mayan lowlands
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
mesoamerica env.
Heterogeneous
Important resources were circumscribed/limited but needed by everyone
So no choice but trade and exchange
Sedentism due to maize agriculture
Staying in one place for a long time
archi and cultural main points
Stepped pyramids, temples, ball courts
Monuments made of stelae
They were propagandist and had inscriptions and rulers
Record keeping in the form of calendars and writing systems
Distinct regional styles, ornaments become important
Commerce and market economies
Shared mythology and worldview
Political authorities were ritually based
domesticates
The American triumvirate
AKA the three sisters
Maize, beans, squash
A protein filled diet
Maize was smaller earlier on and then through selective breeding became bigger
During the American Neolithic
10,000 to 7000 years ago
agricultural base
60% of worldwide foods are American domesticates
Globalized after Spanish conquest
ex.
Maize
Manioc
Cassava
Potato
Beans
Pumpkin
Squash
Quinoa
Peanuts
Mexico, the Andes, the Amazon basin
Chili Peppers
Vanilla
Sun flower
Sweet potato
Avocado
Tobacco
Cacao
Pineapple
Tomato
Cotton
Very few animals
Turkey
Muscovy duck
Llama
Alpaca
Dog
Guinea pig
Stingless bee
4 agricultural centres
Mesoamerica
Highland South America
Eastern North America
The Amazon basin
increasing complexity
2000 BCE
Emergence of sedentary villages
In the valley of Mexico, Gulf Coast, Maya lowlands, oaxaca valley, the Pacific Coast
In arid regions, farmers combined maize and bean slash and burn agriculture along with foraging
Forested areas were cleared and burnt which adds fertilizer to the soil through the form of nitrogen
Other areas
Basic canal irrigation systems
Raised fields in swampy locations
No areas were dry
olmec
On the Gulf Coast
Not the central Highlands
1800 to 500 BCE
2000 years after the earliest civilizations in the old world
Do not know the origin
Probably local lineages held land and those with more became powerful and built locations to express their power through ritual performance
Earliest complex society in mesoamerica
Highlands, Pacific Coast and across MesoAmerica
Traded Obsidian, jade, Serpentine, magnetite, shells, Stingray spines, shark teeth
Symbols, architecture, rituals and concepts of kingship
Centres
San Lorenzo
1400 to 900 BCE
La venta
900 to 400 BCE
Tres zapotes
Around 900 BC
the epi-olmec period
Was not a single state but a series of chiefdoms
Monumental platforms that supported pyramids, basalt carvings, symbolism of kingship
olmec concept of kingship
Intermediary to gods
Power is expressed in art forms
First in mesoamerica to do so
Rulers are put on sculpted Thrones along with other symbolism
Elite alongside images of the cult of the serpent
Sometimes the Jaguar
Ceremonial architecture found in elite centres
Legitimizes the rule
san lorenzo
1200 to 900 BCE
Strategically positioned to trade within and beyond the olmec region
Traded pottery, carvings, figurines in exchange for semi precious stone like Obsidian and jade
Main platform
Had 20 architectural features (mounds) along the edges
They had 20 day months which was related to maize agriculture
Built earth ridges around the platform
Pyramid structure and ball court built on top
Centre had 8 monumental stone heads
mayan sub area
Southern Highlands
Made-up of geologically active east to West band of peaks and valleys
300 to 800 meters above sea level
Causing changes in altitude
Temperature
15 to 25°C
Rainfall
2000 to 3000mm which is objectively high
Lowlands
Subdivided
Southern
Dense broadleaf tropical rainforest
central
eastern
northern (yucatan)
Low scrub vegetation
Low lying karstic plains
Limestone
Temperature = 25 to 35°C
Rainfall
510 to 3050mm
Varied greatly
subsistence
Based on the three sisters
Supplemented by fruits, vegetables, some meat and fish (wild)
Agriculture relies on Land Management strategies that have to change through time and vary based on the region
Canals
In the swampland to provide drainage
Raised fields
Piling sediment above water level along the edges of lakes or swampy areas
Began in the first Millennium BCE
Wetland farming
Terraces
Slopes to trap soil from erosion
How they harvested forest fruit
Milpas
Managed forests
