Histology: Epithelium and Glands
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
types of epithelia
simple
stratified
pseudostratified
types of glands
unicellular, multicellular, simple, compound, exocrine, endocrine
types of secretion
serous
mucous
mechanisms of secretion
merocrine
apocrine
holocrine
2 general classes of epithelia
lining or glandular
polarized
free apical surface, basal surface attached to basal lamina
epithelia are all
avascular
epithelial function
protection, surface transport, absorption, secretion, trans-epithelial transport, reproductive, special sensory, contraction
keratinization cell turnover timeline
3 weeks-1 month
example of apical to basal trans-epithelial transport
kidney tubules transport nutrients from the lumen to basal connective tissue
example of basal to apical trans-epithelial transport
lymph resorption into lymphatics
Epithelial type is determined by _____ and _______
number of layers (simple/stratified)
cell shape at the free surface
what’s an example of reproductive epithelial function?
seminiferous tubule generates sperm
what’s an example of special sensory epithelial function?
tast buds, hair cells in cochlea
what’s an example of contraction epithelial function?
myoepithelium
For most organs, if you know the function of the _______, you
know the function of the organ
epithelium
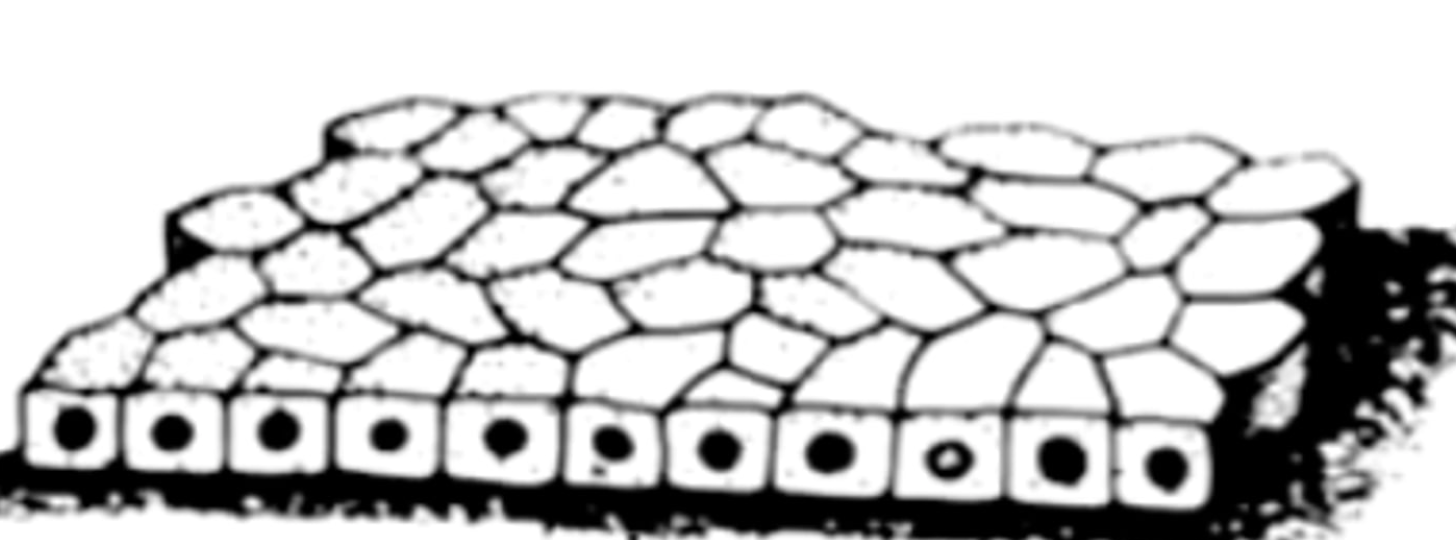
simple (and types)
one cell thick (squamous, cuboidal, columnar)
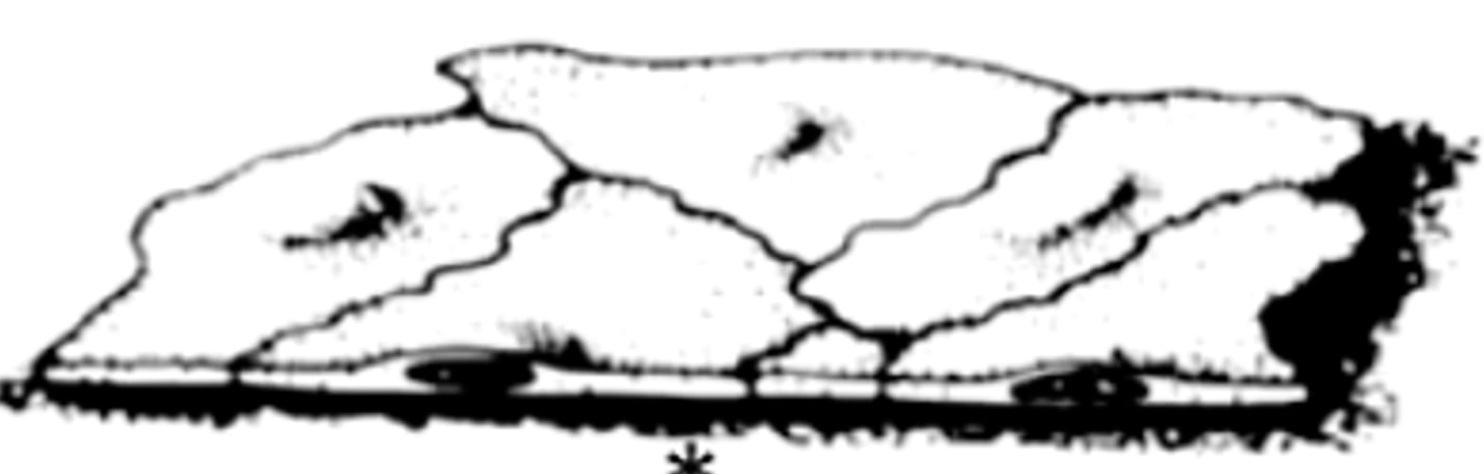
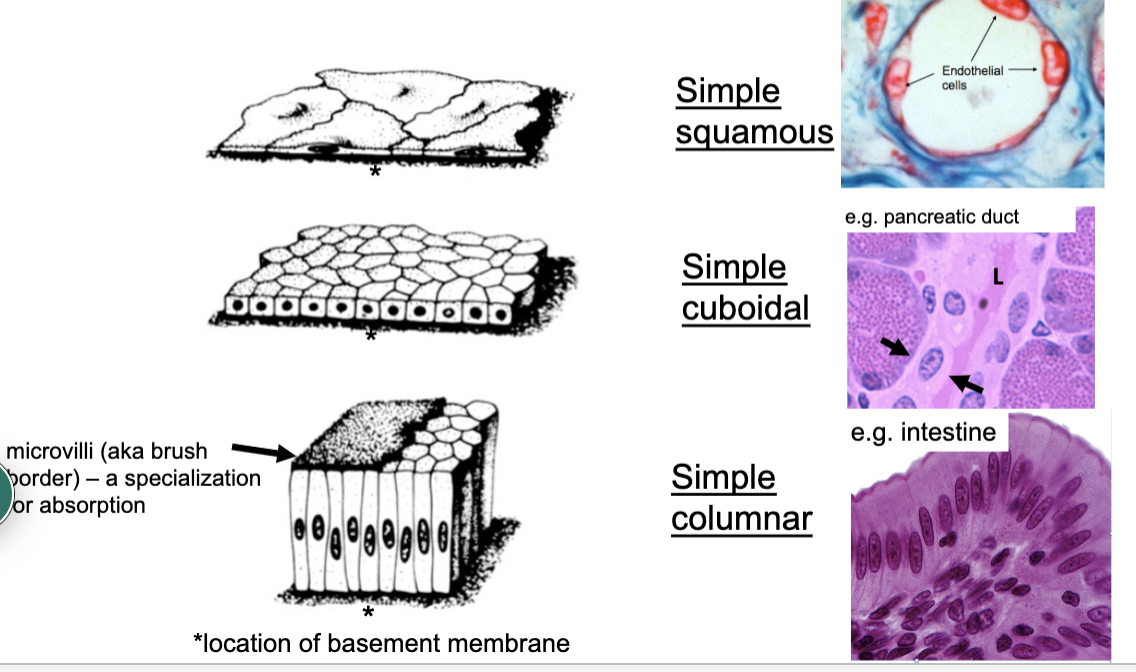

simple squamus epithelium
simple cuboidal epithelium
