Molecular Chemistry
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Is water polar or non-polar?
polar
Does oxygen have a positive or negative charge?
negative
Does hydrogen have a positive or negative charge?
positive
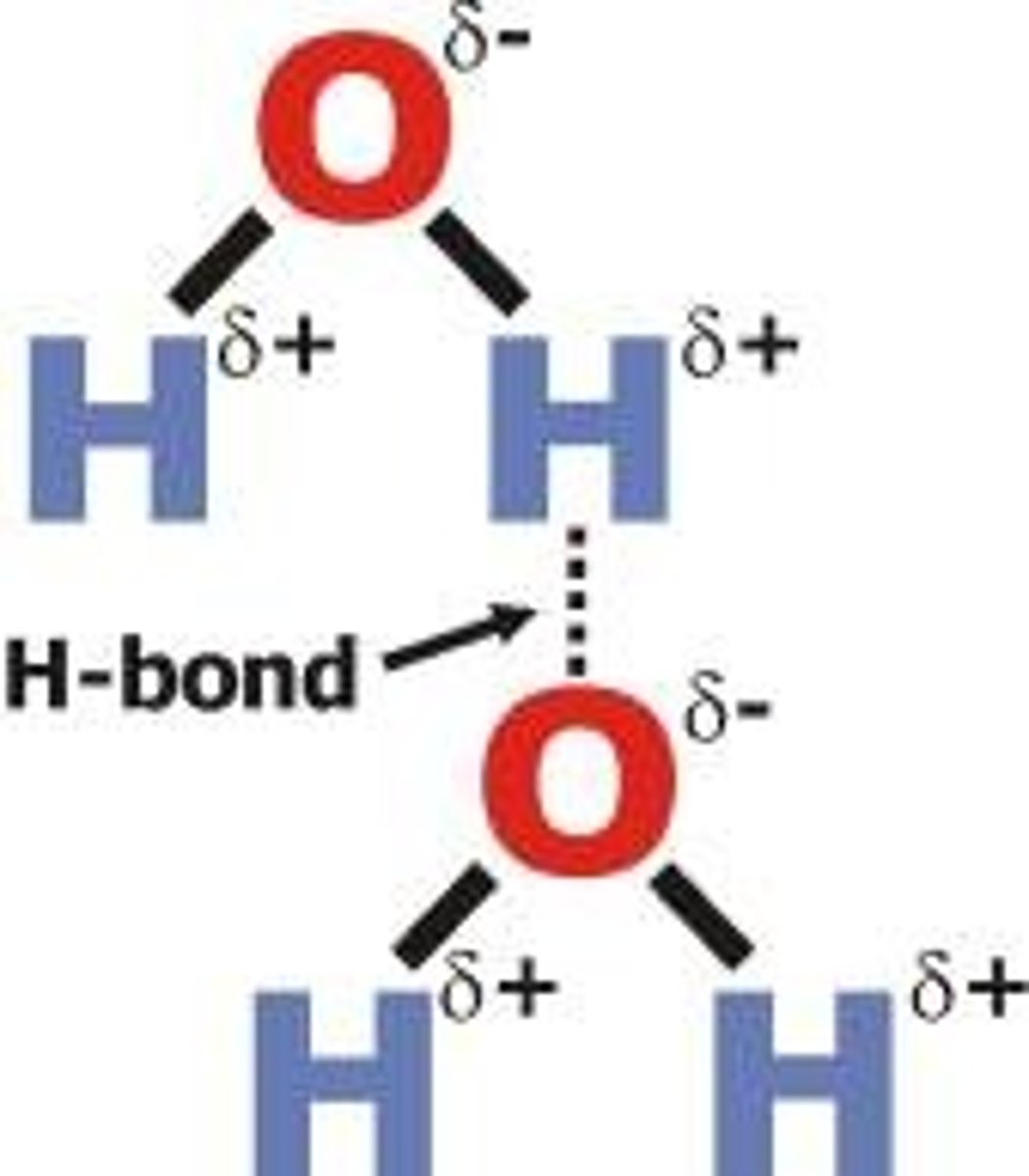
What are hydrogen bonds?
a weak bond between two molecules
Do nonpolar bonds share electrons equally or unequally.
equally
Do polar bonds share electrons equally or unequally.
unequally
What is cohesion?
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
What does cohesion create?
surface tension
What does cohesion allow?
Columns of water to be drawn up xylem vessels in plants
What is adhesion?
An attraction between molecules of different substances
What is a solute?
Substance being dissolved
What is a solvent?
substance that does the dissolving
What is a solution?
a mixture of solute and solvent
Is water a solute or solvent?
solvent
What do all cells exist in?
a water based medium
What does water do in the body?
allows for the transport of soluble materials that must be transported around the body
What is a hydrophilic substance?
A substance attracted to water. (easily dissolves in water)
What is a hydrophobic substance?
A substance not attracted to water. (does not dissolve in water)
Does water have temperature stabilizing capabilities? What does this mean?
yes, liquids absorb a lot of heat, when they evaporate they leave the surface feeling cooler (sweating)
Does water have a high or low density?
high
Does ice have a higher or lower density than liquid water?
lower
What makes carbon a building block of life?
unique bonding properties, it can combine with itself to form long chains
What is a condensation reaction? (Anabolic Reaction)
A reaction in which two molecules combine to form a larger molecule, producing H2O as a by product
What is a hydrolysis reaction? (Catabolic Reaction)
a reaction in which a bond is broken by the addition of a water molecule
What makes a alpha glucose structure?
H on top for c1,c4,
c2 H on top
c3 H on bottom
c5 H on bottom/CH2OH on top
What makes a beta glucose structure?
H on bottom for c1
c2 H on top
c3 H on bottom
c4 H on top
c5 H on bottom/CH2OH on top
What makes a Ribose structure?
