ANATOMY Test 1
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
* common function
1. connective tissue
2. muscle tissue
3. epithelial tissue
4. nervous tissue
1. covering/lining epithelium
1. covers body surfaces and internal body
2. allows the body to interact with the internal and external environment
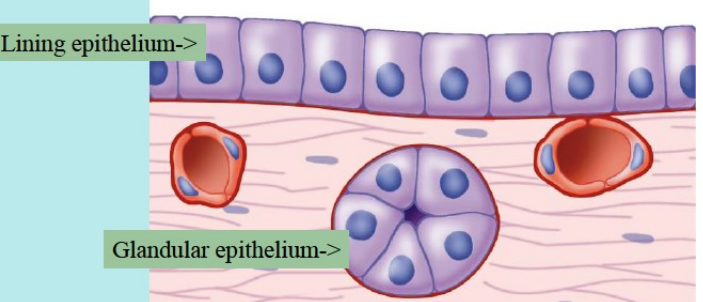
2. granular epithelium
1. formation of glands
1. protect
2. absorb
3. secrete
1. sensory reception
* microvilli → sensory reception
* cilia → helps with movement
* sticky sheet
* joins epithelial tissue and connective tissue
* connective tissue offers support b/c anchoring is stable
* can act as a filter (abosrb, secrete)
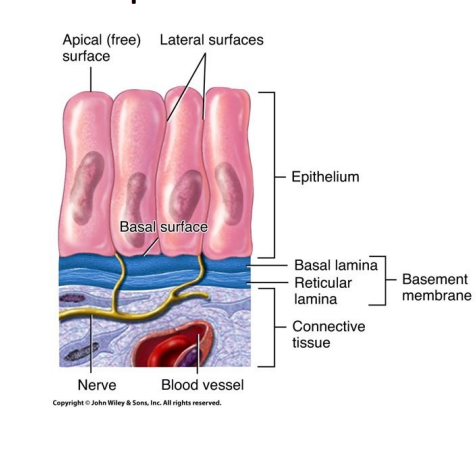
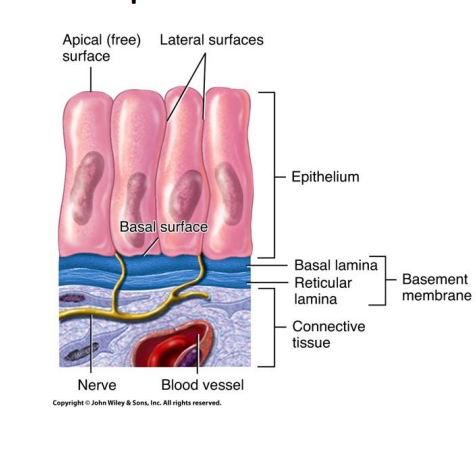
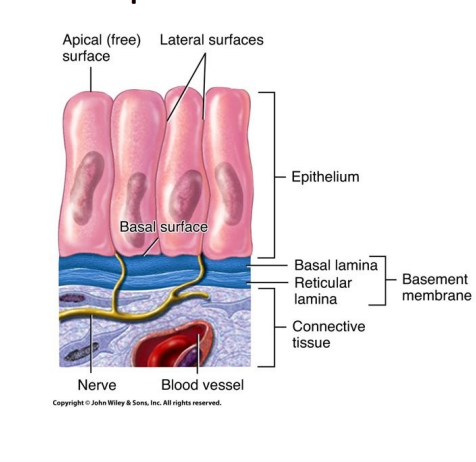
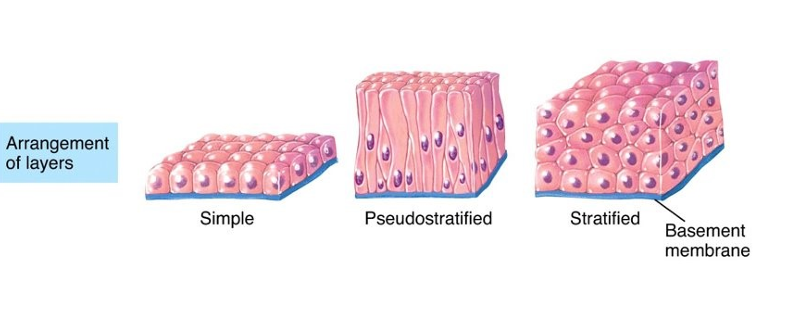
what are the three layers of epithelial tissue `
simple - single layer
substances pass through
lining of apical surface and basal
absorb and secrete
thin
Pseudostratified
each cell has contact with basement membrane
one layer
nuclei in each cell is squeezed
middle ground
protect but important that substance pass through
usually respiratory system
Stratified
multiple layers
not all cells are in contact with the basement membrane
protects (difficult for things to penetrate)
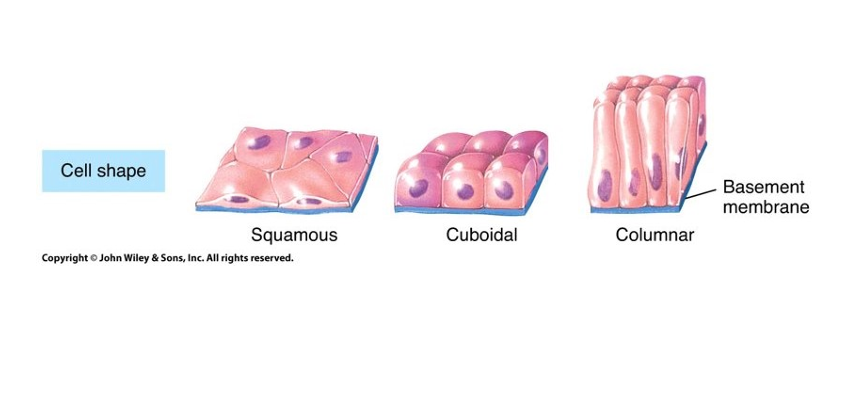
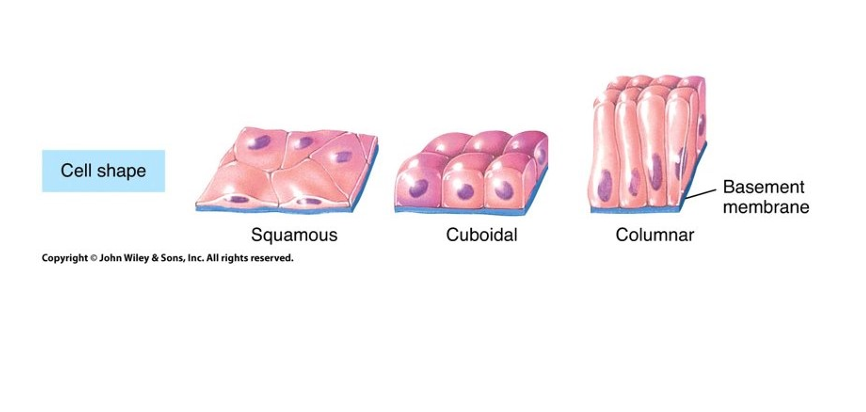
What are the three type of cell shape in epithelial tissue
squamous - flat
Cuboidal - cubed
Columnar - skinny and long
Epithelial tissue
more layers = more protection
single layer = easier for substances to pass through
cilia - helpful in moving substances involved in sensation
What is simple squamous
very thin layer
need to be in areas where absorption and secretion is important