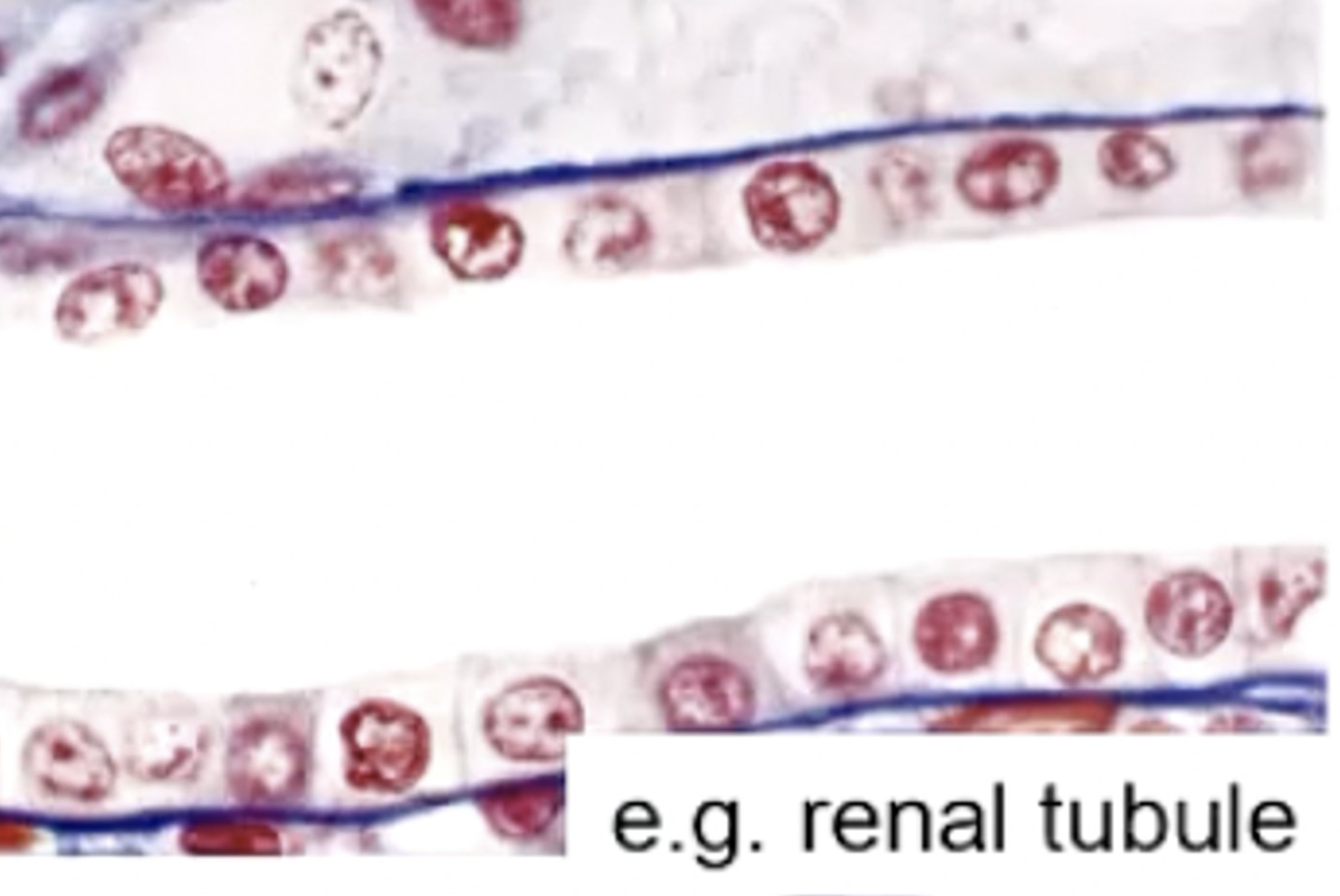
simple cuboidal epithelium
simple columnar epithelium
simple columnar epithelium
stratified columnar epithelium
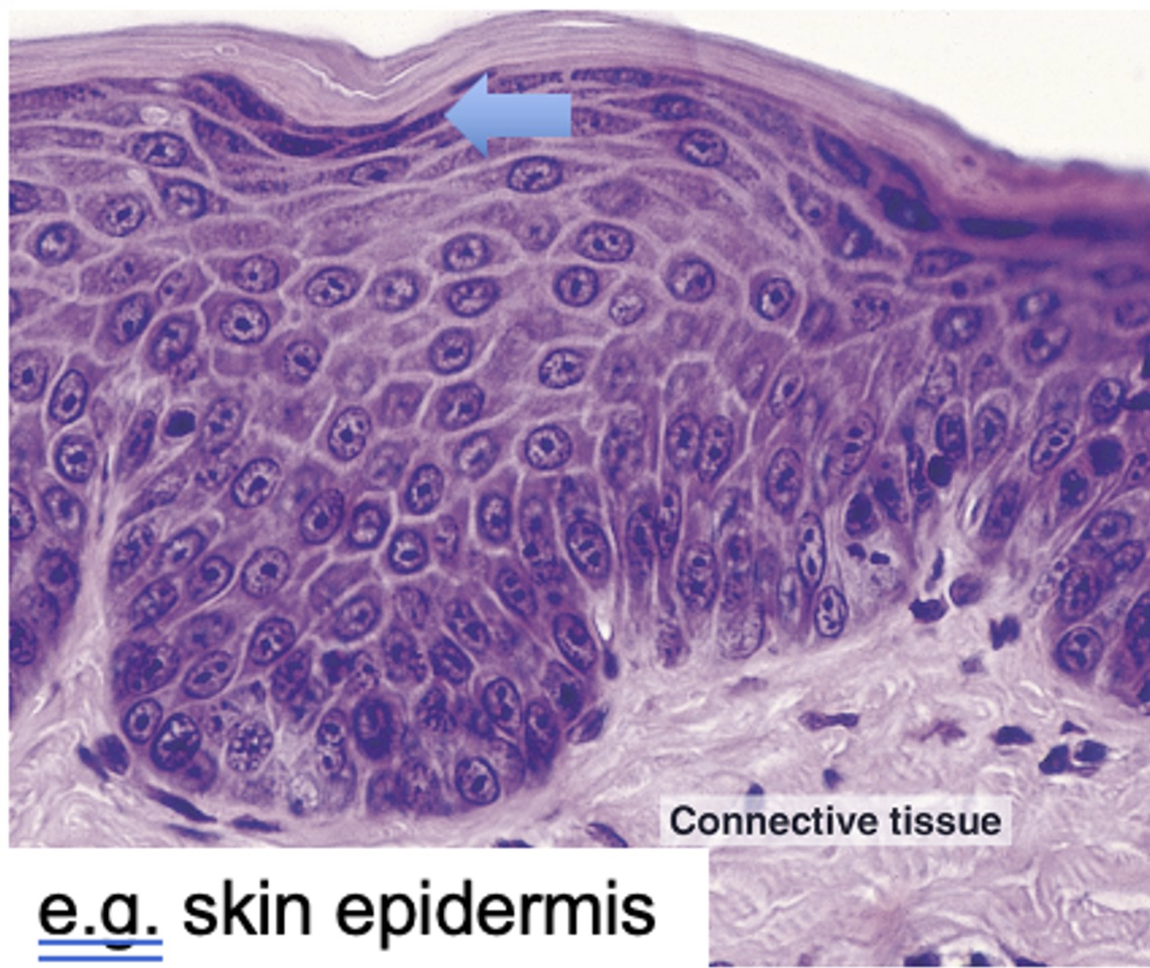
stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium (SSKE)
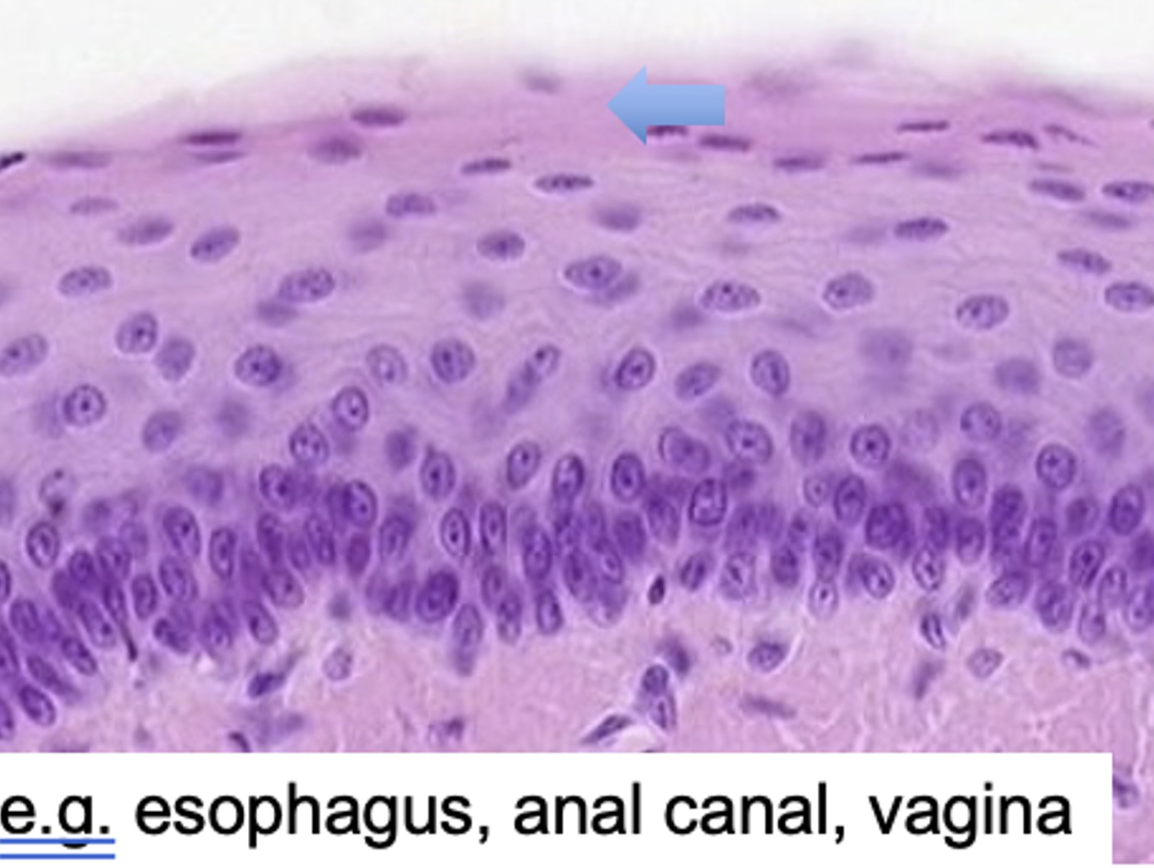
stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium (SSNKE)
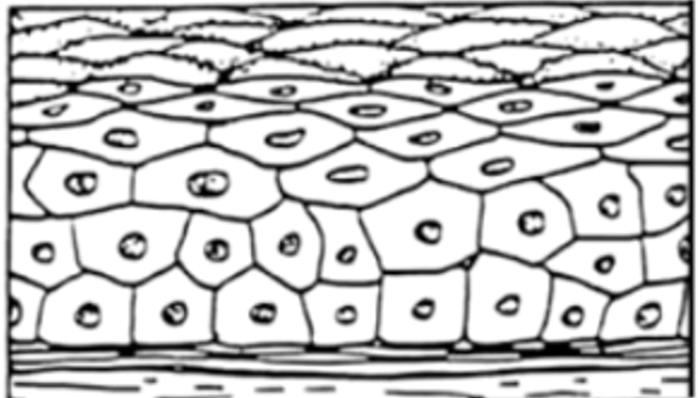
stratified squamous epithelium
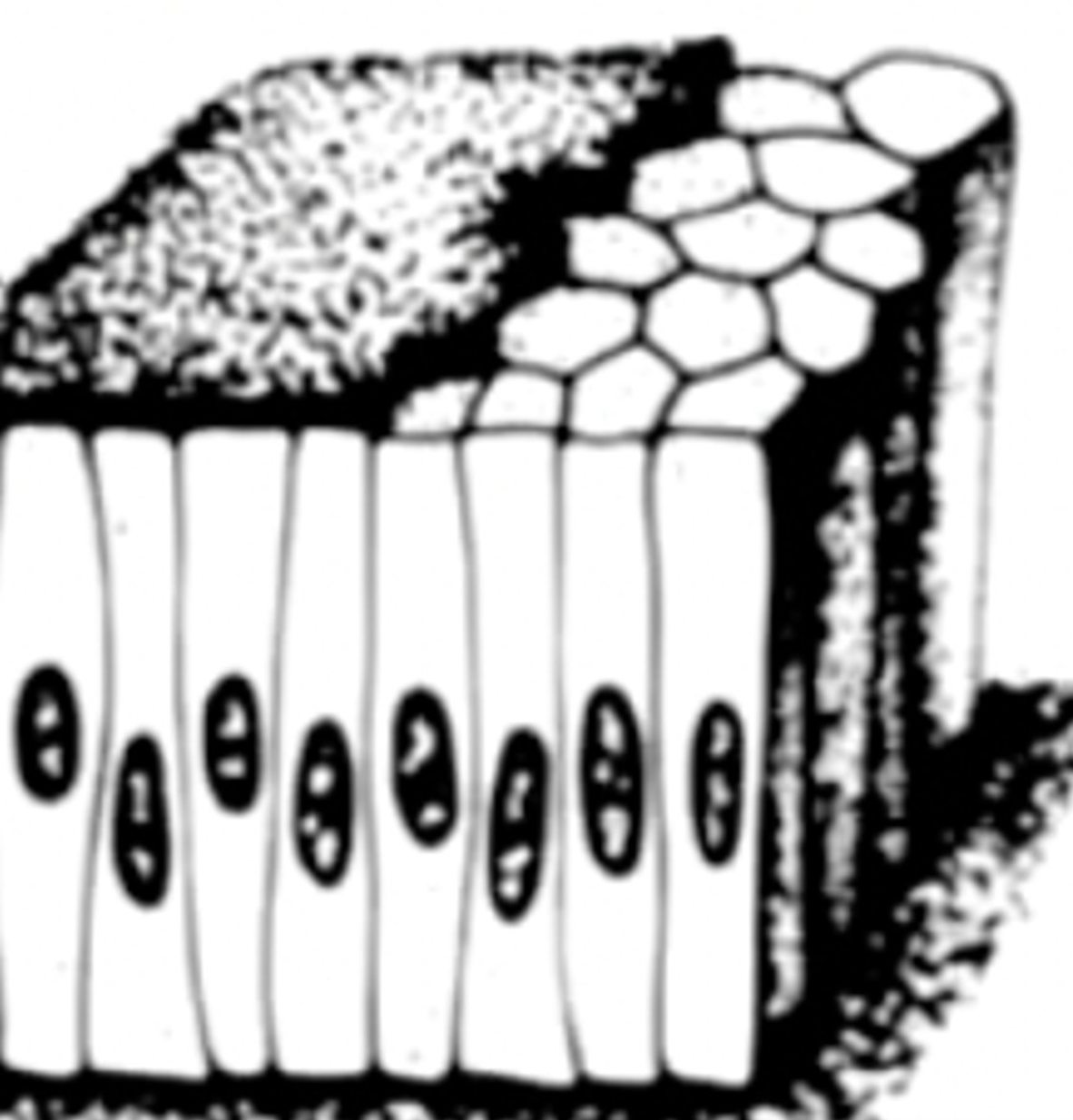
stratified (and types)
multi-cell layered (columnar, squamous)
name determined by shape of cell layer at free surface
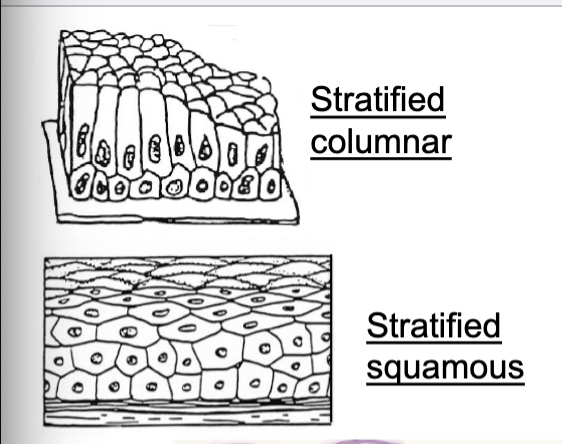
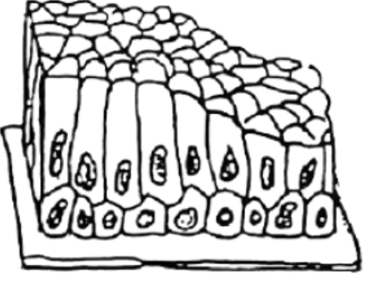
stratified columnar epithelium
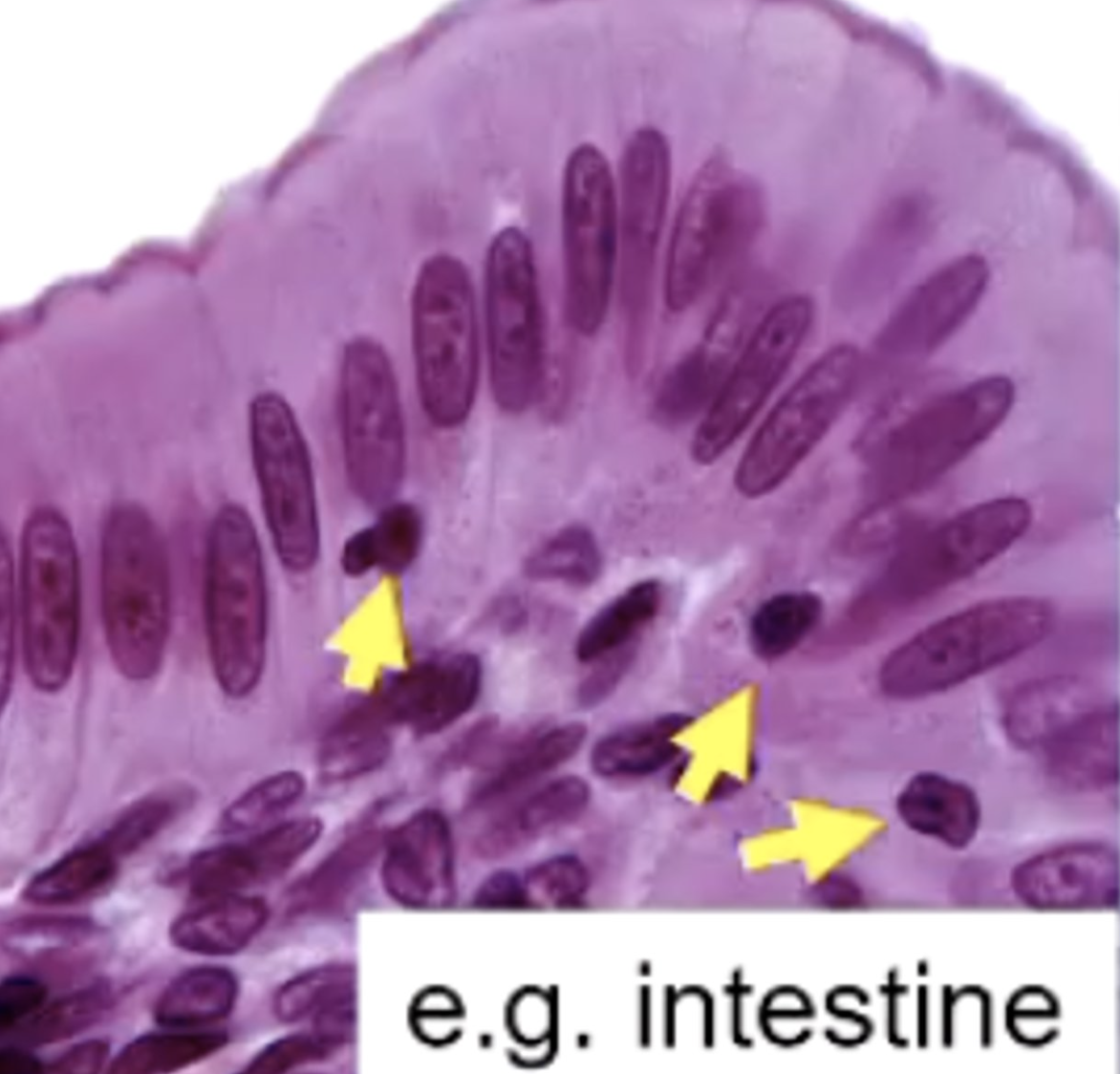
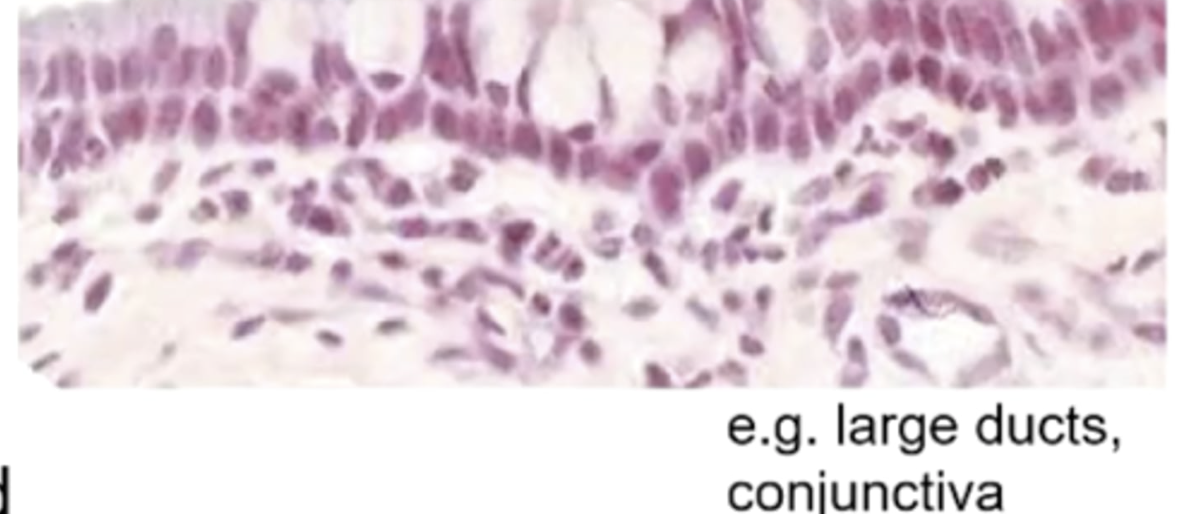
pseudostratified