Pentagon shape
c1 H on top at angle
H on top for c2,c3
c4 H on bottom at angle
O on top
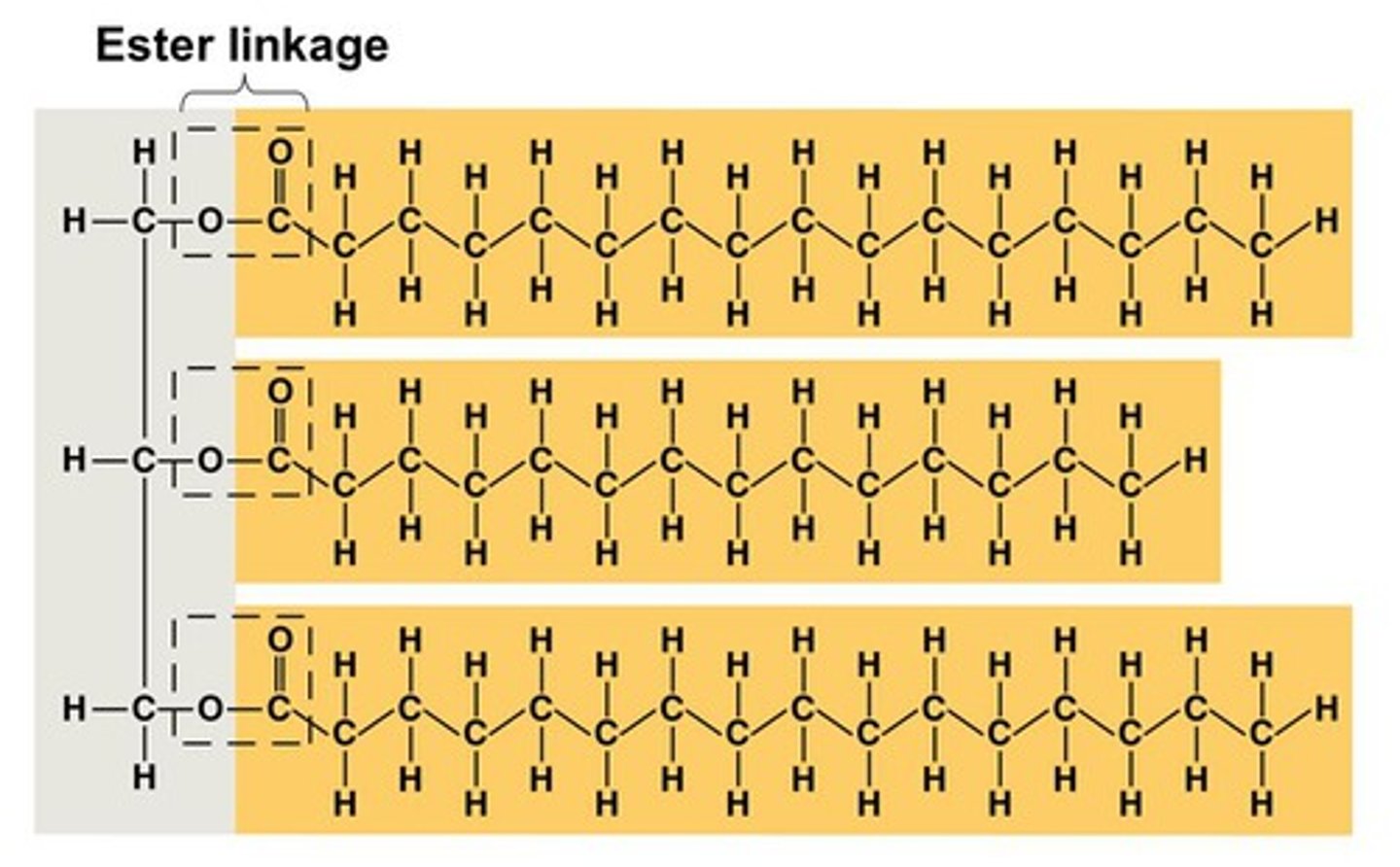
What makes a triglyceride?
glycerol and 3 fatty acids bonded with 3 ester bonds
What makes a glycerol?
3 C
5 H single bonded on left/top & bottom
3 O single bonded on right
What makes a fatty acid?
1st C double bonded to 1 O on top
more than 1 C bonded with a H on all sides
Carbohydrate elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (1:2:1)
Carbohydrates function
main source of energy
Carbohydrate basic unit
glucose
Maltose
glucose + glucose
Lactose
glucose + galactose
Sucrose
glucose + fructose
