respiration in terms of ADP and ATP?
A.
State 3 has a low ADP:ATP ratio, while State 4 has a high ADP:ATP ratio.
B.
Both states have a high ADP:ATP ratio.
C.
State 3 has a high ADP:ATP ratio, while State 4 has a low ADP:ATP ratio.
State 3: high ADP:ATP ratio,
State 4: low ADP:ATP ratio.
The Adenine Nucleotide Translocator (ANT) transports ATP and ADP across the inner mitochondrial membrane. What is the direction of this exchange?
A.
Both ATP and ADP are transported out of the matrix into the cytosol.
B.
ATP is transported into the matrix, and ADP is transported out to the cytosol.
C.
Both ATP and ADP are transported into the matrix.
D.
ATP is transported from the matrix to the cytosol, and ADP is transported from the cytosol to the matrix.
ATP is transported from the matrix to the cytosol,
ADP is transported from the cytosol to the matrix.
A patient is diagnosed with MELAS, a mitochondrial disease affecting the central nervous system and muscles. What is the cause of this disease?
A.
A severe deficiency in Complex II (succinate dehydrogenase).
B.
A mutation that causes a defective Malate-Aspartate Shuttle.
C.
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA that affect either Complex I or Complex IV.
D.
An overactive Creatine Phosphate Shuttle.
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA that affect either Complex I or Complex IV.
What is the mechanism of action of Antimycin A?
A.
It acts as an uncoupler, dissipating the proton gradient.
B.
It inhibits Complex III (cytochrome b-c$_{1}$ complex) by binding to the ubiquinone binding site.
C.
It blocks the transfer of electrons from Complex I to Coenzyme Q.
D.
It inhibits the adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT).
It inhibits Complex III (cytochrome b-c$_{1}$ complex) by binding to the ubiquinone binding site.
In the Malate-Aspartate Shuttle, how does the final electron carrier, NADH, get transported into the mitochondrial matrix?
A.
NADH is transported into the matrix in exchange for a molecule of ATP.
B.
NADH reduces oxaloacetate to malate in the cytosol, and malate is then transported into the matrix.
C.
NADH is oxidized in the cytosol and the electrons are transferred to FAD inside the matrix.
D.
NADH is directly transported by a specific carrier protein.
NADH reduces oxaloacetate to malate in the cytosol, and malate is then transported into the matrix.
What is the primary function of the phosphate translocase?
A.
To export inorganic phosphate from the matrix into the cytosol.
B.
To transport inorganic phosphate and ADP into the matrix in exchange for ATP.
C.
To transport inorganic phosphate (Pi) from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix.
D.
To transport creatine and phosphate across the membrane.
C.
To transport inorganic phosphate (Pi) from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix.
What is the primary role of the creatine phosphate shuttle?
To transport high-energy phosphate from the mitochondrial matrix to the cytosol.
Which of the following clinical conditions is caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA that affect NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (Complex I)?
A.
MELAS
B.
Fatal infantile mitochondrial myopathy
C.
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy
D.
Non-shivering thermogenesis
MELAS
What is the function of the 'c' ring within the F0 subunit of ATP synthase?
A.
It spins as protons (H+) pass through it, transmitting rotational motion to the γ subunit.
B.
It contains the catalytic sites for ATP synthesis.
C.
It acts as a translocator for ADP and ATP.
D.
It is the stationary part of the proton channel.
It spins as protons (H+) pass through it, transmitting rotational motion to the γ subunit.
In the Malate-Aspartate Shuttle, how many ATP are yielded per molecule of cytosolic NADH, and what is the reason for this yield?
A.
2.5 ATP because electrons are transferred to NADH inside the mitochondria, which enters Complex I.
B.
1.5 ATP because electrons are transferred to FADH2 inside the mitochondria.
C.
1 ATP because electrons are transferred directly to ATP synthase.
D.
2.5 ATP because electrons are transferred to Complex II inside the mitochondria.
2.5 ATP because electrons are transferred to NADH inside the mitochondria, which enters Complex I.
If a sample of isolated mitochondria has a high concentration of substrate but a low concentration of ADP, what state of respiratory control is it in, and what would happen if ADP were added?
A.
It is in State 4, and adding ADP would cause a decrease in the rate of oxygen consumption.
B.
It is in State 3, and adding more ADP would not significantly increase the rate.
C.
It is in State 4, and adding ADP would cause a rapid increase in the rate of oxygen consumption.
D.
It is in State 2, and adding ADP would cause a rapid increase in the rate of oxygen consumption.
It is in State 2, and adding ADP would cause a rapid increase in the rate of oxygen consumption.
Why is the Creatine Phosphate Shuttle particularly important in tissues with a high and fluctuating energy demand, such as skeletal muscle?
It acts as a reservoir of high-energy phosphate that can rapidly regenerate ATP in the cytosol.
ow does Oligomycin inhibit oxidative phosphorylation?
A.
It prevents the exchange of ADP and ATP across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
B.
It acts as a competitive inhibitor for succinate dehydrogenase.
C.
It blocks the transfer of electrons from Complex I to Coenzyme Q.
D.
It blocks the flow of protons (H+) through the F0 subunit of ATP synthase.
It blocks the flow of protons (H+) through the F0 subunit of ATP synthase.