All cells contact basal lamina, not all reach free surface
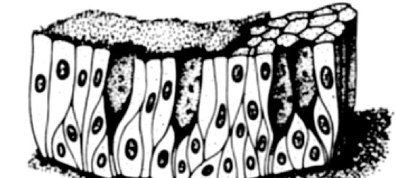
____________ has dead layer on top
Keratinizing epithelium
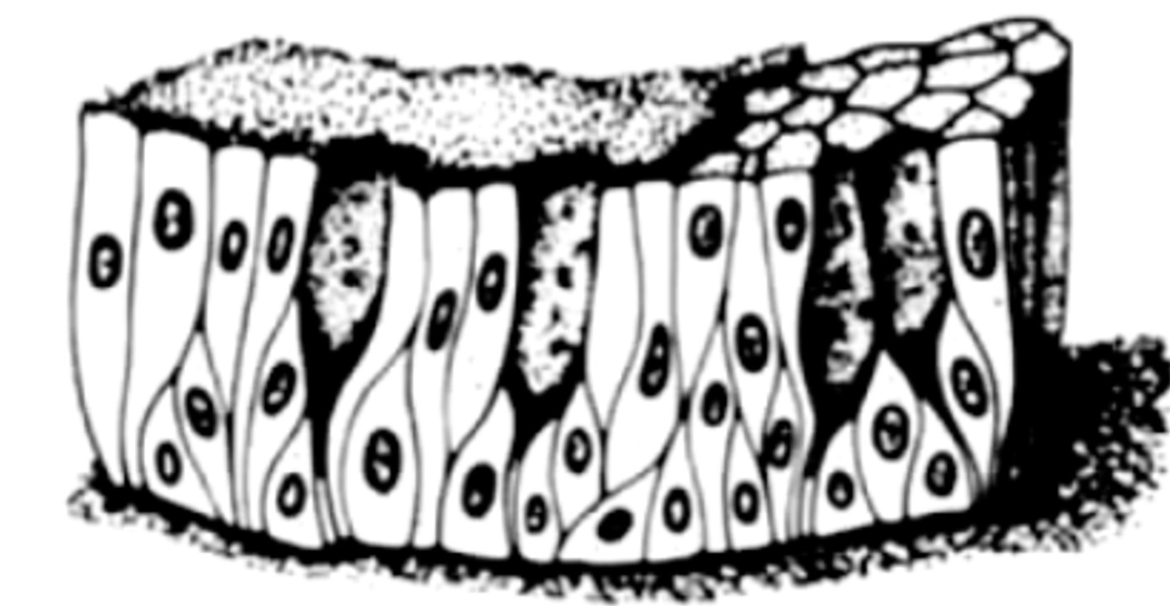
pseudostratified epithelial
pseudostratified epithelial
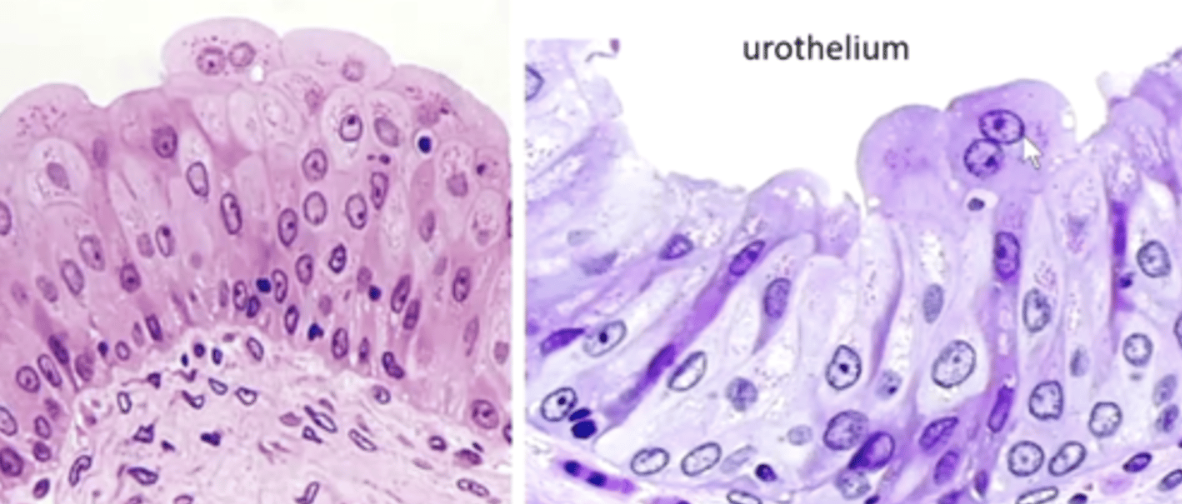
transitional epithelium (unique to urinary system)
transitional
large surface cells, often binucleate (unique to urinary system aka urothelium)
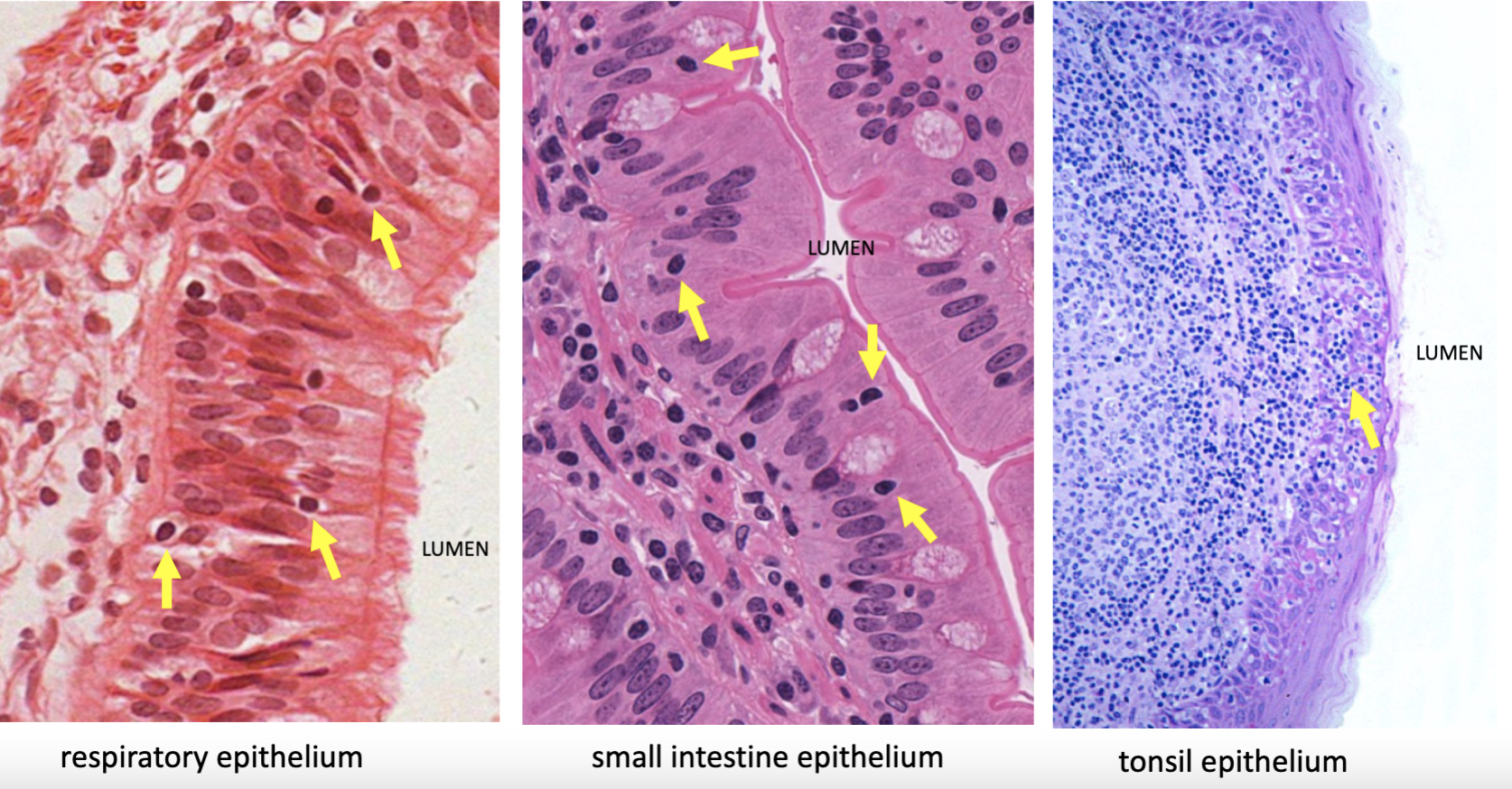
wandering lymphocytes are
specialized white blood cells for immune surveillance
what is the oral cavity epithelium characterized by
mostly stratified squamous (inner cheek, hard and soft palate, lip, gingiva)
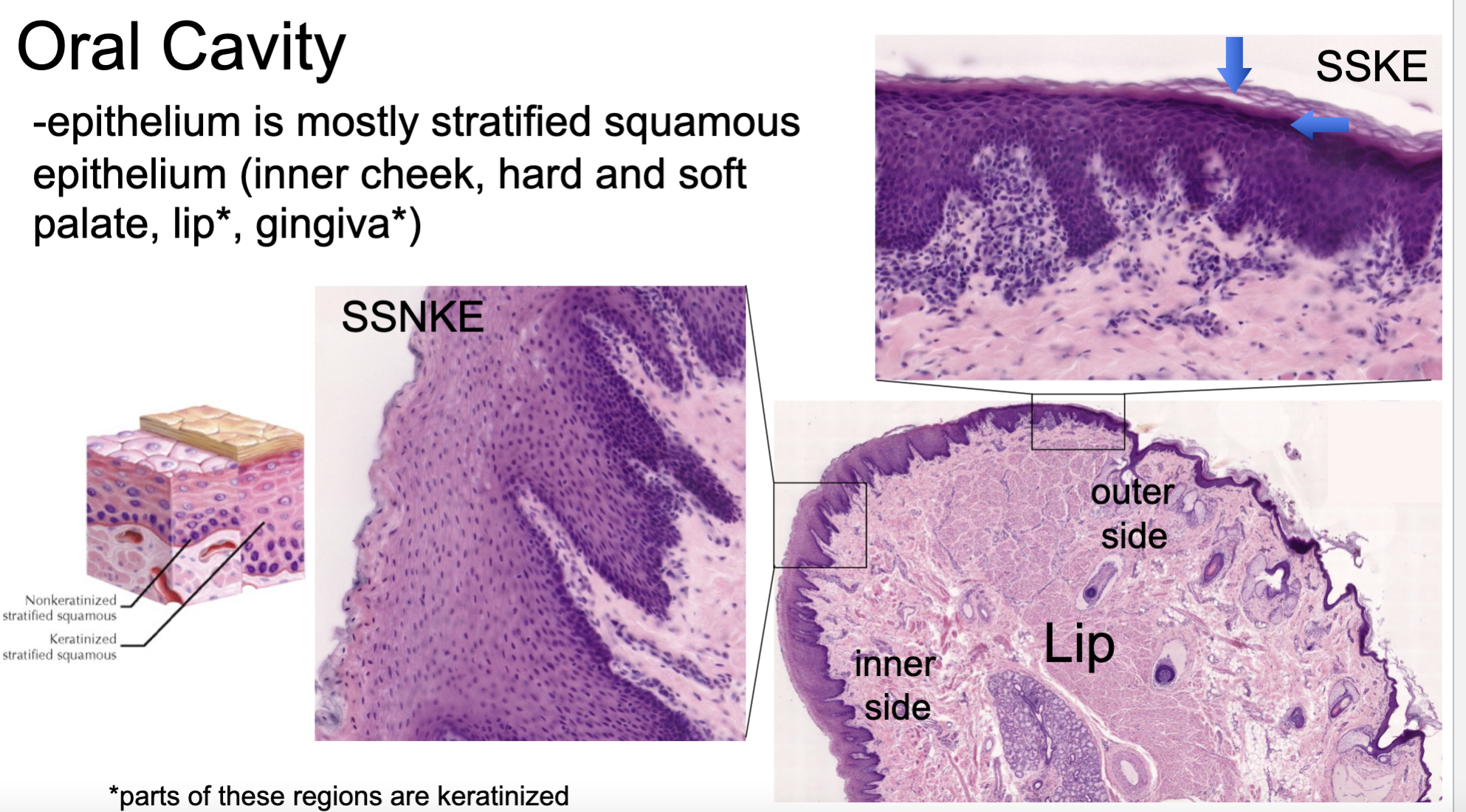
which regions of the oral cavity epithelium are partly keratinized?