What type of bond forms between sugar molecules?
glycosidic bond
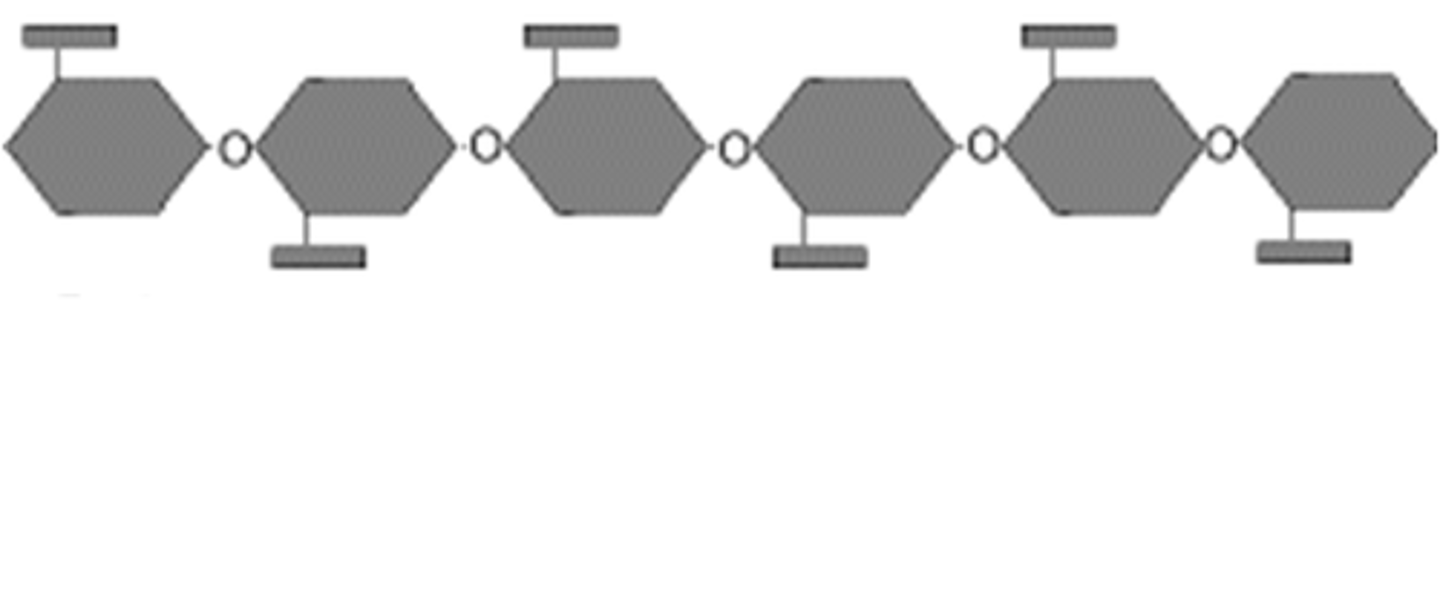
Cellulose
Beta /Alpha
linkage
shape
plant cell wall/energy storage in animals or plants
Beta glucose
1-4 links
linear
plant structure (cell wall)
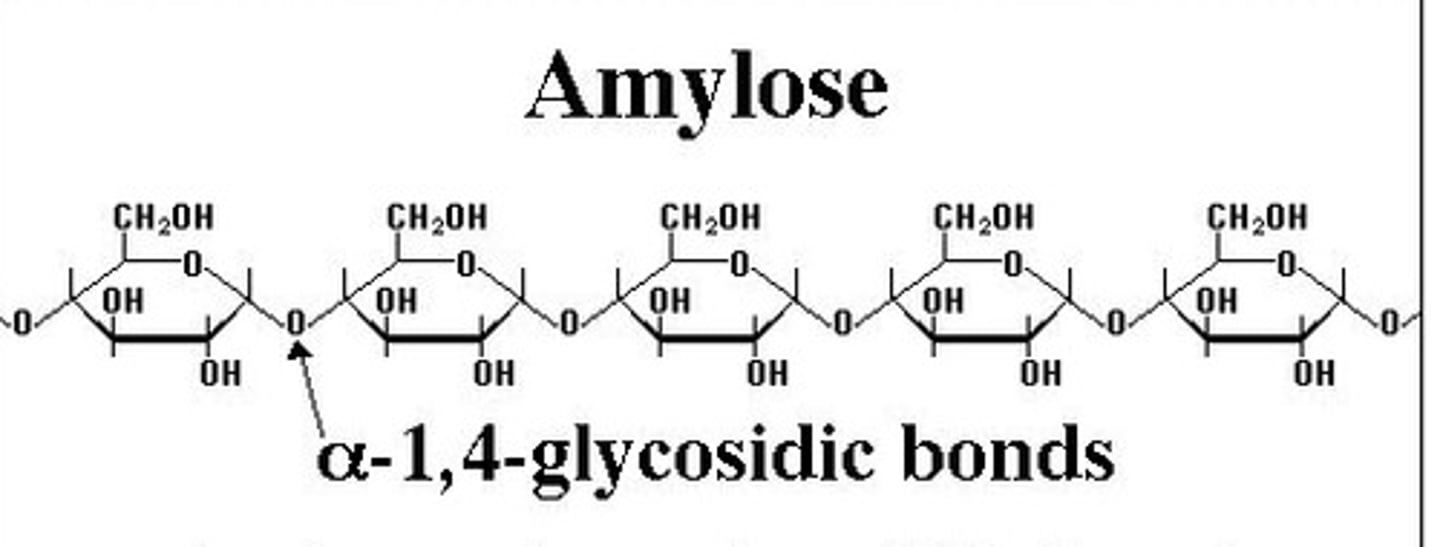
Amylose
Beta /Alpha
linkage
shape
plant cell wall/energy storage in animals or plants
Alpha glucose
1-4 bonds
helical shape
energy storage in plants
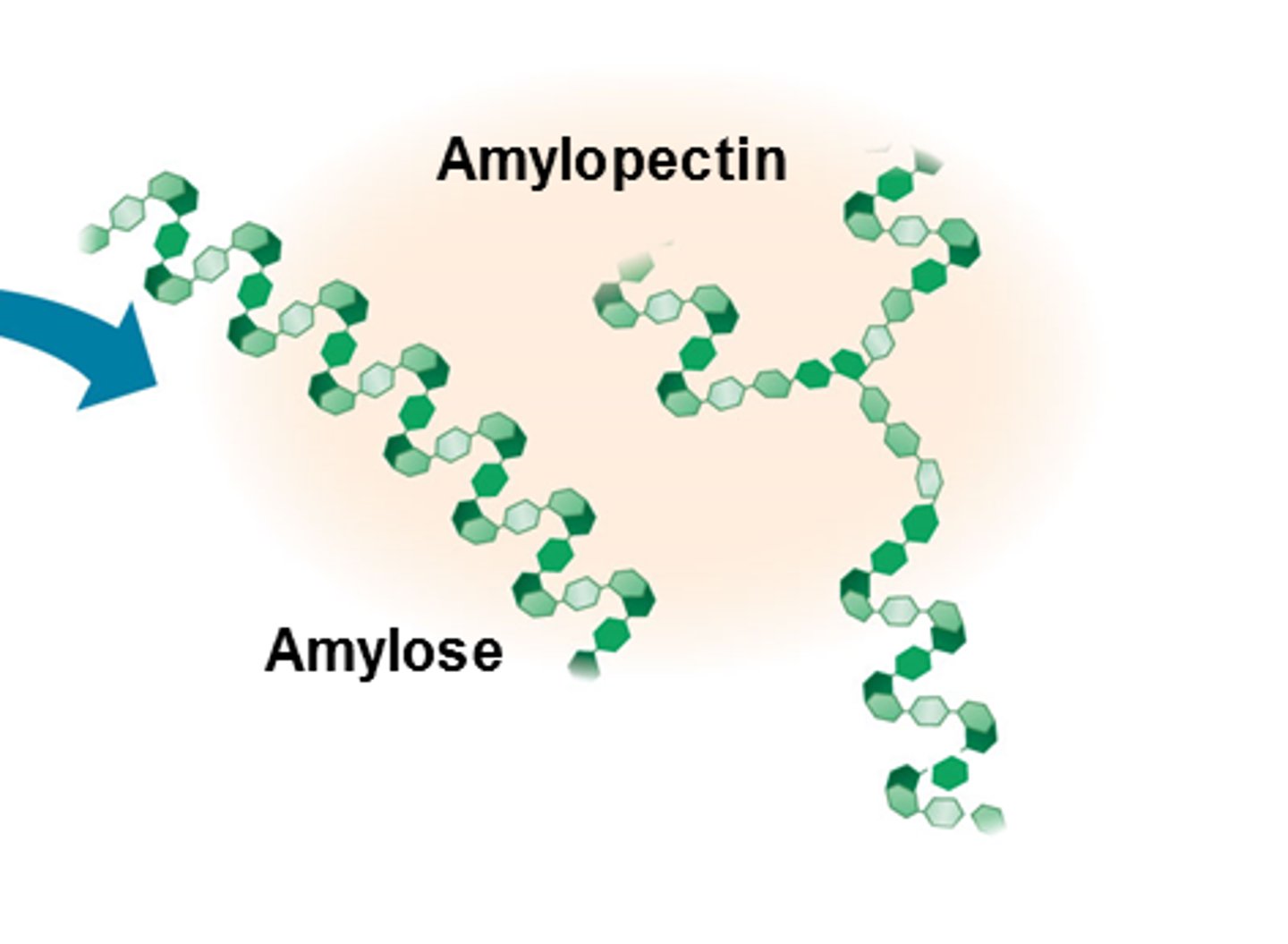
Amylopectin
Beta /Alpha
linkage
shape
plant cell wall/energy storage in animals or plants
Alpha glucose
1-4 & 1-6 bonds
branched shape
energy storage in plants
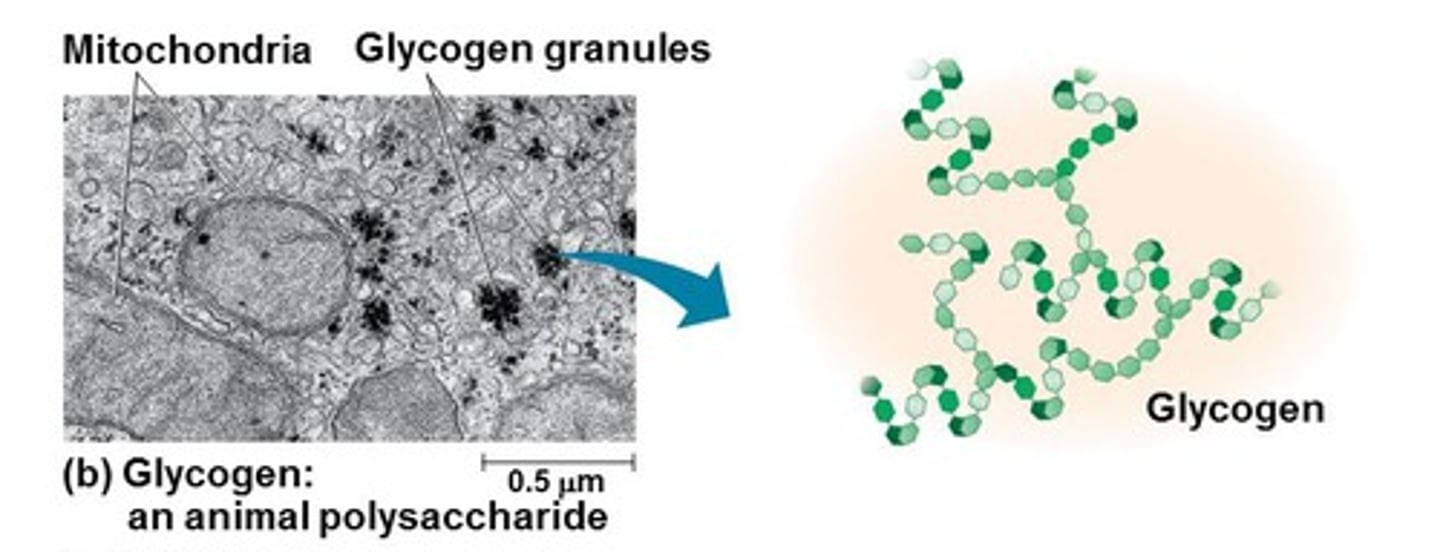
Glycogen
Beta /Alpha
linkage
shape
plant cell wall/energy storage in animals or plants
Alpha glucose
1-4 & 1-6 bonds
highly branched
energy storage in animals
How does the shape of a cellulose molecule differ from that of other polysaccharides?
unbranched
straight-chain polymer of glucose
Lipid examples
fats, oils, waxes, steroids
lipid elements and ratio
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (1:2:very few)
lipid function
Long term energy storage, insulation, buoyancy, and is a part of the cell membrane
lipid basic unit
fatty acids and glycerol
Saturated fats are ____ at room temperature. Animal or plant?
Solid (ex. butter), animal fats.
