testing haematology - anaemia
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
when doing a blood cell count what anticoagulant is used
EDTA - salt, doesnt dilute the blood
what does a full blood count analyse 5
haemoglobin level
white blood cell count - looks at levels of dif types of wbc (automated differential)
red blood cell count
platelet count
red cell parameters
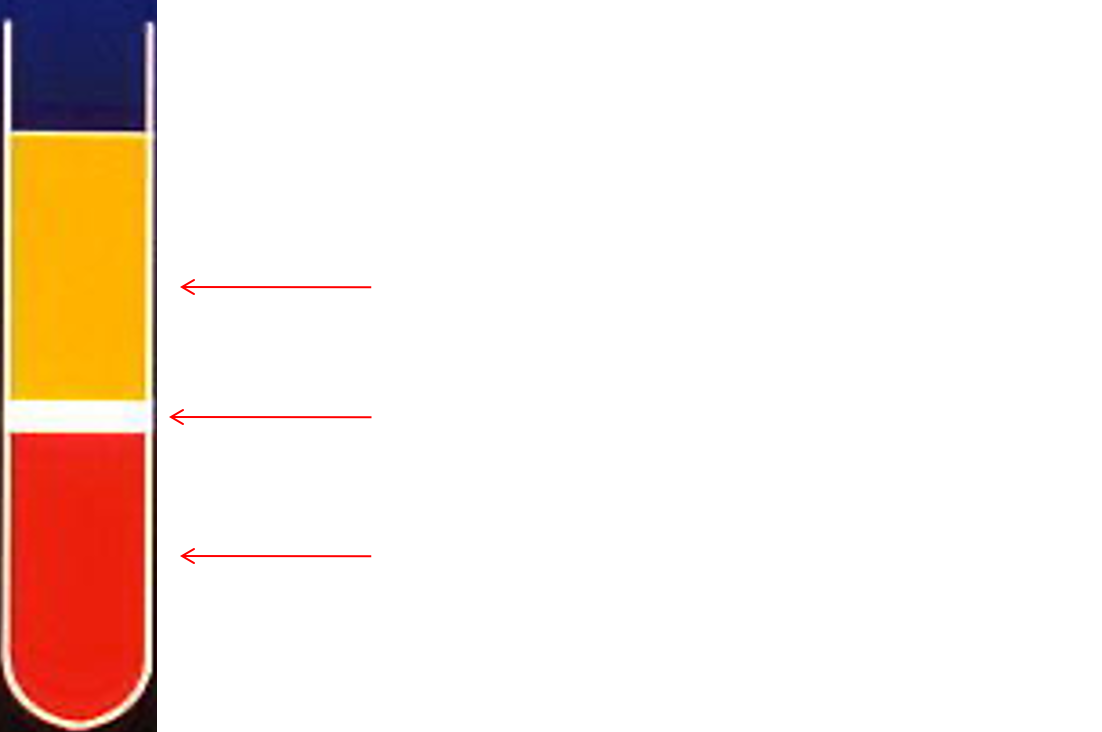
centrifugation of anticoagulanted blood
normal haemoglobin values
MEN 13 - 18 g/dl
WOMEN 12 - 15 g/dl
Red Blood Count (RBC) 4.5-6.5x1012/l 3.8-5.8x1012/l
Mean Cell Volume (MCV) 78-93 fl
Mean Cell Haemoglobin (MCH) 27-32 pg
Packed Cell Volume (PCV) 0.40-0.52 l/l 0.37-0.47 l/l
Reticulocyte Count 0.2-2.0%
normal wbc value
5 – 10 x 109/l
Neutrophils 2.0-7.5 x 109/l 40 - 75%
Lymphocytes 1.5 – 4.0 x109/l 20 – 45%
Monocytes 0.2 – 0.8 x109/l 2 – 10%
Eosinophilia 0.04 – 0.4 x109/l 1 – 6%
Basophils <0.01 – 0.1 x109/l 1%
normal platelet values
150 – 400 109/l
how haemoglobins measured
►Measured by haemiglobincyanide (HiCN) method
►Blood diluted in solution containing potassium cyanide and potassium ferricyanide
►Hb, Hi, and HbCO converted to HiCN.
►The absorbance of the solution is measured in a spectrophotometer at 540nm
►Can use Sodium lauryl sulphate instead of KCN to reduce toxicity.
mean cell volume =
Hct (haemltocrit) x 1000/rbc
size of RBC
►MCH - mean cell haemoglobin
►MCH = Hbx10/RBC
haemoglobin count
►MCHC - Mean cellular haemoglobin concentration
►MCHC = Hb/Hct
RDW - Red cell distribution width
►This is a volume distribution histogram which allows different populations of red cells to be seen.
