AP Biology Exam Review
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
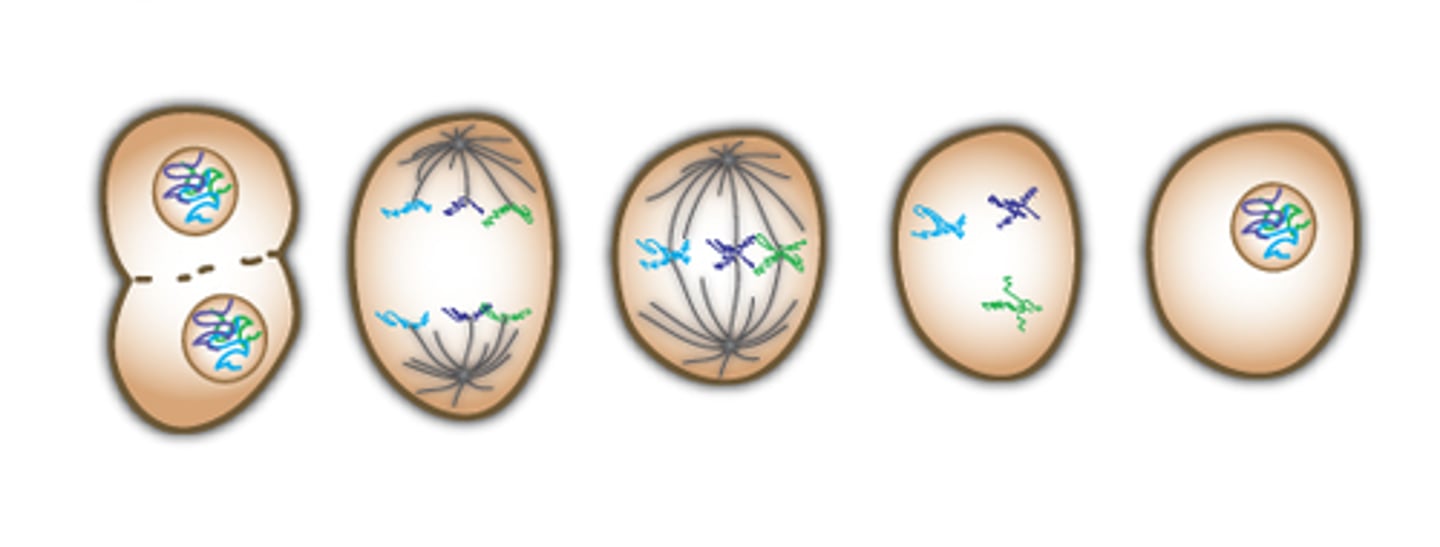
mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
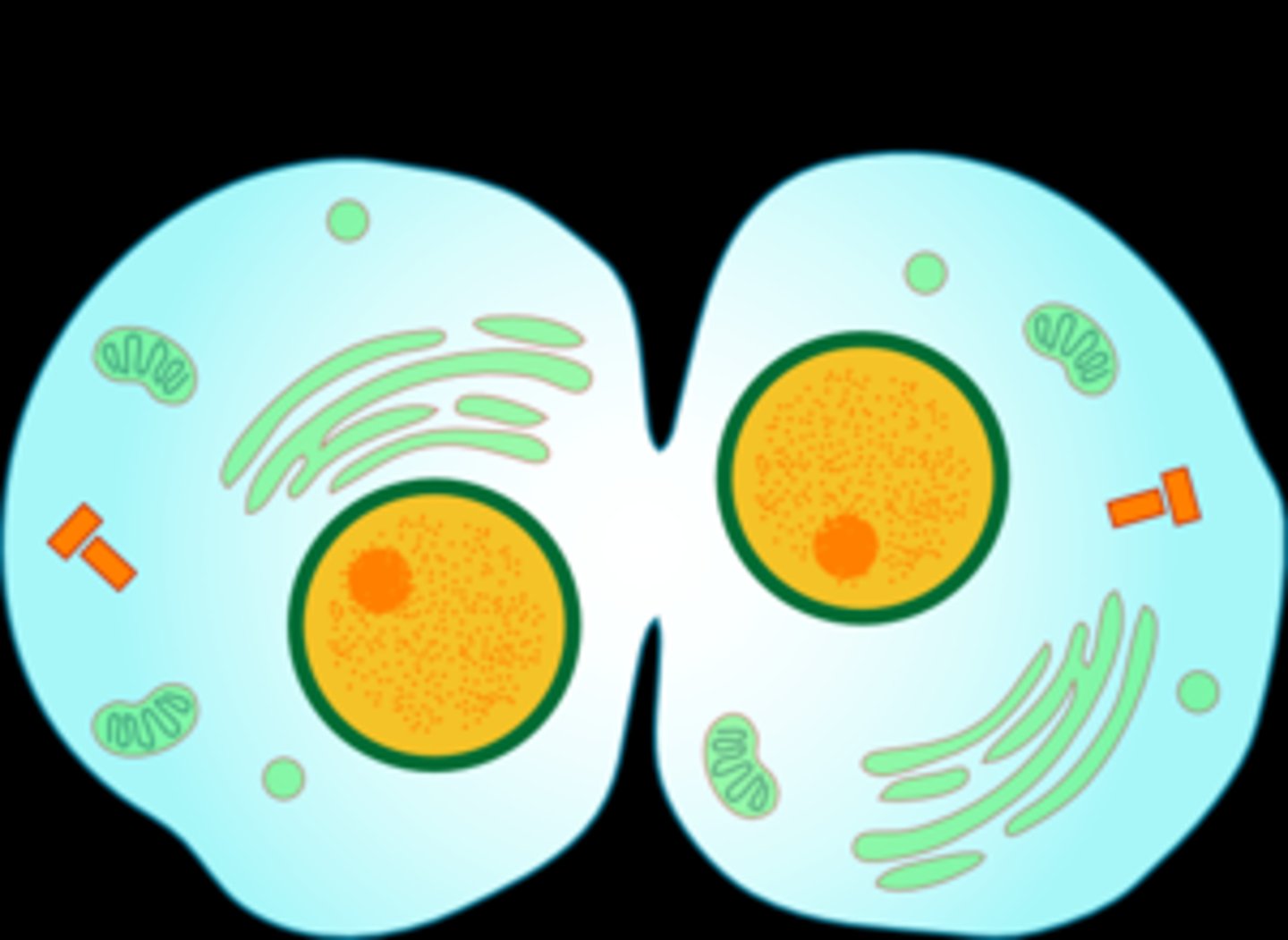
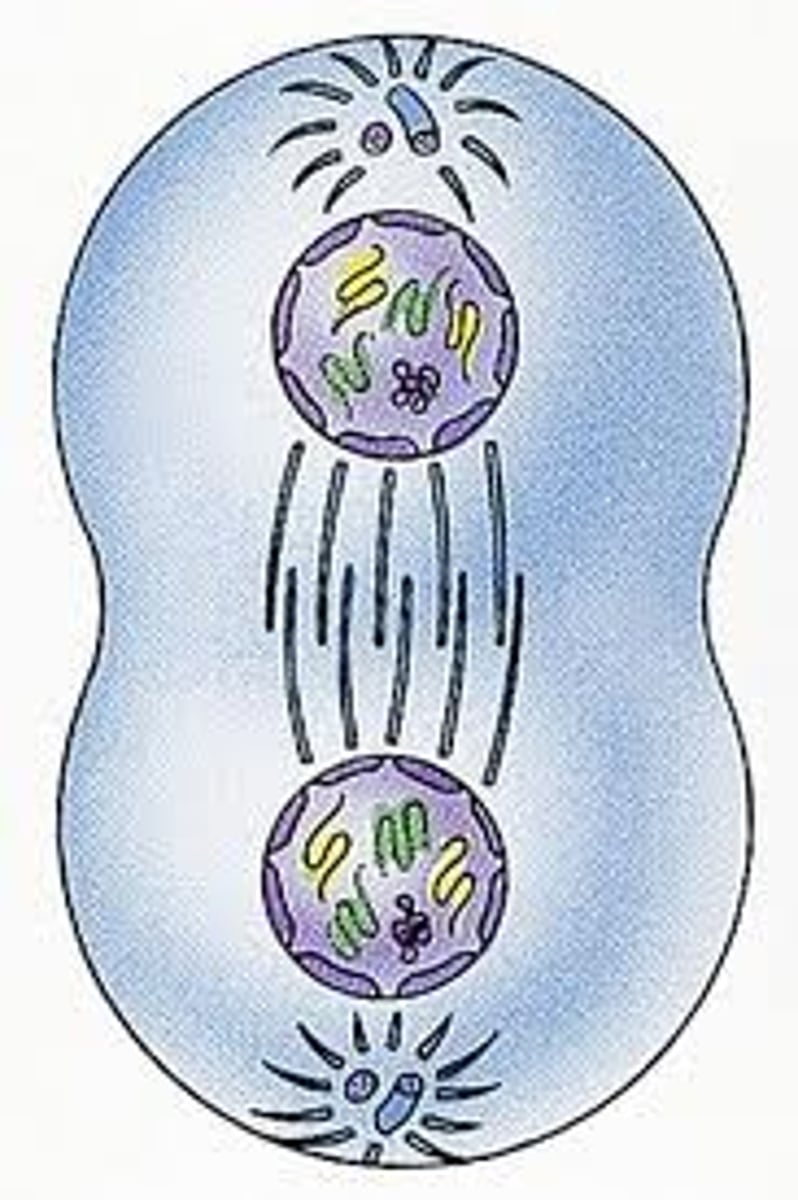
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm during cell division
chromatids
one of the two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
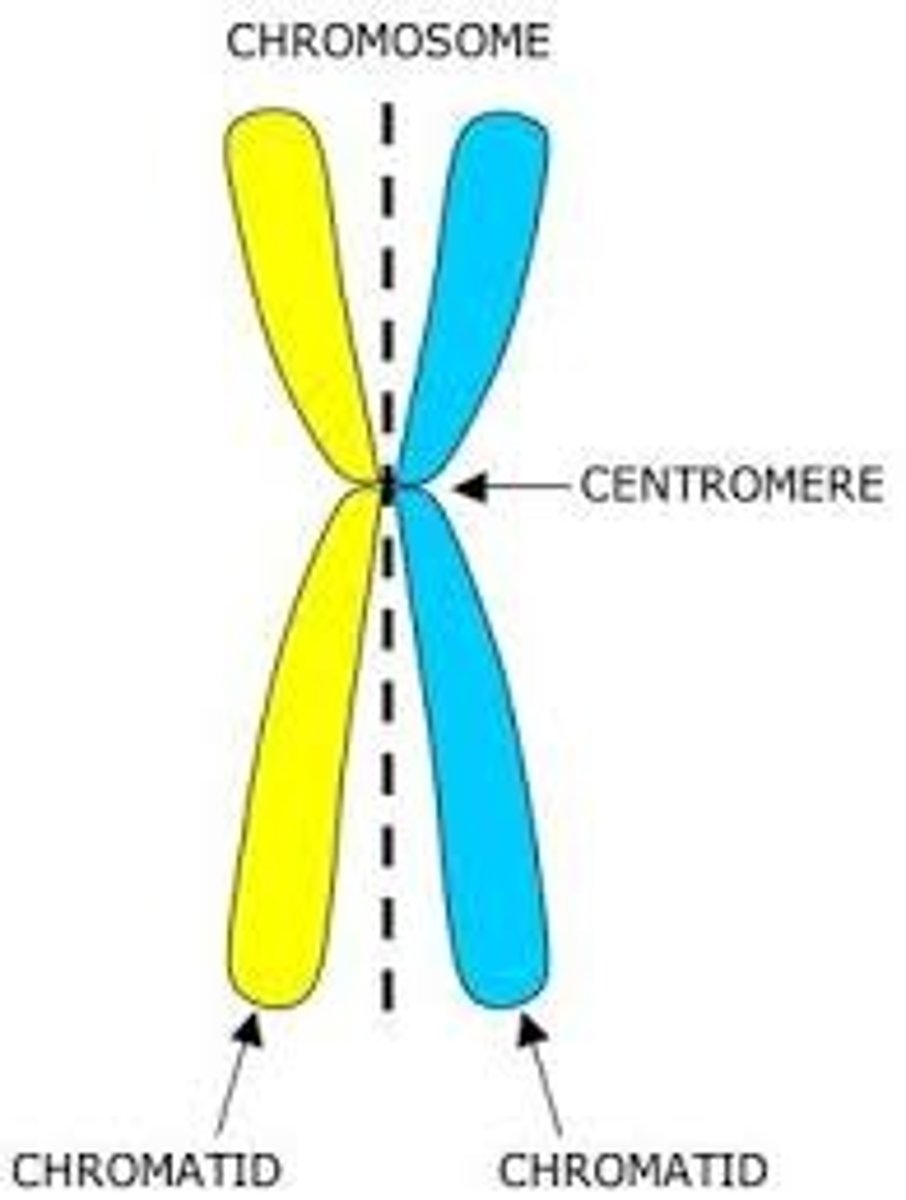
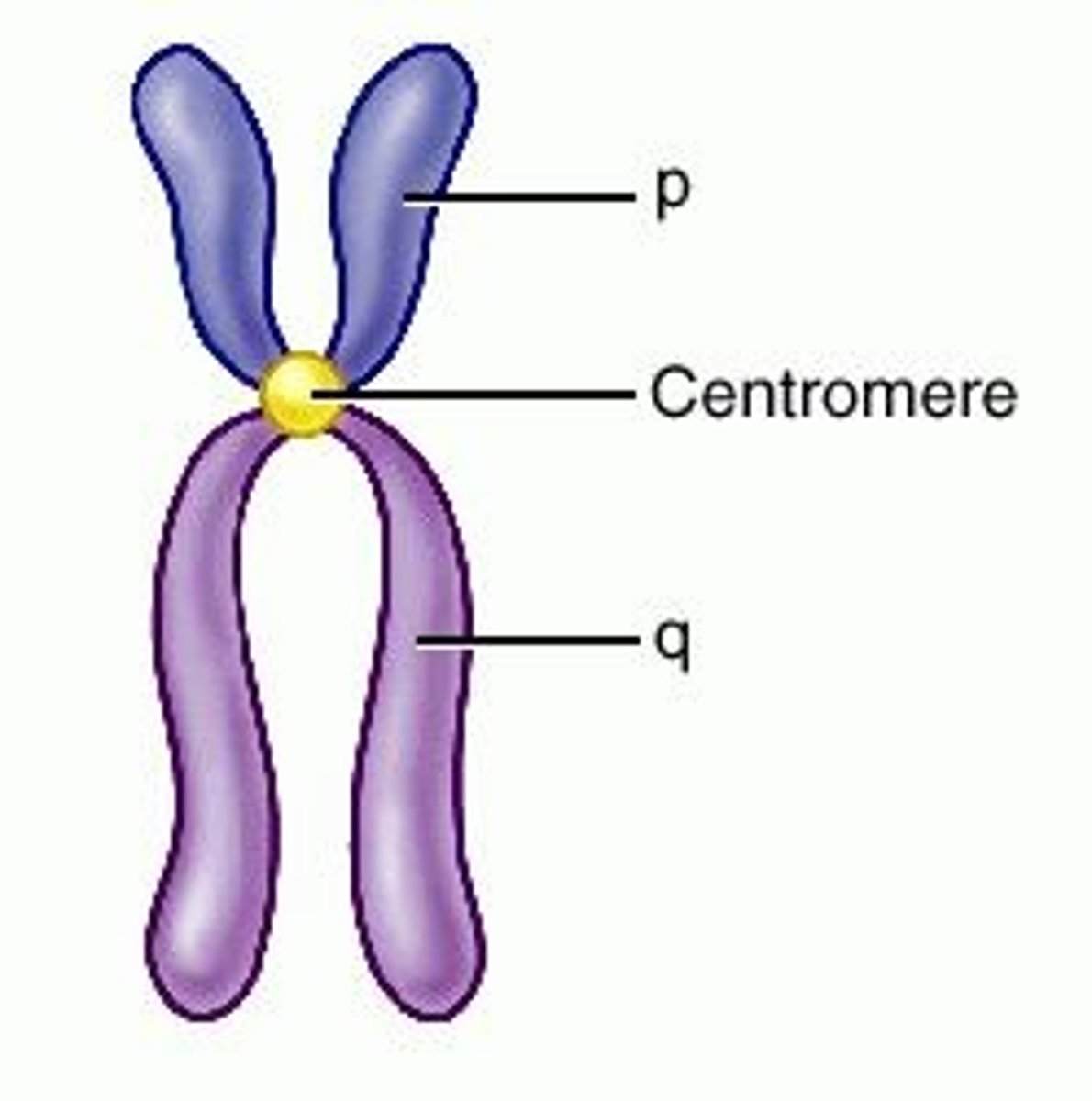
centromeres
area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell division
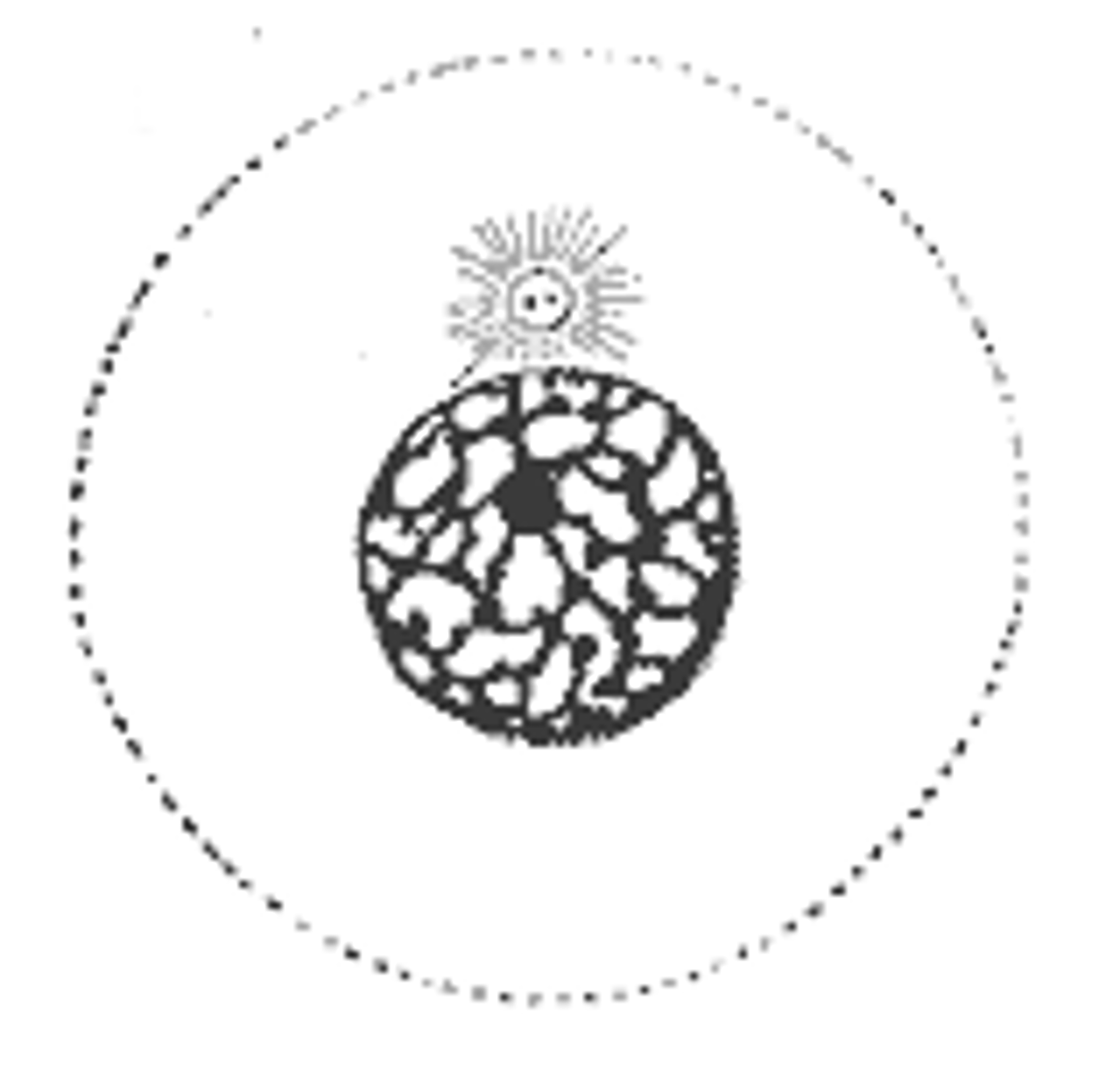
cell cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
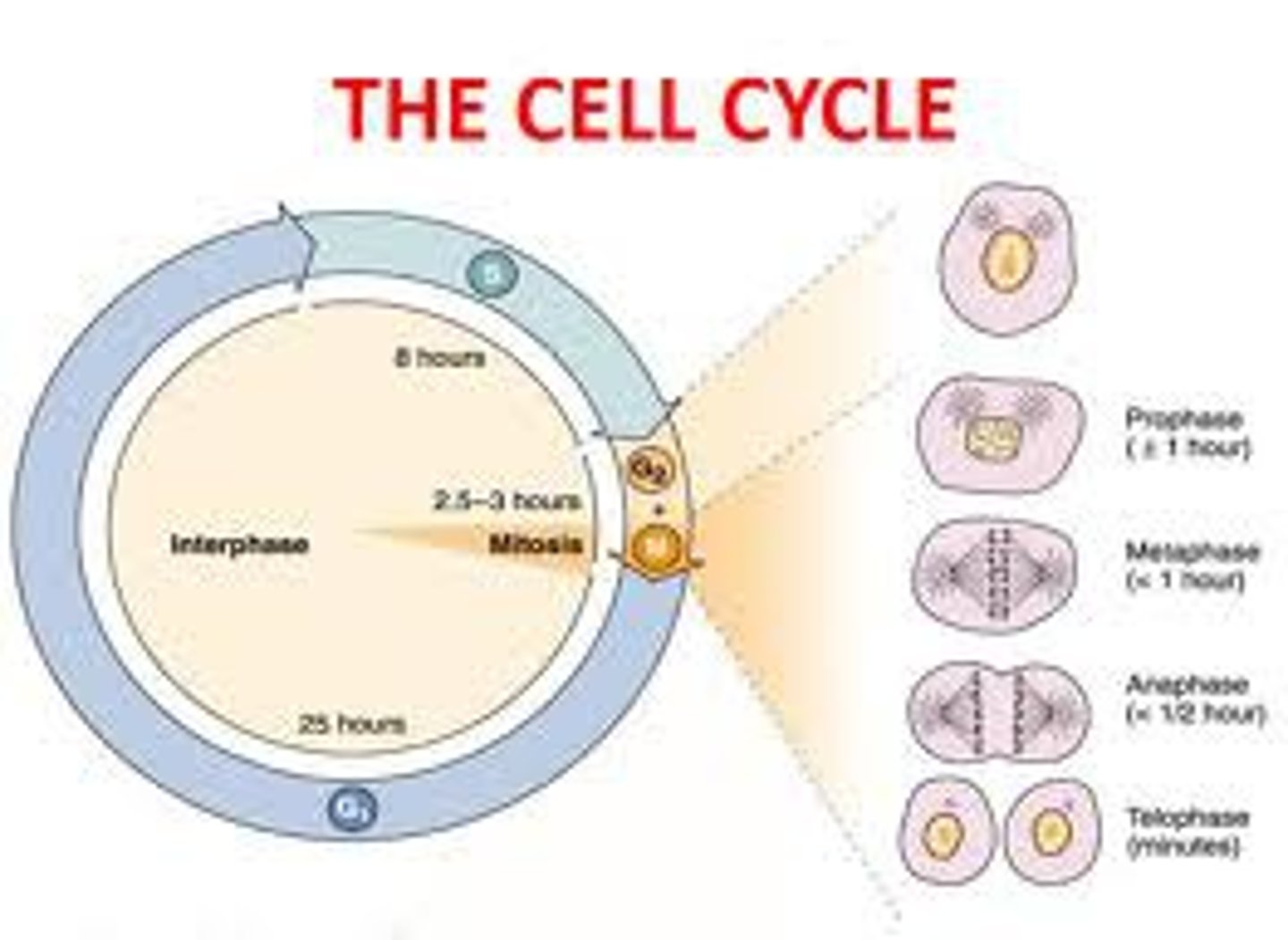
prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the cell's DNA
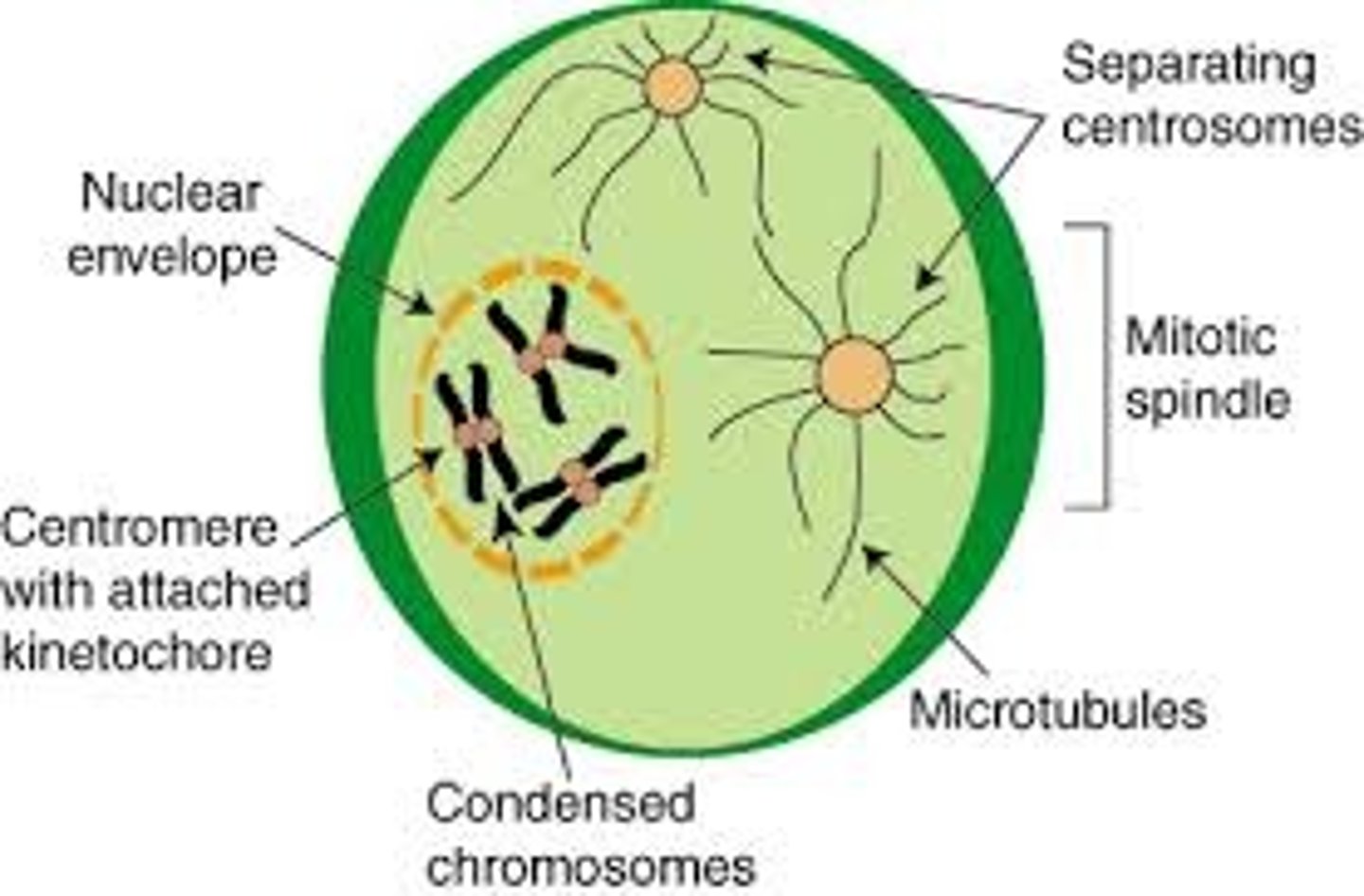
centrioles
one of the two tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cels near the nuclear envelope
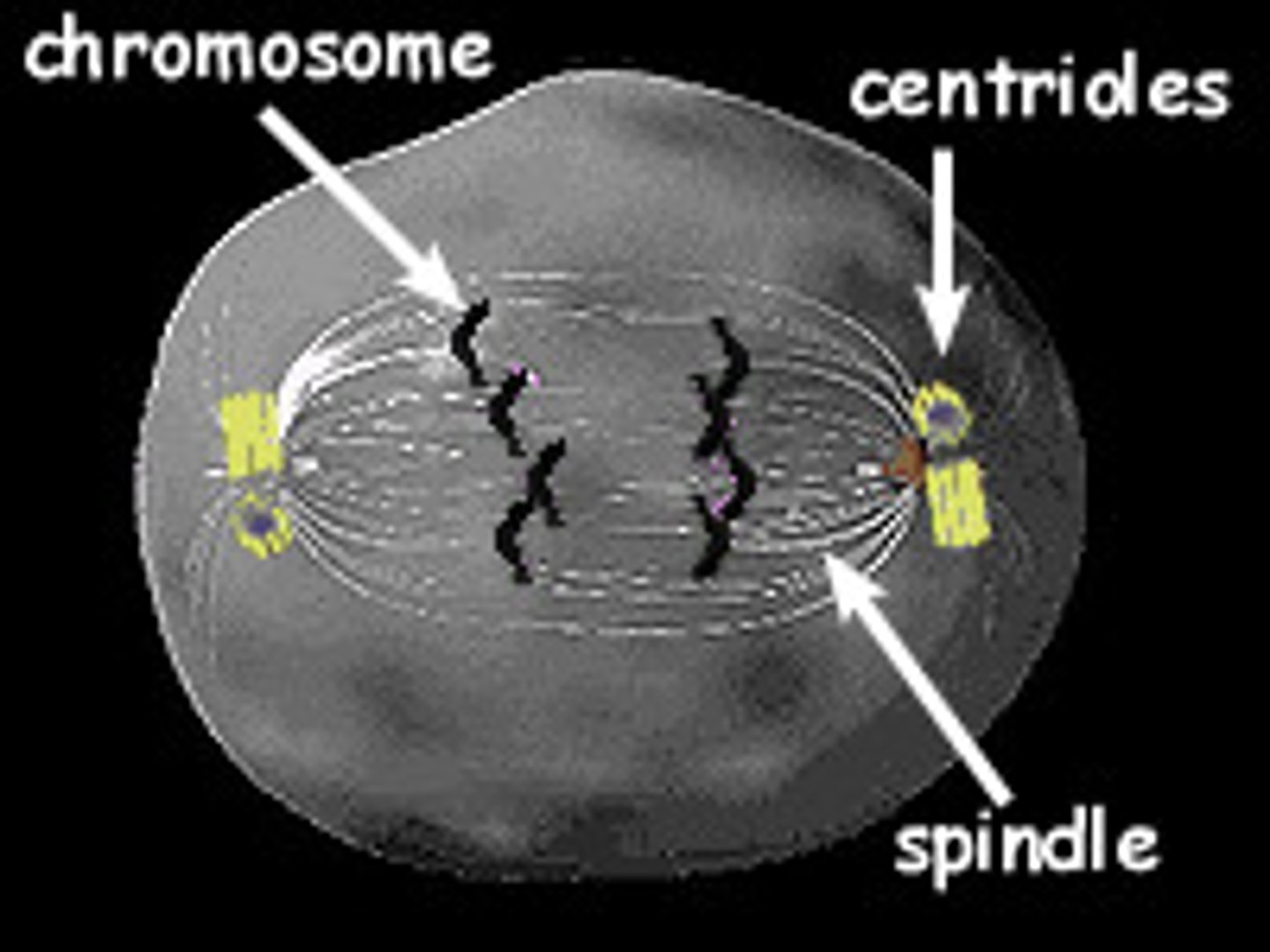
spindle
fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes during mitosis
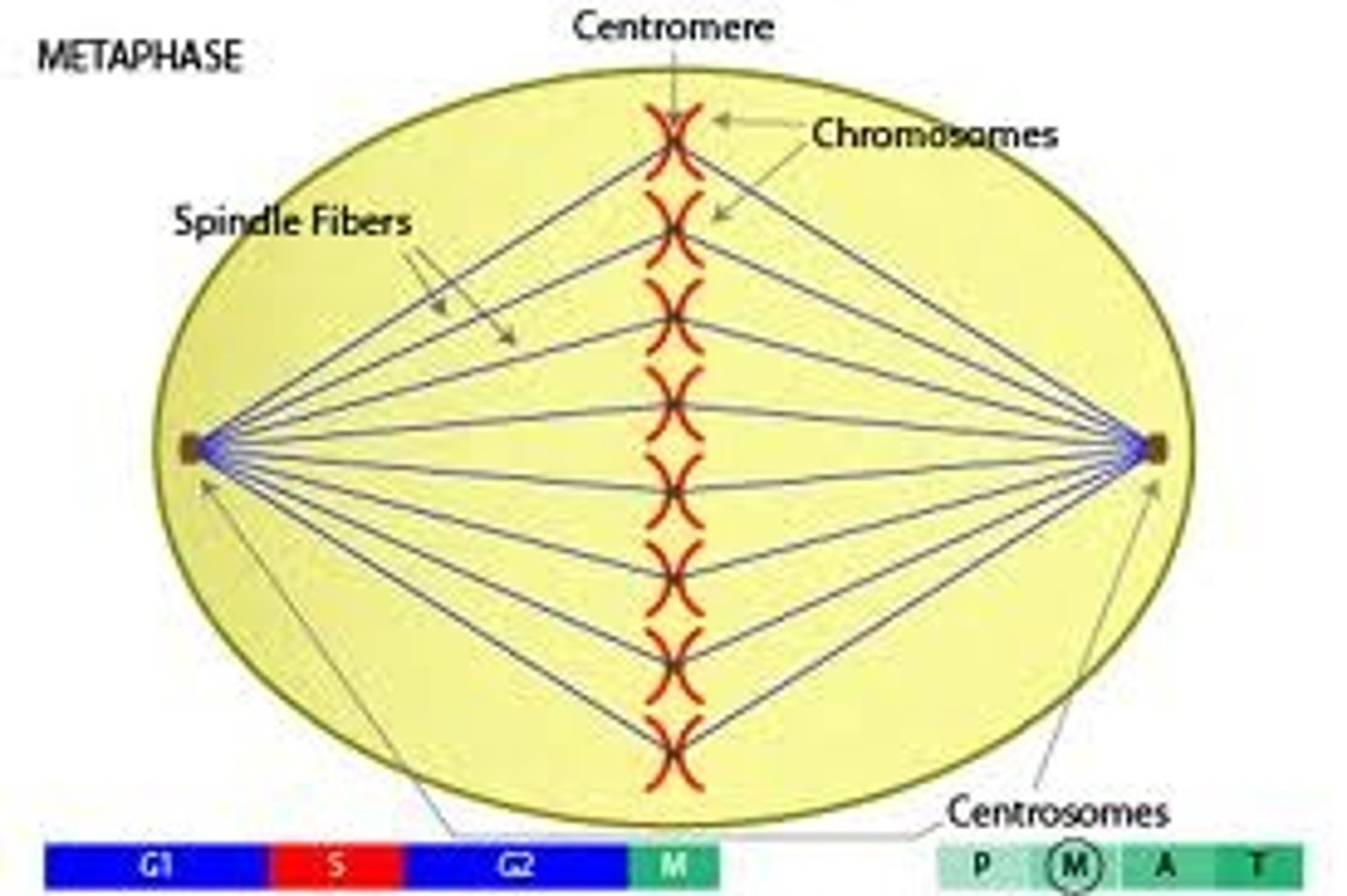
metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
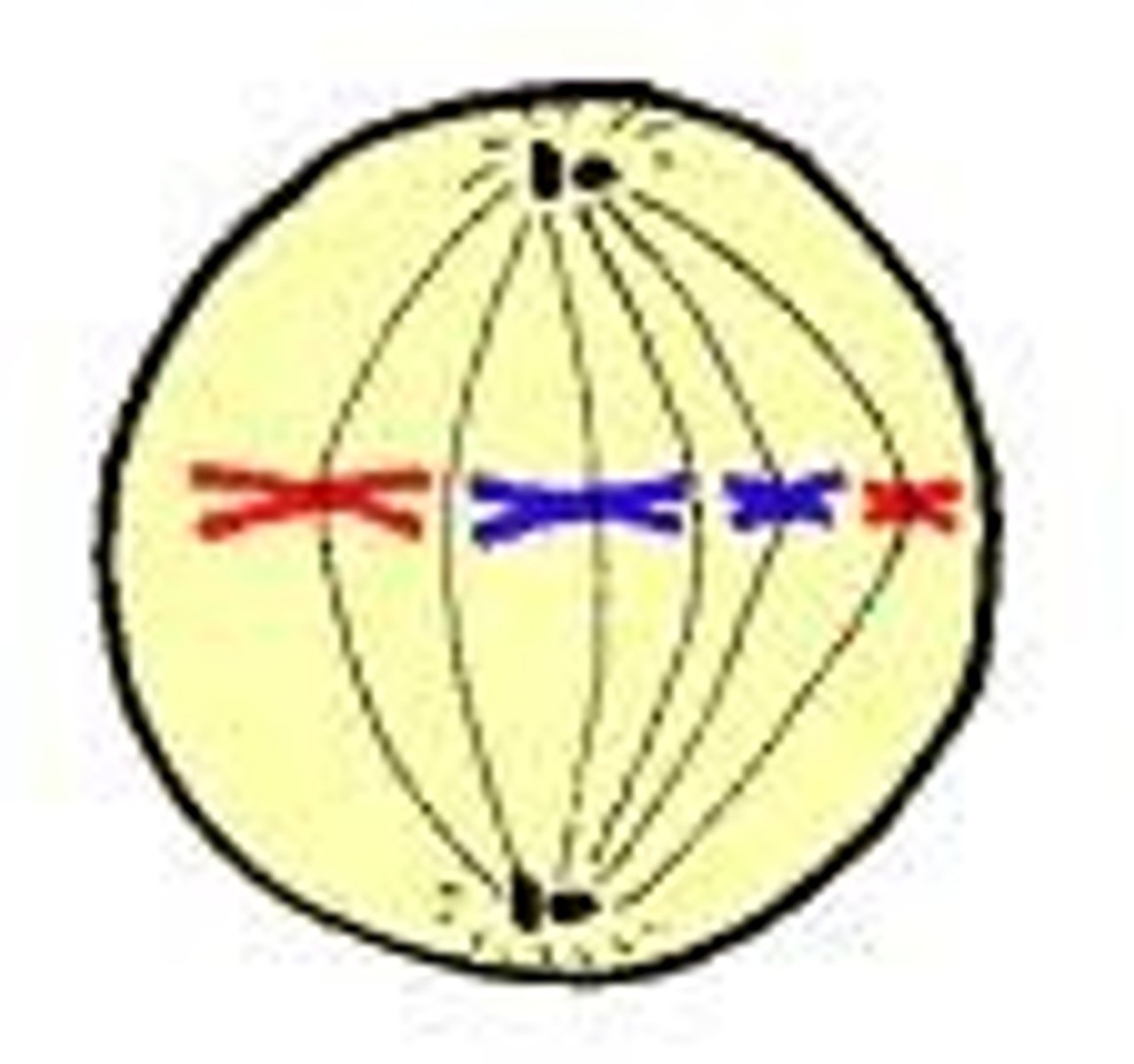
anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
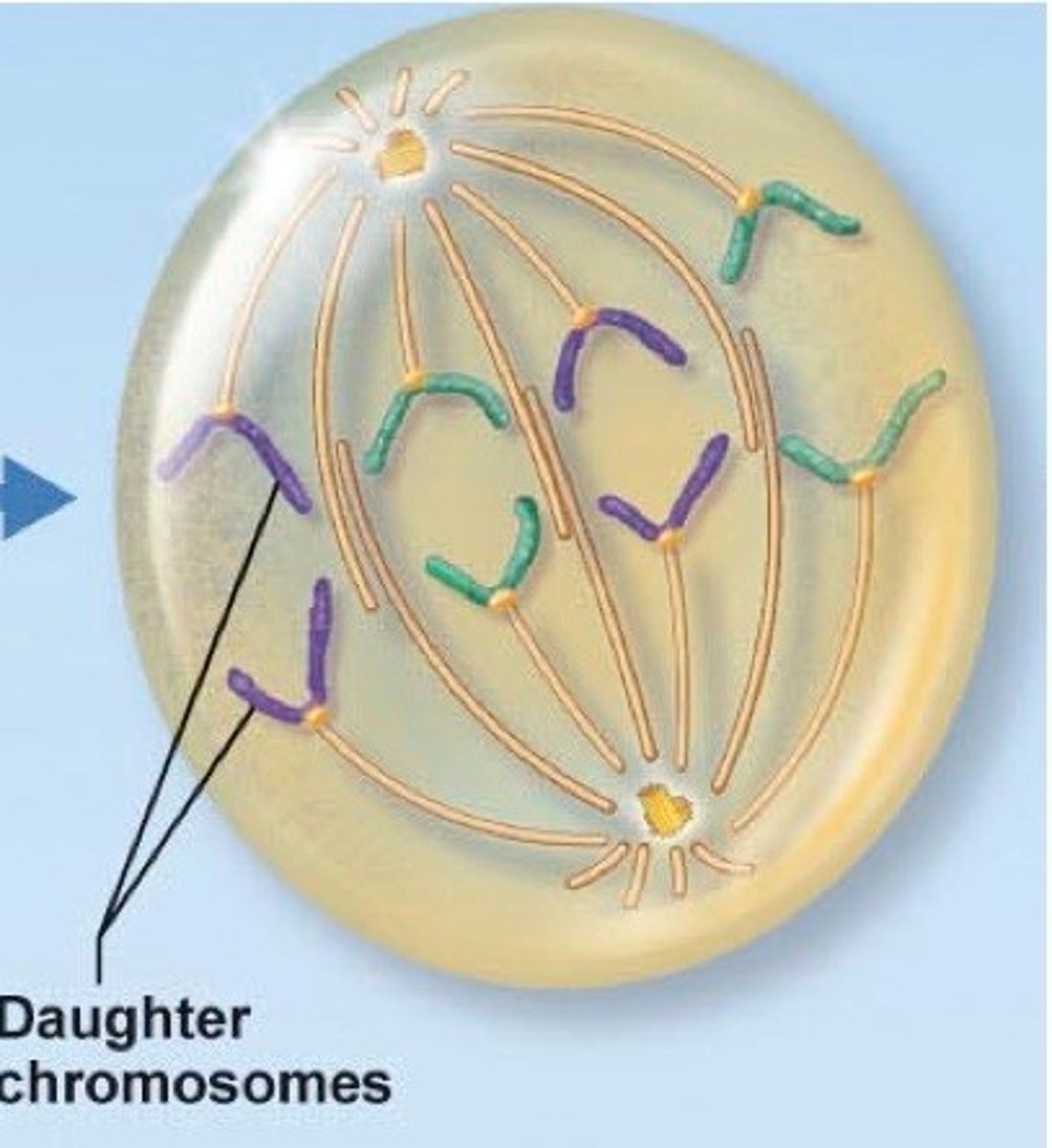
telophase
fourth and final phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes begin to disperse into a tangle of dense material
cyclin
one of a family of closely related proteins that regulate the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells
