Final Exam
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
20 mmHg
what do you inflate the cervical stabilizer to?
22; 10
for the cervical stabilizer the patient performs a chin tuck to _____ mmHg for ____ seconds
2; 30
for the cervical stabilizer, patients can progress to ____ mmHg at a time up to _____ mmHg (10s holds for all)
40 mmHg
what do you inflate the cuff to for lumbar stabilization?
60
for the lumbar stabilizer the patient performs TA activation inflating the cuff to _____ mmHg for a 10s hold
5
for the lumbar stabilizer we do not want more than ____ mmHg of movement during the hold
TA
for the lumbar stabilizer we can progress by performing BKFO, mini marches, and SLRs while holding the ____ activation and keeping the pressure at 60 mmHg
precautions of aquatic exercise
fear of water
neurological disorders (ataxia, heat-intolerant MS, epilepsy)
respiratory disorders (hydrostatic pressure inhibits lung expansion)
cardiac dysfunction (angina, abnormal BP, heart disease)
small, open wounds (post-surgical patients must have a healed incision)
contraindications for aquatic exercise
-cardiac failure or unstable angina
- respiratory dysfunction (VC < 1L)
- severe PVD
- Danger of bleeding/hemorrhage
-open wounds w/o oclcusive dressing, colostomy, and skin infections
- uncontrolled bowel or bladder
- menstruation w/o internal protection
- water and airborne infections or diseases
- uncontrolled seizures during past year
buoyancy
upwards force exerted by the water on an object
- works against gravity
- provides joint unloading and resistance to movement
hydrostatic pressure
pressure is exerted equally on all surface areas of an immersed object at rest at a given depth
- deeper = greater force (high pressure at ankles_
- limits or reduces swelling
- assists venous return
- induces bradycardia