blood vessels, air sacs in lungs (tiny molecules need to pass through)
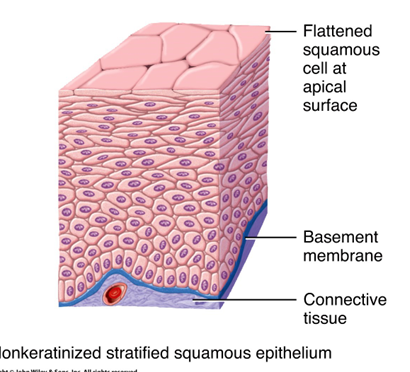
Stratified Squamous
very thick
protection is needed
ex. skin
more cubes towards the basement membrane
Glandular Epithelium
glands has more or one cell
make or secrete a particular substance (saliva, hormones)
What are the two types of Glandular Epithelium
endocrine - secreted into bloodstream
not controlled and flows throughout body
Exocrine - travels via duct to destination
controlled and localized
What does connective tissue do?
supports body structure
What are the 4 types of connective tissue
connective proper tissue
cartilage
bone
blood
Mesenchyme
all come from the same type of blood when developing
ORIGINAL CELL type
What are the 5 functions of connective tissue
binding and supporting
protecting
insulating
storing reserve fuel
transporting substances
Connective tissue structure - reticular fibers
consists of collagen and glycoproteins
provide support in blood vessel walls and form networks around cells
Connective tissue structure - Elastic fibers
stretchable and strong fibers made of proteins and elastin and fibrillin
found om skin, blood vessels and lung tissue
Connective tissue structure - Collagen fibers
strong, flexible and bundles of collagen
most abundant proteins in body
Ground substance fibers
non-living/extracellular matrix
What do fibers do to connective tissue
add integrity to structure
Ground substance
material between cells and fibers
fluid
made up of water and organic molecules
supports cells and fibers
binds together and provide a medium for exchanging substances between blood and cells
connective tissue
living
Connective proper tissue
binds
resist tension/mechanical stress
ligaments → connects bones together at joint