cancer
disorder in which some of the body's own cells lose the ability to control growth
genetics
scientific study of heredity
fertilization
process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells join to form a new cell
true-breeding
term used to describe organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves if allowed to self-pollinate
trait
specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another
hybrids
offspring of crosses between parents with different traits
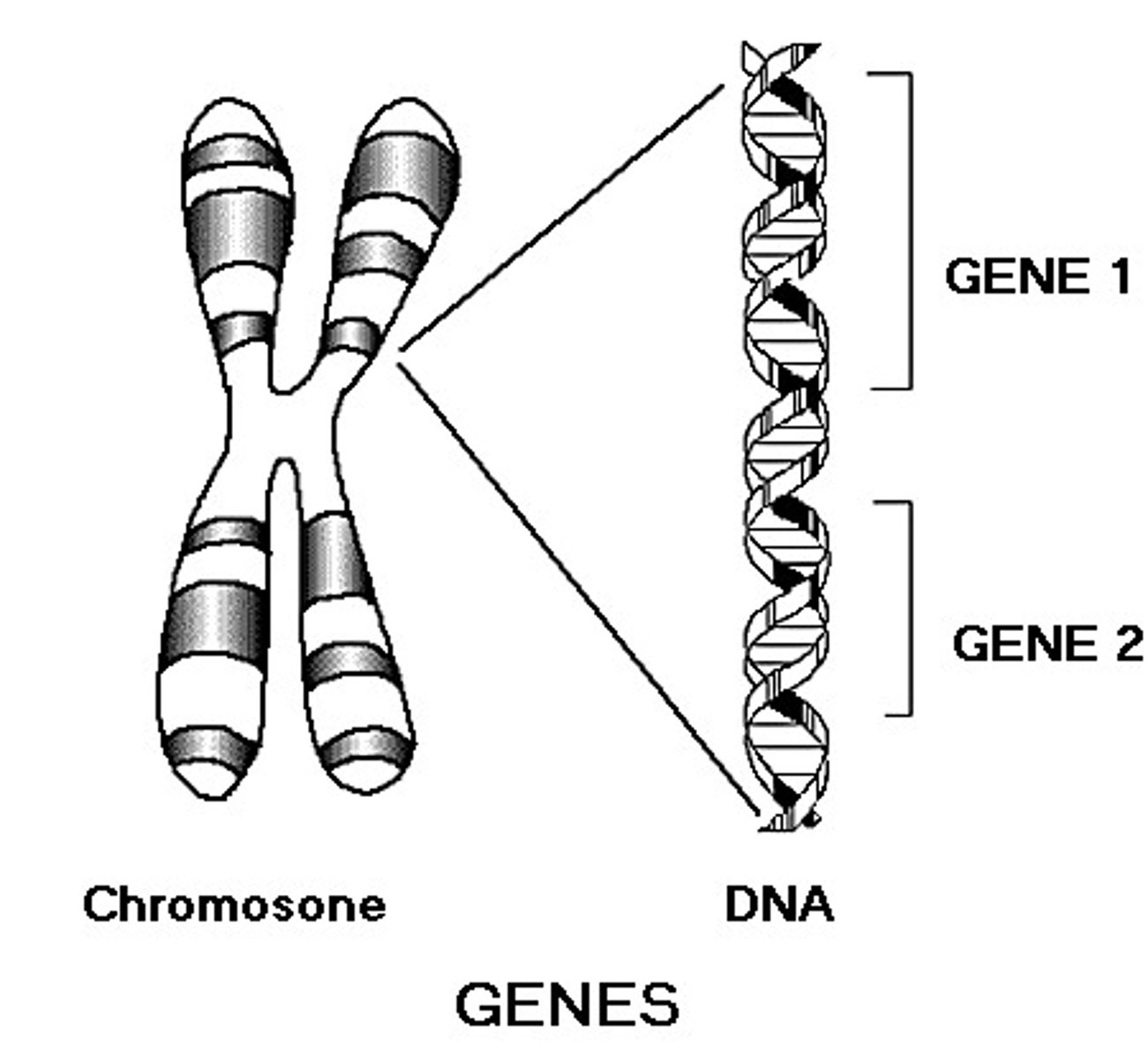
genes
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait
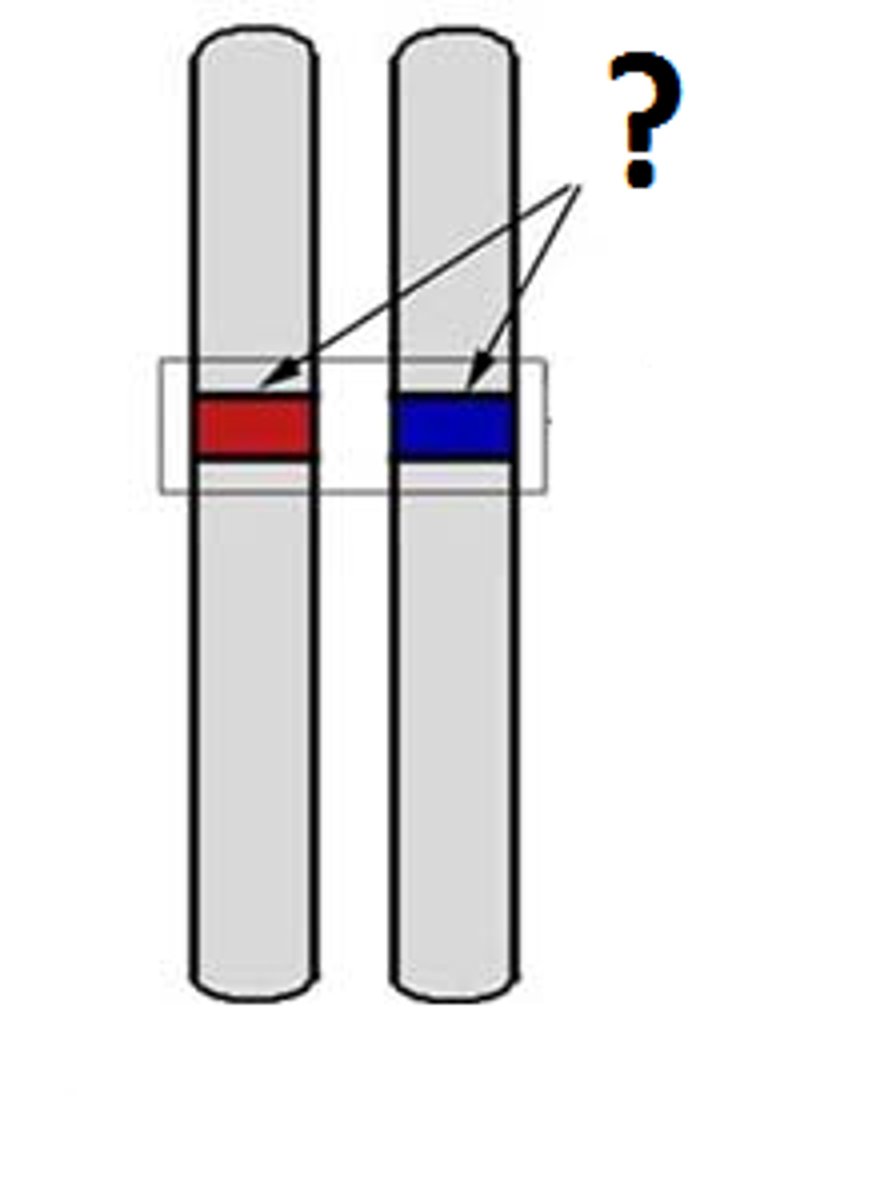
alleles
one of a number of different forms of a gene
segregation
separation of alleles during gamete formation

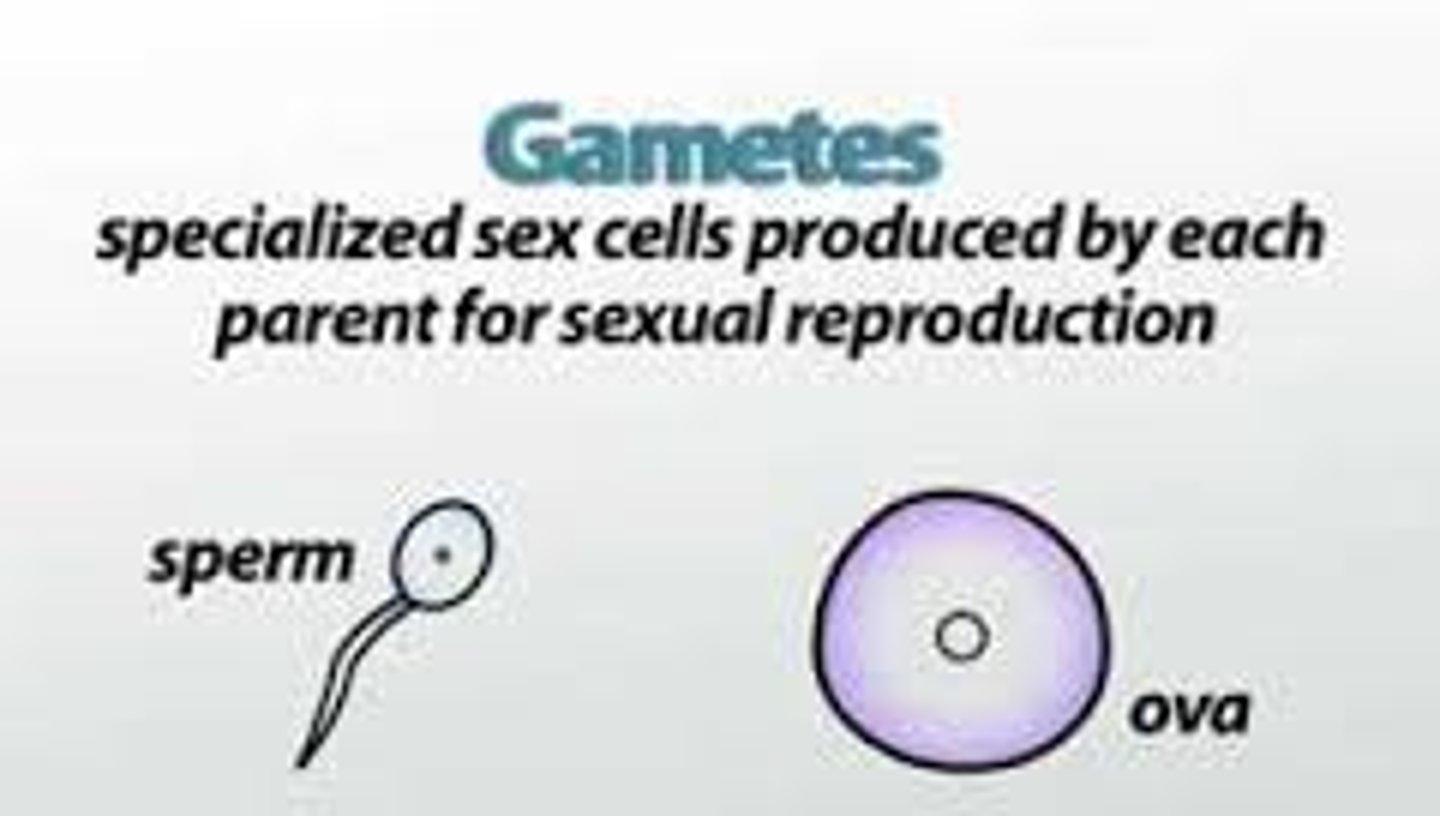
gametes
specialized cell involved in sexual reproduction
probability
likelihood that a particular event will occur
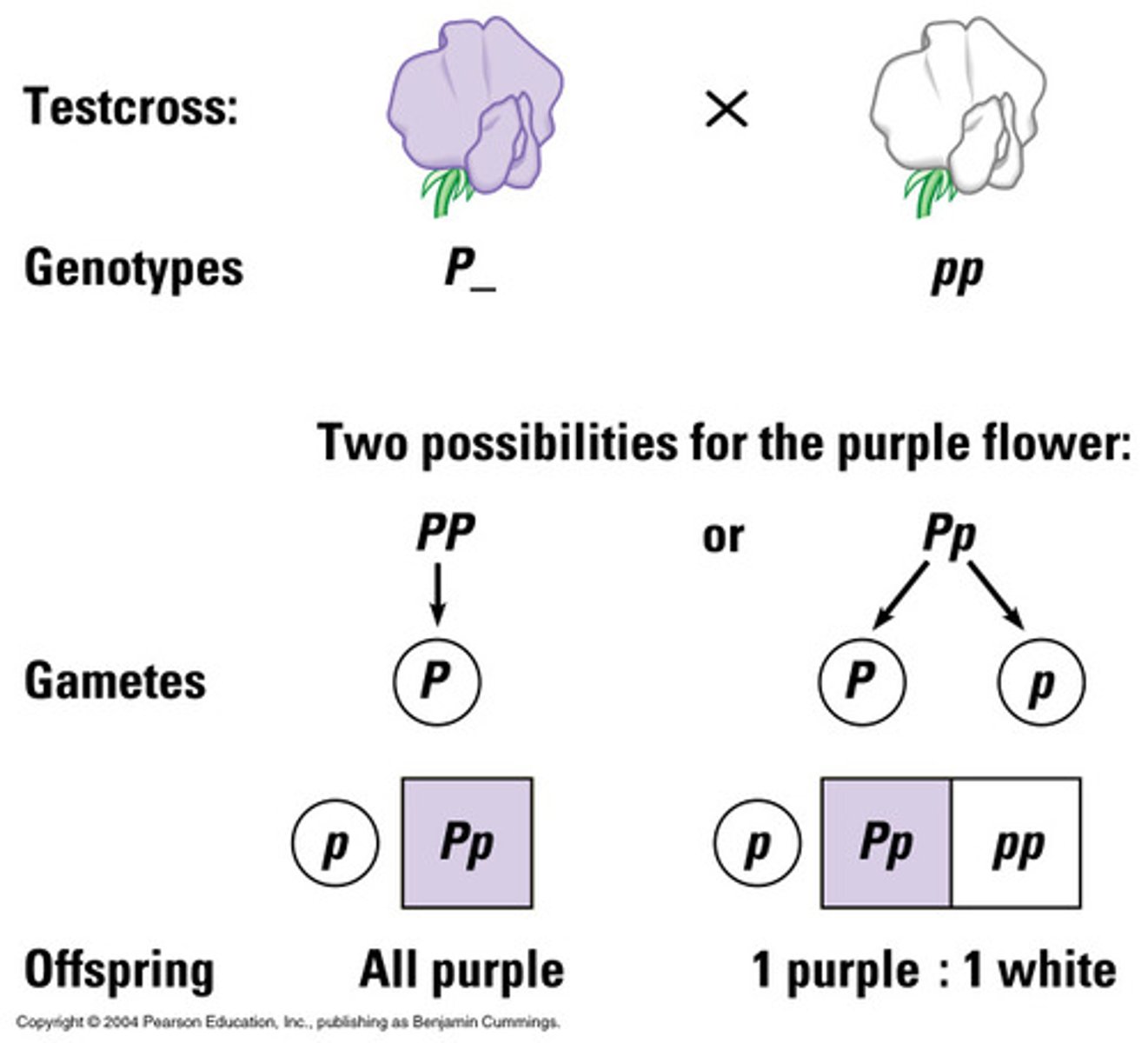
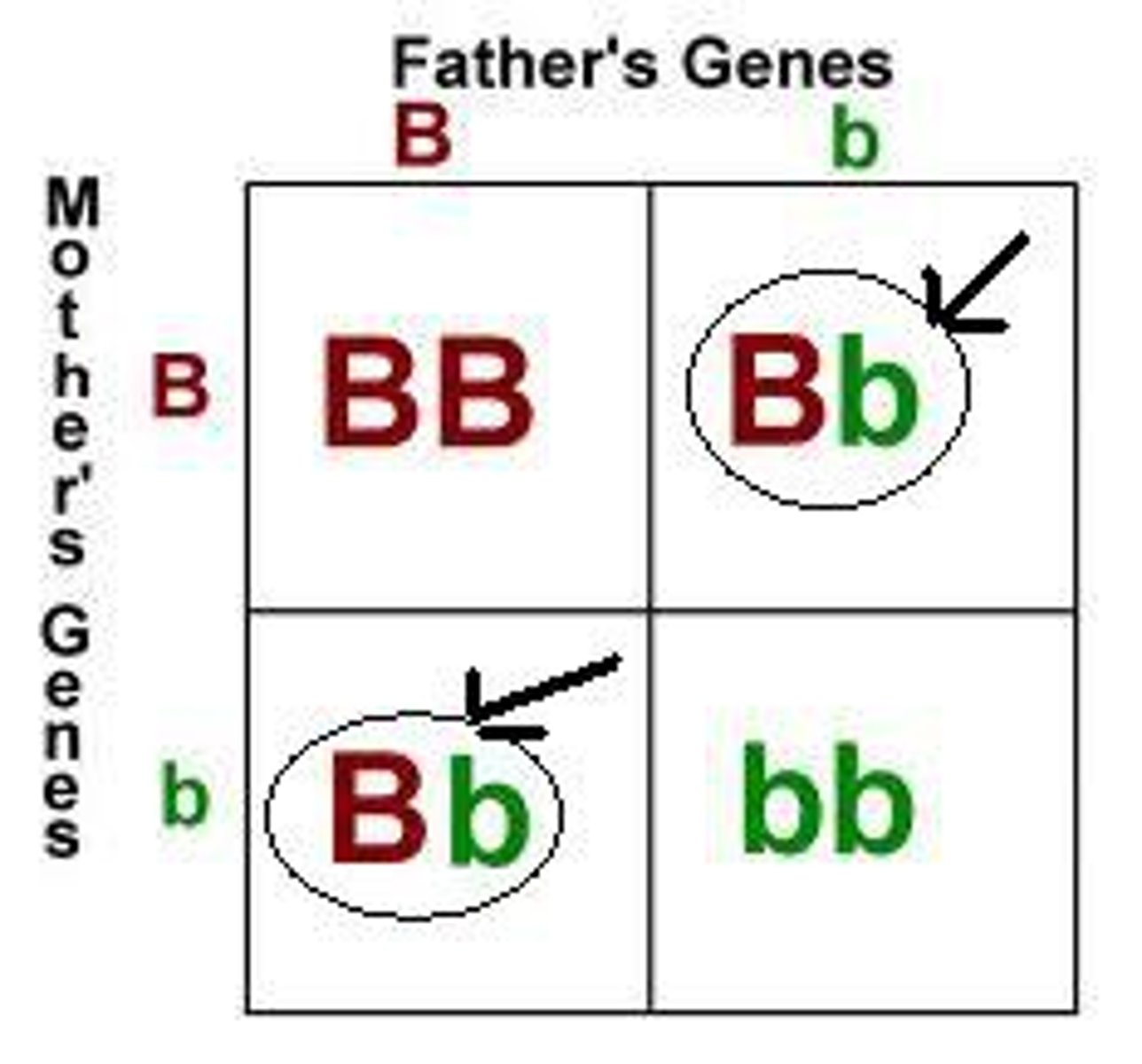
punnett square
diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross
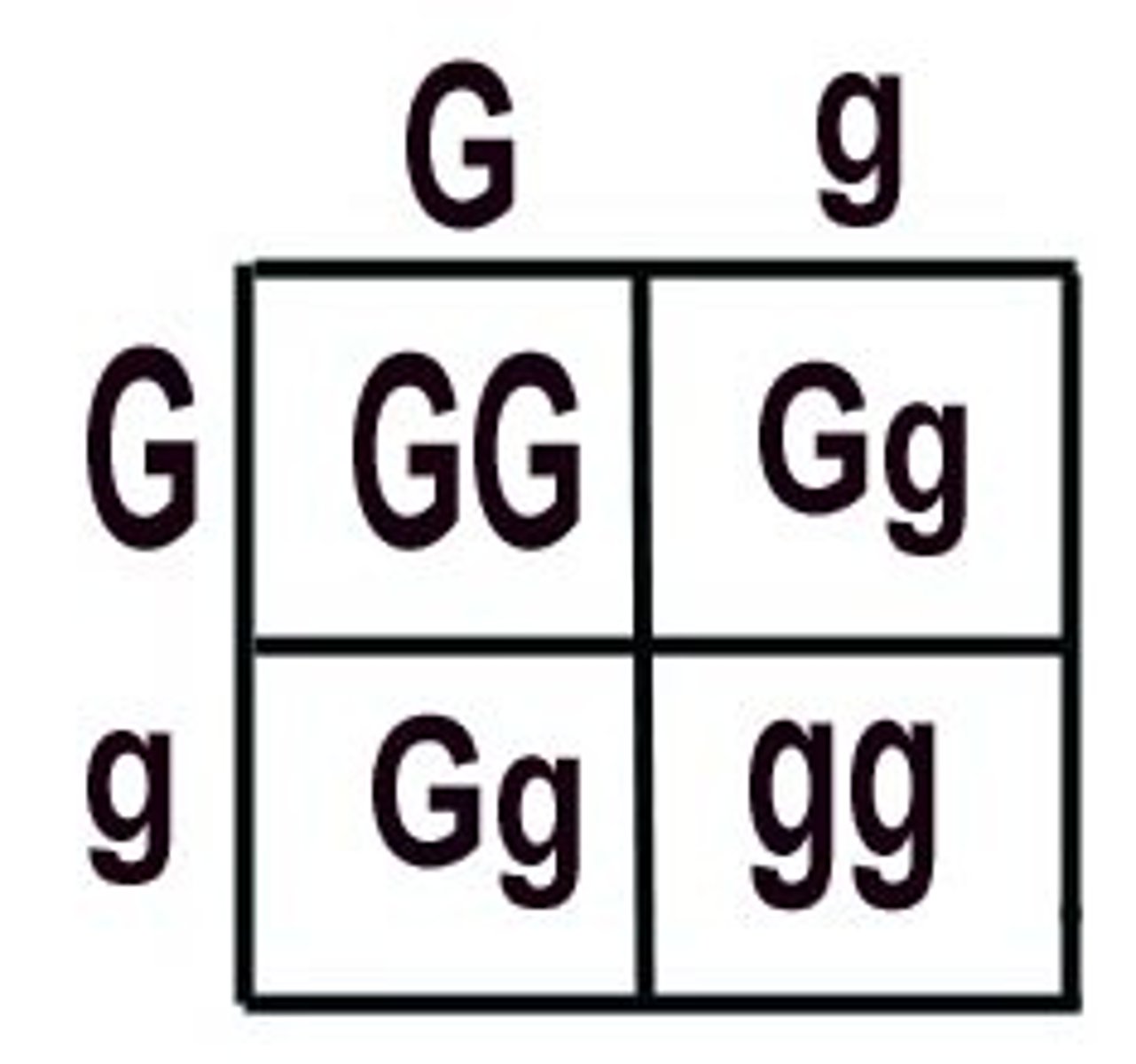
homozygous
term used to refer to an organism that has two identical alleles for a particular trait
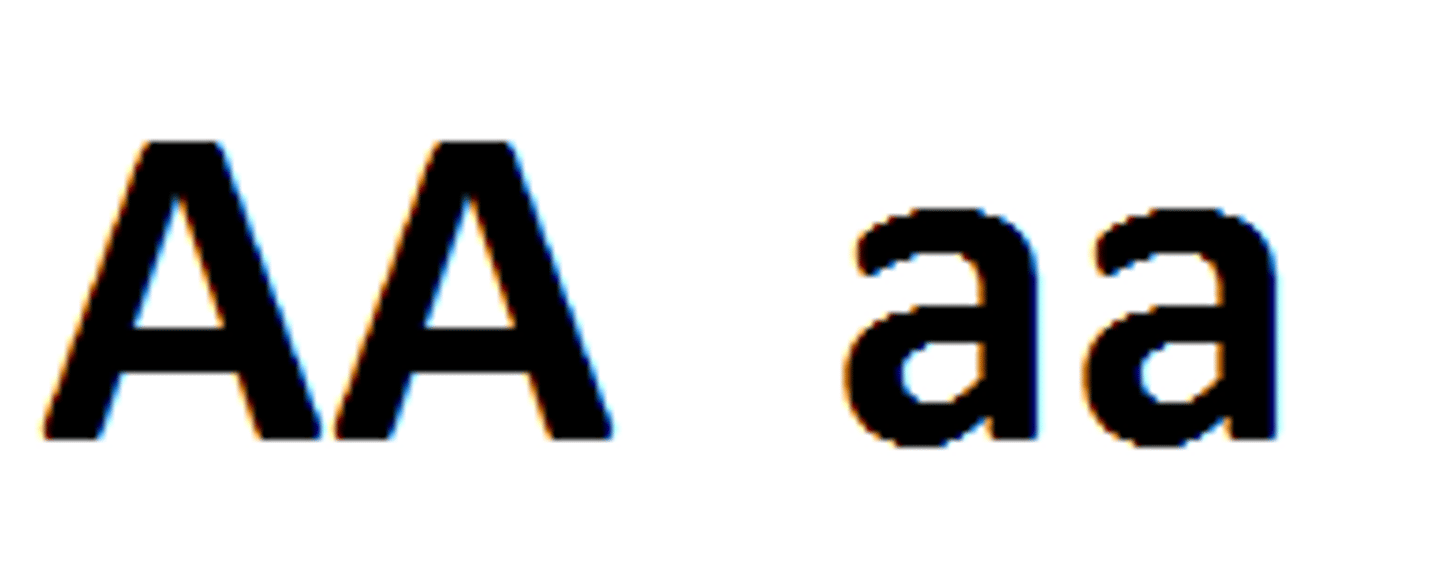
heterozygous
term used to refer to an organism that has two different alleles for the same trait
phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism
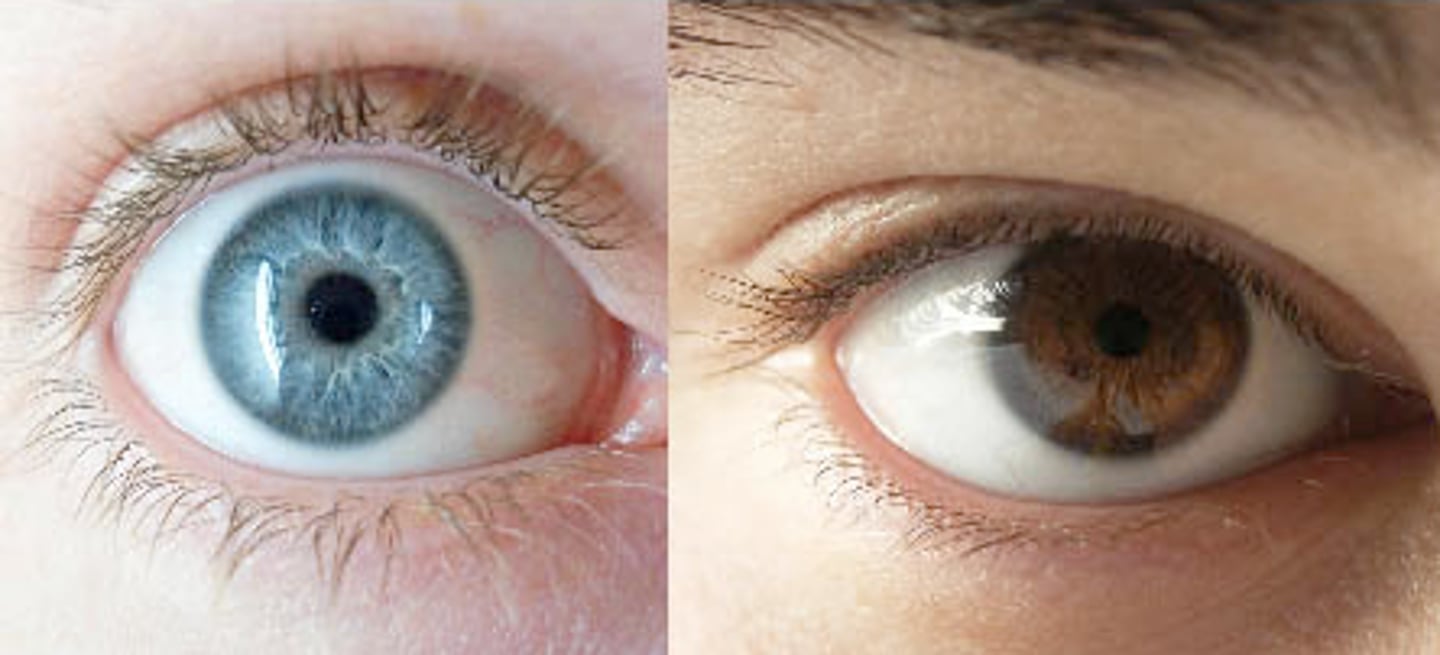
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
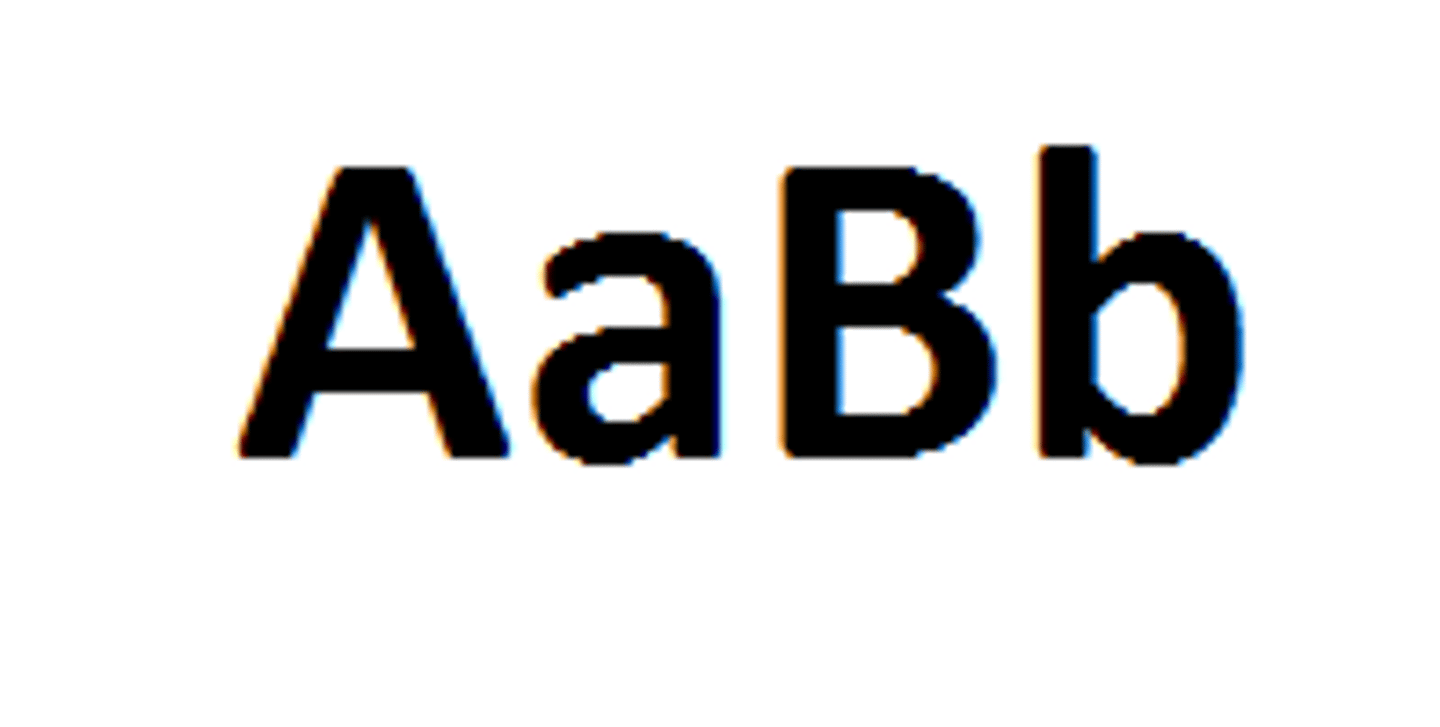