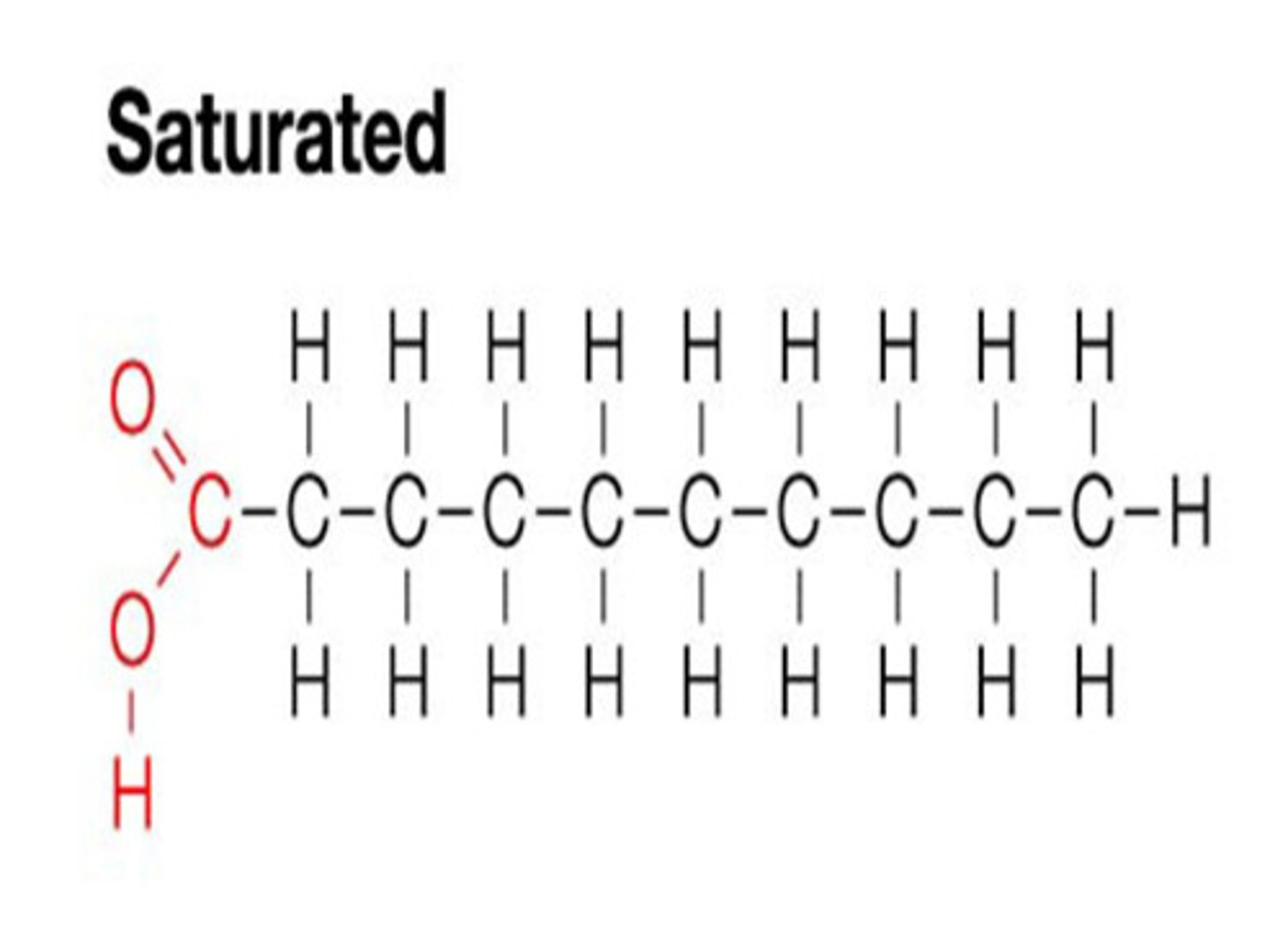
monounsaturated fats are ____ at room temperature. Animal or plant?
liquid, plant fats
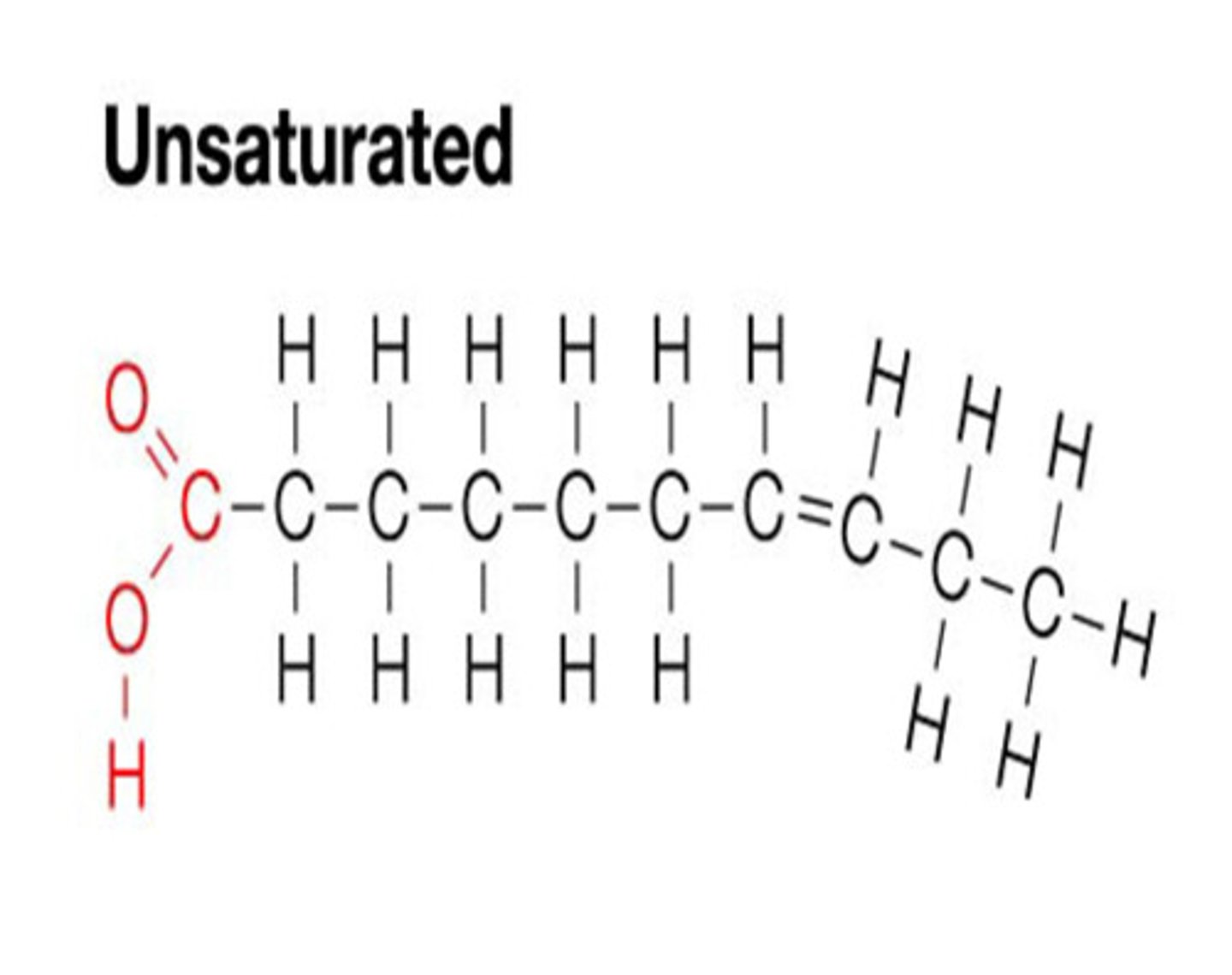
polyunsaturated fats are ____ at room temperature. Animal or plant?