►Expressed as a CV of the red cell volume (%)
►Can all be used as diagnostic markers
Reticulocyte Counting
►RBCs released from the Bone marrow in the last 3 days
still has Ribosomal RNA
(normal rbc dont have nucleus)
Romanowski Stain - pH 6.8
methylene blue - stains nucleus plus
eosin y - stains haemoglobin
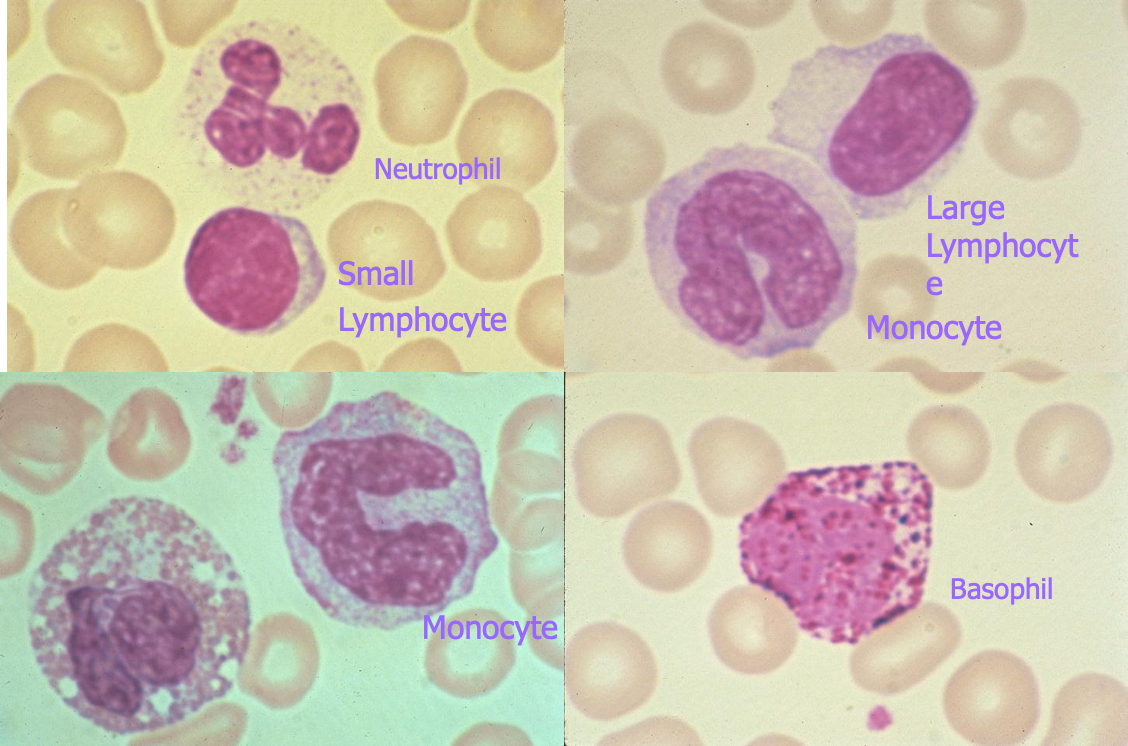
Normal Peripheral White Blood Cells
what is anaemia
►A reduction in oxygen-carrying capacity due to a lower haemoglobin concentration than is usual for that individual.”
►Anaemia occurs when red cell destruction is greater than red cell production.
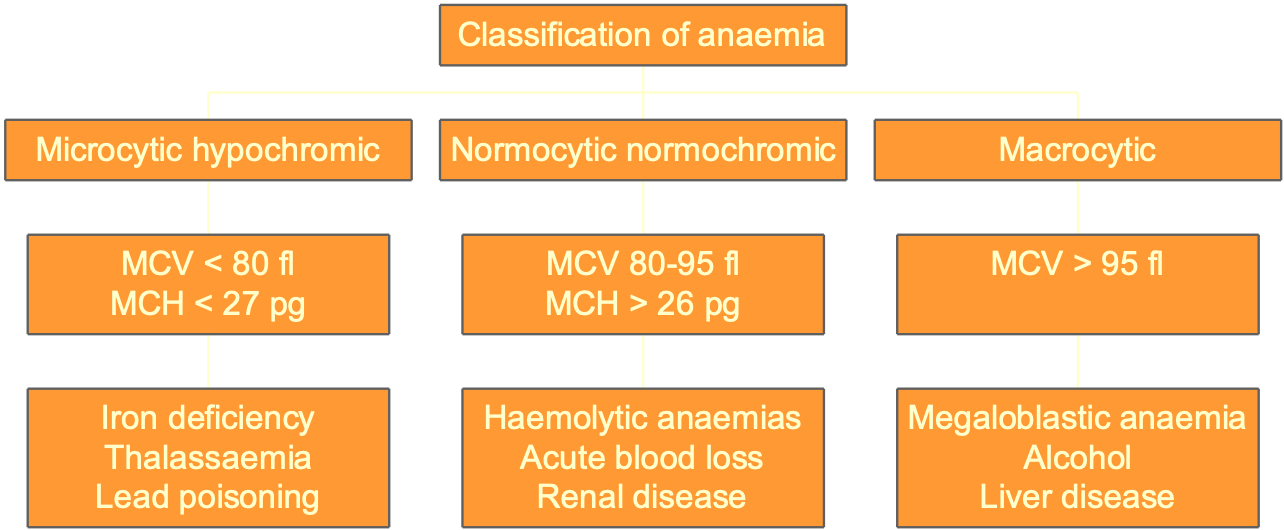
Classification of anaemia
morphologic classification based on appearance and size of rbc
►Red cell indices obtained from analysers.