Household gardens
Allowed for a major increase in population
8 to 10 million people by 800 AD
Evidence gathered through aerial photos, traditional survey, lidar
Rich environment due to fish, water lilies, birds, insects, reptiles
aguada feniz
1200 to 800 BCE
Very early on in the civilization
Tabasco region of Mexico
East of the olmec
Found through lidar in 2020
Oldest monumental construction found in the Mayan area
One of the largest in mesoamerica
Made of earth and clay
Ceremonial complex
E group assemblage at the centre
Astronomical observatory
East to West orientation
North-south aligned
Artificial T shaved platform with ramps
20 mounds lining the exterior representing the months in the 260 day calendar
Communally built
Other similar complexes in the region
Between the olmec heartland and Mayan lowlands
Similar pottery found in southern Mayan region showing they probably had interaction
Similar layout to San Lorenzo and la venta
san bortolo mural
During the end of the middle pre classic and the start of the late preclassic
Modern day Guatemala
400 to 200 BCE
Oldest Mayan mural
Shows 9 figures
Maize God
Central figure
Depicted as defoliation of the corn plant
Part of his creation story
Life death and renewal
Symbolic of Maize agricultural cycle
Related to myths found in the Gulf Coast
Shows the coronation of a ruler
It was probably named in the glyphs
The glyphs have not been deciphered

el mirador
300 BCE to 150CE
Late preclassic
13.5 kilometers from the nakbe
Largest centre in the region as of 350 BCE
Core includes platforms on natural rise is surrounding by low lying swamp (bajos) that is rich of nutrients
Multi terraces
Topped by three buildings
Triadic groups
One large structure flanked by two smaller structures facing the shared courtyard
La danta
Stucco relief shows the first known images of the poul vuh
hero twins who defeat lord of underworld to get back the maize god (his sons)
Includes the largest pyramids ever built by the mayans
Extensive network of roads (sacbes)
mayan cosmology
World is square
Made of 3 worlds
Underworld
Watery
9 levels
World of the gods, demons, ancestors
Made of caves
Middle world
Stoney
Floats in the sea on the back of a crocodile like animal (caiman) or turtle
Upper world
Sky
Held by 4 gods located in the cardinal directions
Most important one is the caiman who sheds blood as rain
Story arch of heaven has 13 levels
Includes gods and supernatural beings
3 realms are linked together through the world tree
Used to move between the other worlds
Waka Chan

others worlds
Determine the fate of the living
Needs to be nourished by the living
Mayan kings and Queens were shamans who could access it through ritual performance
Through dressing like them or bloodletting (auto sacrifice)
Bloodletting causes them to be lightheaded so they enter an altered state
Through Obsidian, Stingray spines, ropes made of thorns
Ensures the success of the living
In return the king is owed tribute through labour, goods, the devotion of the people
Nourished the other world
Let on to paper that was then burned, God communicate through smoke
Opens the world tree which is a portal to the other worlds
To seek advice and favor from ancestors
Kings are portrayed as the world tree
popol vuh
Mythology and history of the kiche people of highland Guatemala
Creation myth
The exploits of the hero twins
Translates to " book of the community or book of council"
Transcribed by a Dominican priest in 1701
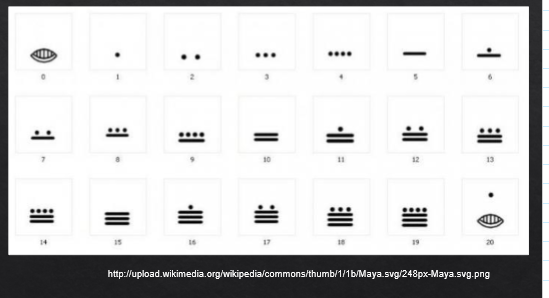
mayan number systems
20 based
vigesimal
Independently invented 0
Could add, subtract, multiply, divide
Three main symbols
dot = 1
bar = 5
shell = 0
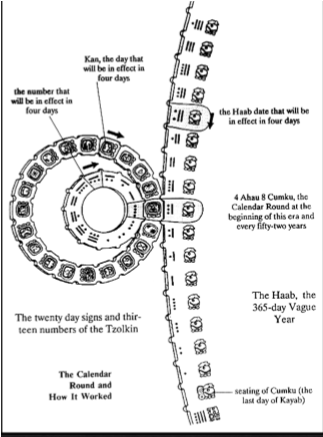
calendars
Sacred Almanac
aka the zolcin calendar
260 day calendar
Solar calendar
365.242 days
Similar to the Gregorian calendar which is 365.2425
High tech calculation shows it to be 365.2422
Mayans are more accurate
Intermeshed both calendars for a 52 year cycle
used by Mayans and other mesoamerican civilizations
maya classic period
250 to 900 AD
mayan city states
Never unified
Independent but shared culture, iconography, religion
elites had a shared language but diff. city states had separate languages too
Ended due to competition and warfare
Thousands of cities