lip and gingiva
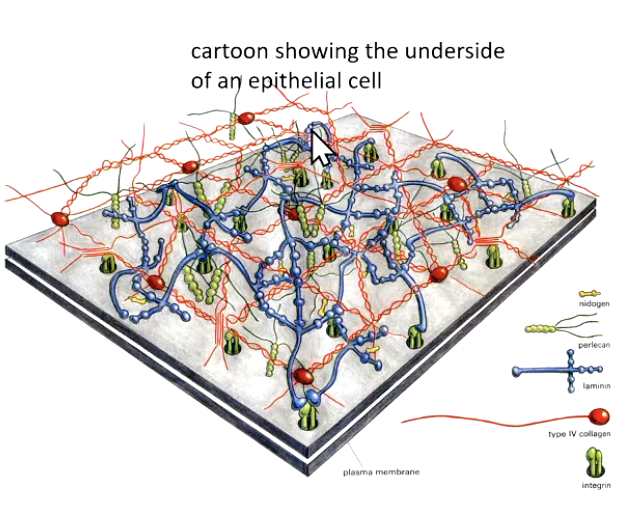
basal lamina is comprised primarily of
type IV collagen
laminin
(both form “chicken wire” networks
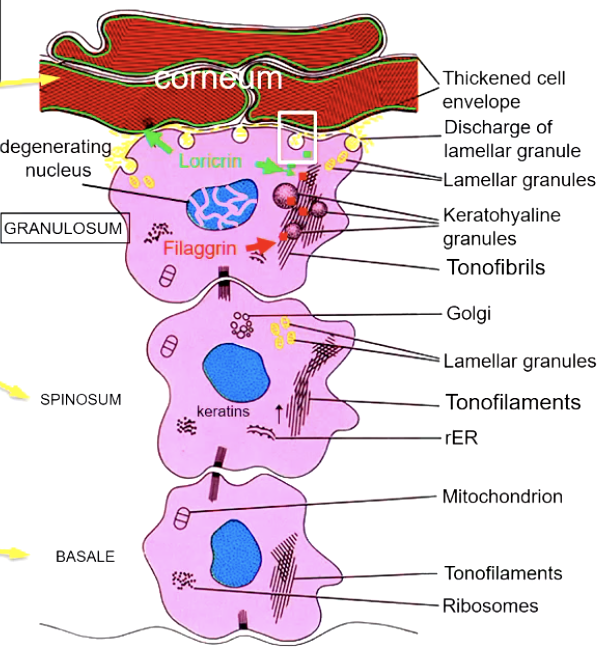
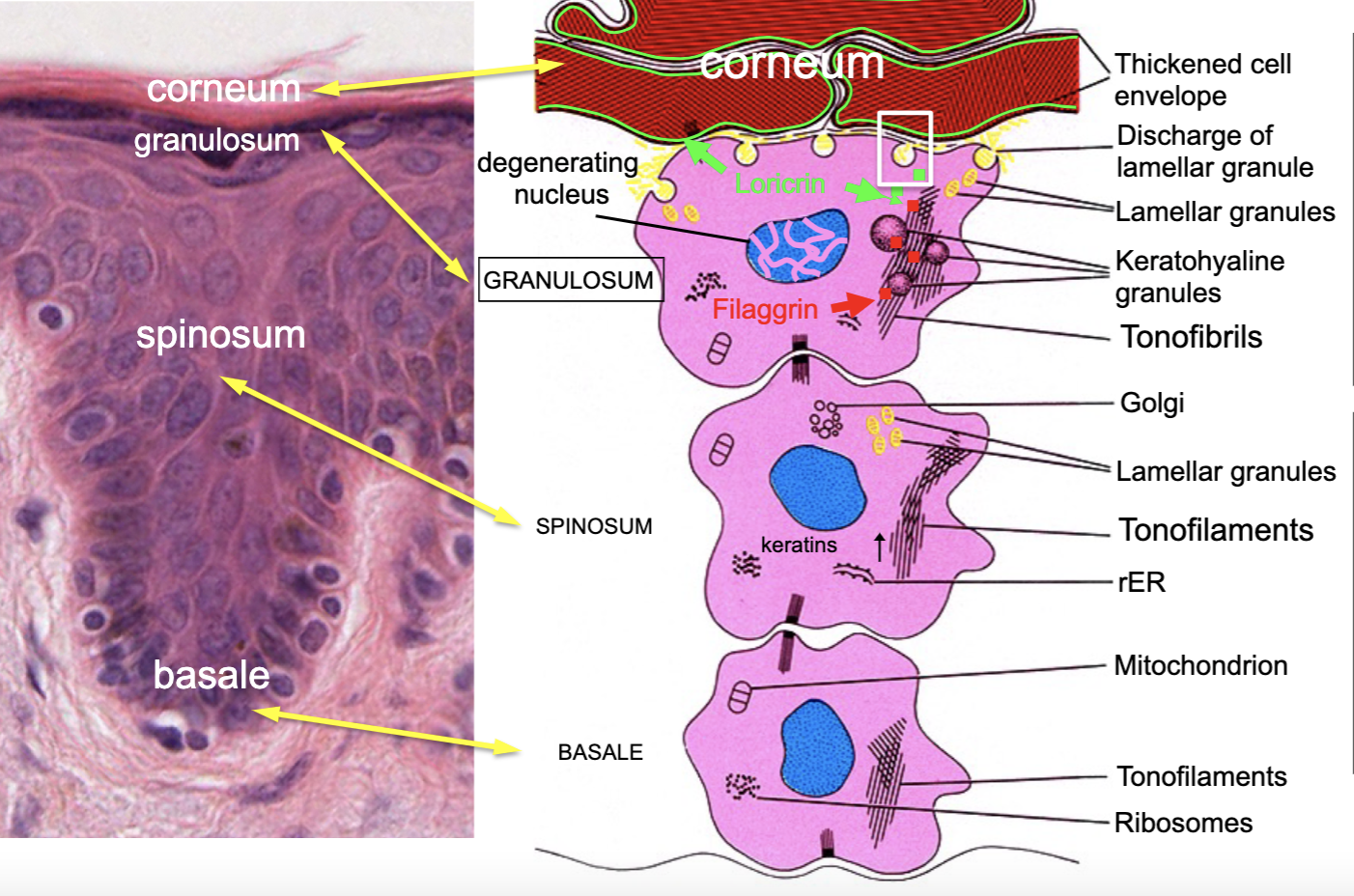
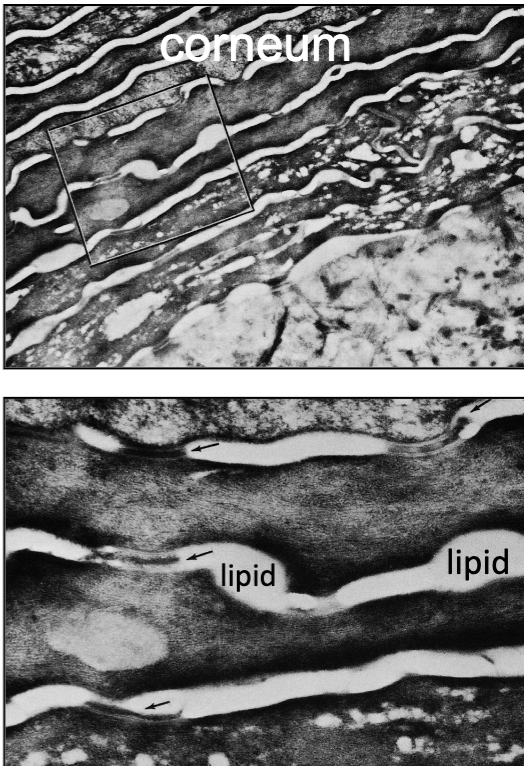
the ______ is the most surface level of skin (dead skin) during keratinization
corneum
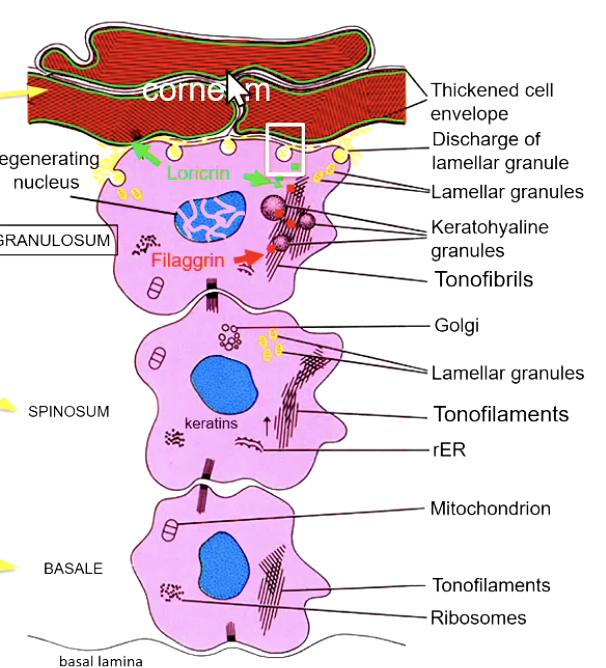
cornuem cells have _______ but no _______
cell membrane; nucleus/organelles
what is the “dark layer” right beneath corneum
stratum granulosum (has lots of protein)
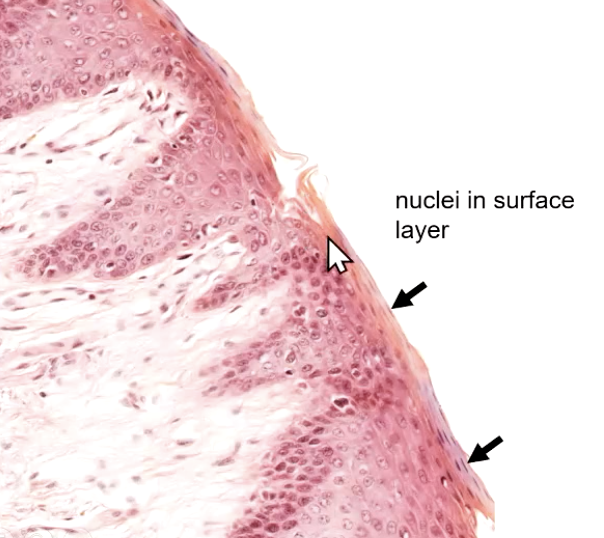
in para-keratinization, there is no “dark layer” aka no
no stratum granulosum
in between the stratum corneum cells, there is
lipid (water proofs skin and keeps fluid in!!)