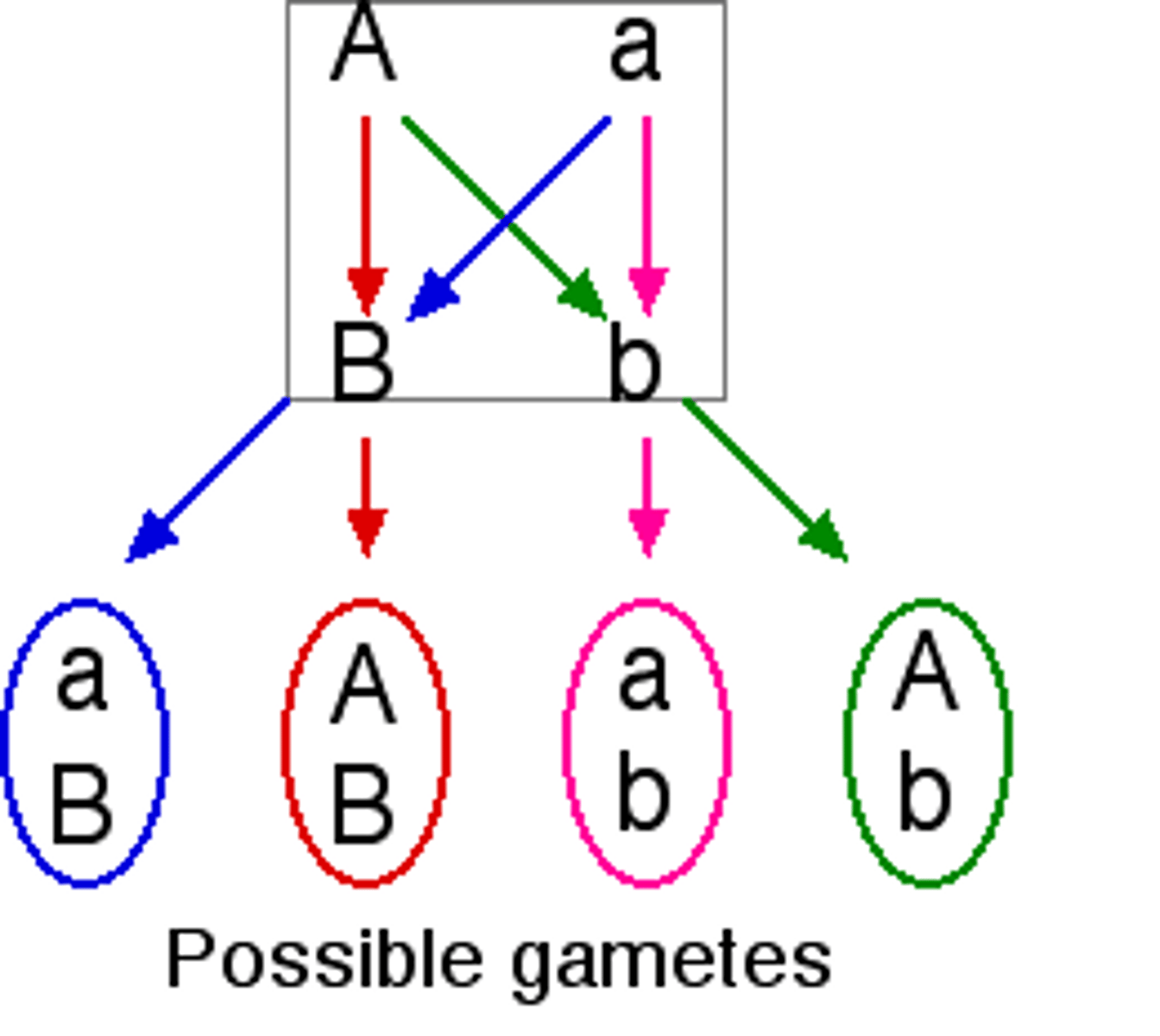
independent assortment
independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes
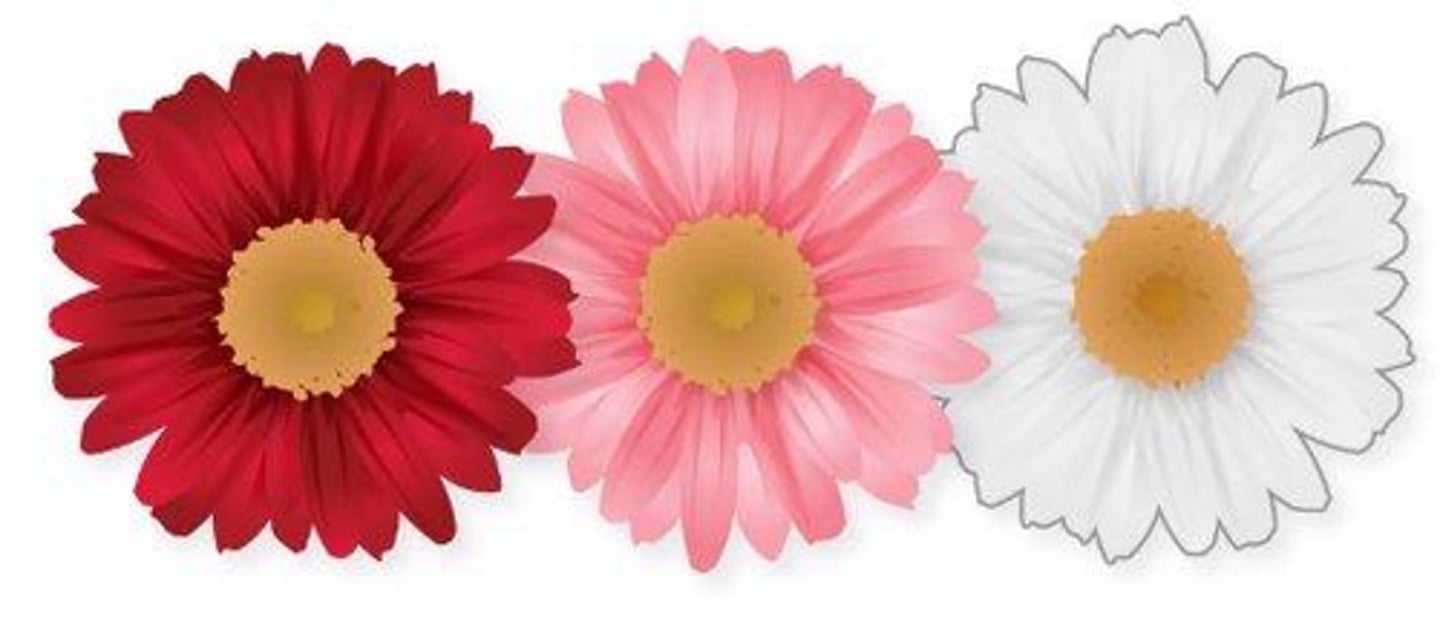
incomplete dominance
situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another

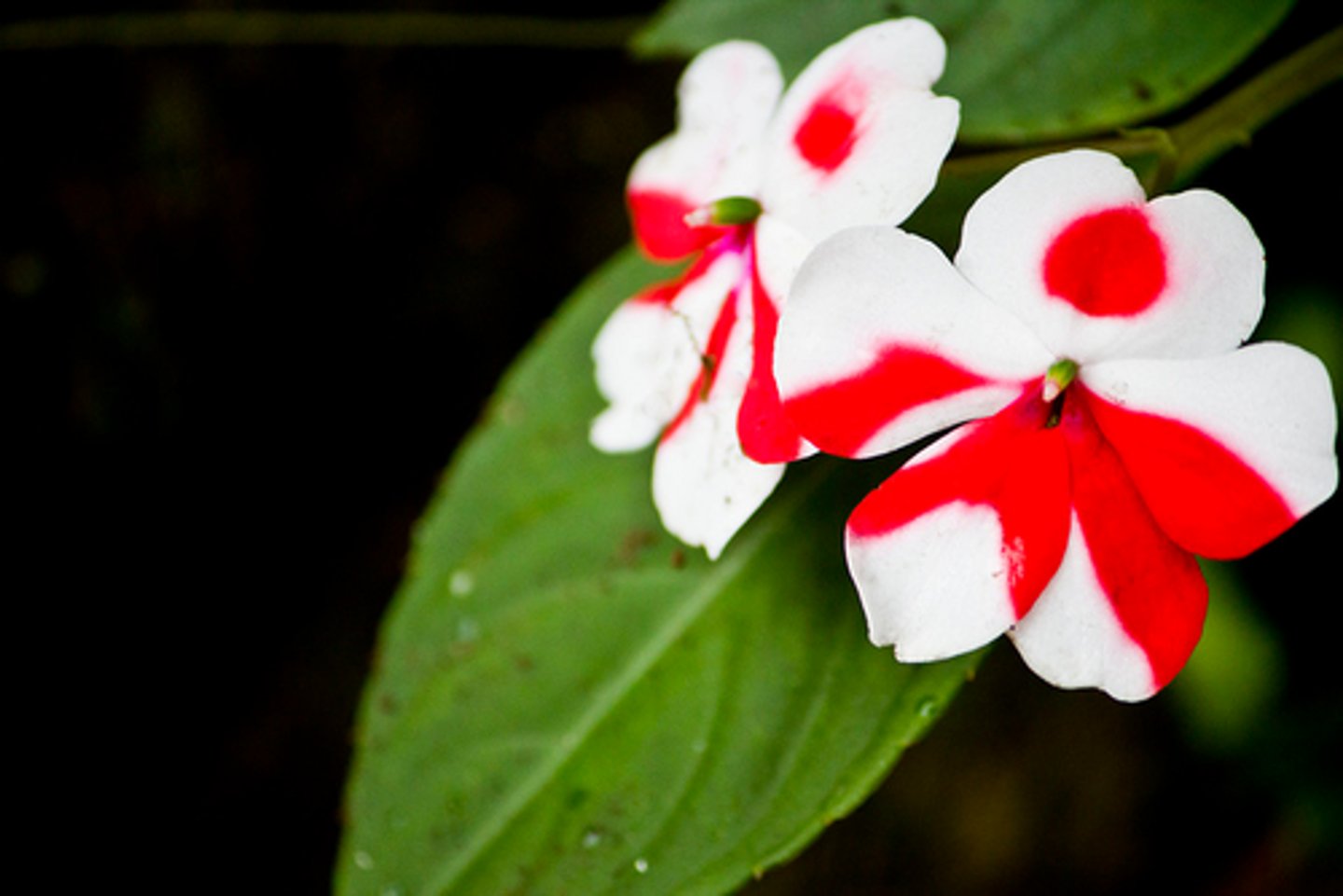
codominance
situation in which both alleles of a gene contribute to the phenotype of the organism

multiple alleles
three or more alleles of the same gene

polygenic traits
trait controlled by two or more genes
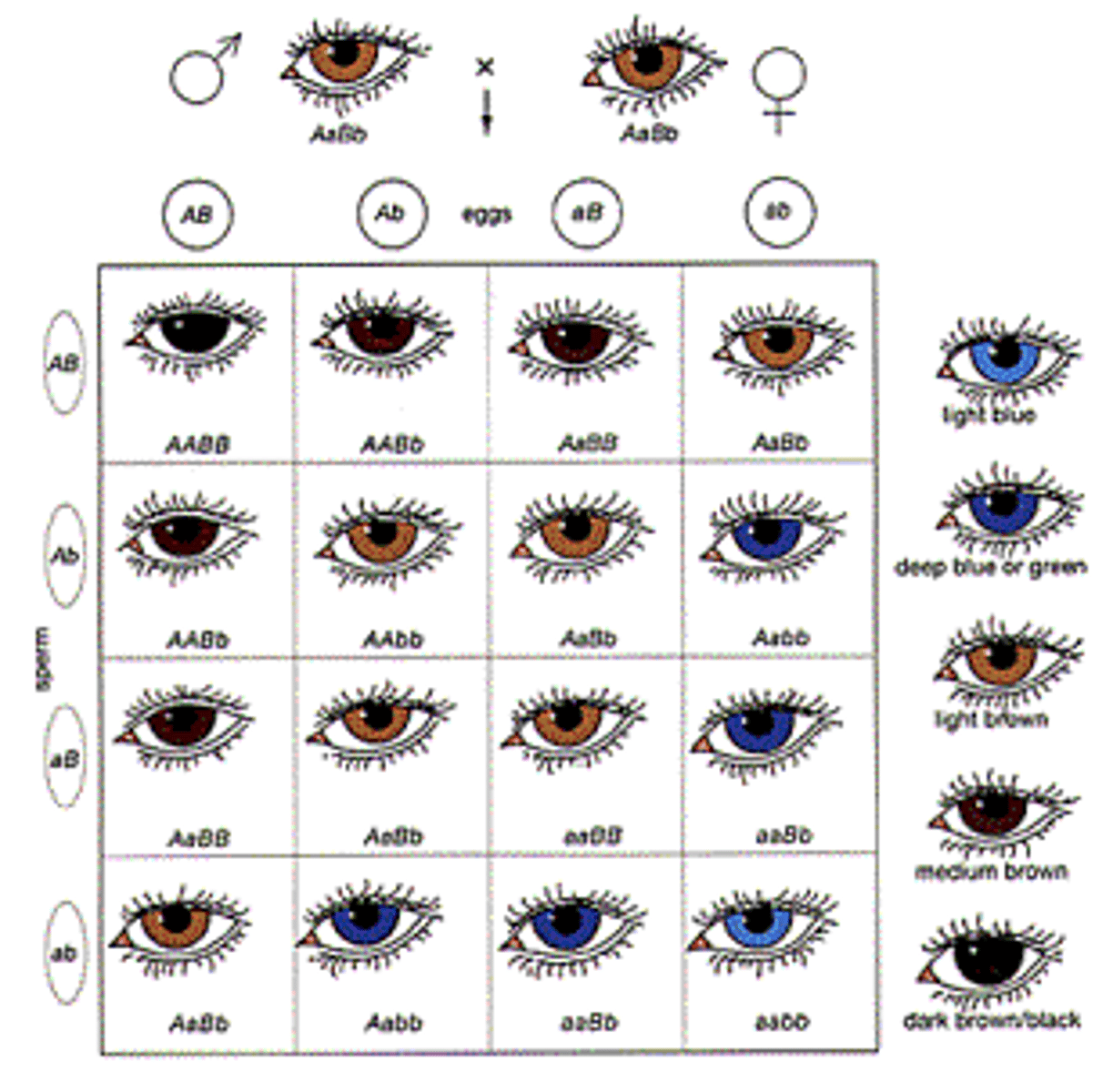
homologous
term used to refer to chromosomes that each have a corresponding chromosome from the opposite-sex parent
diploid
term used to refer to a cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes
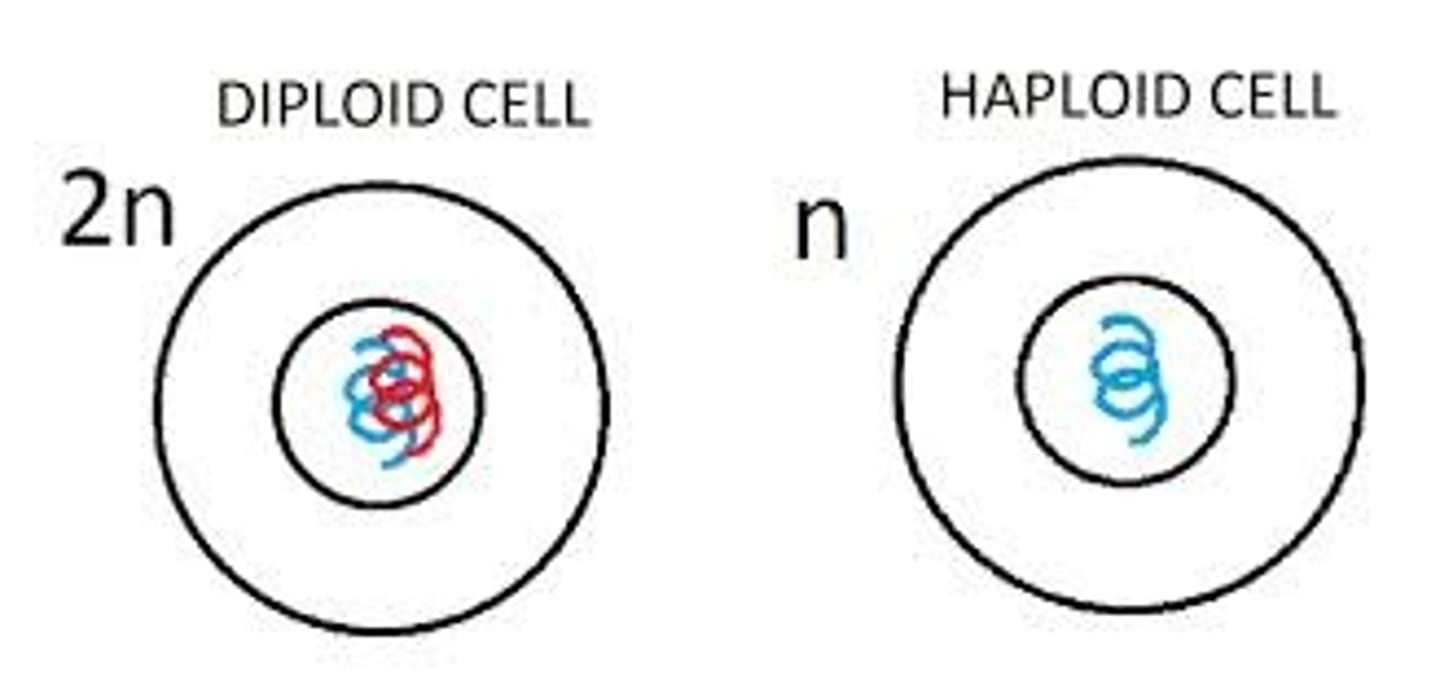
haploid
term used to refer to a cell that contains only a single set of chromosomes and therefore only a single set of genes
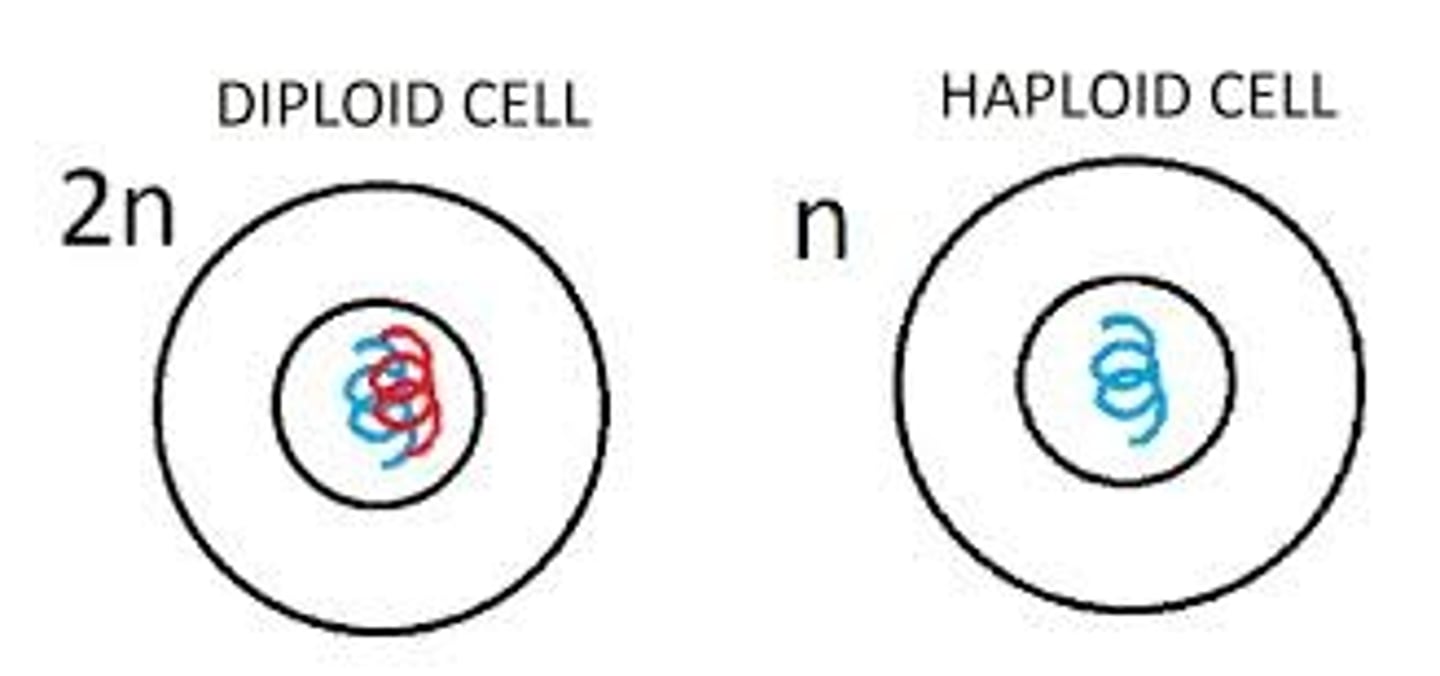
meiosis
process by which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell
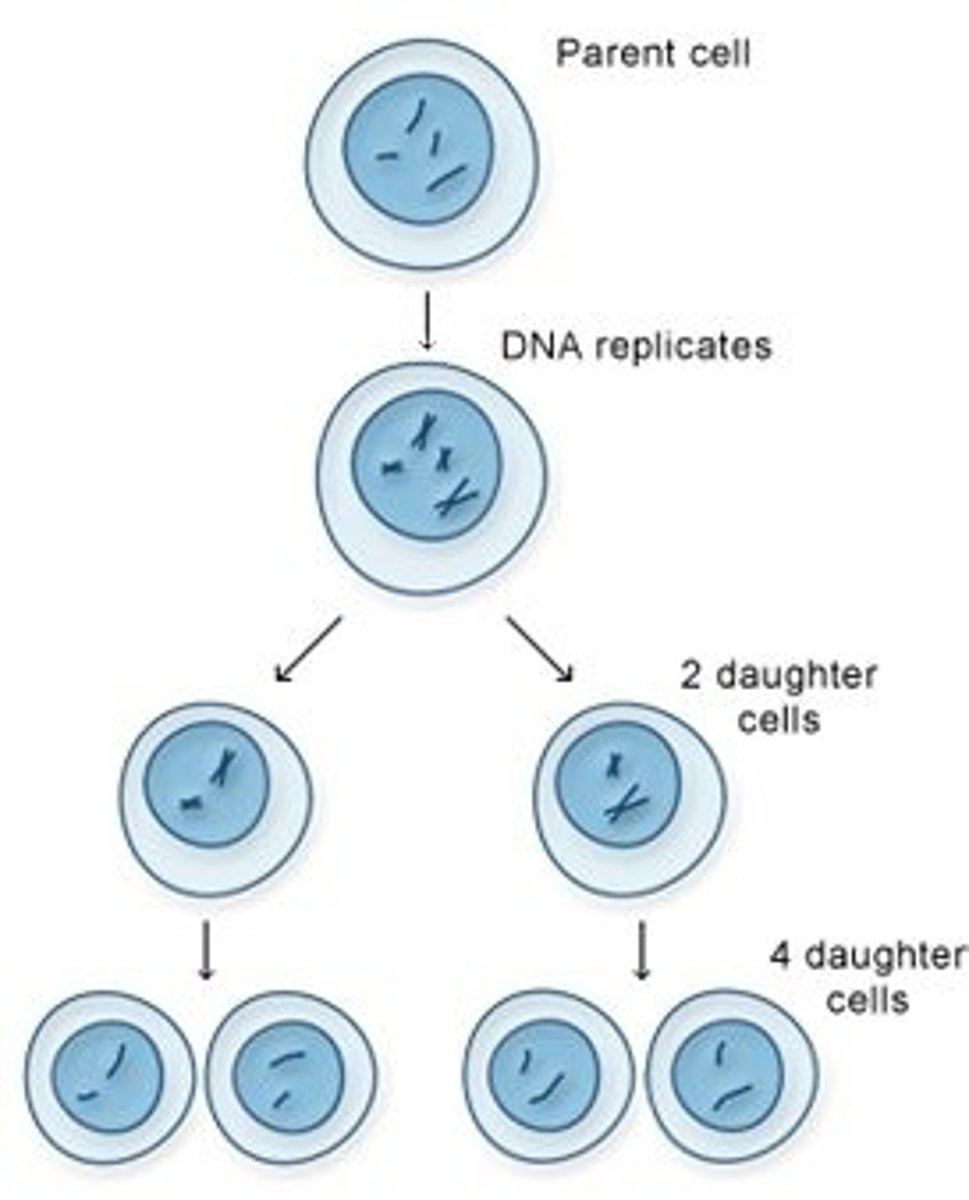
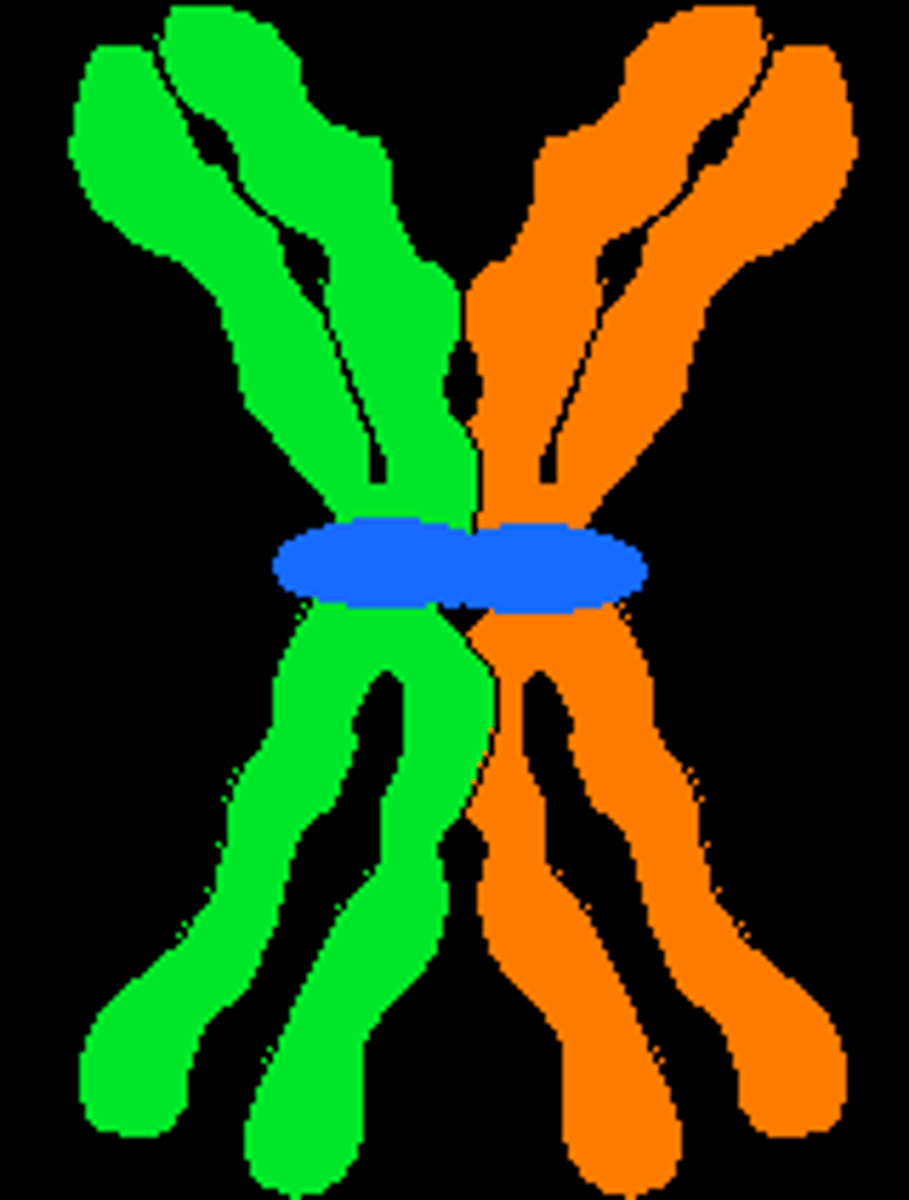
tetrad
structure containing 4 chromatids that forms during meiosis
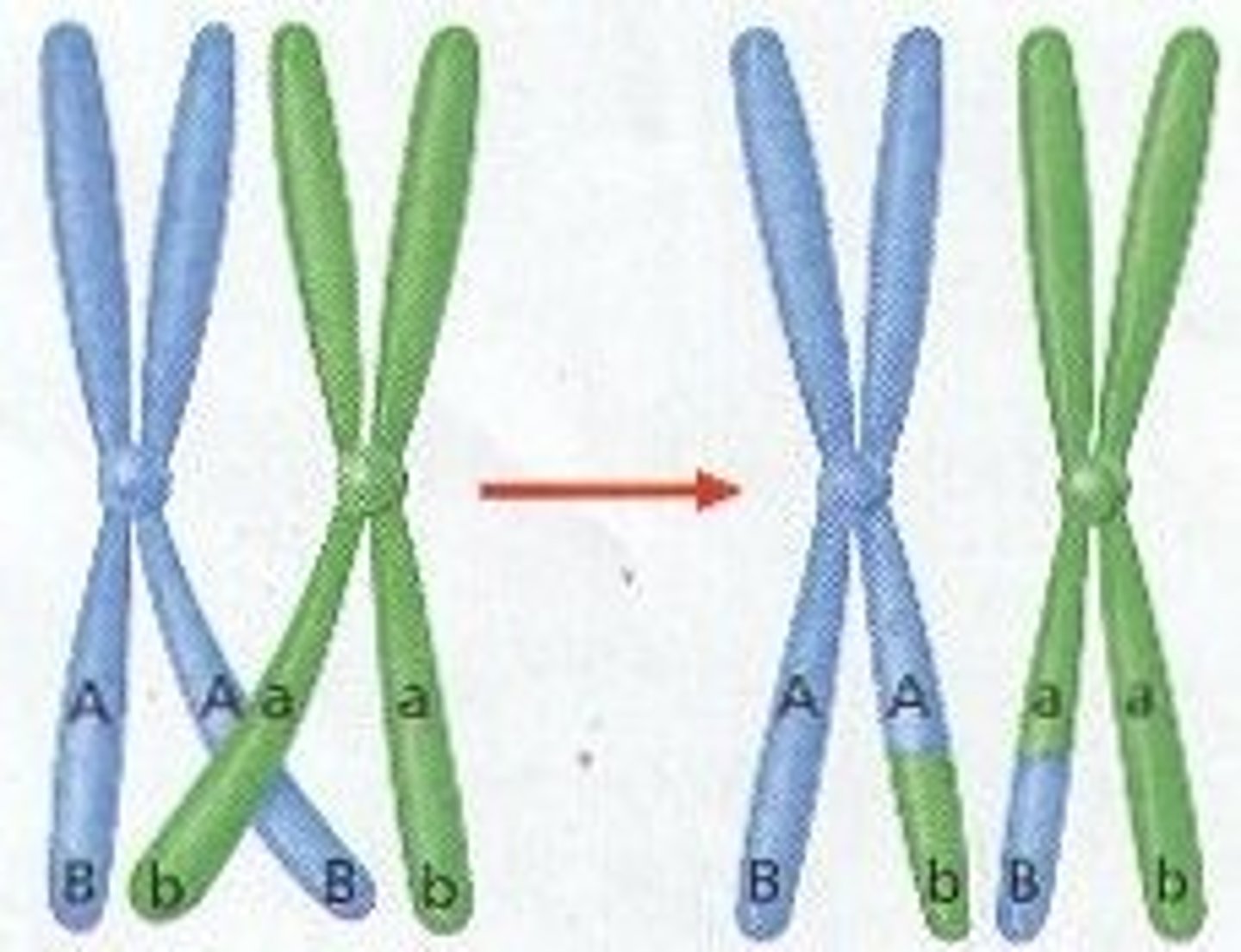
crossing-over
process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis
Cell
Basic functional unit of all living things
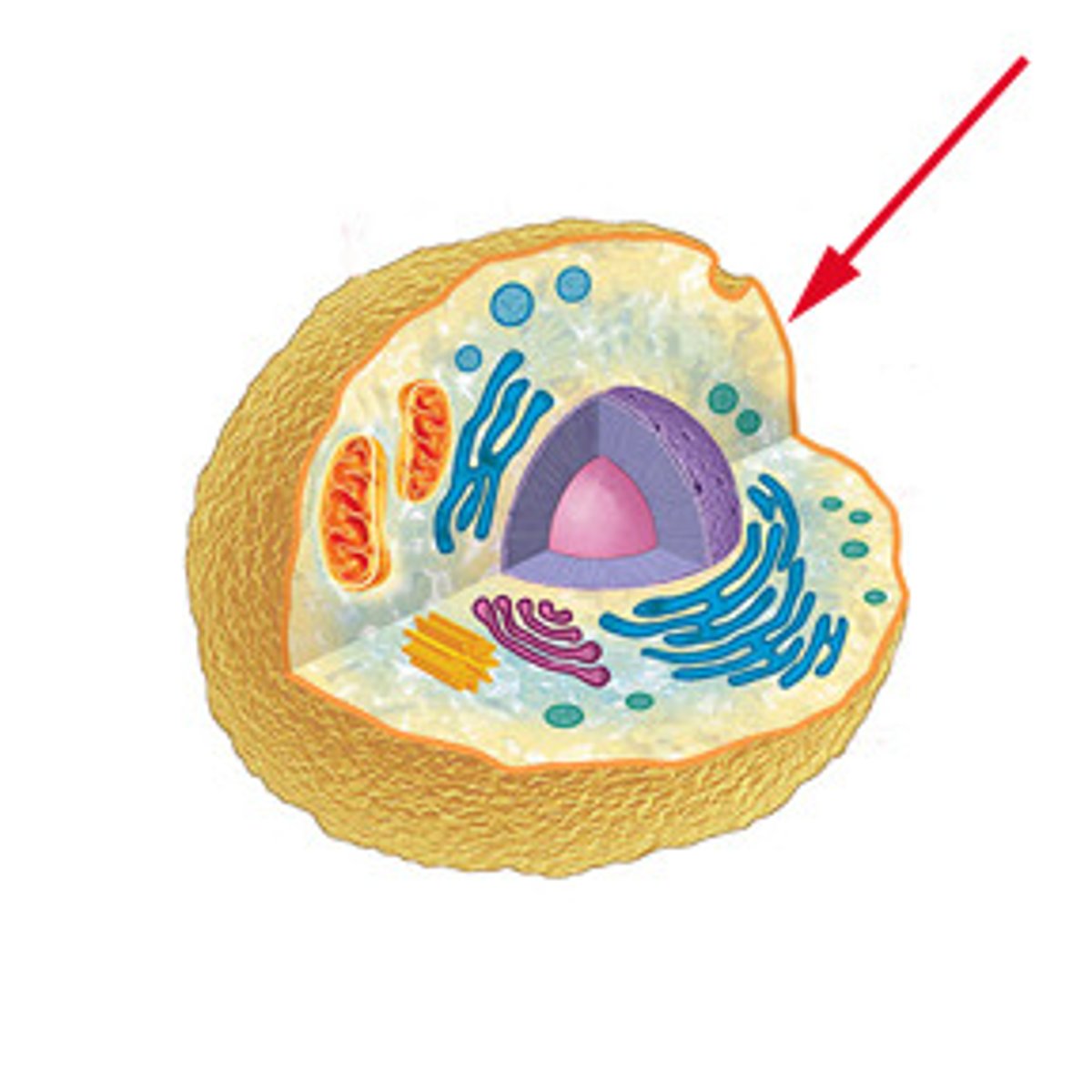
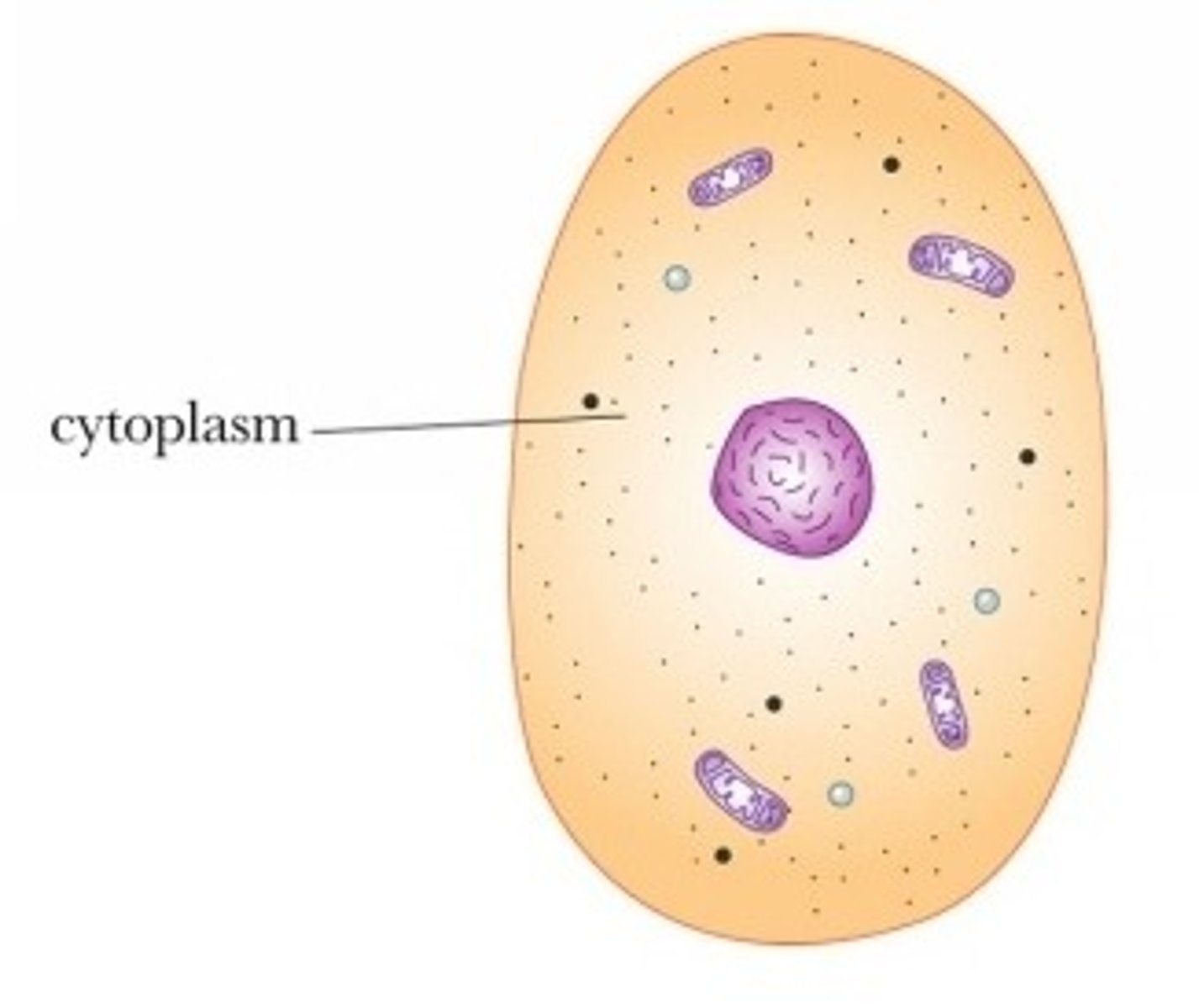
Cytoplasm
Consists of specialized bodies (organelles) suspended in a fluid matrix (cytosol)