§Haematocrit
§ Mean cell volume
§Mean cell haemoglobin
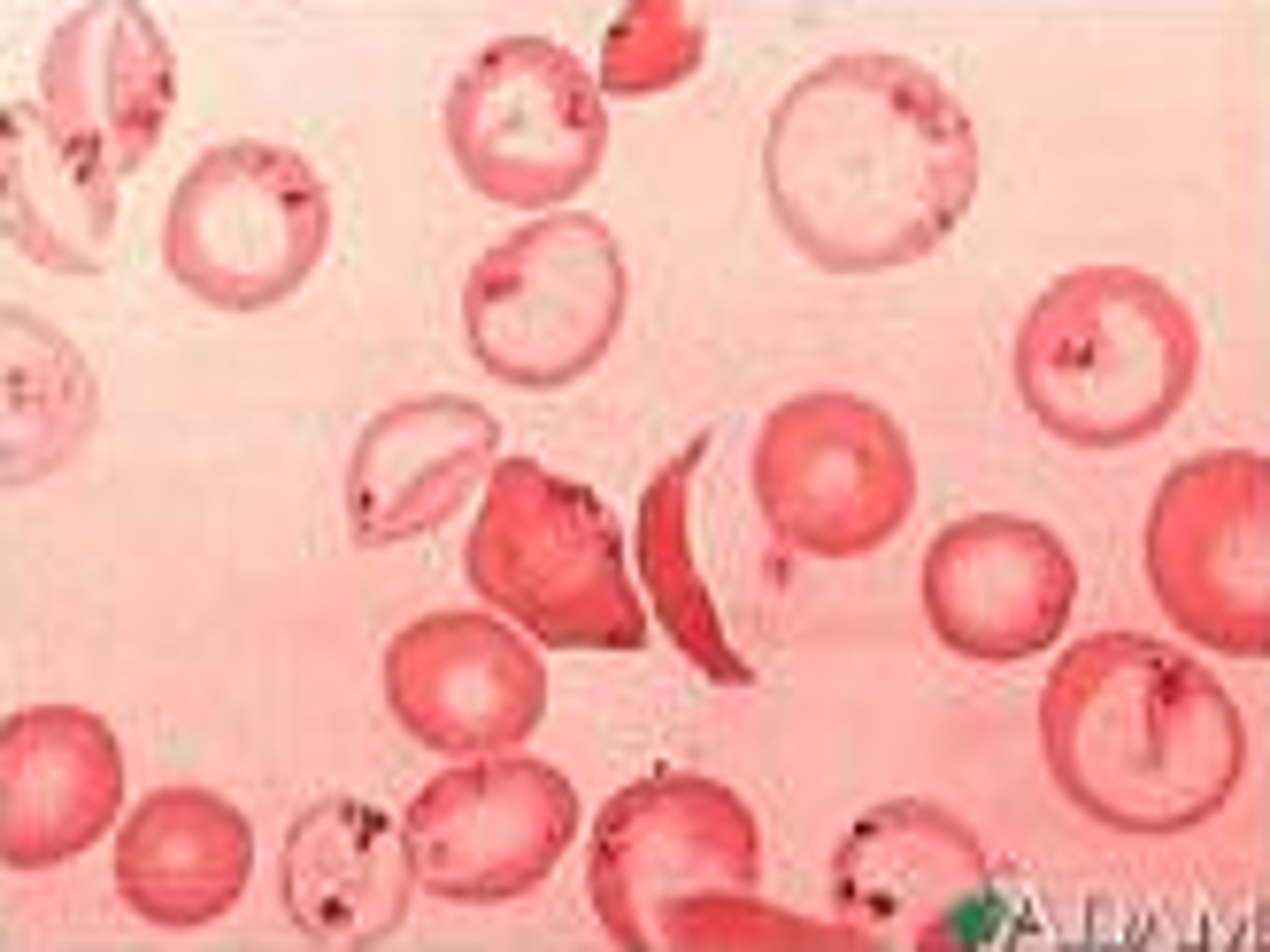
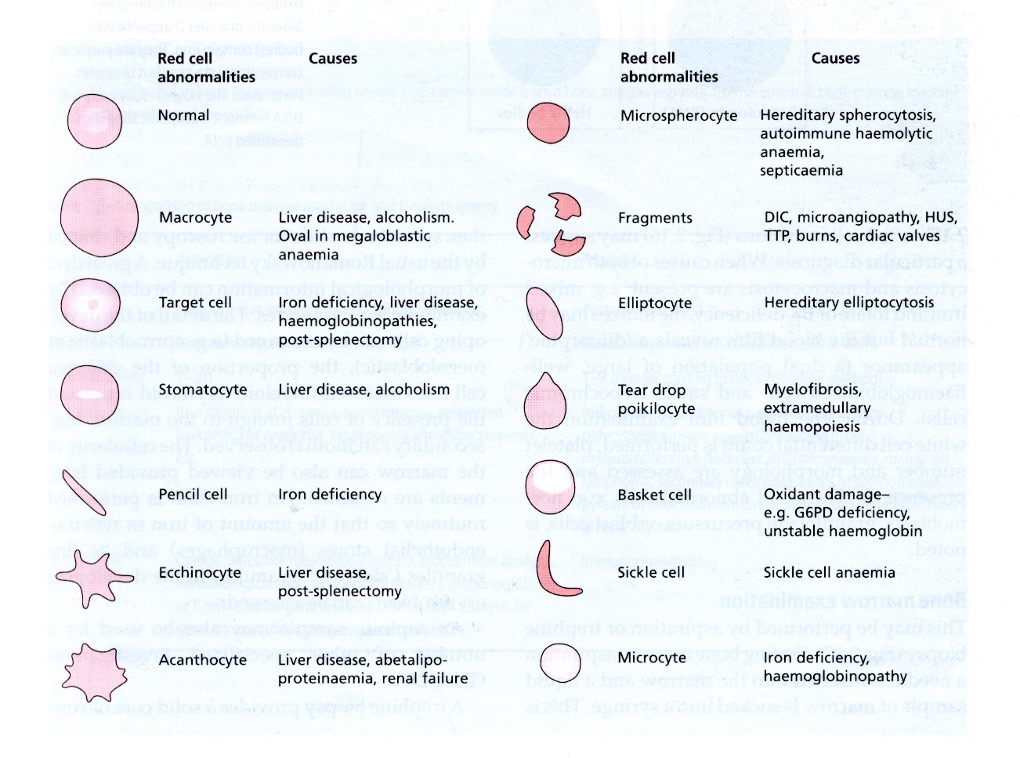
red cell morphology
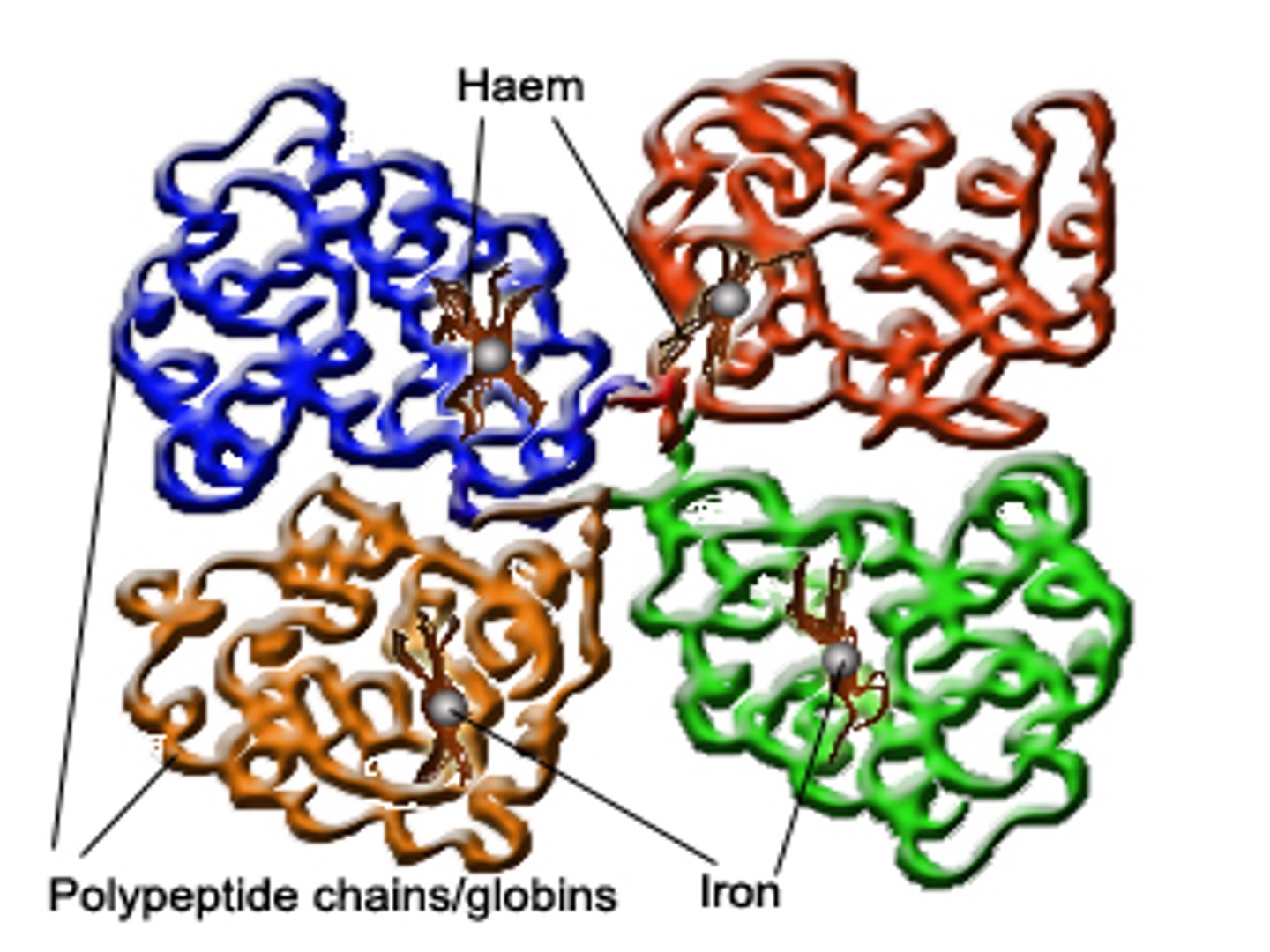
haemoglobin structure