you can develop para-keratinization via
diet
keratinization occurs on surfaces that need extra
protection (hard palate for example)
surface cells in para-keratinization are
living (have nuclei)
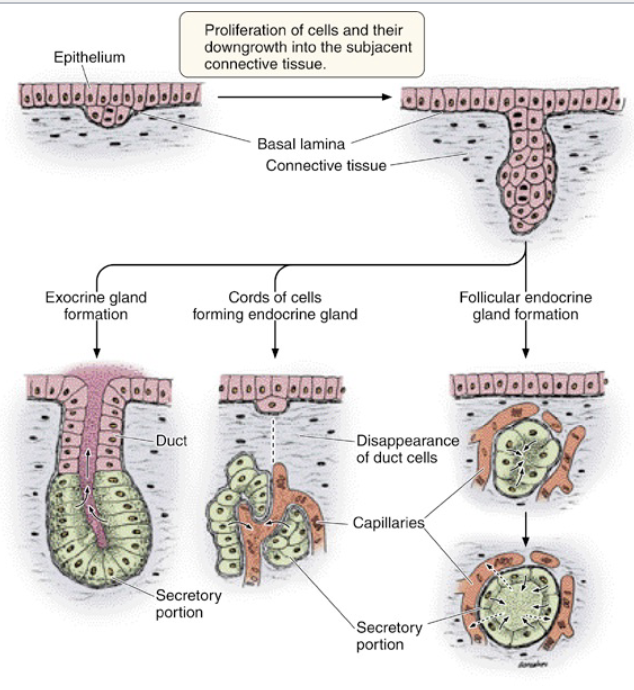
all glands begin as
epithelial ingrowth from surface
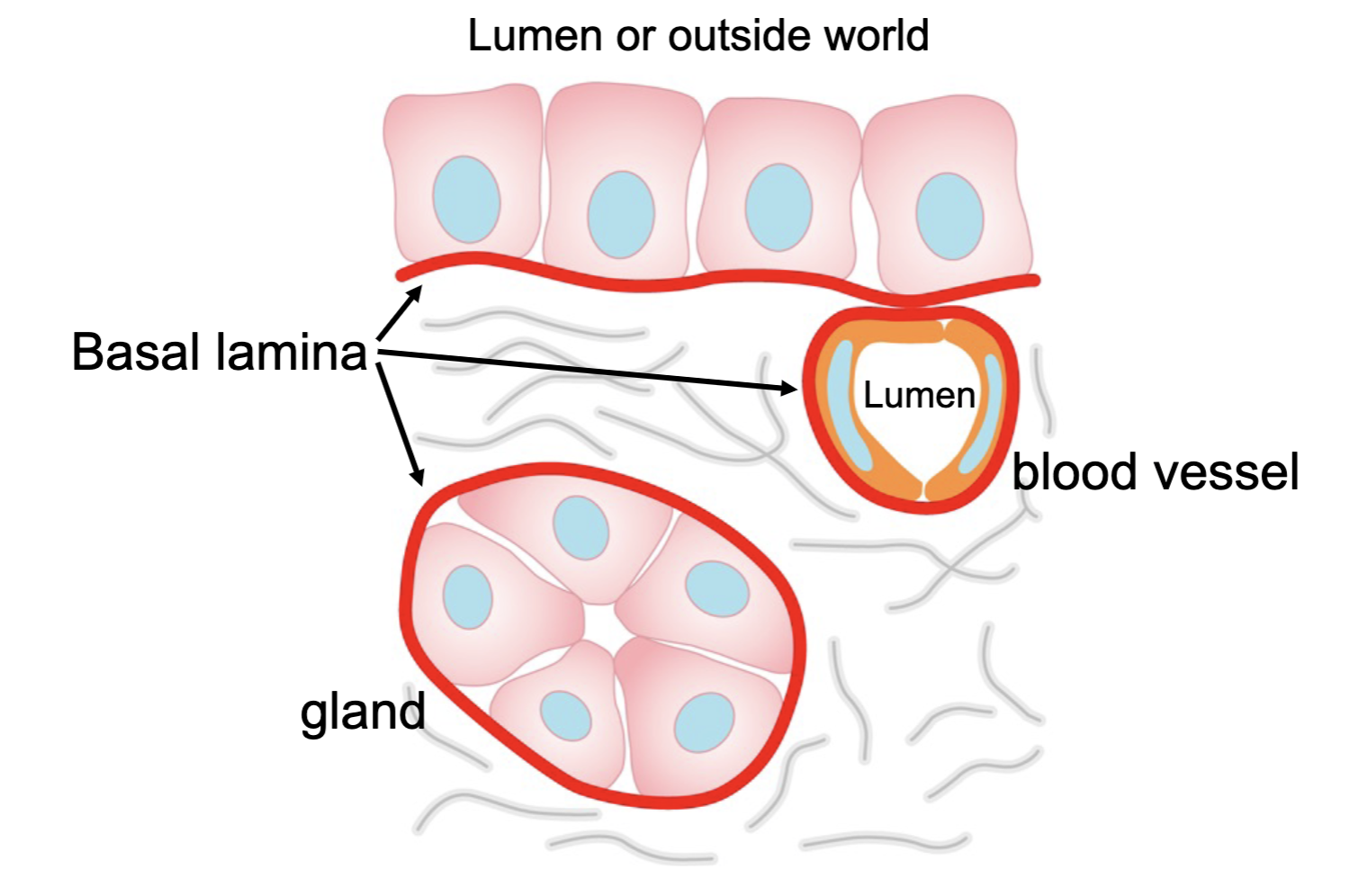
all epithelia rest upon a
basal lamina
basal lamina function
support for epithelia
development, differentiation, morphogenesis
cell migration
filtration barrier
many non-epithelial cells have an
external lamina (these non-polarized cells have no basal surface)
what are some non-epithelial cells
adipocytes, muscle cells, Schwann cell
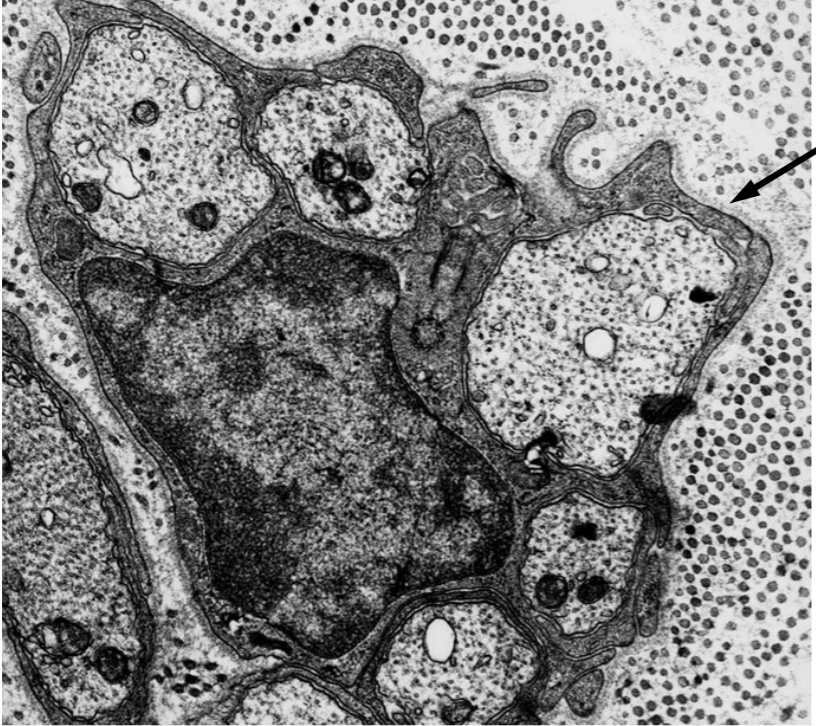
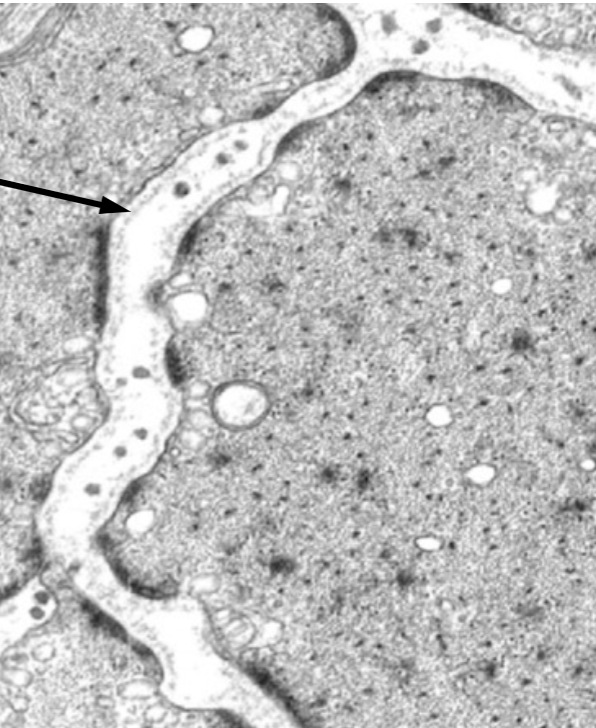
what cell is this and what is the arrow pointing to
Schwann cell
pointing to external lamina
what cell is this and what is the arrow pointing to
smooth muscle cell
pointing to external lamina
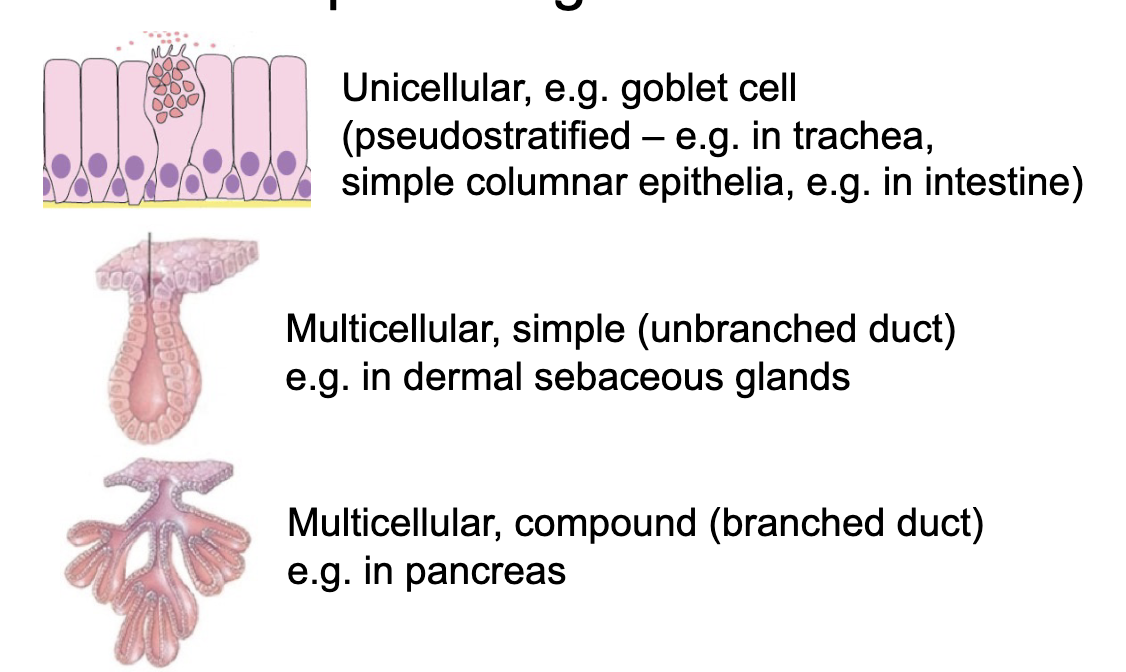