fat storage
provide reservoir for water and salts
6 TYPES - different types have diff. functions
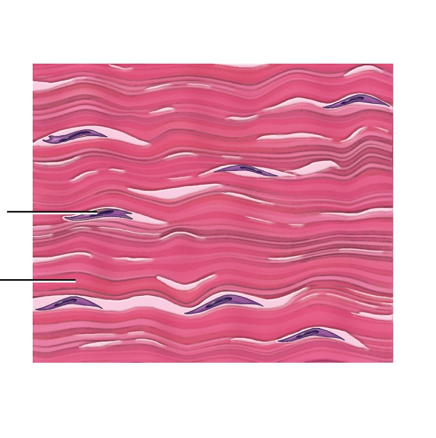
where can connective proper tissue
adipose (fat)
Under (supporting) epithelia
Ligaments (connect bones)
Connective tissue - Cartilage
resist compression (high level of H2O in matrix (ground substances)
found in joint
cushion and supports body structure to avoid bones rubbing together
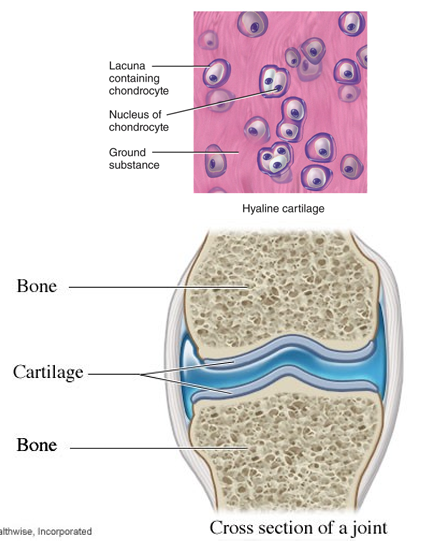
What are the three types of cartilage
Hyaline - within joint
Elastic - ears, nose
Fibrocartilage - tough and not common, more mobility
Connective tissue - bone
very hard
resist compression and tension
support of body structure
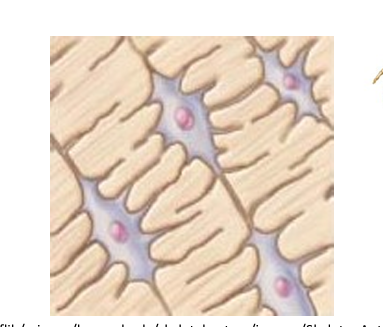
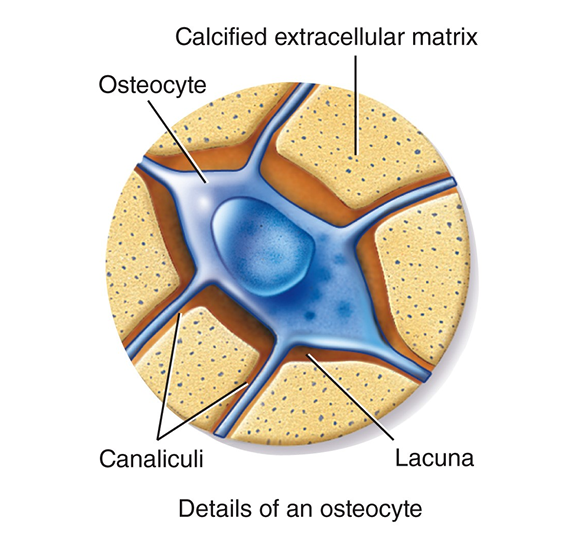
What are the two types of bones
compact
spongy
collagen fibers and calcium give bones its strength
Muscle
cells packed tightly together
increased blood supply
responsible for majority of body movements
Connective tissue - blood
fluid tissue
carries O2 and CO2, nutrients, waste and other substance
transport
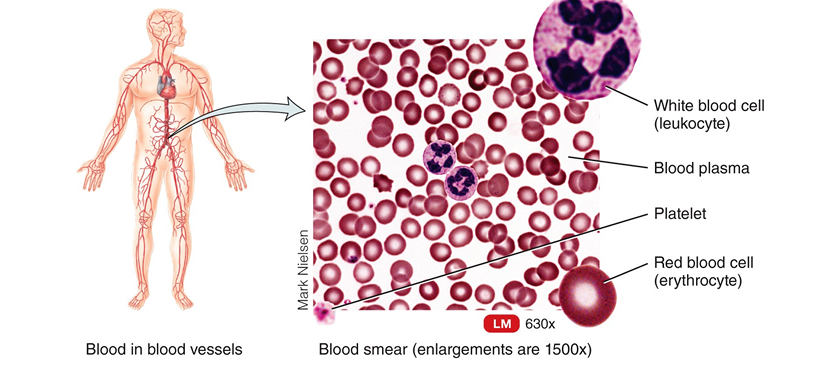
What are the three types of muscle
cardiac muscle cell
skeletal muscle cell - voluntary muscle movement
smooth muscle cell - organs and blood vessels/involuntary
Nervous Tissue
bring and receive info
What are the main components of nervous system
brain, spinal cord and nerves
What are the two types of nervous tissue
neurons - electrical signal
supporting cells - no electrical signal
Bones
they are organs
made up of more than one tissue
What are the functions of bone
dynamic structure ]
marrow - within bones
Support
protect
anchorage - solid anchor for other structure
mineral/growth factor storage - calcium
blood cell formation- marrow