- centralizes peripheral BF
viscosity
friction between molecules of liquid, resulting in resistance
- increased velocity of movements = increased resistance
surface tension
acts as a membrane under tension
- an extremity that moves through the surface performs more work than kept underwater
- can use equipment at the surface to increase resistance
10
at C7 our body is _____ percent WBing
25-30
at the xiphoid process our body is ____ to _____ percent WBing
50-60
at ASIS our body is _____ to _____ percent WBing
78-95 degrees
what temperature is required for mobility/flexibility, strengthening, gait training, and muscle relaxation?
78-82 degrees
what temperature is required for CV training and aerobic exercise?
71-78 degrees
what temperature is required for intense aerobic aquatic exercise?
adverse mechanical neural tension
inability of nervous tissue or dura to sufficiently lengthen
subjective s/s of AMNT
deep ache or stretch with movement
paresthesia (burning/tingling/prickling sensation)
objective s/s of AMNT
guarding to keep nerve slacked
positive special tests
median nerve
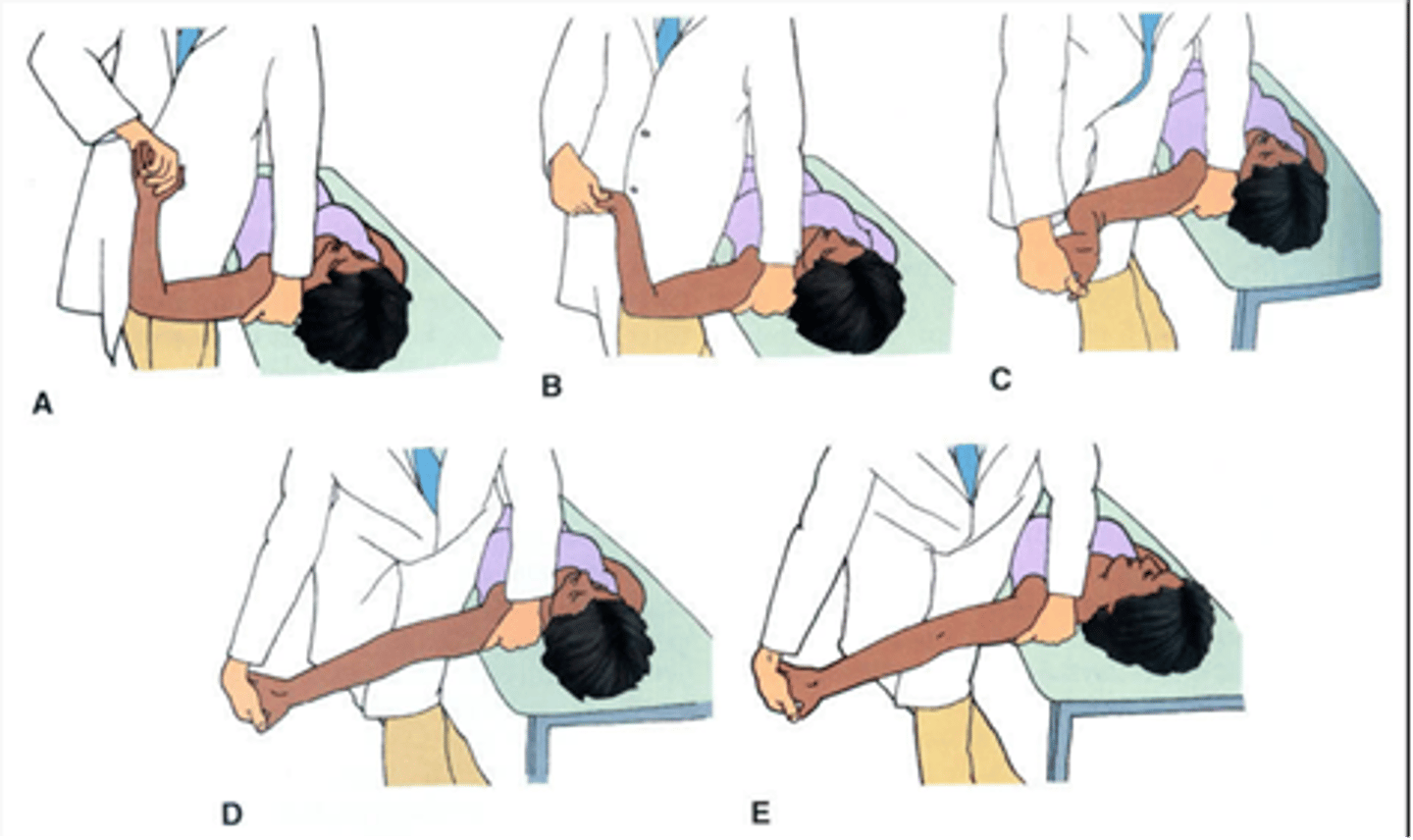
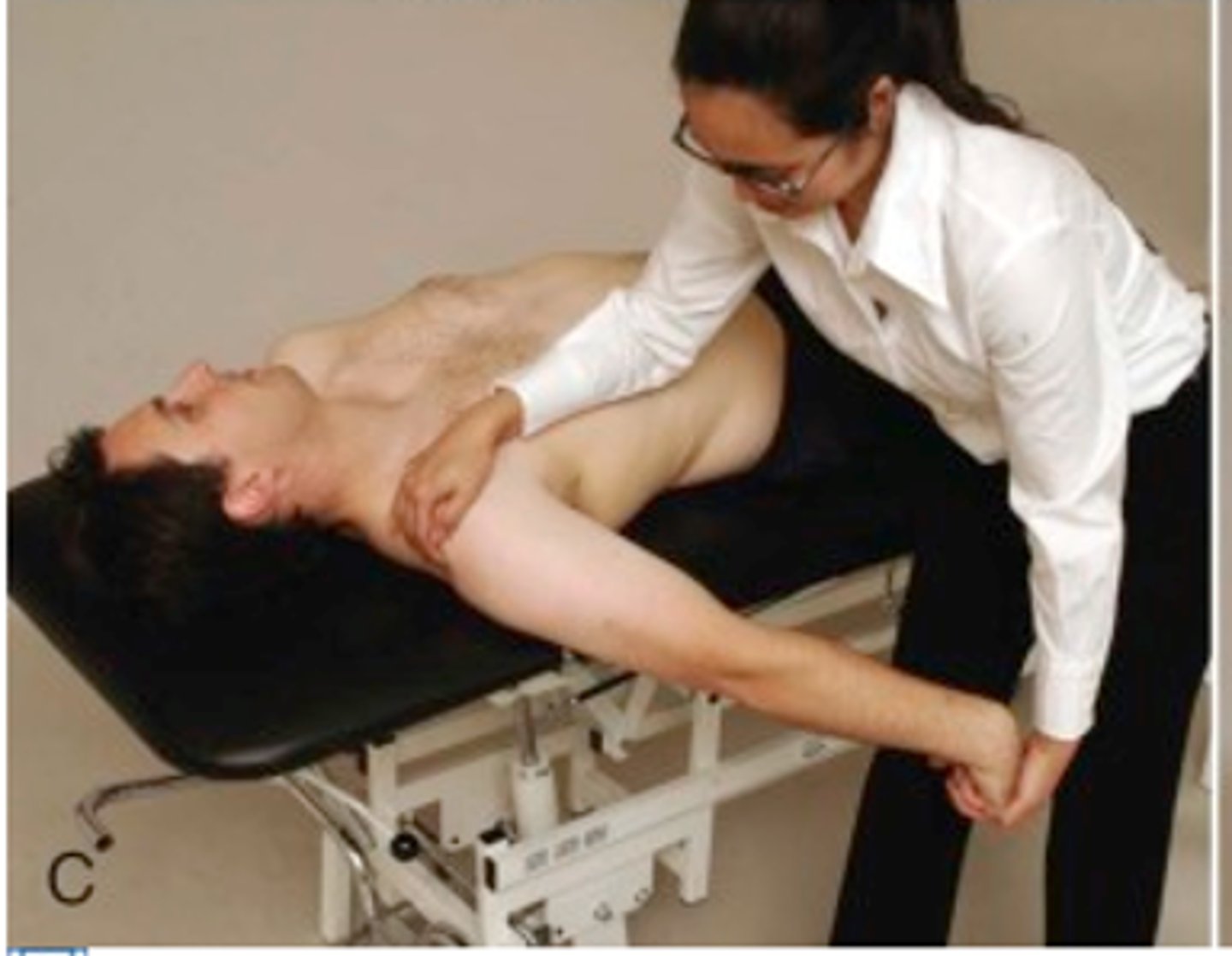
radial nerve
test at 110 GH abd
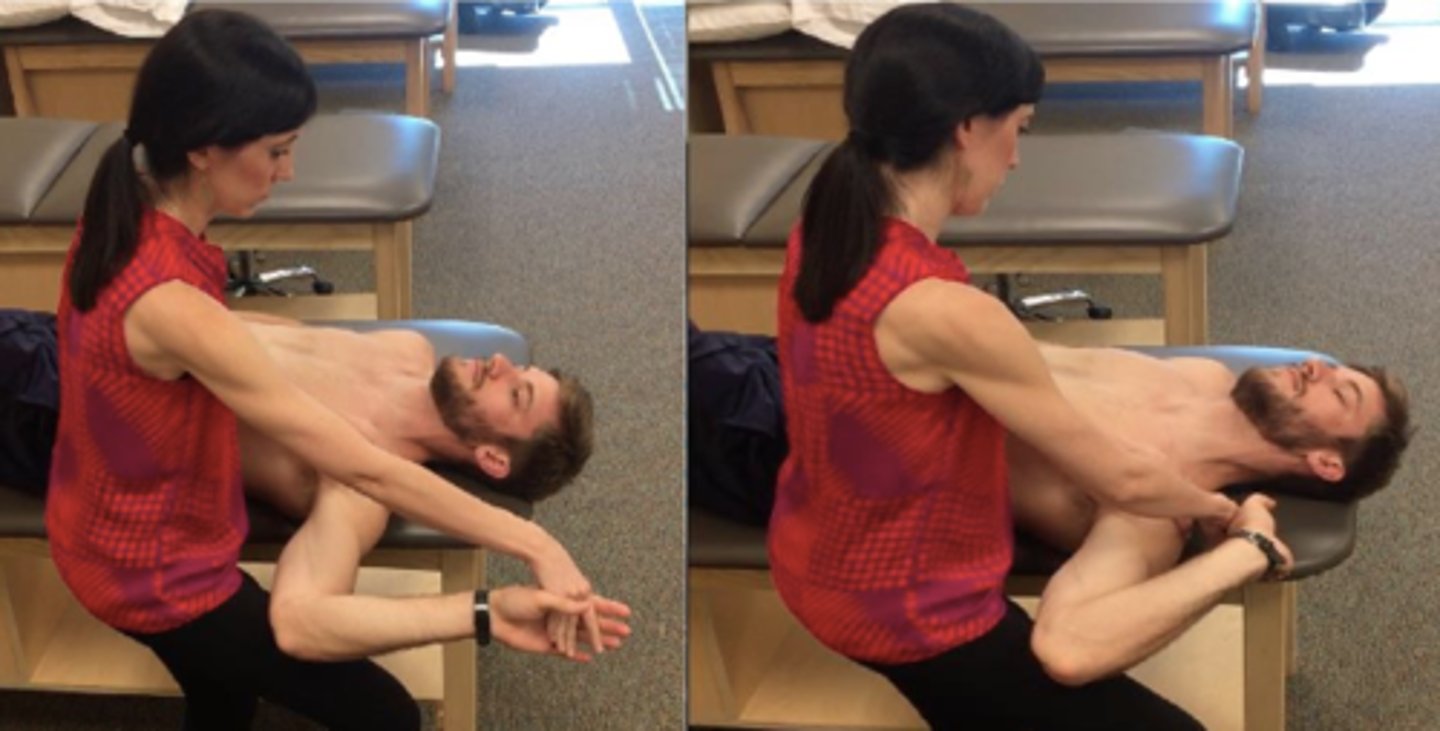
ulnar nerve
sciatic nerve
can add cervical flexion to increase symptoms and extension to decrease symptoms
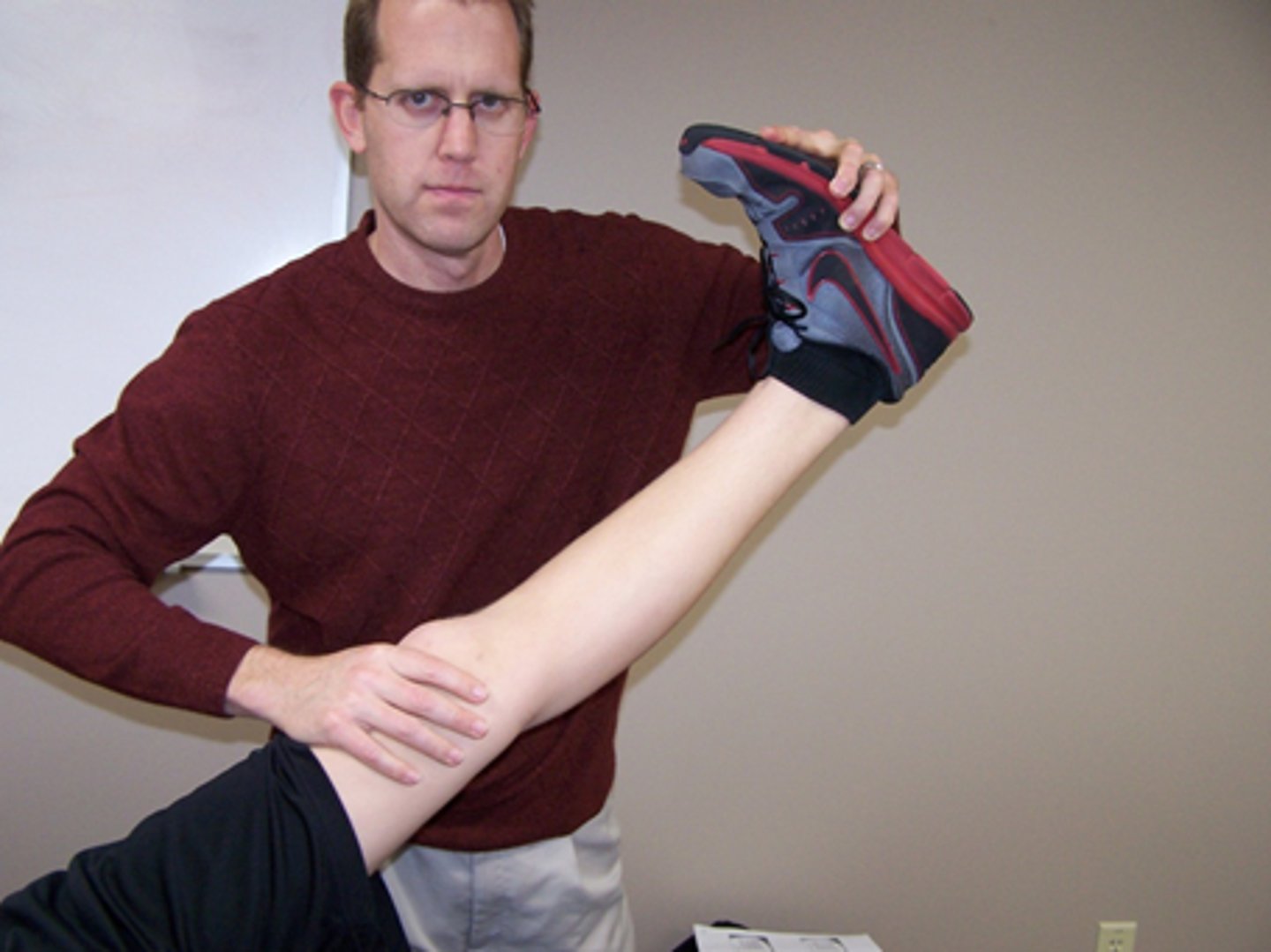
flossing
increase tension on one end of the nerve track while slacking the other end
slow and gentle oscillations 3-4 min, 5-6x/day
contraindications for neural mobilizations
- acute/unstable neurological signs
- weakness/paralysis
- seizure
- loss of sensation
- cognitive changes
- pain
- decreased alertness
- cauda equina symptoms (changes in bladder/bowel function and perineal sensation)
- SCI or symptoms of SCI
- neoplasm and infection (mass of tissue, rapidly growing cells)
postural balance
keeping your COG within your BOS
12.5 degrees
what is the normal amount of AP sway?
16 degrees
what is the normal amount of ML sway?
ankle strategy
used during small displacements
DF (tibialis anterior)
at the ankle, if there is a posterior displacement of the COG, what strategy would be used?
PF (gastroc/soleus)
at the ankle, if there is an anterior displacement of COG, what strategy would be used?
hip strategy
used when ankle motion is limited, displacement is greater, and standing on unstable surfaces
HS and paraspinals
at the hip, if there is a posterior displacement of COG, what strategy would be used?
abs/quads
at the hip, if there is an anterior displacement of COG, what strategy would be used?
stepping strategy
used when displacement is large enough that a forward/backward step is used to regain postural control