types of epithelial glands
unicellular
multicellular, simple (unbranched)
multicellular, compound (branched)
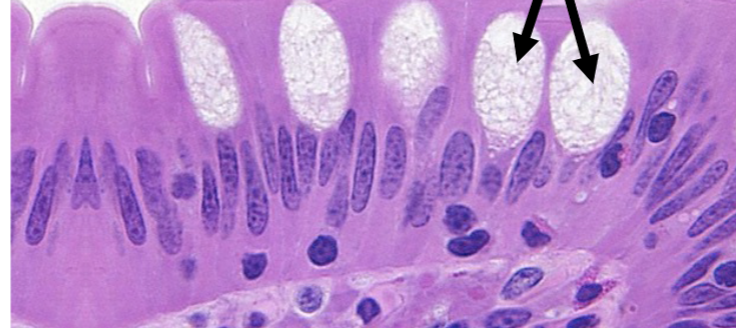
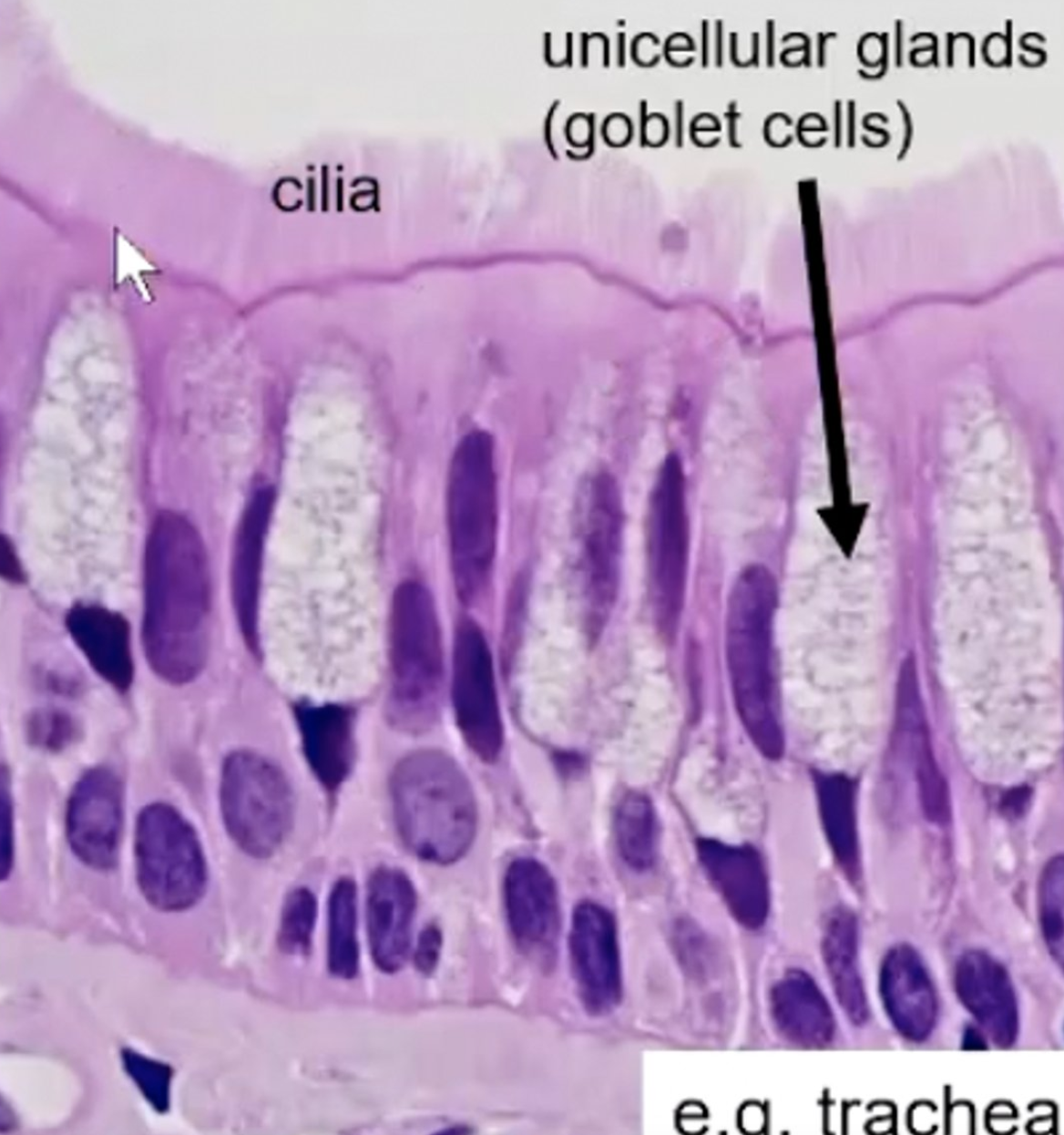
what are the arrows pointing to
goblet cells
all glands begin as
an epithelial ingrowth from the surface
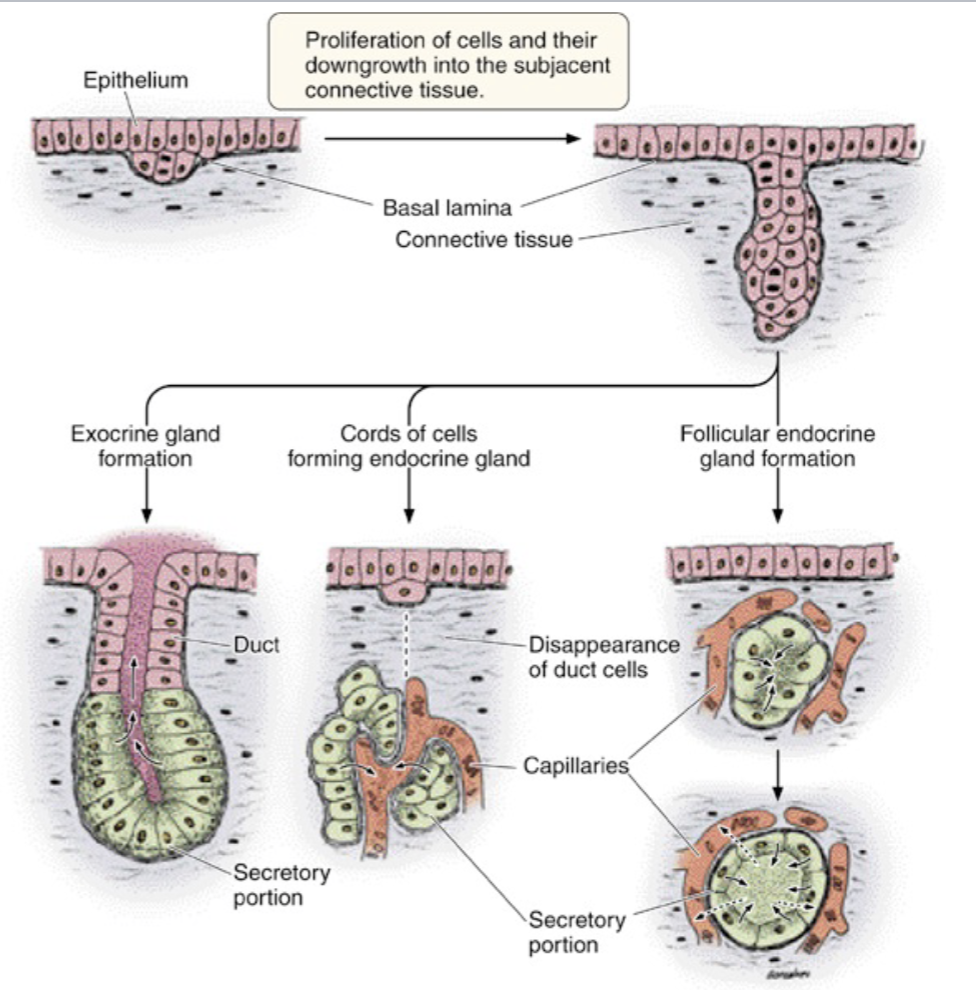
modes of gland secretion
exocrine (merocrine, apocrine, holocrine, mixed)
endocrine
types of exocrine secretion
merocrine
apocrine
holcrine
mixed (merocrine/apocrine)
all exocrine secretion secretes into
lumen via ducts
endocrine secretion secretes into
connective tissues/capillaries (interstitial space)
exocrine glands ________ contact with surface epithelium
maintain
endocrine glands ________ contact with surface epithelium
lose
merocrine
secretion by exocytosis (only produce is released)
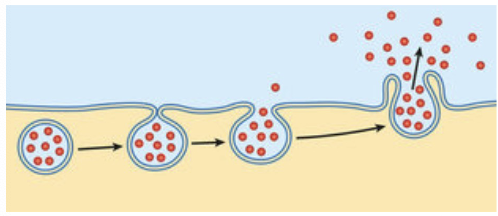
example of merocrine secretion
pancreas
example of endocrine glands
thyroid
what are some typical secretions from merocrine glands?