§Four globin chains (2 alpha, 2 beta).
§Each globin chain has an iron containing haem molecule.
The iron in thehaemmolecule binds to oxygen
genetics
in foetus - Hb F
►In normal adults 96 – 98% of haemoglobin is HbA, Hb A2 (2 – 3%) and HbF (<1%) constitute a minor component of the total haemoglobin.
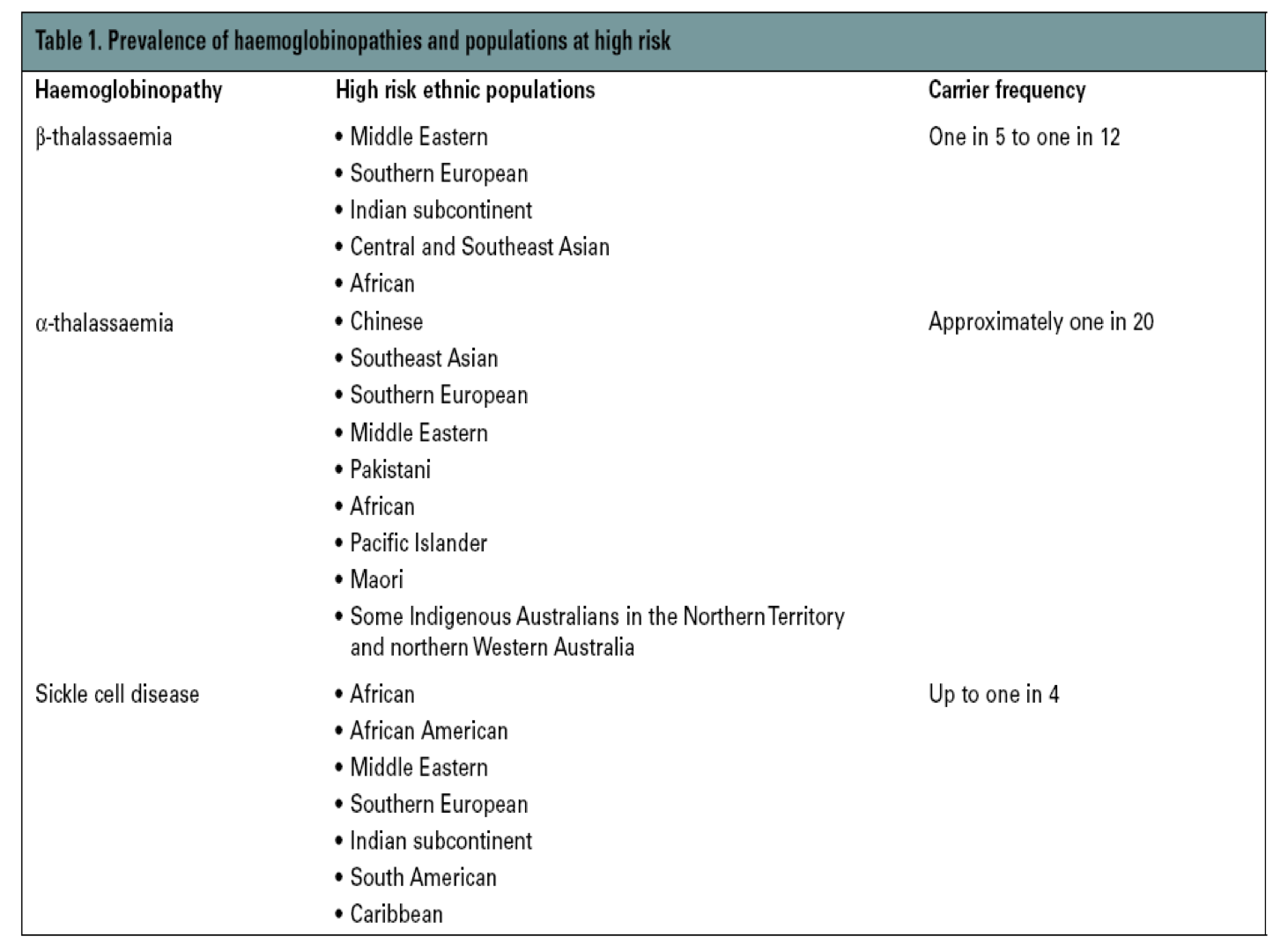
geography
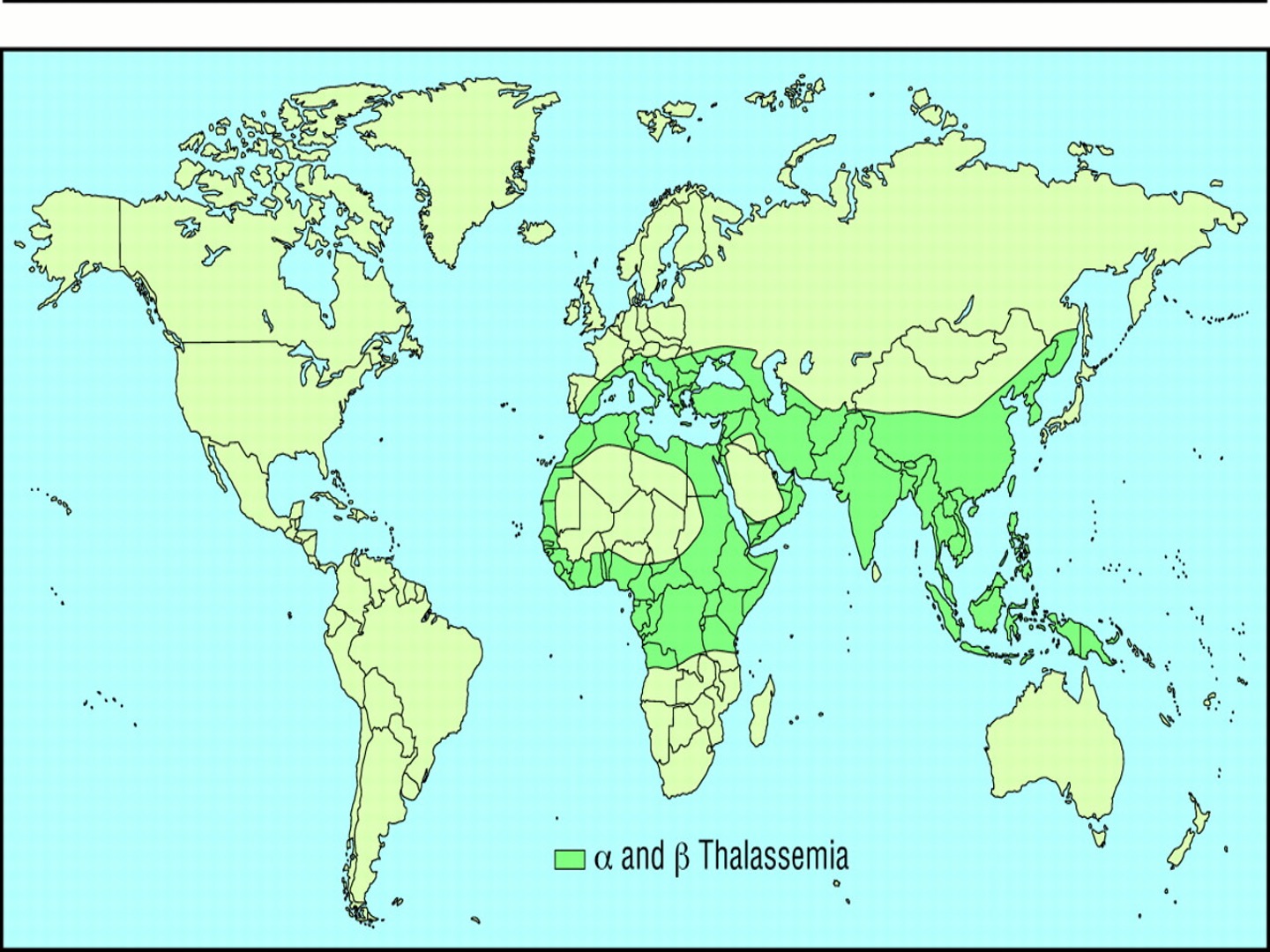
thalassaemia
§is a reduced rate of synthesis of globinchains.
