Overview of Database Systems and Their Functions
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
DATABASE
Database is a structured collection of related data. It is designed to manage large bodies of information.
Structured Collection of Related Data
A database is structured in a way that data is organized and connected logically, involving defining tables with rows and columns.
Rows
Rows represent individual records in a database table.
Columns
Columns represent attributes or fields in a database table.
Relationships between tables
Relationships between tables reflect the connections between different types of data.
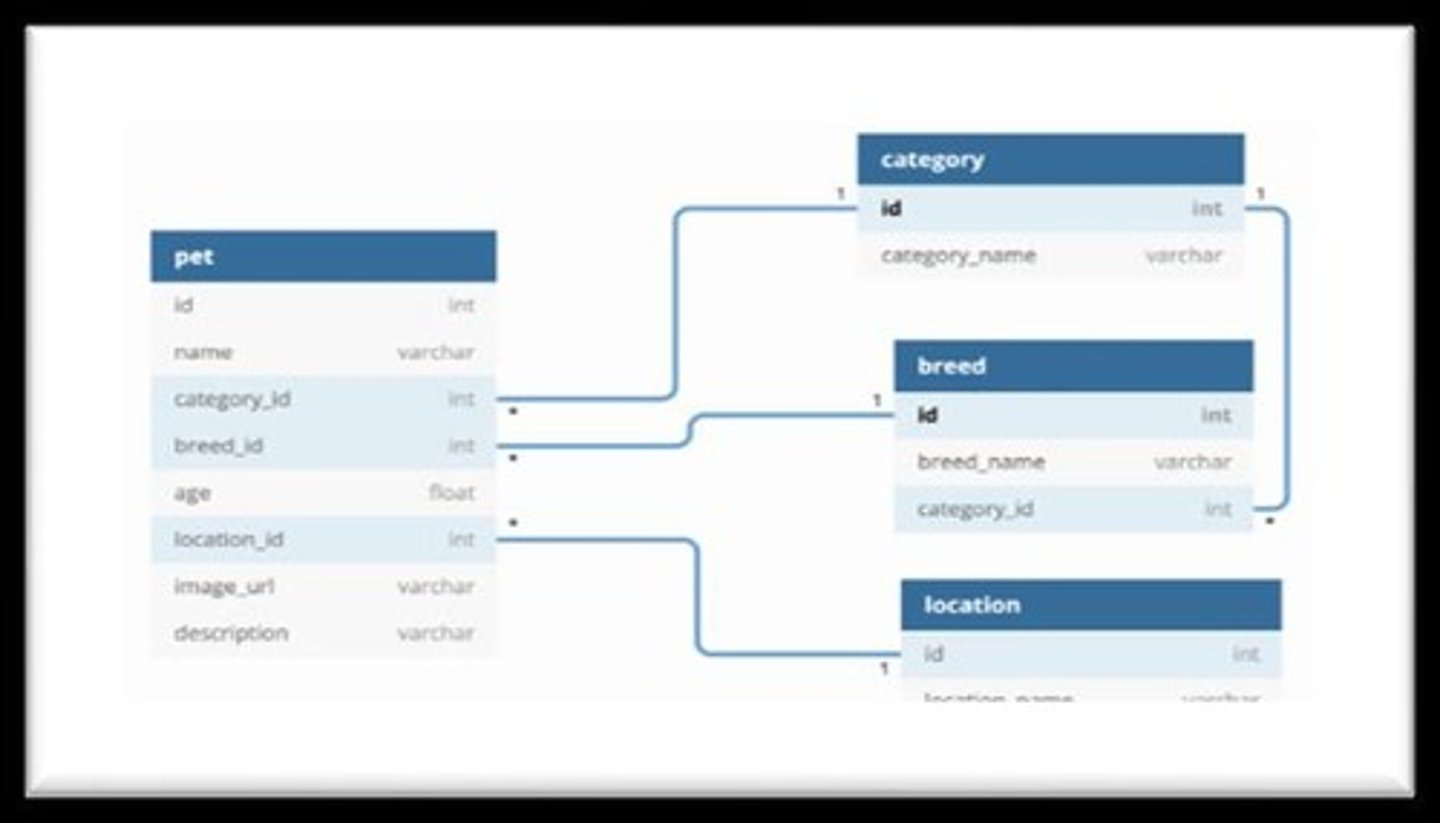
Example of University Database
In a university database, there may be tables for students, courses, and professors, with relationships indicating which students are enrolled in which courses and taught by which professors.
Designed to Manage Large Bodies of Information
One of the key purposes of a database is to handle and manage vast amounts of data efficiently.
Scalability of Databases
Databases are designed to scale and accommodate increasing volumes of information.
Systematic Storage and Retrieval
The structure and organization of a database facilitate the systematic storage and retrieval of data.
Data Integrity Constraints
Databases often incorporate data integrity constraints and normalization techniques to enhance the reliability and accuracy of the stored information.