triglyceride (fat) storage - adipose tissue - marrow
Hormone production - lets nervous system know whats going on in the bones
Bone classification
location
shape
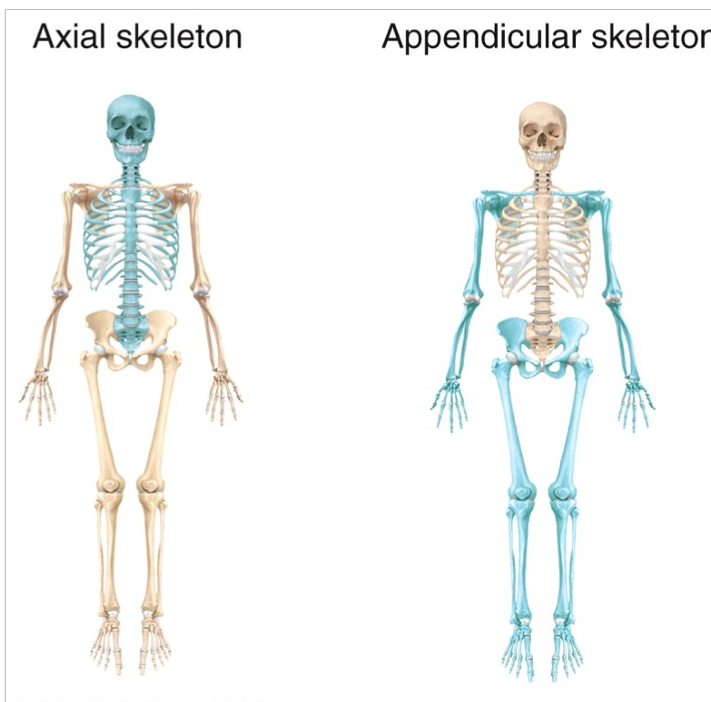
Bone classification - location
axial
main axis which body moves
Appendicular
appendages - limbs
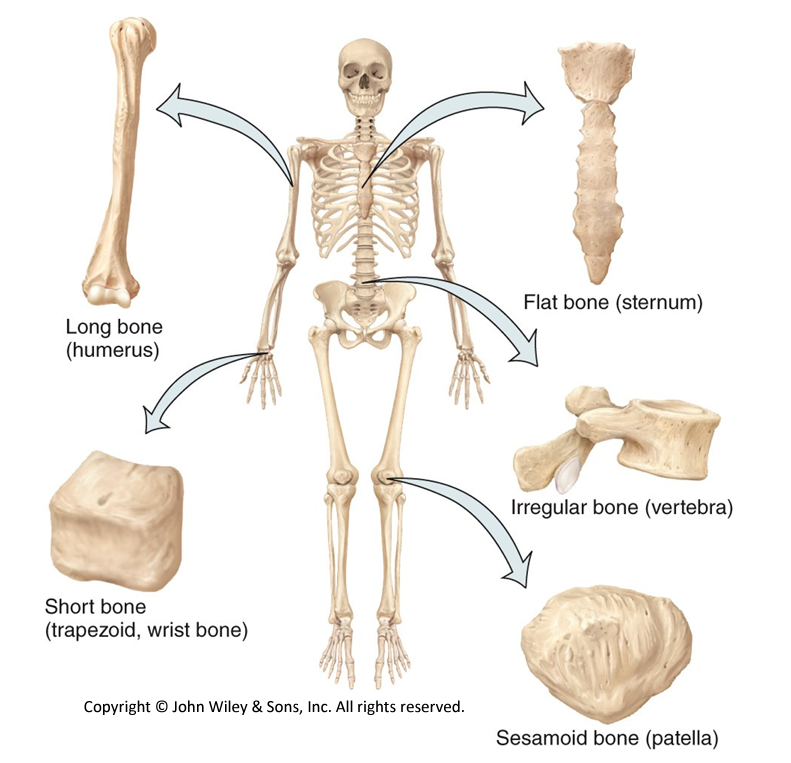
Bone classification - shape
long
short
flat
sesamoid
irregular
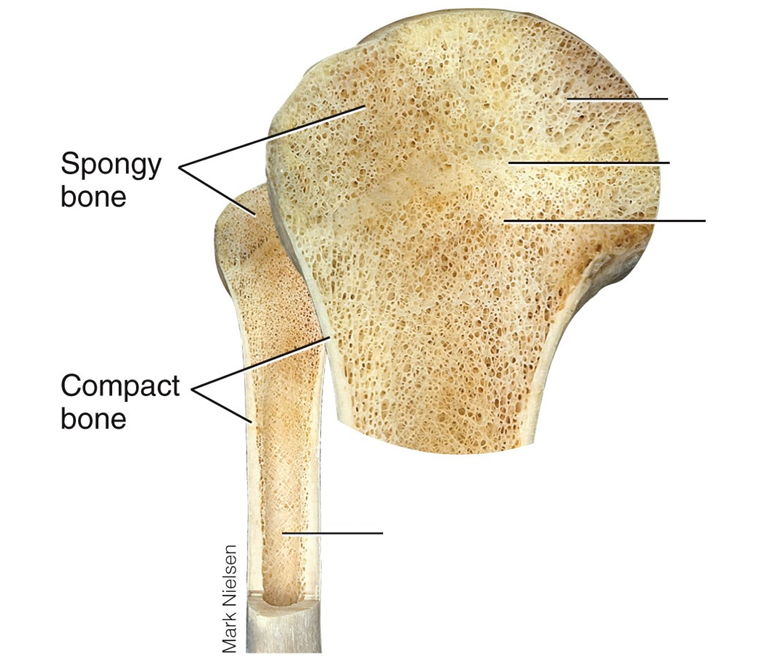
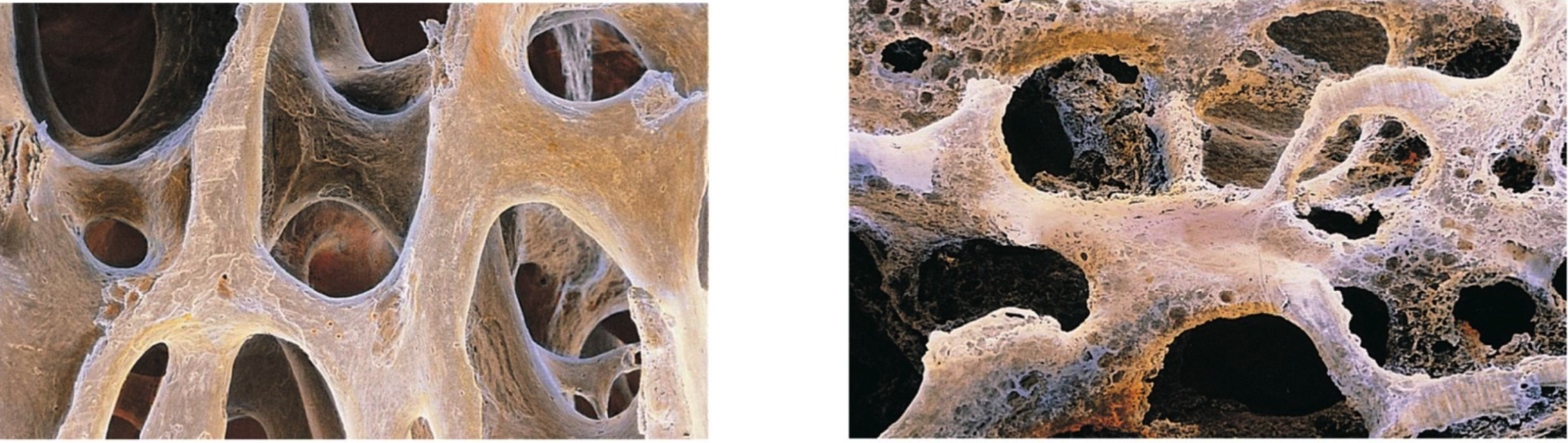
Compact vs spongy bone
compact
strong outer layer
smooth and solid
Spongy
strips of bone that creates honeycomb shape
internal layer
contains marrow - can store more due to shape
Structure of long bone
diaphysis
thick compact bone wall
spongy bone and medullary cavity - marrow stored
epiphysis
thinner compact bone outside covering
ton of spongy bone
Hyaline cartilage
shock absorbent
Metaphysis - growth in bone
Epiphyseal line - compact bone
Wider ends, narrow middle
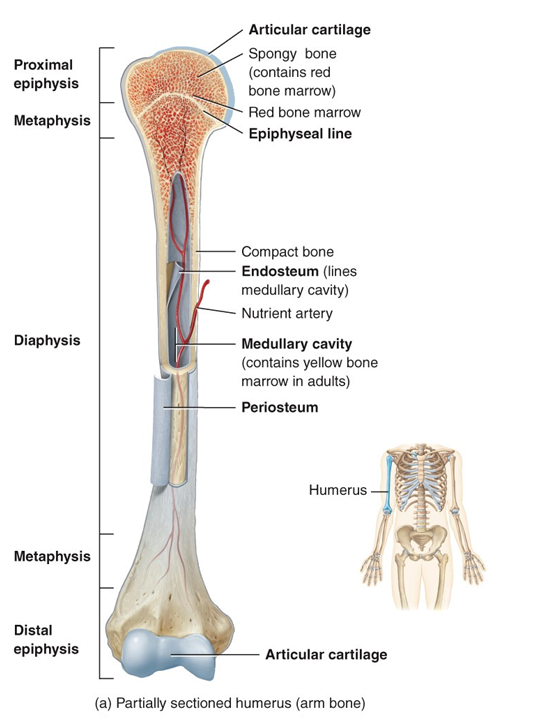
Red Marrow
blood production
RBC
in trabecular cavities of long and flat bone
trabecular cavity - spongy bone and medullary cavity
Yellow marrow
fat storage
can turn back into red marrow in adults with severe anemia, low RBC and O2 w/anemia
Newborn Marrow
medullary cavities and spongy bone full of red marrow and gets replaced with yellow marrow overtime
Cartilage in Skeleton
Hyaline
Elastic
Fibrocartilage
What is the purpose of cartilage in the skeleton
Resilient: resist compression
resilient b/c has lots of water
absorb compression
What is Hyaline cartilage
Provides support with flexibility and resilience
MOST abundant skeletal cartilage
Locations:
articular - joints
respiratory
costal (ribs)
what is costal
rib
what type of cartilage can be found in the nose?