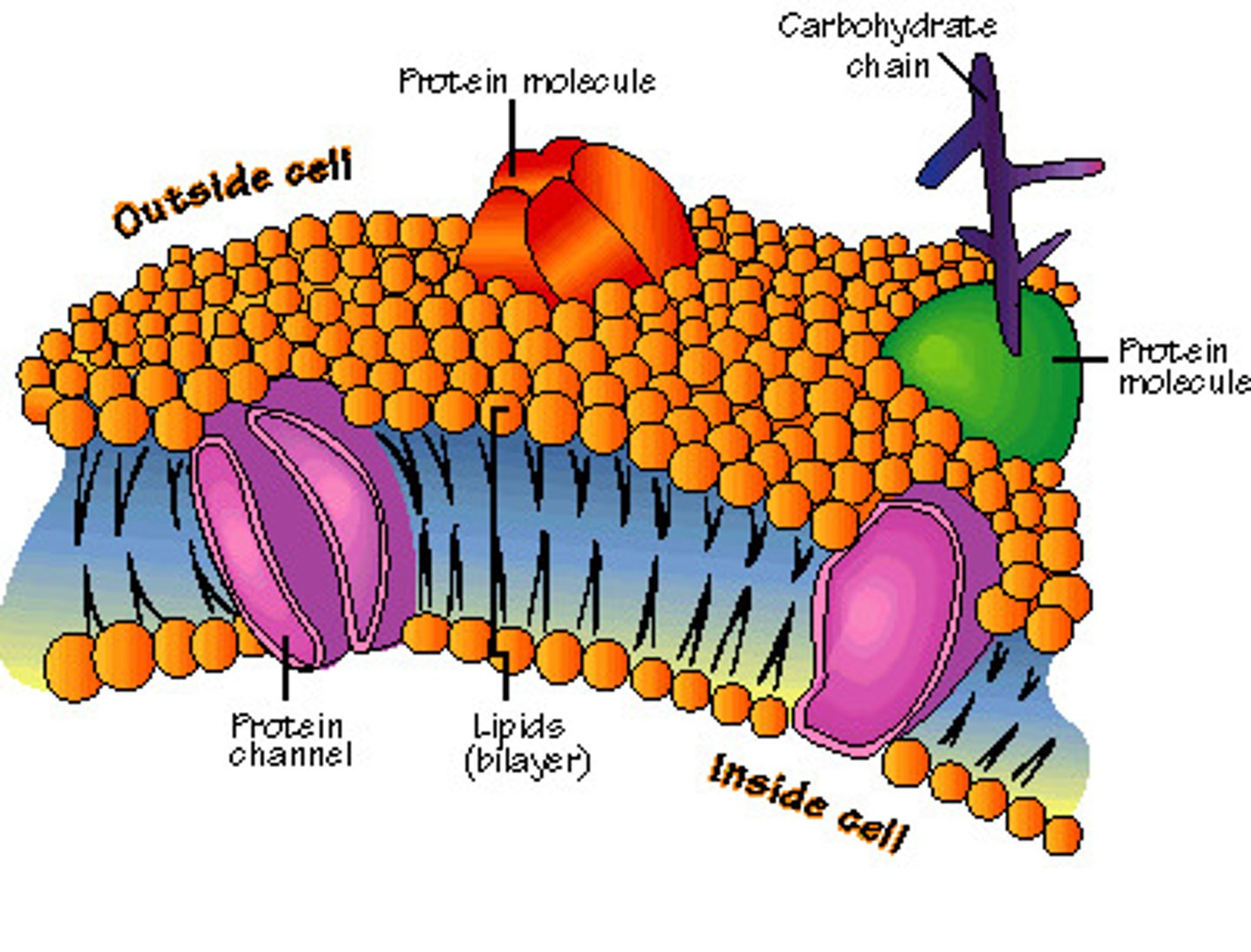
Plasma Membrane
Separates internal metabolic events from the external environment; controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell (selective permeability); lipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails, proteins, cholesterol to provide some rigidity, and a glycocalyx of glycolipids (lipids + oligosaccharides) and glycoproteins (proteins + oligosaccharides)
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins that attach to the inner or outer surface of the membrane
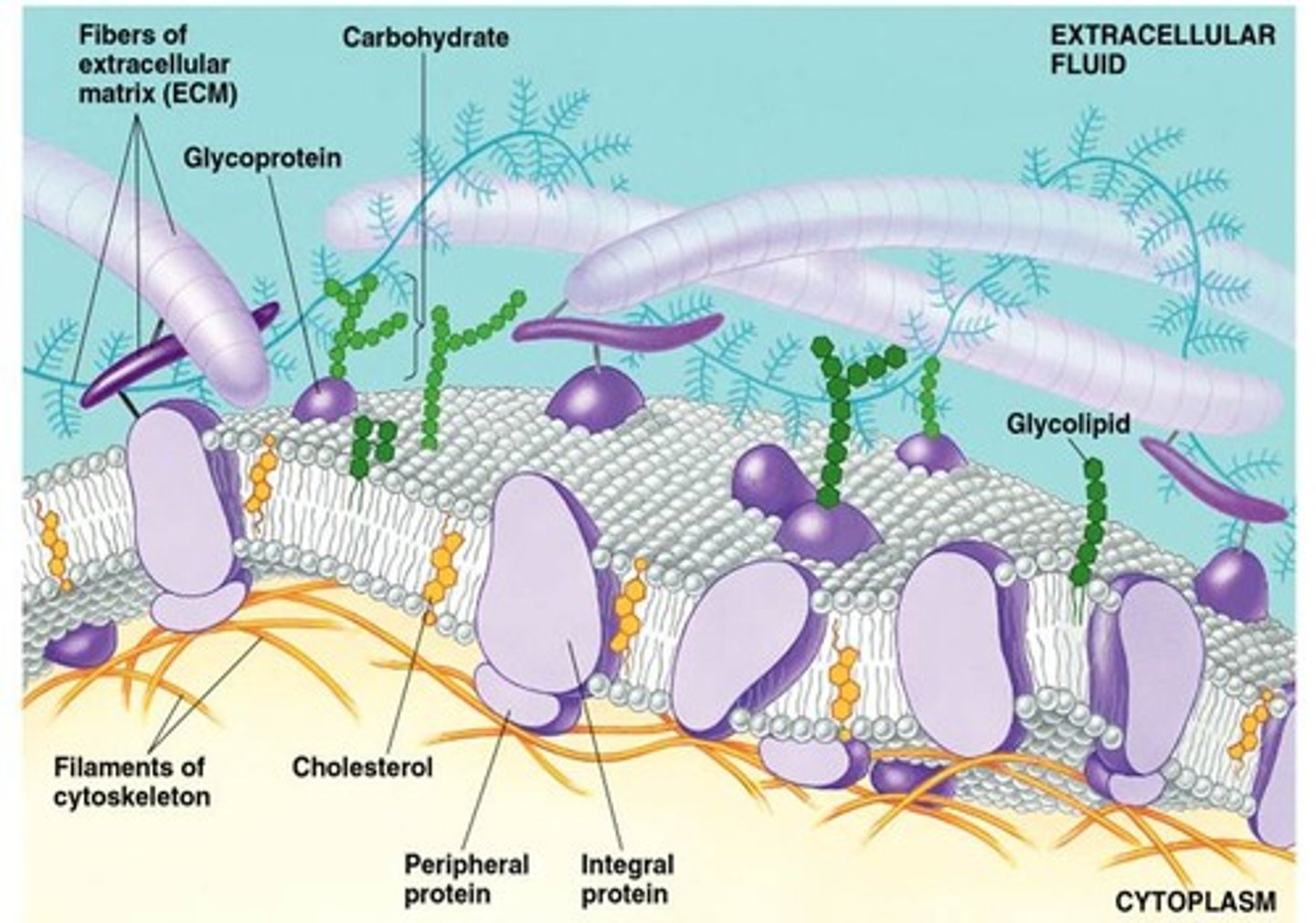
Integral Proteins
Proteins that extend into the membrane
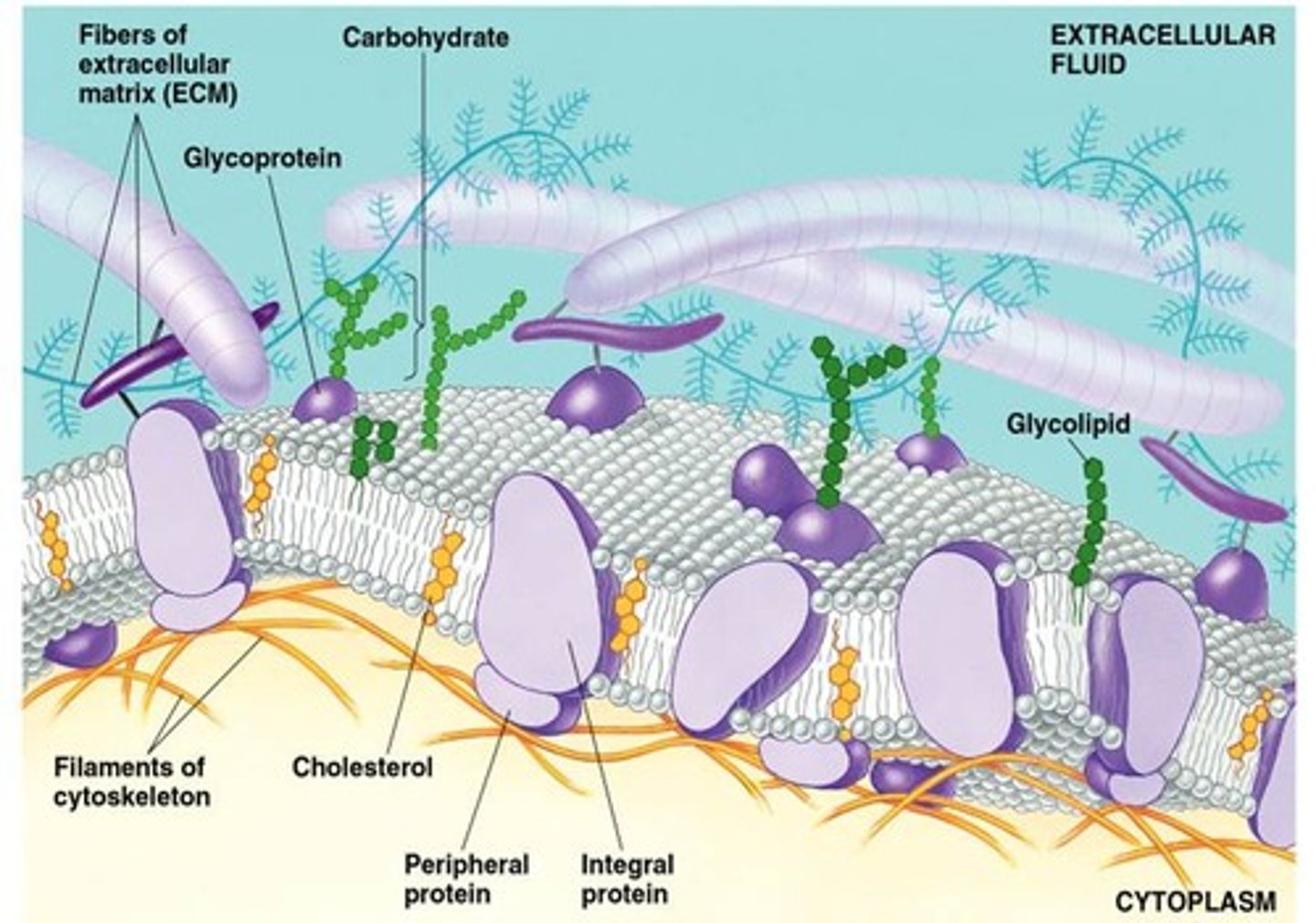
Transmembrane Proteins
Integral proteins that span completely through the membrane; held in place by hydrophilic/hydrophobic regions
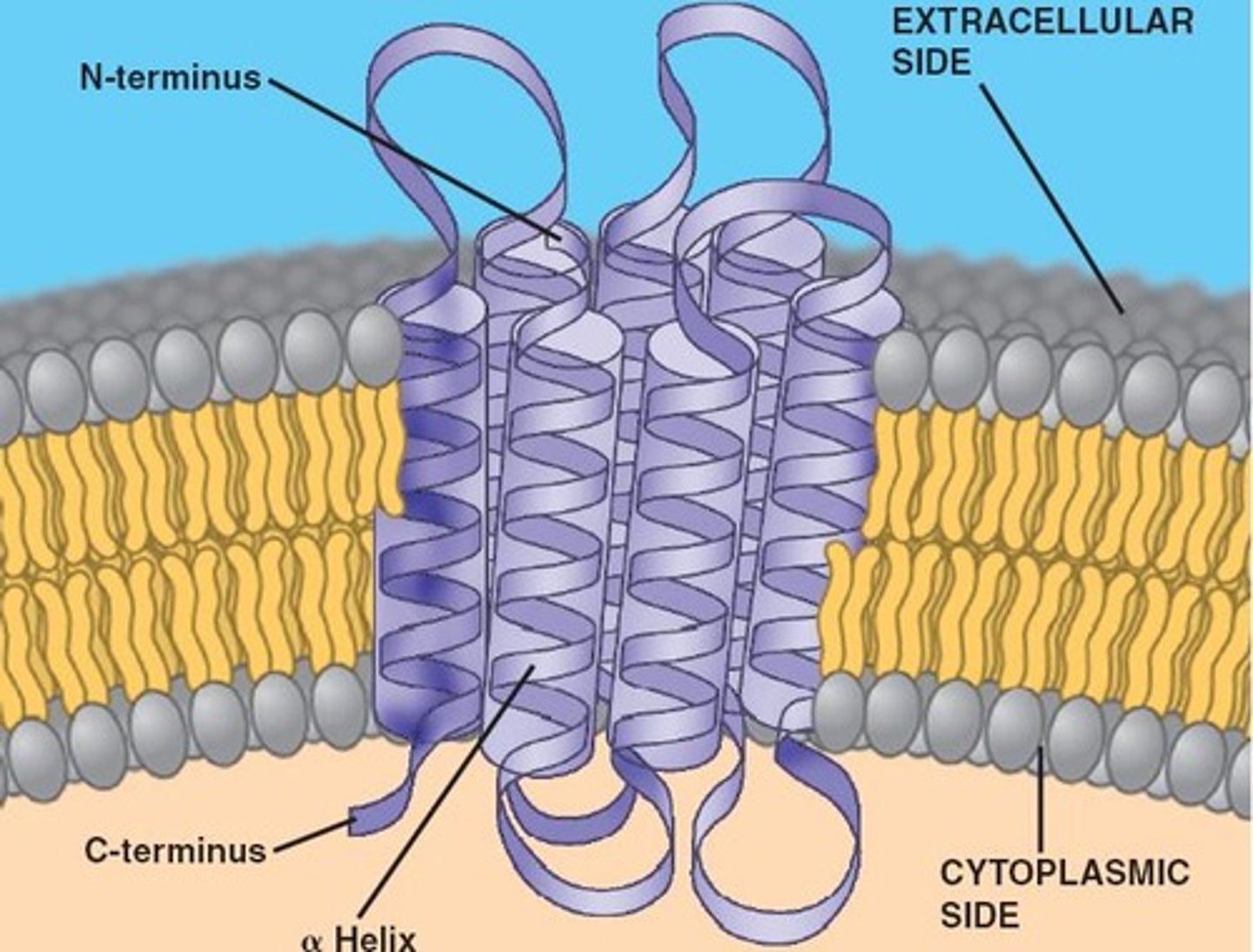
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes structure of the plasma membrane; scattered proteins within a flexible matrix of phospholipids
Channel Proteins
Provide open passageways through the membrane
Ion Channels
Allow the passage of ions across the membranes; gated channels open and close in response to specific stimuli i.e. Na+ and K+
Porins
Allow the passage of certain ions and small polar molecules; aquaporins increase the passage rate of water molecules
Carrier Proteins
Bind to specific molecules, undergo a change in shape, and then transfer the molecules across the membrane; i.e. the passage of glucose
Transport Proteins
