Chapter 8: Transport in animals
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Function of circulatory system
To transport materials around the body
take glucose and oxygen to cells for respiration
Taking carbon dioxide and water away from cells because of respiration
Circulatory system consists of
heart (the pump) to keep the blood moving
Blood vessels: arteries (away from the heart), veins (to the heart) and capillaries
Valves to ensure blood flows in one direction
Blood (transport medium)
Types of circulation
single circulation: heart pumps once to get around the whole system
Double circulation: heart pumps twice (one to lungs and once to the body) to get around the whole system
Advantages of single circulatory system
Less risky for things to go wrong within the system
Less complex as it takes less nutrients and oxygen
Advantages of double circulatory system
pumps with more pressure so blood moves faster around the body
More oxygen for more aerobic respiration will be transported
More energy can be released
Single circulatory system pathway
Heart → gills (to oxygenate) → body → heart
Double circulatory system pathway
Heart → lungs (to oxygenate) → heart (to pump again) → body
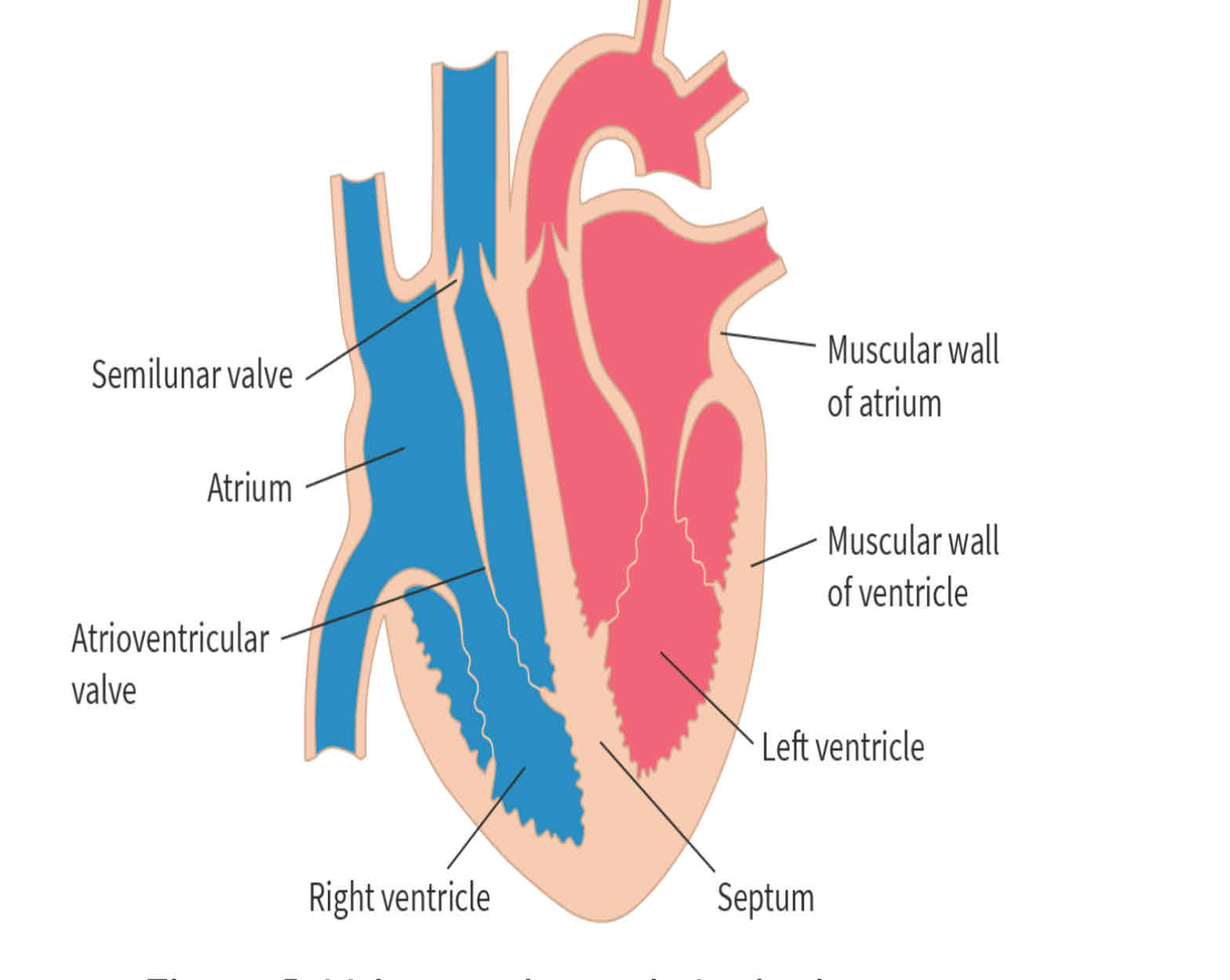
Heart diagram
left ventricle has thickest wall because it pumps blood the furthest distance so more force must be generated
September: separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
How to measure heartbeat
Pulse: caused by expansion and recoil of artery due to pressure of blood pumped from the heart
Listening: “lub dup” sound
Electrocardiogram (ECG): small electrodes are fastened to record the electrical activity of the heart.