hyaline and elastic
What is elastic cartilage
more elastic fibers compared to hyaline
better able to stand up to repeated bending
Where can elastic cartilage be found?
external ear
epiglottis → bend and rise to prevent food from entering the lungs
What is fibrocartilage
has great strength (very strong and made up of thick collagen fibers)
located where there is a lot of pressure and stretching
where can fibrocartilage be found
menisci of knee
intervertebral discs (allow for flexibility)
Cartilage in the growing skeleton
cartilage makes up the majority of the fetal skeleton
has lots of elastic and water (resilient)
ideal for fast growth → can turn into bones after growth
no nerves or blood vessels
what is avascular and importance
no blood or nerves
brings in nutrients such as O2 from nearby vessels
What is ossification
cartilage to bone (usually takes around 8 weeks in fetus)
are break and fracture the same thing?
yes
What is a non displaced done
ends of bones retain NORMAL position
what is a displaced bone
OUT of alignment
What is complete break
bone is broken through
what is an incomplete break
bone broken only part way through
what can an incomplete break also be known as?
harline fracture
what is a closed (simple) fracture
bone DOESN’T penetrate the skin
what is an open (compound) fracture
bone DOES penetrate the skin
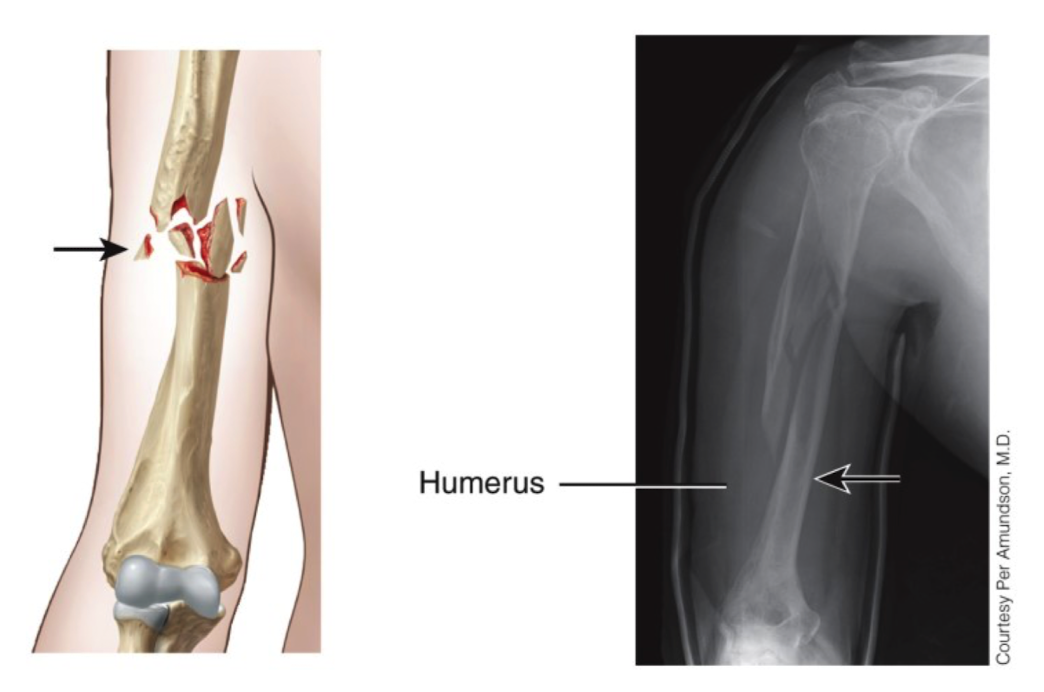
What is a comminuted fracture and where does it take place
in humerus
splintered/crushed or broken into pieces
bone fragments are present at site of fracture
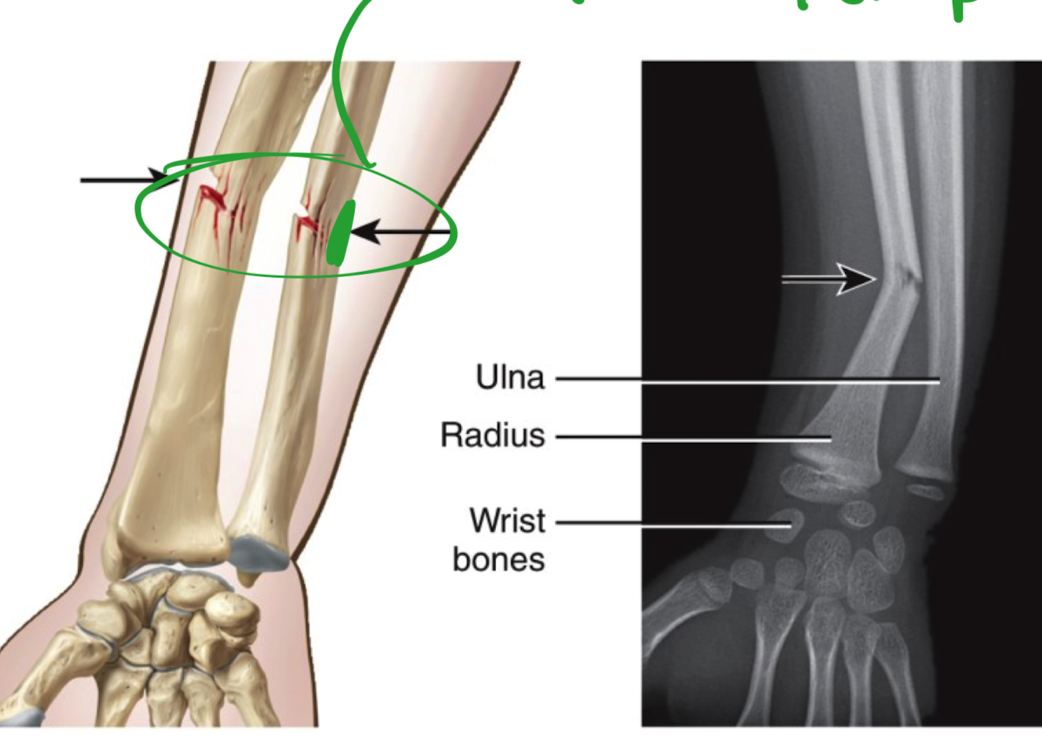
What is a greenstick fracture and where does it take place
in ulna
partial fracture - bends and snaps
occurs ONLY in children
bones are fully ossified
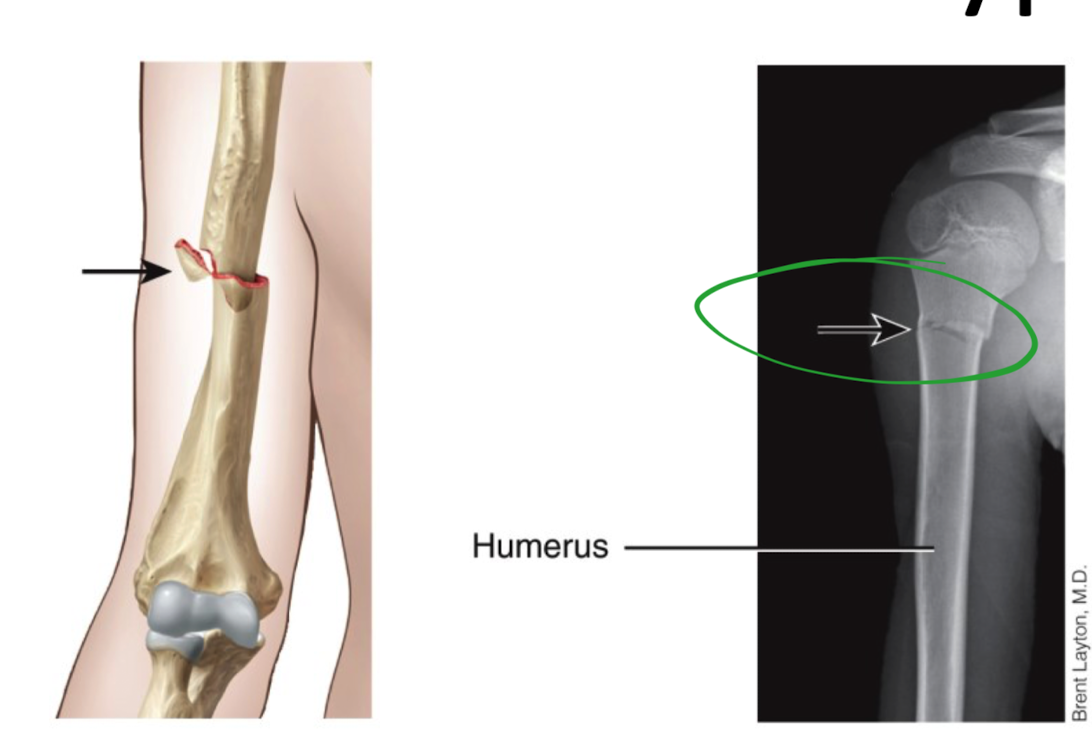
What is a impacted fracture and where does it occur
in humerus
one end of the bone is forcefully driven into other end of bone
“Jamming motion”
What is a pott fracture and where does it occur?
in the ankle
one of the malleoli (bump on ankle)
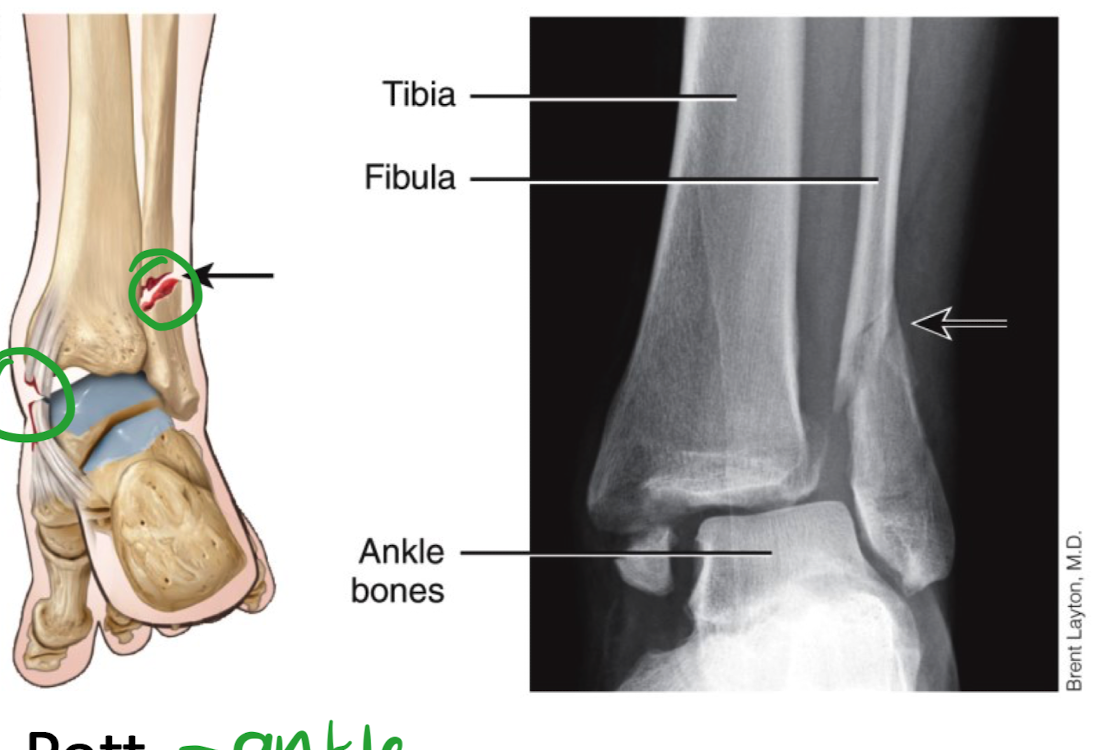