Use ATP to transport materials through active transport; i.e. sodium-potassium pump maintaining higher sodium and potassium concentrations on opposite sides of the membrane
Recognition Proteins
Give each cell type a unique identification so it can distinguish between "self" and "foreign" cells
Adhesion Proteins
Attach cells to neighboring cells and give cell stability
Receptor Proteins
Provide sites that hormones or other trigger molecules can bind to in order to activate a cell response
Nucleus
Bounded by the nuclear envelope (consisting of two phospholipid bilayers); contains DNA in chromatin form; serves as the site of chromosome separation during cell division
Chromatin
Threadlike form of DNA
Chromosomes
Chromatin condenses during cell division into rod-shaped bodies
Nucleosomes
Before cell division, histones organize DNA into bundles
Nucleolus
Concentrations of DNA within the nucleus that are in the process of manufacturing components of ribosomes
Ribosomes
Consist of RNA molecules and proteins; the two subunits move across the nuclear envelope into the cytoplasm to be assembled; ribosomes assist in the assembly of amino acids into proteins
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Stacks of flattened sacs with ribosomes; as ribosomes assemble polypeptides, polysaccharides are attached to them to create glycoproteins
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Without ribosomes; synthesizes lipids and hormones
Golgi Apparatus
Flattened sacs arranged like a stack of bowls; modify and package proteins and lipids into vesicles; these vesicles bud out from the Golgi apparatus, migrate to the surface, and merge with the plasma membrane to release contents
Lysosomes
Vesicles from the Golgi apparatus that contain digestive enzymes; break down food, debris, and foreign invaders; they DO NOT occur in plant cells
Peroxisomes
Break down substances (i.e. hydrogen peroxide, fatty acids, and amino acids)
Mitochondria
Carry out aerobic respiration to obtain ATP from carbohydrates
Chloroplasts
Carry out photosynthesis to convert energy from sunlight into carbohydrates
Microtubules
Made of tubulin; provide support and motility for cellular activities; found in spindle apparatus of mitosis, and in cilia and flagella
Intermediate Filaments
Provide support for the cell
Microfilaments
Made of actin; involved in motility of cell
Flagella and Cilia
Structures that protrude from the cell membrane and make wavelike movements; flagella are long, few and move in snakelike motion; cilia are short, numerous, and move with back-and-forth movement; "9 +2" array of microtubules
Storage Vacuoles
In plants; store starch, pigments, toxic substances (i.e. nicotine)
Central Vacuole
Large bodies in plant cells; exert turgor pressure on cell walls when full and maintain rigidity this way
Cell Wall
Provide support outside the plasma membrane; made of cellulose in plants; made of chitin in fungi
Anchoring Junctions
Protein attachments between adjacent animal cells; desmosomes bind adjacent cells together and are associated with protein filaments that extend into the cell interior to hold structures together