liquid (ex. oils), plant fats
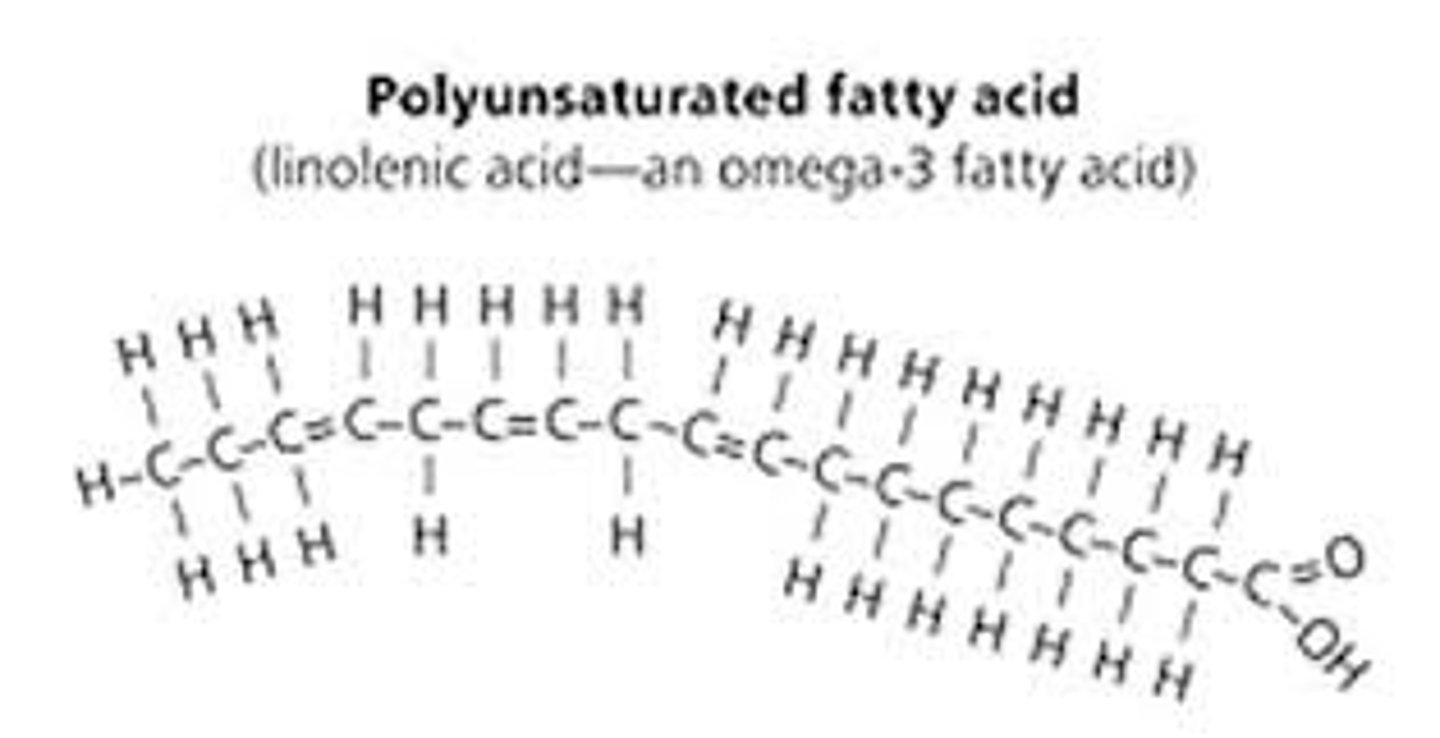
cis unsaturated fatty acid H placement
hydrogen atoms are nearly always on the same side of the two carbon atoms that are double bonded
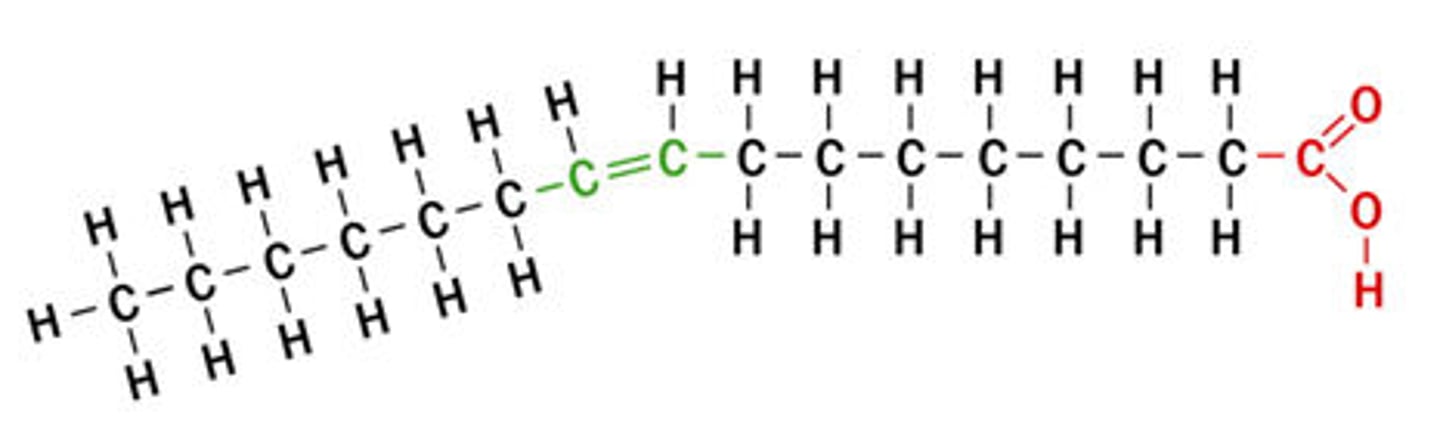
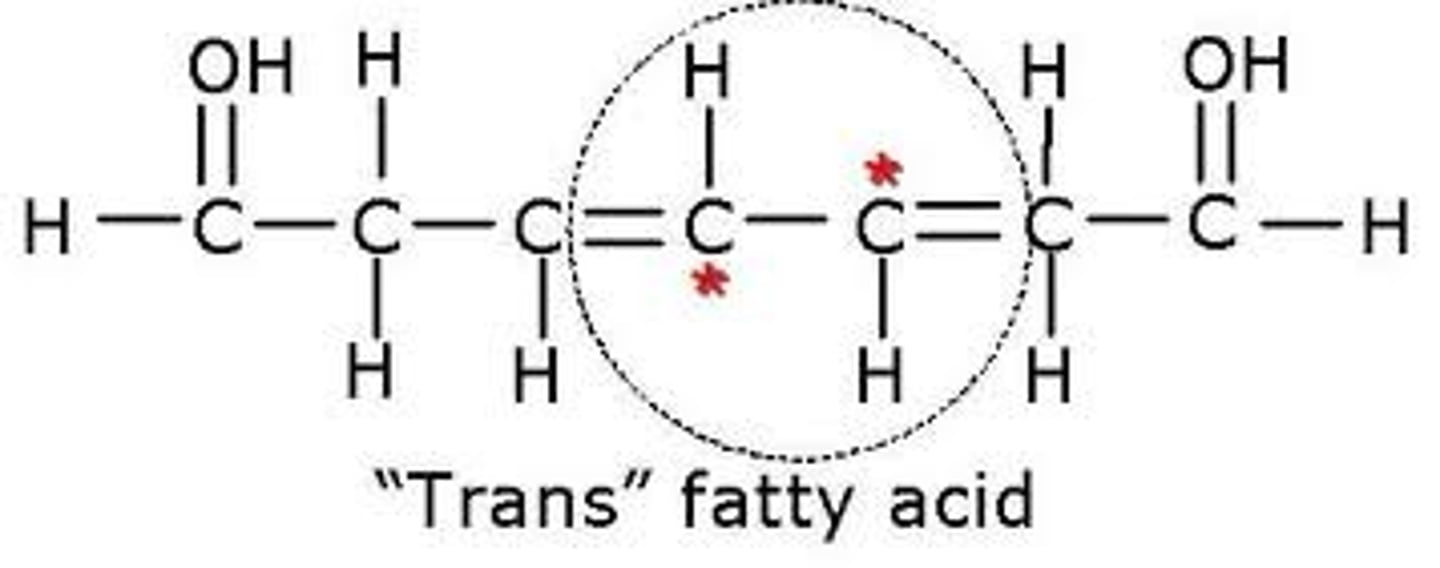
trans unsaturated fatty acid H placement
hydrogen atoms are on alternate sides or opposite from each other, produced artificially
ester bonds
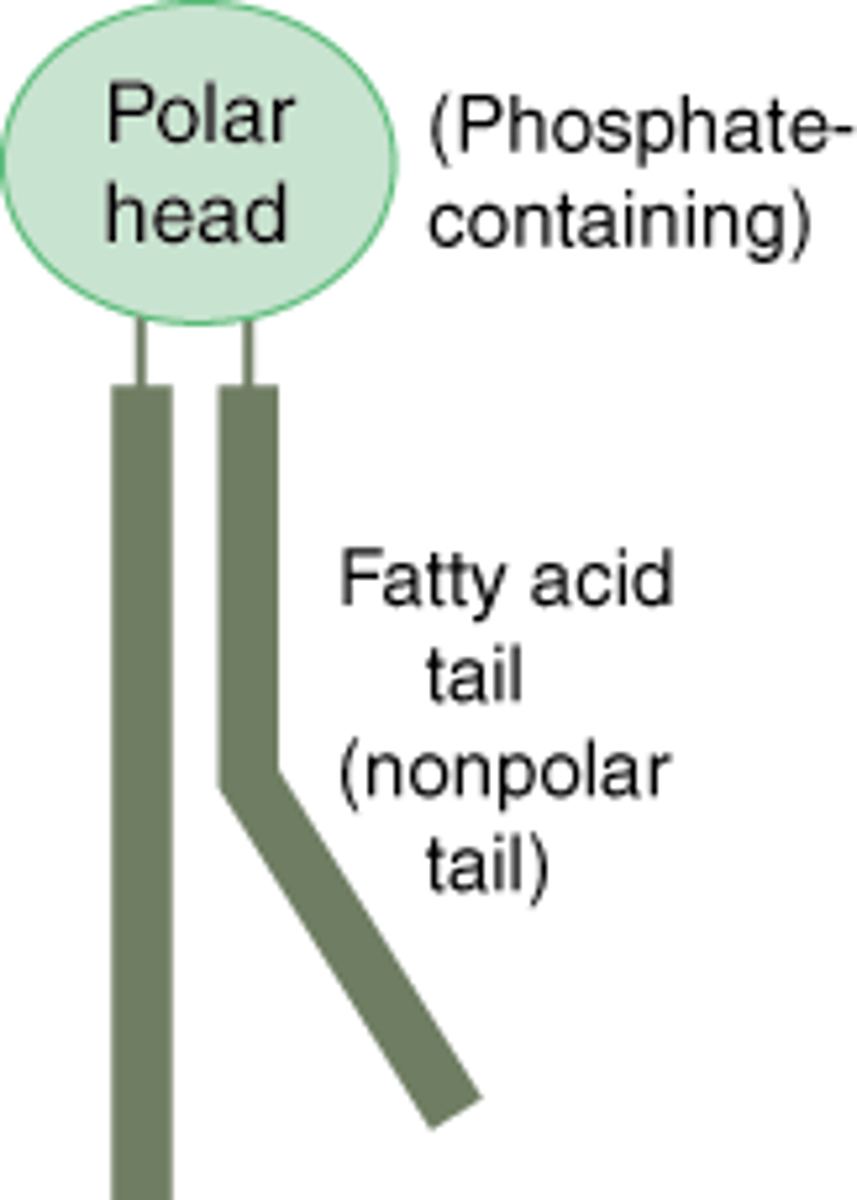
Phospholipids makeup. Which side is hydrophilic? Which side is hydrophobic?
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic tails
+HOH type of water
metabolic water
How do fats provide energy?
They have a lot of stored energy used to make energy for other aspects of the organism.
How do fats provide water?
Condensation reactions release metabolic water which is immediately used for the body.
How do fats provide insulation?
increased body fat reduces heat loss to the environment.