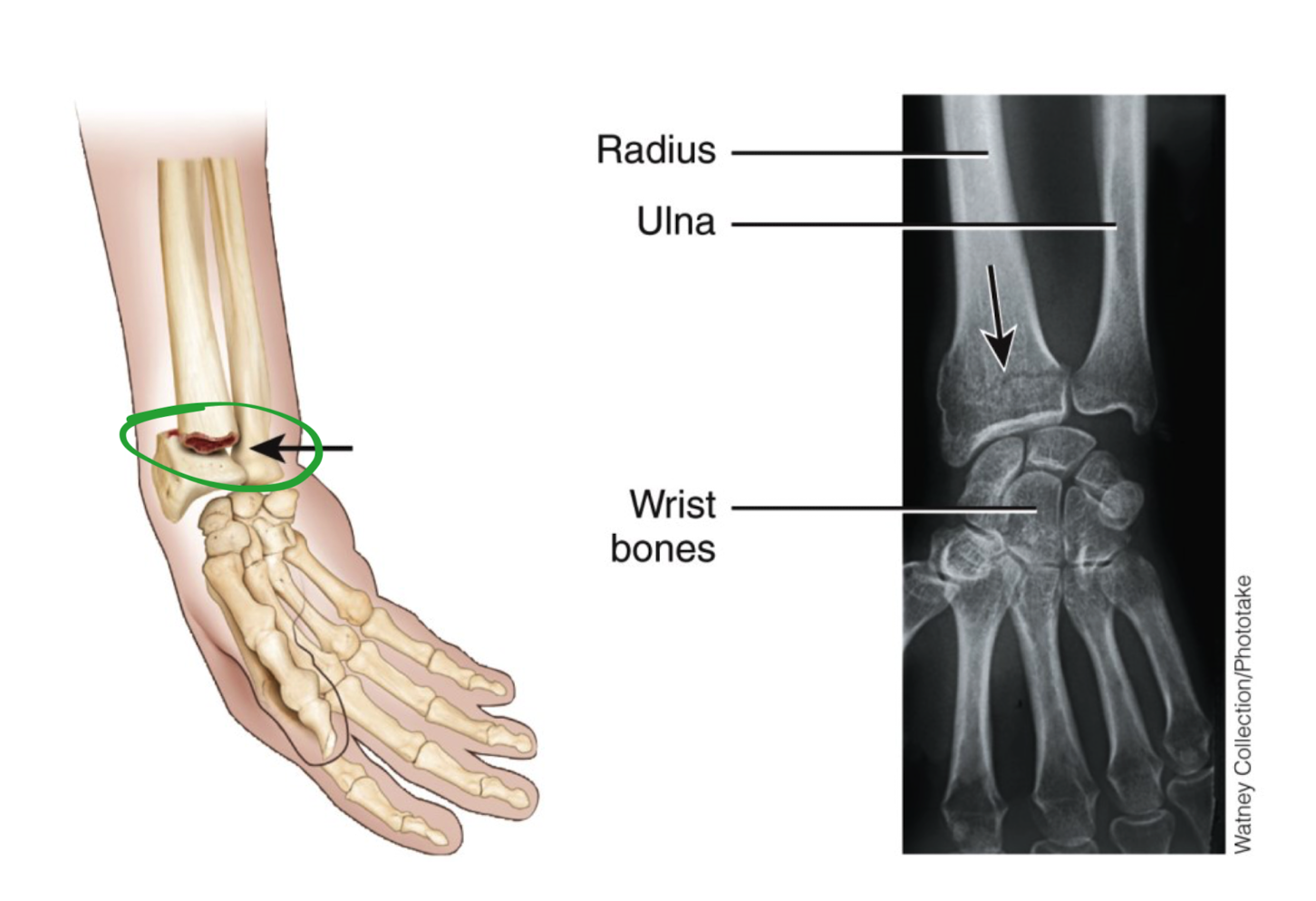
What is a colles fracture and where does it occur
wrist bones
distal end of radius
Fracture repair - closed (external) reduction
physically manually coaxes bones back into position
lots of force and painful
Fracture repair - open (internal) reduction
bone ends are secured surgically with pins and wires
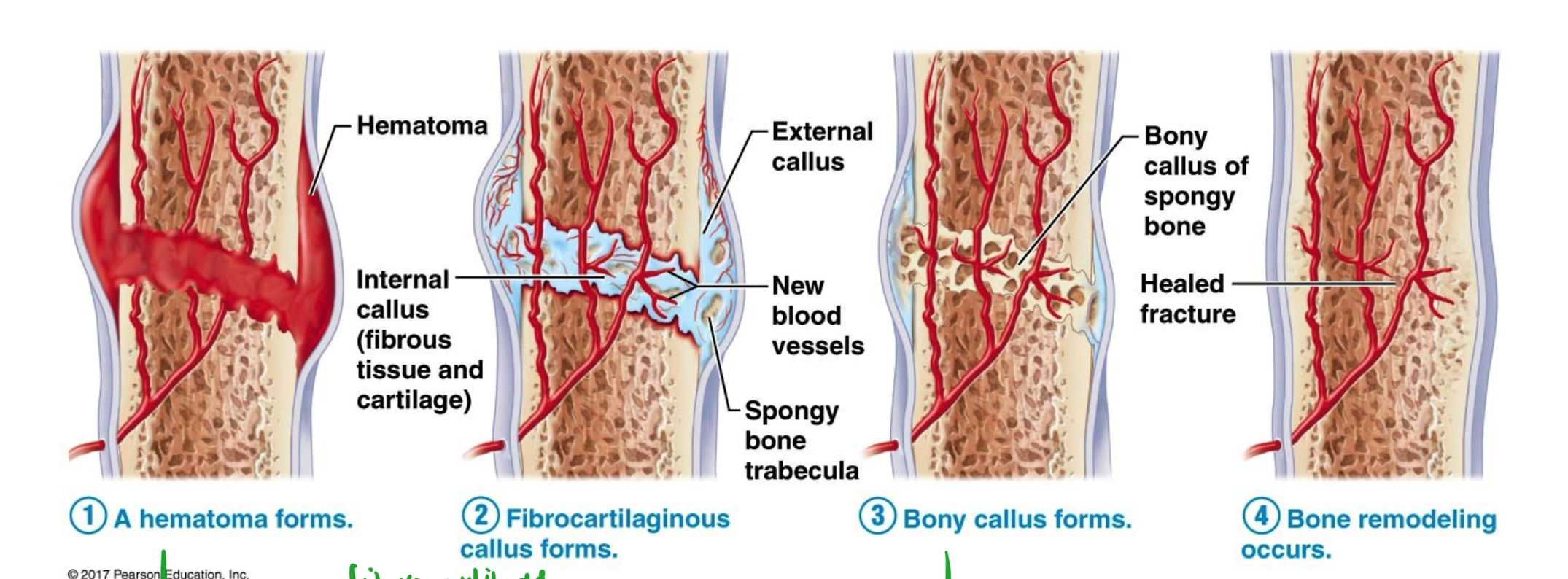
Fracture healing repairing steps
hematoma forms
bunch of blood rushes to the area
Fibrocartilaginous callus forms
fibrocartilage is present
replace blood with fibrocartilaginous
Bony callus forms
fibrocartilage gets replaced with bone
Bone remodelling occurs
want bone to be smooth
specialized cell eat up extra stuffy and gt shape we want
When does fracture healing occur
immediately after
How long does a fracture take to heal
couple of months
How fast do reductions of bones usually happen
usually within a couple of hours
needs to happen ASAP
Osteomalacia
soft and weak dones
due to POOR mineralization
usually vitamin D or calcium def.