Tight Junctions
Tightly stitched seams between animal cells; prevents passage of materials between cells so that materials must pass through them
Communicating Junctions
Allow the transfer of materials; gap junctions between animal cells involve connexins which prevent cytoplasm from mixing but allow the passage of ions and small molecules; plasmodesmata between plant cells involves with a desmotubule surrounded by cytoplasm and plasma membrane going between the two cells, with exchange occurring through the cytoplasm
Solute
Substance being dissolved
Solvent
Substance that the solute is being dissolved in; i.e. water
Hypertonic Solution
The solution that has a higher concentration of solutes than the other solution
Hypotonic Solution
The solution that has the lower concentration of solutes than the other solution
Isotonic Solution
The solution has the same concentration of solutes as the other solution
Passive Transport
Movement of substances from higher to lower concentration; does not require energy
Simple Diffusion
Random movement from high to low concentration
Osmosis
Diffusion of WATER molecules across a selectively permeable membrane
Dialysis
Diffusion of SOLUTES across a selectively permeable membrane
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion of solutes or water through channel proteins
Countercurrent Exchange
Diffusion of substances between two regions in which they are moving by bulk flow in oposite directions
Active Transport
Movement of solutes against a gradient, requiring the expenditure of energy
Exocytosis
Vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents to the outside
Endocytosis
The plasma membrane engulfs a substance and enters the cytoplasm in a vesicle; phagocytosis (undissolved, solid material) and pinocytosis (dissolved, liquid material), receptor-mediated (specific molecules bind to receptors)
Ecology
study of the integrations between organisms and the environment in which they live in; can range from individual (organismal) to global
Organismal ecology
has to do with how an organism's structure, physiology, and behavior interact with its environment; includes physiological, evolutionary, and behavioral ecology
Population
group of individuals of the same species living in an area; ex: painted turtles living in a pond
Population ecology
studies the factors that affect population size and how and why a population might change over time
Community
a group of populations of all different species living in an area; ex: the whole pond ecosystem of organisms
Community ecology
studies the interactions between species; including predation, competition, commensalism, symbiotic, etc; and how it affects a community's structure, organization, relationship
Ecosystem
community of organisms in an area and the physical factors that they interact with; ex: the pond the organism live in
Ecosystem ecology
studies the energy flow and chemical cycling between organisms and their environment (aka study of ecosystem and organism's interaction)