Steriods
Estrogen
Testosterone
Progesterone
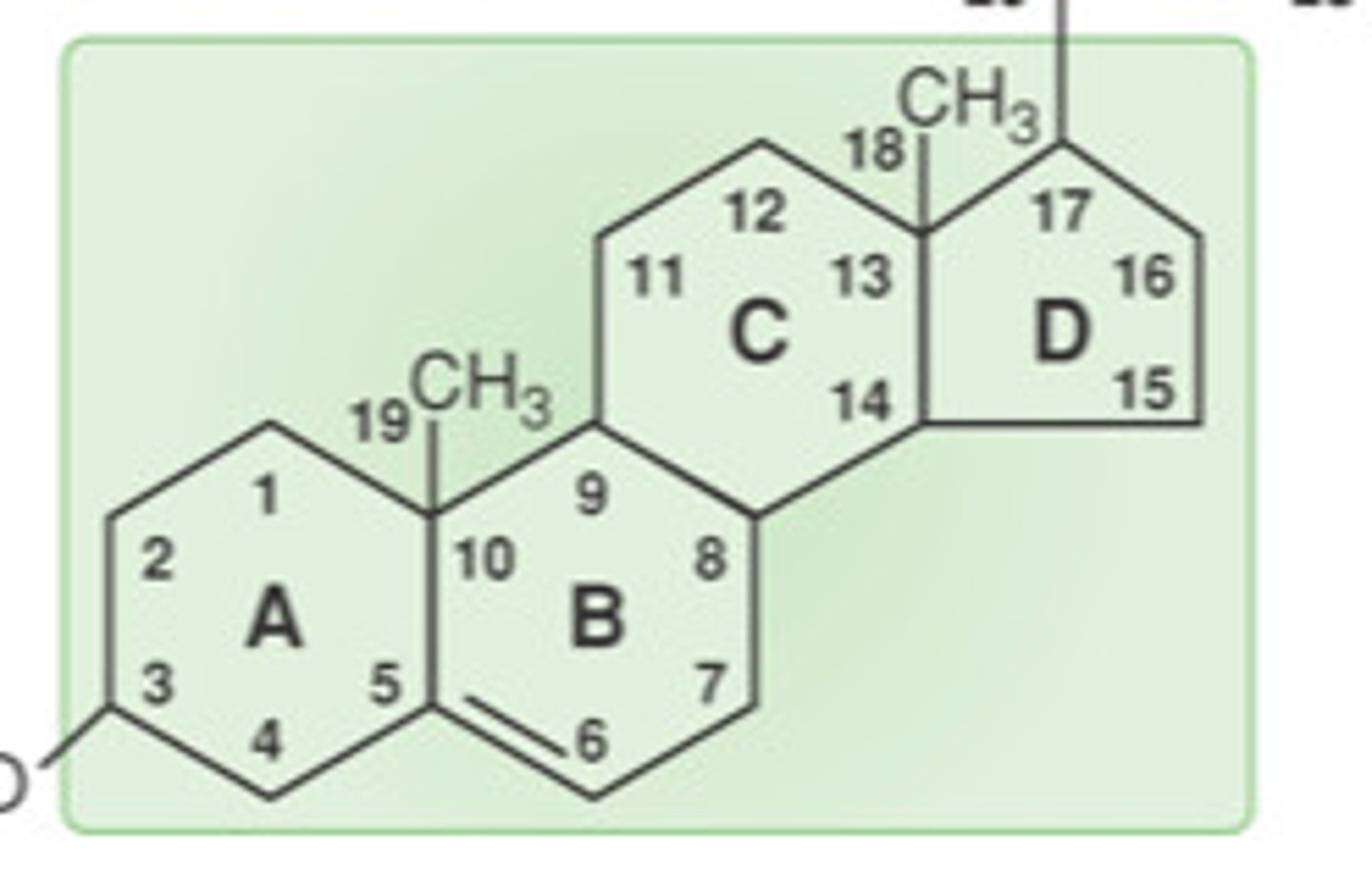
What do structural polysaccharides do? Examples.
found in cell walls of plants
Cellulose
Chitin
What do storage polysaccharides do? Examples.
responsible for being converted to energy later for body functions
Amylose
Amylopectin
Glycogen
Protien examples
meat/nuts/antibodies/Enzymes
protien elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (CHON) Sometimes S
protein functions
Structure (bones & muscles)
Transport substances in & out of cells
Immune system (antibodies)
control reaction rates & regulate cell processes (enzymes)
communication
Protein basic unit
amino acid
How many different types of amino acids are there?
20 humans can synthesize 8, plants can synthesize all 20
Amino acids are linked by what type of bonds?
peptide bonds
proteins are chains of what
amino acids
what is in the amino group
NH2
What is a carboxyl group?
COOH O on top is double bonded
what does the R group do?
gives each amino acid its distinct properties
Dipeptide
Two amino acids bonded together
oligopeptide
4-10 amino acids joined together
Polypeptide
more than 10 amino acids bonded together
amino acids can be
polar or nonpolar
amino acids with nonpolar R groups are
hydrophobic they fold away from water
amino acids with polar R groups are
hydrophilic they are exposed to water
primary protein structure
sequence of a chain of amino acids
secondary protein structure
alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
tertiary protein structure
The 3D folding of a polypeptide chain (may include prosthetic group)
Quaternary protein structure
the way that 2 or more proteins interact and fold
What two types of proteins are there
fibrous and globular
Fibrous proteins
shape
interaction with water
examples
fold into long narrow shapes
insoluble in water
collagen (skin) / Keratin (hair/fingernails)
Globular Proteins
Shape
interaction with water
examples
fold into compact rounded shape
soluable in water
enzymes/antibodies/hemoglobin
function of enzymes
catalyze chemical reactions
function of hormones
decrease blood sugar by increasing cellular uptake of glucose
function of defense proteins
protection against disease (antibody)
function of transport proteins
carry a molecule throughout an organism
function of structural proteins
to support (connective tissue)
Lipoproteins
protein combined with cholesterol/triglycerides/phospolipids
Glycoproteins
proteins combined with oligosaccharides
nucleic acids
chain of nucleotides
example of nucleic acid
DNA and RNA (chromosomes)
elements in nucleic acids
C, H, O, N, P
function of nucleic acids
store and transmit genetic information, control cell activity
nucleic acid basic unit
nucleotide (contains a phosphate group, sugar(ribose/deoxyribose), and nitrogenous base)
Nitrogen base
Purines
double ring
Adenine
Guanine
Nitrogen base
Pyrimidines
single ring
cytosine
thymine
how do the two parts of the nitrogeen base bond
2 rings bond to 1 ring
DNA
double/singe
shape
alternating groups
rung makeup
double stranded
double helix
sugar and phosphate covalently bonded
single purine hydrogen bonded to a single pyrimidine
RNA
double/single
shape
alternating groups
rung makeup
single stranded
helical
sugar and phosphate covalently bonded
(Uracil instead of Thymine) single purine (A/G) or a single pyrimidine (U/C)