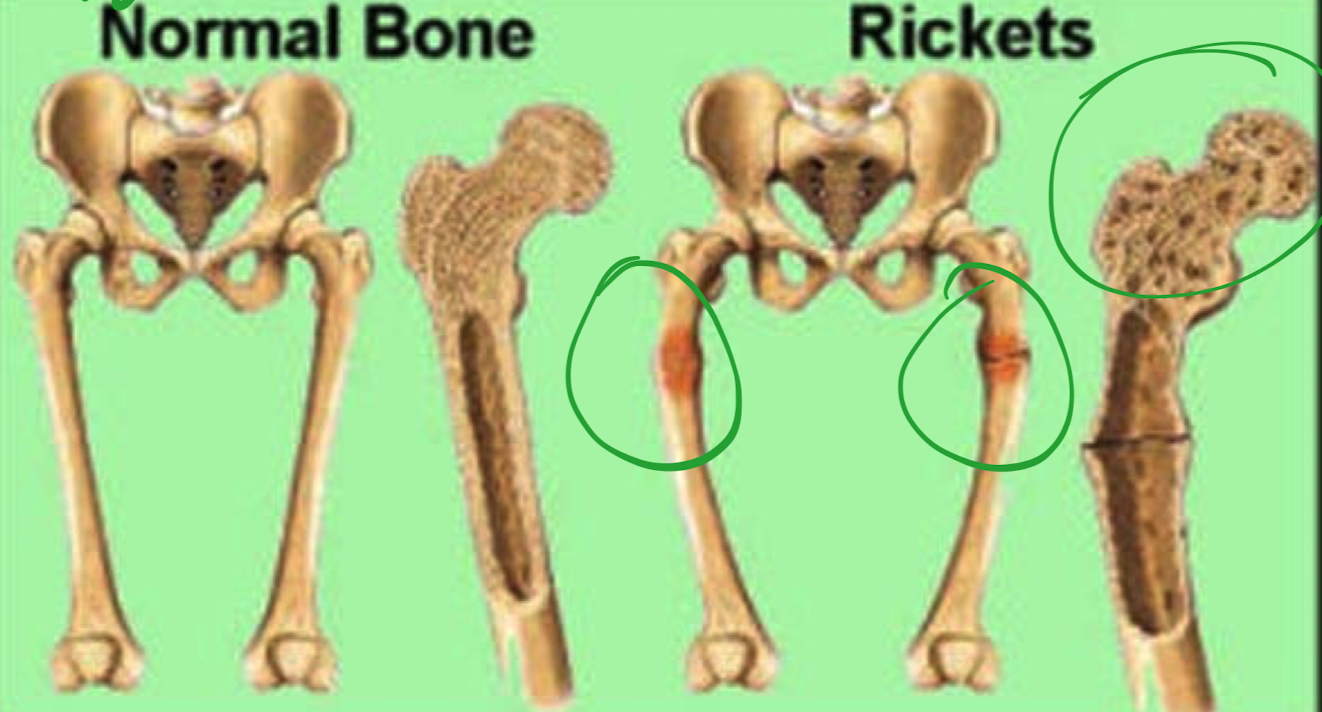
Rickets
disease in children
dangerous to children due to their bones growing rapidly
epiphyseal plate cannot calcify so long bones become enlarged
cannot support weight
bending under the pressure
Osteoporosis
bone resorption (breakdown of bone) happens more than deposition (laying down new bone)
common in older adults
decreased sex hormone (ex. estrogen)
Osteoporosis treatment
Ca2+
Vit. D
hormone replacement therapy
Osteoporosis prevention
adequate nutrition, load bearing exercise
promote bone deposition throughout lifespan
what does the axial system protect?
Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs
Bone benefits do the bones of the skull
framework of face
contain cavities for special sense organs (taste, smell, sight)
provide OPENINGS for air and food passage
secure teeth
What are the cranium bones and how many do we have?
frontal (1)
Occipital (1)
Sphenoid (1)
Parietal (2)
Temporal (2)
What are the facial bones and how many do we have of each
mandible (1)
Vomer (1)
Maxilla (2)
Zygomatic (2)
Nasal (2)
How is the vertebral column divided
Cervical (7)
Thoracic (12)
Lumbar (5)
Sacral (5)
Coccygeal (4)
What bones in the vertebral column are fused
sacral
coccygeal
Intervertebral disc
starts at C2
cartilage and gelatinous interior
helps with support of weight and movement
fibrocartilage rings surround annulus fibrosus
distribute weight evenly across the intervertebral disc
Atlas - C1
connects to skull
no vertebral body or spinous process
Axis (C2)
Dens - allows C1 to rotate around C2 (atlantoaxial joint)
Transverse ligament holds atlas in place and allows rotation movement
C7
inferior of cervical vertebrae
spinous process is not bifid
DOES have transverse foramina
How many ribs do we have in total
12
How many of true ribs do we have
7
How many false ribs do we have
5