psychology psychological problems
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
changes in addiction overtime
then: concerned with substance misuse, regular users are thought to be prescribed (substances) for medical reasons, statistic suggests that the number of addictions are rising
now: includes behavioural addictions (internet, video games..) regular users are considered to be addicts, sources of addiction are becoming cheaper to access
changes in depression overtime
then: people were less likely to be diagnosed, less awareness, lifestyle then was relatively stressfree
now: more people are being diagnosed with depression, more awareness of symptoms, more stressful
how depression affects us individually
social: withdraw from family and friends, no longer do activities that they previously found fun
emotional: worthlessness and sadness (more suicide),
occupation: do not have the motivation to work (feels demanding and tiring and has lack of sleep)
healthcare: treatment is costly
how depression affects society?
crime: 10-15% of people with depression commit suicide
costs: expensive to give sick pay and work cover
how addiction affects individuals?
social: ignore friends and families, spend money on addiction not necessities
emotional: denial, guilt, fear, helplessness, anger
occupation: health problems → unable to work → take time off → fired
healthcare: costly to support individual for treatment
how does addiction affect society?
crime: turn to crime to fund addiction
costs: drug related crimes costs lots for governments, costly to police, punishments are expensive
addiction
the need to have or do a particular thing or activity in order to be able to go by their normal routine
withdrawal
unpleasant physical or psychological symptoms that someone gets when they are trying to quit
Dependence disorder
dependent on a substance such as alcohol and cocaine
behavioural addiction
dependence on activity such as gambling
symptoms of dependence disorders
ignoring evidence that use of substance is harmful to them
feeling that the person needs to take the substance
stopping the use of substance is very difficult
tolerance of substance increases
physical withdrawal symptoms
symptoms of behavioural addiction
ignore the evidence that the activity is unhealthy
need to do the activity regularly
spend more time doing activity than other things they used to enjoy
reducing activity is very difficult
genotype
set of genes in our dna which is responsible for a particular trait (phenotype)
monozygotic and dizygotic
monozygotic: share 100% of genes
dizygotic: share 50% of genes
genetic explanation of addiction
identical twins: if one was a smoker there is a high chance the other twin will also smoke
genes: heavy users of cocaine are likely to have a particular version of dopamine receptor
gene and alcoholism: adopted children with one biological parent with alcohol addiction are highly likely to show signs of alcohol addiction themselves
environmental influences: alcohol misuse in adoptive family, child has a greater risk of developing the same addiction
strengths of genetic explanations of addiction
lots of scientific evidence
twin and adoption studies could explain addiction
weaknesses of genetic explanation of addiction
some people are more likely
reductionist: fails to take other social factors into account
explains only some people why they’re addicts
learning theory of addiction
classical conditioning
operant conditioning
social learning theory
classical conditioning
learn through associations
experience one thing → automatically triggers other thing
operant conditioning
behaviour repeated when they lead to positive consequences
social learning theory
behaviour learned as a result of observing people and modeling their behaviour
positive reinforcement
adding a pleasant reward to increase behaviour
negative reinforcement
removing something unpleasant to increase a behaviour
vicarious reinforcement
repeating a behaviour that someone else got a reinforcement for
strengths of learning theory of addiction
Assumes addictive behaviors can be unlearned, allowing development of effective treatments.
Operant conditioning (OC) acknowledges biological factors, like brain release of ‘feel good’ chemicals reinforcing drug use.
weaknesses of learning theory of addiction
Mainly ignores biological causes of addiction.
Does not explain why many try addictive substances but only some become addicted.
treating addiction
medication → cope with effects of detoxification
SSRIs: increases amount of serotonin in brain
detoxification → when addicts tries to stop taking the substance they are addicted to
CBT - cognitive behavioural therapy
help people understand triggers for their addictive behaviours and how to control them
stages of CBT
functional analysis → identify triggers
skills training → learn and use new skills to avoid engaging in the addictive behaviours
homework → between sessions patients are asked to keep a diary of important events and record progress
strengths of drug therapy for addiction
research evidence
help patients access other types of therapy
weaknesses of drug therapy for addiction
evidence is mixed
patients may become dependent on medication
strengths of CBT for addiction
supported by research
aims to give patient control on their own behaviour by building new forever skills
weakness of CBT for addiction
requires patient to have motivation to stop
learning coping skills does not mean it will reduce the problem behaviour
Young et al study?