Defined by imbalance αβ ratio
lower rbc count and haemoglobin count
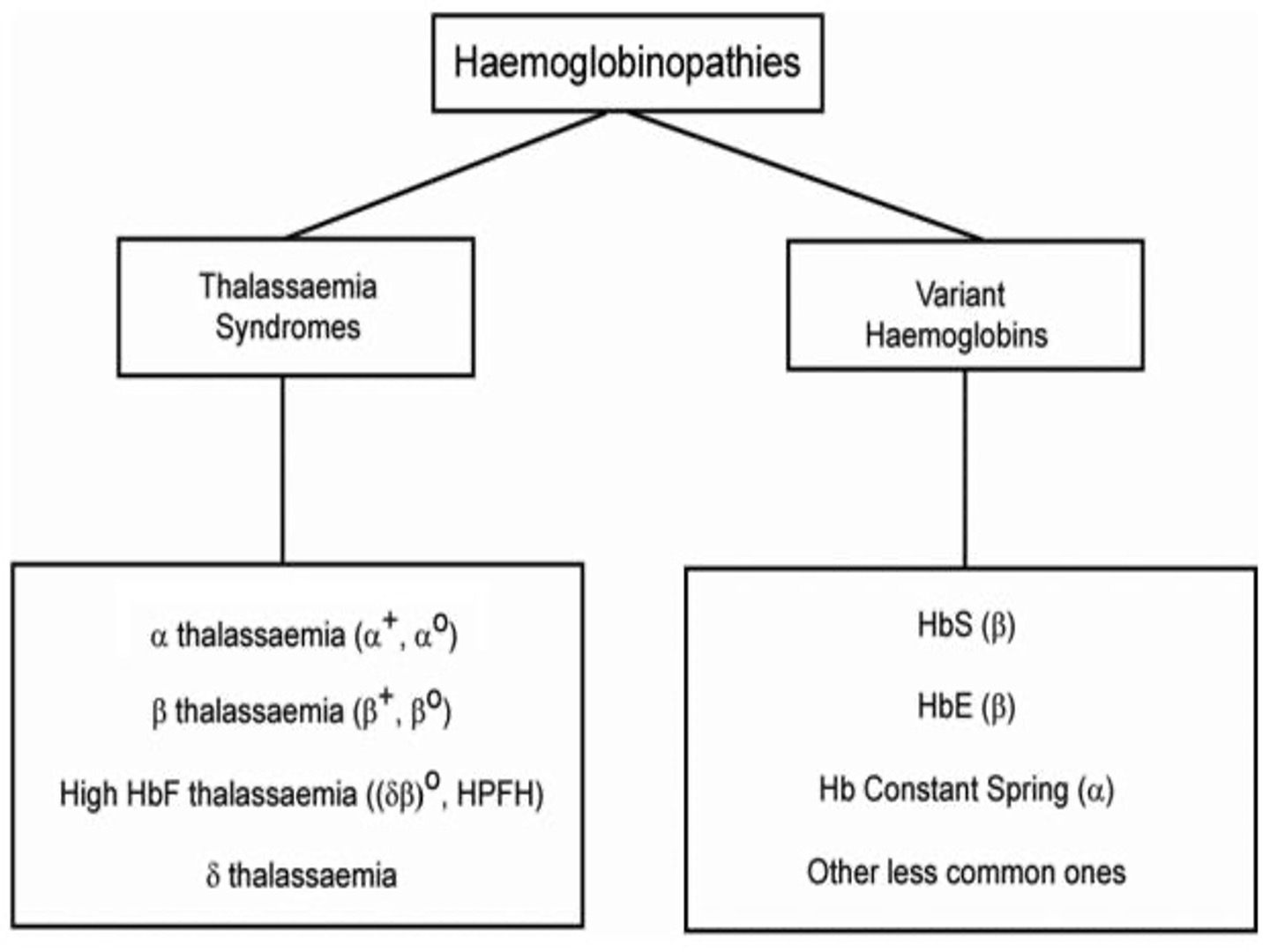
alpha thalassaemia classification
gene deletion
►α trait due to deletion of one or two of the four alpha genes, asymptomatic (eg - α/ α α, --/ α α, - α/- α).
►Haemoglobin H disease is the lack of three of the four α genes resulting in alpha thalassaemia major.
►Haemoglobin Bart’s Hydrops Foetalisresults from absence of all four αgenes, incompatible with post natal life.
beta thalassemia classification
reduction in beta chain production
β thal major - severe phenotype
β thal minor - asymptomatic
β thal intermedia - intermediate phenotype
►β 0 syndromes are characterized by the affected gene producing no beta chain.
►β + syndromes are characterized by the abnormal gene producing beta chains at a reduced rate.
►Usually due to point mutations.
variant haemoglobin classification
disorders of globin chain synthesis
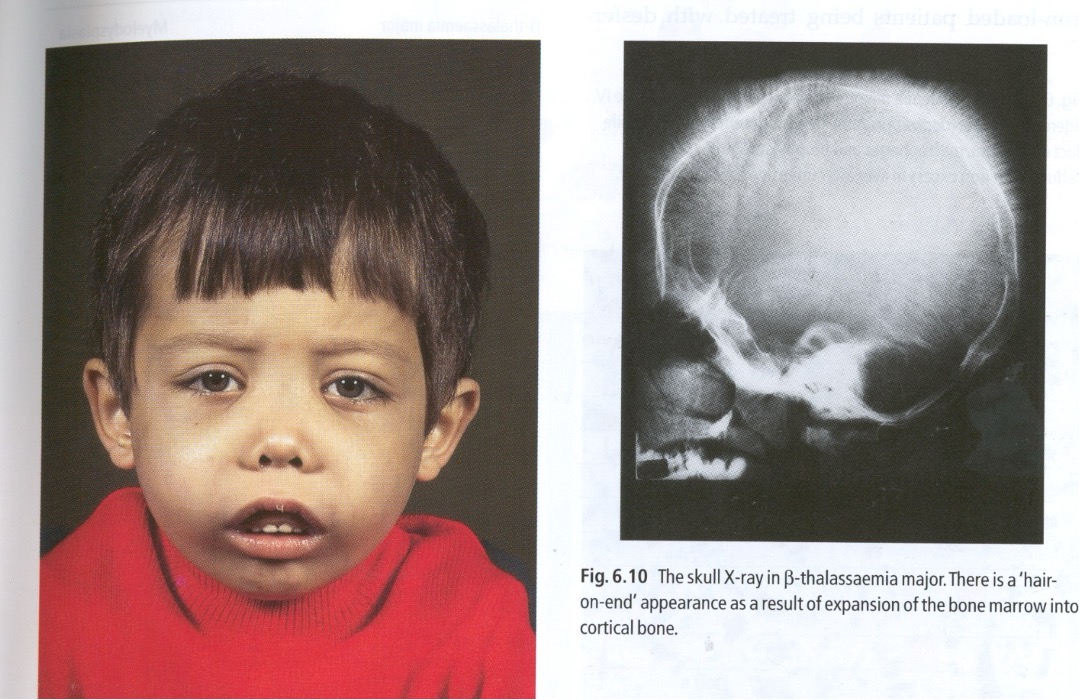
Clinical features of b - Thalassaemia major
iron overload causes liver damage ]
delayed or absent puberty
Diabetes
excess melanin
prone to infection
b - Thalassaemia major treatments
►Regular blood transfusions
►Regular folic acid.
