bio46 cell signaling from week 11 comprehension ws
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
proximity tagging
compared to Co-IP, tells you if two proteins directly interact; by encoding half of GFP into each protein and looking at fluorescence; fluorescence localization and duration in certain areas → where and for how long proteins interact directly
epistasis analysis
knocking out inhibitors to see downstream signaling effects
G-coupled signaling overview
extracellular signal causes conformational change in GPCR; GPCR exchanges GDP for GTP on G-alpha, causing G-alpha to separate from G-beta/omega; G-alpha involved w adenylyl cyclase to produce cAMP → kinase A or lipid signaling pathway; G-beta/omega interact with ion channels when released
protein kinase A structure
2 regulatory subunits, each with two cAMP sites; 2 catalytic subunits w ATP site, substrate binding site, and regulatory unit binding site
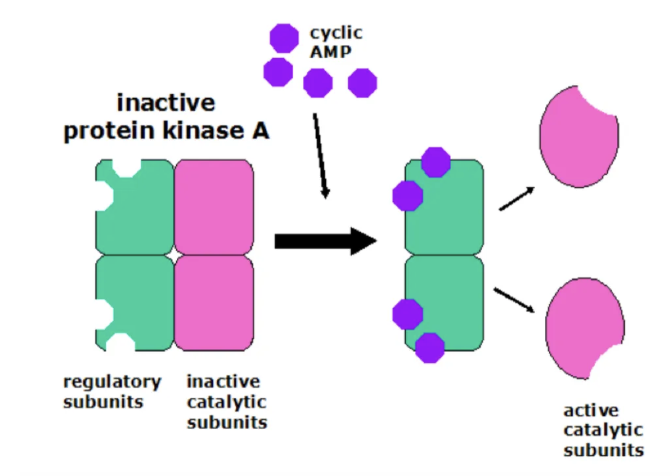
PKA production
translated in cytosol; 2 genes encode for different subunits; subcellular localization regulated bc diffus-ability changes depending if regulatory elements are bound or not so fast and slow signaling effects
RTK
receptors tyrosine kinases; when brought tgt, phosphorylate each other, then activate intracellular signaling proteins, which then activate Ras proteins via GDP → GTP, which then activate kinase cascade/amplification
CREB
cAMP response element binding protein; transcription factor