Detailed stages in heartbeat
Blood flows from the veins to the atrium
Atrium contracts
Blood pumped into the ventricles
Decreases in pressure causes the atrial ventricular valves to close
This prevents back flow of the blood
Ventricles contract
Blood is pumped into the arteries
This causes the pressure in the ventricles to decrease
This makes the semilunar valves close
Detailed journey of the blood from the heart
From the right atrium, the blood flows past the atrial ventricular valves to the right ventricle.
From the right ventricle, the blood flows past the semi lunar valves into the pulmonary arteries.
The blood goes to the lungs, get oxygenized by gas exchange then flows back to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein
The blood from the left atrium flows past the atrial ventricular valves to the left ventricle
Blood from the left ventricle travels to the aorta, passing the semilunar valves, around the body
After traveling around the body, blood flows through the vena cava and into the right atrium
Blood vessels types and definition
Arteries: carry blood away from the heart
Veins: carry blood towards the heart
Capillaries carry blood between the cells
Characteristics of arteries
small lumen: to maintain high pressure
Thick layers of muscle and elastic fibers to waist and the high pressure
Smooth lining to decrease friction
No valves
Blood is at high pressure
Characteristics of veins
large lumen: to help blood flow
Thin walls
Blood is at low pressure
Valves: to prevent backflow of blood
Characteristics of capillaries
Tiny vessels with narrow lumen to fit between cells
Walls are thin: one cell thick to reduce diffusion pathway
Blood is at low pressure
No valves
How arteries maintain high pressure
small lumen to help wrist and high pressure
Elastic recoil of the artery wall as this pressure pushes out
How enough pressure is maintained by veins
being compressed by skeletal muscles
Valves
Blood vessels that go/come to/from…
lungs: pulmonary
Liver: hepatic
Kidney: renal
Coronary arteries
Supplies blood to the heart itself with nutrients and oxygen
Coronary heart disease
This is when coronary arteries are unable to supply oxygen and nutrient rich blood to the heart muscles because of the blockages in them.
Effect of blockages in coronary arteries
cardiac muscles dependent on it cannot produce enough energy for contraction → leading to death of heart muscles
Blood cells cannot move through the artery because blockages reduces the diameter of the coronary arteries, making it ore difficult for blood to flow through.
Risks for CHDs
age
Diet
Smoking
Stress
Foods that increase chances of CHDs
red meat
Buttered popcorn
Chocolate
Foods that don’t increase chances of CHDs
salads
Fruits
Oily fish
Olive oil
Components of blood
red blood cell: carry oxygen from lungs and deliver it throughout the body
Plasma: transports blood cells, soluble nutrients, hormones and carbon dioxide in the it
Platelet: prevents/stops bleeding and travel to injured areas
Lymphocyte: produces antibodies to defend against pathogens
Phagocyte: does phagocytosis to destroy pathogens
Blood clotting
Fibrinogen, a soluble protein, is activated by the substances released by activated platelets at the injury
This converts fibrinogen to fibrin
Red blood cells, white blood cells, fibrin and platelets come together at the injury site
Fibrin produces a mesh, trapping red blood cells and platelets, forming a blood clot
When blood clot dries, a scab forms. Under the scab, healing takes place