►Iron chelation therapy.
►Vitamin C
►Endocrine therapy
►Immunisation against Hep B
►Bone marrow transplantation.
Automated Cell Counting methods
(Erythrocytes / Leucocytes / Platelets) 2
electricalimpendance
laser light scatter
electrical impedance
the electrical resistance of a particle passing between 2 electrodes is proportional to the particles volume
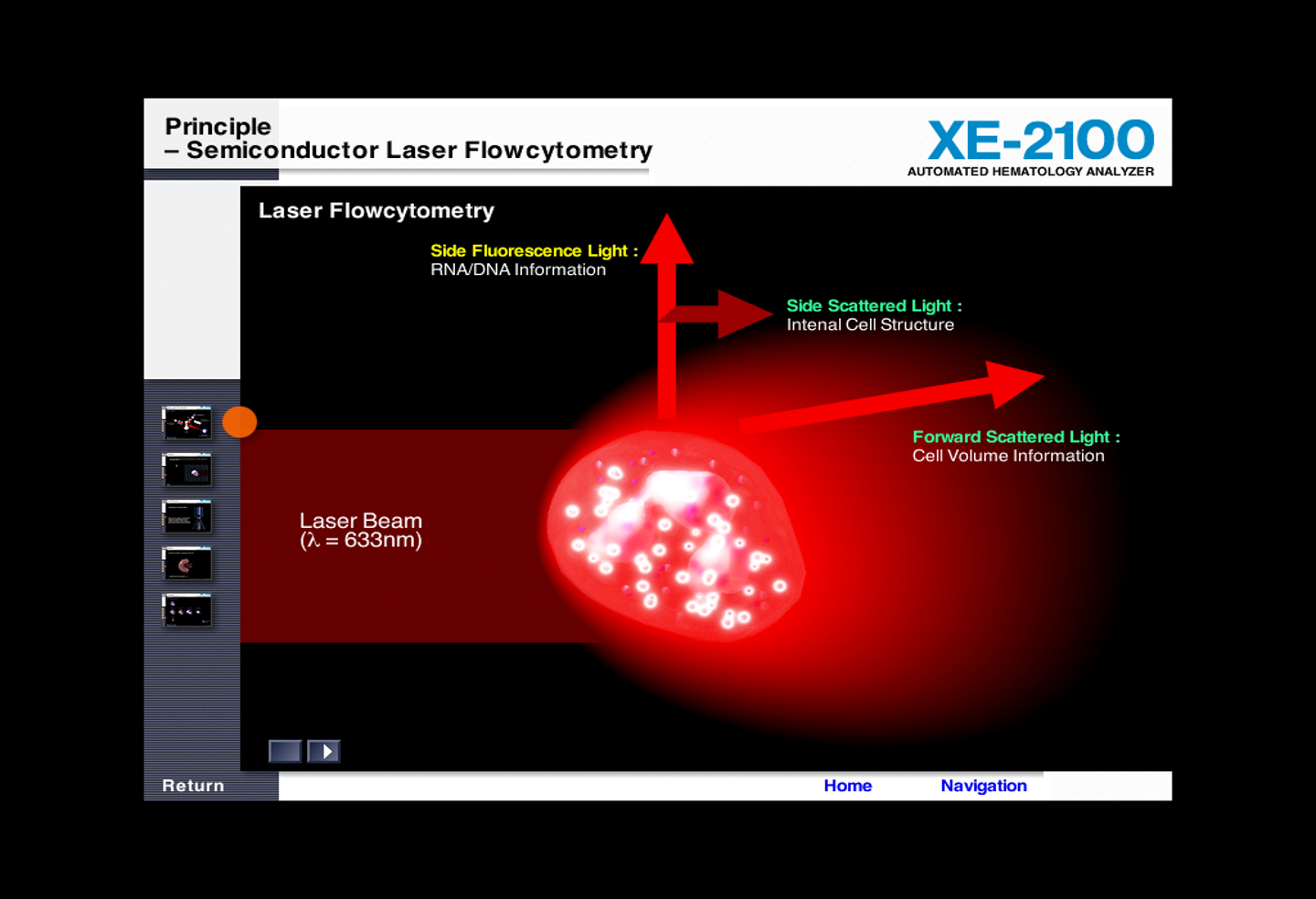
laser light scatter
the light scattered by a particle passing a beam of laser light is proportional to the particles volume
haemoglobin abalysis - spectrophotometric methodology
Absorbance proportional to Hgbconcentration
►
(Hgb less than optimum = Anaemia)
fbc thalassaemia
►RBC often increased in thal but decreased in iron deficiency and ACD.
►Hb typically normal in thal minor but decreased in intermedia and major syndromes.
►MCV is the most valuable parameter in predicting thal.
Hb H inclusions
►Hb H is an insoluble tetramer consisting of four beta globin chains, due to a lack of alpha chains in alpha thal major.