CBT on internet addicts
Young et al aim
investigate the effect of using CBT to treat a group of patients diagnosed with internet addiction (how the problem behaviour improves during the therapy, after the therapy session have ended)
procedure of young et al
114 participants recruited from the Centre for Online Addiction
Completed the Internet Addiction Test (IAT)
Online CBT sessions
3rd, 8th & 12th online therapy session – 6 months after
12 questions – rated their behaviour and or feelings on a 5-point Likert-type scale.
Measured clients’ attitudes towards CBT sessions, including the relationship the client felt towards their therapist.
findings
questions in questionnaire: motivation to stop using online apps, time management, relationship function, sexual function
There was some improvement over the 12 weeks of therapy
There was no significant drop in ratings 6 months after
strength of young
Generalisability: Large sample of internet users, relevant to at-risk groups.
Reliability: Used a standardized questionnaire based on addiction criteria.
Application: Helps develop treatments like CBT.
Validity: Measures key addiction symptoms accurately.
Ethics: Low risk, with informed consent and confidentiality.
weaknesses of young
Generalisability: Sample may not represent all ages or cultures.
Reliability: Self-reports can be biased or inaccurate.
Application: Focuses on diagnosis, not causes of addiction.
Validity: May oversimplify addiction, missing biological factors.
Ethics: Risk of stigma from labeling participants as addicted.
depression
An extreme lowering of mood that is persistent which affects day to day functioning.
key symptoms of depression
Disturbed sleep
Poor concentration or indecisiveness
Low self-confidence
Poor or increased appetite
Suicidal thoughts or acts
Guilt or self blame
Agitation or slowing of movements
features of depression
mild: 4 symptoms
moderate: 5-6 symptoms
severe: 7+ symptoms
genetic explanation of depression
Genetic Predisposition: Tendency to become depressed as a result of their genes
Diathesis-stress model: People have gene but is only triggered by a stressful event
evaluation of genetic explaination
Lots of research evidence.
We can explain depression by looking at genes people might inherit.
Reductionist – fails to take in to account other factors that can explain why someone may develop depression.
cognitive explanation of depression
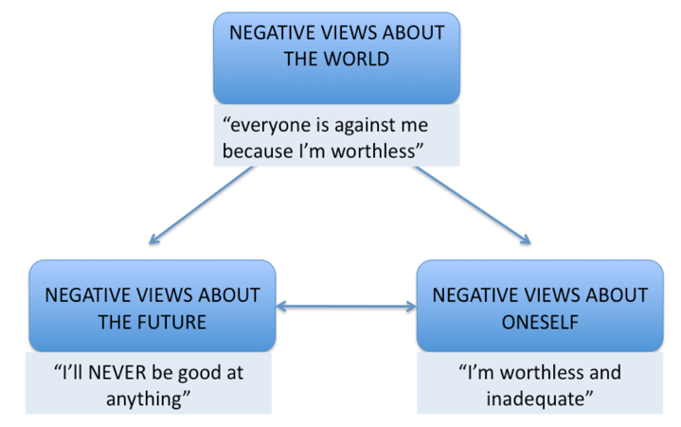
ellis abc model
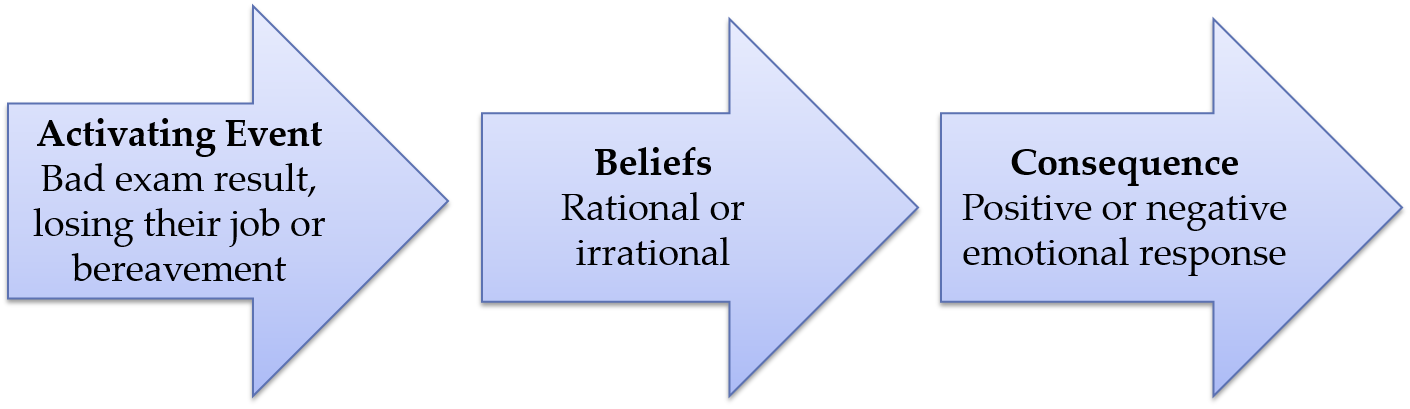
evaluation of cognitive explanation of depression
Takes into account the events in the person’s life
It is difficult to tell whether irrational thought are a cause or a symptom of depression
Some types of depression may not be so easily explained by thought possesses.
The Cognitive Theory explanation has been applied to CBT
treatments of depression