One every 10 kilometers
Each had a civic and ceremonial core made of temples, royal palaces, plazas, causeways, monuments
They shared their gods but each would favor a different one
Own kings and Queens and royal dynasties
Surrounded by towns, villages, Hamlets, rural areas which was a continuum of the settlement
classic mayan society
Large divide between elites and commoners
King = supreme ruler
Divine but not to the extent of Pharaohs
Mediates between the mortal realm and the gods in the other worlds
Passed down through lineages unless someone managed to kill the king
Kin groups were ranked
Tiers of elites
Overlord
Divine Lord
Subservient Lord or regional governor
Neighborhood head
Specialization increased as population increased
Resulted in the middle class made of artisans, merchants, traitors, low ranking priests, soldiers, bureaucrats
Commoners were the vast majority and farmers
mayan cities
true Urban core
Different elements symbolize different things
Temples = caves
Pyramids = mountains
stelae = forests
Records history of kings and political events
don’t know if commoners could read the monuments
The main Power Points of the landscape and portals into the other worlds
Connects kings to deities
Provided urban services, places of commerce and residents for up to 100,000 people
Neighborhoods provided face to face contact
Lived in plazuela
Multiple structures that share a central patio
classic mayan city states
600 AD
Dozens
4 main for each region
Tikal
calakmul
palenque
copan
Each ruled over the surrounding hinterland
Rival centres fought each other for economic dominance and caused downfall
At some point had alliances but they dissolved
Cause periods of fluorescence and decline
3 main dynasties of early classic
kan'ul
at dzibanche
later capital moved to calakmul
suutz
at naatchun
mutul
at tikal
Main rivalry in the southern Mayan lowlands was between the main superpowers
tikal and calakmul
early classic tikal
one of the largest regional capitals in the southern Mayan lowlands
Home of the mutul dynasty
At peak had a population of 45,000 to 62,000 people
120km ^2
Economic powerhouse
` controlled trade routes from the Highlands and the coast
Highlands: Obsidian and greenstone
Coast = Stingray spines and salt
caused them to encircle calakmul
Most well known ruler
chak tok ich'aak
kan’ul
In the 6th and 7th century
dzibanche
Divine rulership
First known ruler is named
yuknoom ch'een I
They conquer tikal in 562 AD with the assistance of caracol who is a former tikal vassal
Destroys the tikal-teotihuacan alliance
Throne moves to calakmul in 636
Causes a civil war in dzibanche
entrada
378 to 550 AD
Influence moves from the central Highlands to the lowland and highland areas
Dynastic disruption at tikal
A vassal of a warlord arrives in 378 AD
sihyaj k'ahk
The same day chak tok ich'aak dies
sihyaj k'ahk installs the son of the warlord on the throne
but tikal is still an economic powerhouse
Then calakmul establishes alliances
6th cent.
Other powers try to reverse the encirclement
late classic period
calakmul apogee and decline
636 calakmul peaks
yuknoom ch'een II rules until he dies in 686
He expanded to naranjo in the east, el Peru waka and the West and to dos pilas And Cancuen in the South
This effectively encircles tikal
His son takes over and in 695 is defeated by the tikal jasaw chan k'awaii
This is recorded on a wooden lentil at a temple in calakmul
Which starts the decline
jasaw chan k'awaii's son defeats the naranjo and el-peru waka in 744
Completely collapsing calakmul Henry gaining access to the east West trade route
he then shifts his focus to the north in the late 8th century
terminal classic
Southern Mayan collapse
800 to 830
Period of upheaval
Pyramid constructions, erection of Stella, production all declined
Issues
High population and low sustainability
Drought
Warfare
Political instability
Divine kingship is abandoned causing major social reorganization
Some places were quickly abandoned but most experienced compression
elite and the poorest commoners leave first while the middle class and land holders stayed for several more generations
By 10th century most lowlands abandoned and move north to the northern lowlands
City is like chichen itza, uxmal, ek balam rise