-zymogens
-sweat
-mucus
-lysozyme
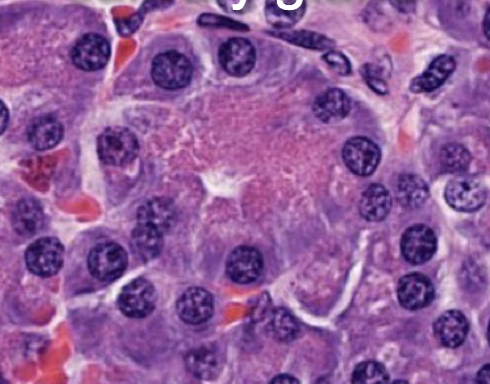
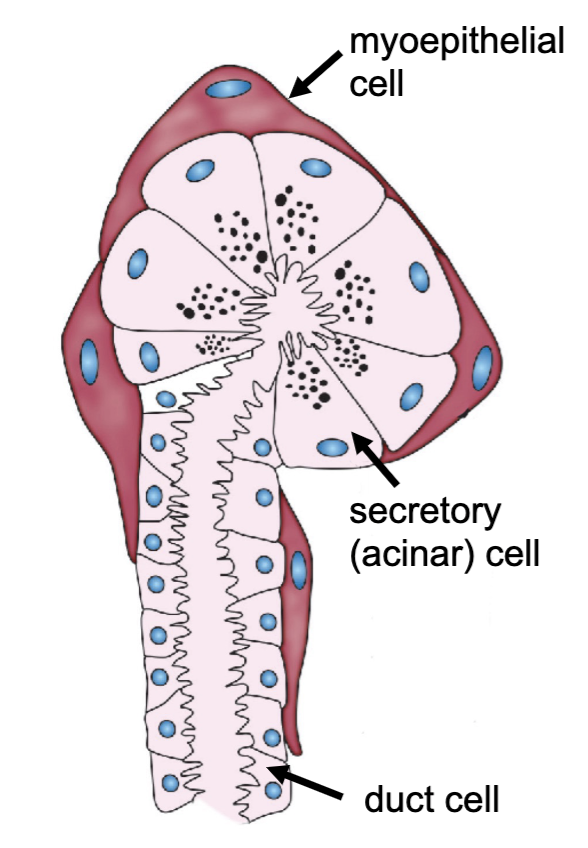
what is this gland?
salivary gland
apocrine
(aka decapitation secretion)
a portion of the apical membrane & cytoplasm is released along with the product
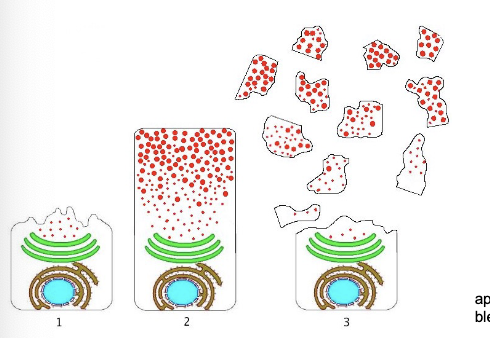
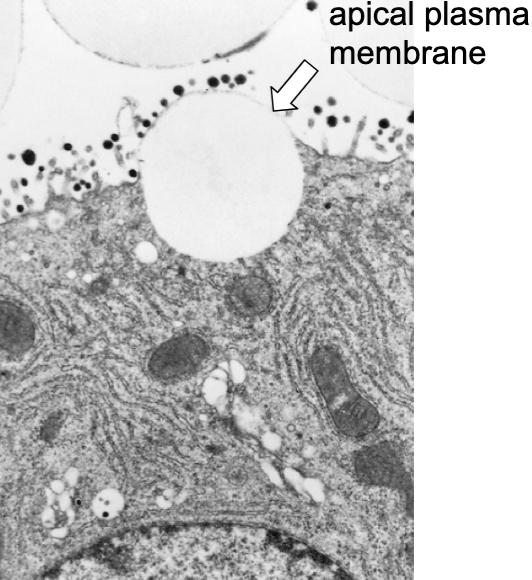
what gland is this
mammary gland
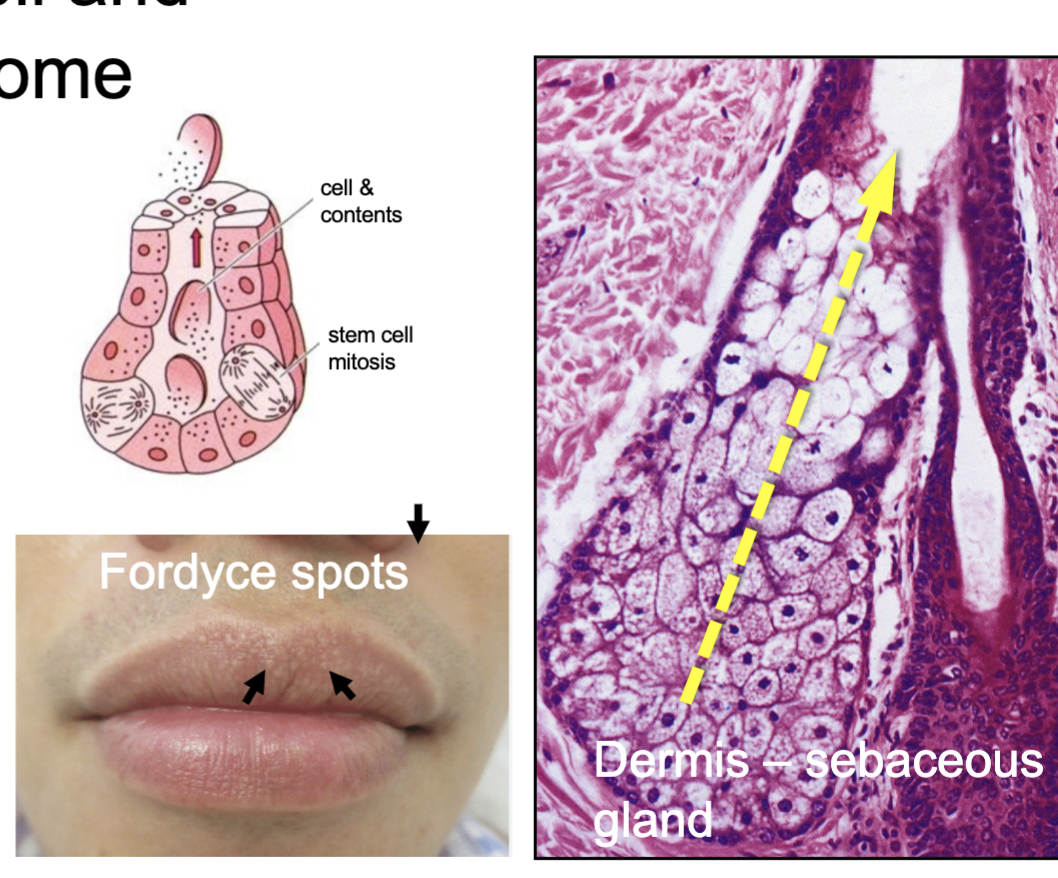
holocrine
the entire cell and its contents (sebum) become the secretory product
what are examples of holocrine secretion
Fordyce spots
sebaceous gland
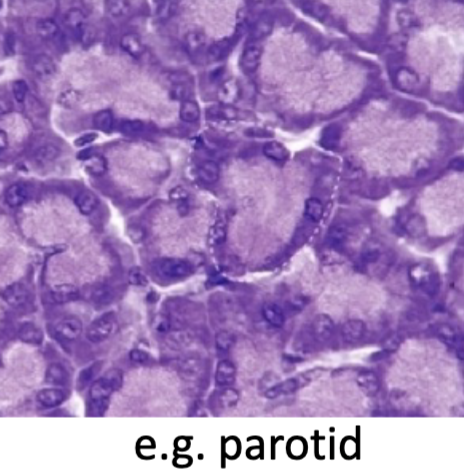
nature of secreted products (2 types)
serous
mucous
serous secretion
-watery secretion
-abundant RER
-round nucleus
-cells well stained
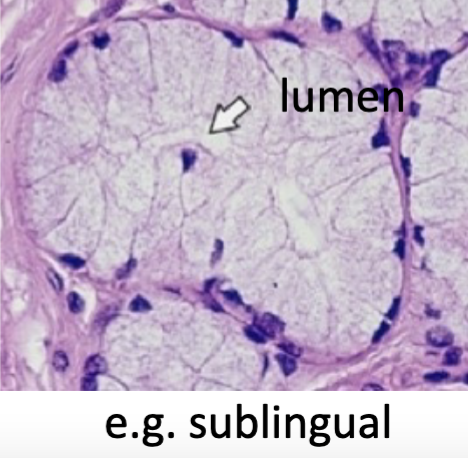
mucous secretion
-thick secretion
-clear cytoplasm
-flat nucleus (artifact of preparation)
-cells poorly stained
_____________ cells (derived from epithelium) help to expel the secretory products
myoepithelial