►In Hb H disease 30 – 100% of RBCS contain Hb H inclusions.
►In alpha thal minor there is one cell with Hb H inclusions per 1000 – 10,000 RBCS
►When there is a reticulocytosis a rare Hb H inclusion may be missed – operator experience crucial.
►Detection of Hb H inclusions points to an alpha chain mutation and narrows the amount of DNA analysis required.
►False negatives problematic, even with 2 alpha gene deletions no inclusions may be seen after several minutes of searching.
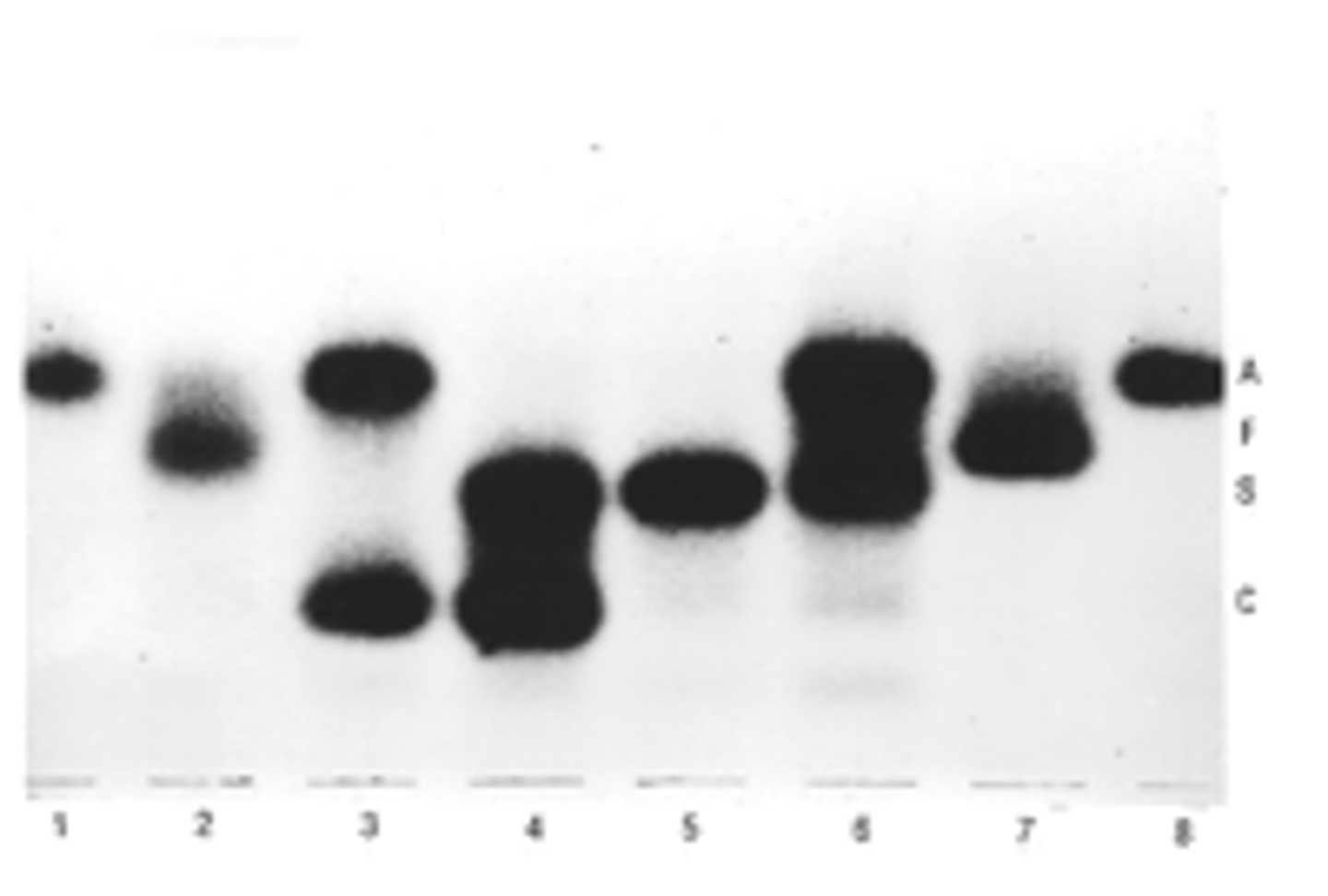
Electrophoresis principles
►Separation of haemoglobins with electrophoresis at pH 8.4 (alkaline) and pH 6.2 (acid).
►Scanning allows quantification of the haemoglobin present, bands are seen by staining.
►At alkaline pH Hb C, E, A2 and O migrate together to form a single band, Hb S, D and G also co migrate.
Electrophoresis interpretation
HbA2 range | Interpretation |
> 7.0 % | Rare, repeat to verify test. Exclude a structural variant. Can be due to rare β thal mutations. |
3.8 – 7.0 % | Beta thal trait or unstable Haemoglobin. |
3.4 – 3.7 % | Fe deficiency in β thal trait; Δ chain variant with β thal trait. Interaction of α and β thal traits; rare β thal mutations. HbS making measurement inaccurate; interaction of α - Hb S. |
2.0 – 3.3 % | Normal. Δ and β thal (but HbF should be elevated); alpha thal trait. Rare cases of β thal trait coexisting with either Δ or α thal trait. |
< 2.0 % | Δ β thal (but HbF should be elevated). Alpha thal trait; Hb H disease; Δ variant or delta Thalassemia. Iron deficiency. |
sickle solubility tests
►Detects HbS at conc. > 20% and differentiates HbD and G which migrate with Hb S on cellulose acetate electrophoresis at alkaline pH.
►Positive results are also obtained on samples containing both HbS and beta globulin mutations.
►False positives can occur in leukocytosis, hyperprotienemia and unstable hemoglobin states.
►False negatives can occur in patients with anaemia or if outdated buffer is used and in infants less than 6 months.