Database Design Considerations
The design of a database includes considerations for security, access control, and backup and recovery mechanisms.
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
DBMS are employed to interact with databases, providing tools and functionalities for creating, modifying, and querying data.
Purpose of Database
The fundamental purpose of a database is to systematically organize, efficiently store, and effectively retrieve data.
Structured Repositories
Databases serve as structured repositories designed to store and manage information.
Easy Access and Retrieval
Databases facilitate easy access and retrieval of information when needed.
Predefined Structures and Relationships
By employing predefined structures and relationships, databases enable the seamless organization of data.
Organized Warehouses for Data
In essence, databases act as organized warehouses for data, streamlining the process of data management and retrieval.
Primary Function of a Database
The primary function of a database is to organize data systematically.
Organizing data
Arranging information in a structured format, often using tables, rows, and columns.
Store
Databases serve as secure and structured storage spaces for data, ensuring data integrity and accessibility.
Retrieve
The process of obtaining or extracting specific information from the database when needed.
SQL
Structured Query Language, a powerful querying mechanism used to retrieve specific data based on user-defined criteria.
Functions of Database
The roles that databases play in managing data, including eliminating duplication, maintaining consistency, and ensuring security.
Eliminate duplication of data items
Databases help by making sure you only store information once, preventing confusion and mistakes.
Maintain strict consistency of file contents
Databases ensure that all information stays accurate and consistent, reflecting changes across related data.
Make program independent files
Databases allow different computer programs to operate without interfering with each other.
File security
Databases implement security measures to ensure that only authorized individuals can access and modify data.
Purpose of a database
To bring order to the chaos of information, providing a structured environment for organizing, storing, and retrieving data.
Data integrity
The accuracy and consistency of data stored in a database.
Centralized location
A single storage point for data, often on a server or cloud platform.
Querying mechanisms
Tools provided by databases to facilitate quick and efficient access to relevant information.
Data types
Definitions of the kind of data that can be stored in a database, such as integers, strings, or dates.
Constraints
Rules applied to data in a database to ensure its accuracy and integrity.
Relationships
Connections between different pieces of information in a database that define how they interact with each other.
Complex data analysis
Advanced methods of examining data to extract meaningful insights, often facilitated by databases.
Application-specific needs
Requirements tailored to particular uses or applications of data stored in a database.
Streamline processes
To make operations more efficient and effective through the use of databases.
Secure environment
A protected space provided by databases for managing and accessing valuable information.
File System
A file system is a method used by computers to organize and store data. It manages files and directories in a hierarchical structure, allowing users to create, modify, and retrieve individual files.
Database System
A database system is a structured way of organizing, storing, and managing data. It uses tables with rows and columns to represent and relate different pieces of information, providing a more organized and efficient approach.
Data Structure in File System
In a file system, data is typically organized in files and directories. The data is stored in a hierarchical structure, and each file may have its own format and structure.
Data Structure in Database System
In a database system, data is organized in tables with rows and columns. The tables are interrelated, and the relationships are defined to represent the logical structure of the data.
Data Integrity in File System
File systems do not provide inherent mechanisms for enforcing data integrity. Users and applications must implement their own methods to maintain the consistency and accuracy of the data.
Data Integrity in Database System
Database systems offer features like constraints, transactions, and referential integrity to ensure that data remains accurate and consistent. ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties are often maintained to guarantee the reliability of transactions.
Data Redundancy in File System
Redundancy is common in file systems. Data may be duplicated across multiple files, leading to potential inconsistencies and inefficiencies.
Data Redundancy in Database System
Database systems aim to minimize data redundancy through normalization. Normalization helps eliminate data duplication and reduces the risk of inconsistencies.
Query Language in File System
Accessing and manipulating data in a file system often requires low-level programming using file I/O operations.
Query Language in Database System
Database systems provide a high-level query language (e.g., SQL - Structured Query Language) that allows users to interact with the data using declarative statements.
Concurrency Control in File System
File systems may lack built-in mechanisms for managing concurrent access to data, which can lead to issues like data corruption and conflicts.
Concurrency Control in Database System
Database systems incorporate concurrency control mechanisms to handle simultaneous access to data by multiple users, ensuring that transactions are executed in a controlled manner to maintain data consistency.
Scalability and Performance in File System
Scaling a file system can be challenging, especially when dealing with large volumes of data and complex relationships.
Scalability and Performance in Database System
Database systems are designed to handle large-scale data and provide optimizations for performance, including indexing, caching, and query optimization features.
Example of File System
For example, your computer's file explorer or finder, where you create folders to organize documents, images, and other files.
Example of Database System
For example, a system that stores and manages data for a business, where information is organized into tables, and relationships between data are defined.
Efficiency in File System
File systems are suitable for basic data storage and retrieval.
Efficiency in Database System
Database systems offer a more structured and efficient approach for managing and organizing data, particularly when dealing with complex relationships and ensuring data integrity in multi-user environments.