drug therapy: antidepressants (SSRIs)
blocks the reuptake of serotonin, increases levels of serotonin in the brain, improving mood
evaluation of drug therapy
Drugs improve symptoms but do not treat the disorder: Patients become more likely to relapse after treatment
Drug therapy can have unpleasant side effects: Drowsy, nauseous and dizziness.
They improve patients symptoms enough for them to access other psychological therapies.
Evidence to support: 50-60% of patients with moderate to severe symptoms show improvements compared to 20-30% who were given a placebo
evaluations of CBT
Long term benefits: Matthejts Beltman et al. (2010) Depressed patients treated with CBT improved more than those still waiting for treatment or not receiving treatment.
Patients learn to control their own symptoms: It may be longer lasting than only using antidepressants – reduces feelings of helplessness.
Patients must be motivated to change for CBT to be effective: If patients are unmotivated, CBT will not be effective
Ethical Issues: CBT assumes patients’ thoughts are wrong and attempts to change the way they think
caspi et al study?
This study looks at whether a gene (5-HTT) linked to the neurotransmitter serotonin makes some people more likely to be depressed after stressful life events than others.
aim of caspi
To investigate why stressful life events seem to lead to depression in some people and not others.
procedure of caspi
There was 847 participants split into three groups depending on the length of their allele.
It was a longitudinal study as participants were researched from an early age
Group one: 2 copies of the short allele
Group two: one short and one long allele
Group three: two copies of the long allele
Participants were asked to complete two questionnaires
Stressful life events between 21-26 years old.
Symptoms of depression before one year prior to their 26th birthday
findings of caspi
Participants with a short version of the 5-HTT gene who experienced stressful life events were more likely to be diagnosed with depression.
strengths of caspi
Large sample including both males and females improves generalisability.
Used standardized measures and natural gene variation, enhancing reliability.
Demonstrated gene-environment interaction, useful for targeted depression treatments.
Biological basis and multiple measures support validity.
Low physical risk to participants, meeting ethical standards.
weaknesses of caspi
Sample limited to ages 21–26 and lacked cultural diversity, reducing generalisability.
Relied on self-report data, which may be biased and less reliable.
Oversimplifies depression by focusing mainly on genetics, ignoring social and cognitive factors.
Reductionist approach and some replication issues limit validity.
Possible psychological distress from recalling stressful events raises ethical concerns.