Newton’s laws of motion and momentum
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
State Newton’s 1st law?
An object will remain at rest or continue to move at constant velocity unless acted upon by a resultant force
Give an example of Newton’s First Law?
A Cyclist travelling on a straight road at constant velocity
State Newton’s 2nd law?
The net (Resultant) force acting on an object is directly proportional to the rate of change of its momentum, and is in the same direction
Give an example of Newton’s Second Law?
A Rocket launching
Show that f=ma is a special case of Newton’s 2nd law when mass is constant?
F(Force)=p(momentum) / t(time) → mv-mv/t → m (v-u/t) = acceleration
Therefore F=ma
State Newton’s 3rd law?
When 2 objects interact, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other
Give an example of Newton’s 3rd law?
Bouncing a ball on the ground
List the characteristics of Newton’s 3rd law?
(Magnitude, direction, type of force, object acting on etc.)
The pair of forces will have the same magnitude but in opposite directions (Same type of force as well)
Act on different bodies
Act of the same type
Define linear momentum?
Momentum depends on mass and velocity
Momentum= Mass X Velocity
p=mv
What are the SI units of momentum?
kgms^-1
Is momentum a scalar or vector quantity?
Vector
Define impulse?
The product of force and time for which the force acts on an object
Impulse= change in momentum
F(Force) X ∆t (time)= ∆p
Show the relationship between Newton’s 2nd law and impulse?
Newtons 2nd law → F= ∆p/∆t → rearranged for impulse which is
F X ∆t = ∆p
What is the link between impulse and momemtum?
Impulse= Change in momentum
What are 2 possible units of impulse?
N (Newton) or Kgms^-1
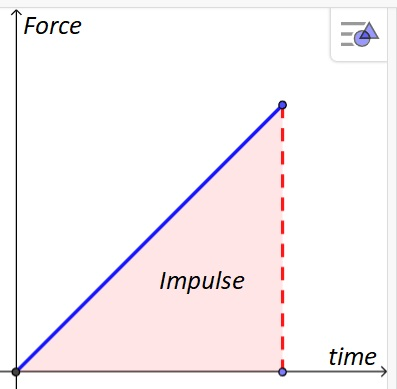
How can impulse be determined from a force- time graph?
Include a diagram
Area under the graph
Explain why is it a good idea to position your hands backwards when catching a ball?
The impulse applied by the ball decreases as the time period increases (ball slows down)
State the principle of conservation of momentum?
For a system of interacting objects, the total momentum in a specified direction remains constant, as long as no external forces act on a system
How is the principle of conservation of momentum useful for dealing with questions involving collisions?
Total momentum before and after a the collision is the same, You can use this to predict the motion of interacting objects
Use the principle of conservation of momentum to explain what happens when a bullet is fired from a gun?
A Gun recoils when a bullet is fired
The total momentum of a system remains the same and is equal to 0
The momentum of the gun and the momentum of the bullet have the same magnitude but act in opposite directions
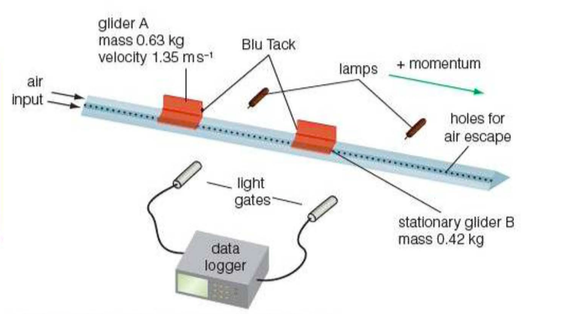
Produce a labelled diagram of apparatus that can be used to investigate the conservation of momentum?
Which 2 quantities are always conserved during a collision?
Momentum
Total energy
What is an elastic collision?
When all the kinetic energy can be retained by the objects after the collision
What is an inelastic collision?
When some of the kinetic energy after a collision may dissipate into the surroundings (as heat, sound etc)
What is a perfectly inelastic collision and when does this occur?
When the maximum amount of kinetic energy of a system is lost
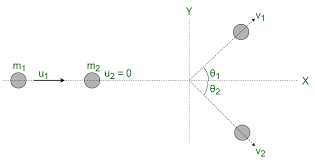
In collisions and interactions, linear momentum is conserved in all directions. Which 2 methods can be used to solve momentum problems involving collisions in 2D?
Vector Triangles
Resolving Vectors
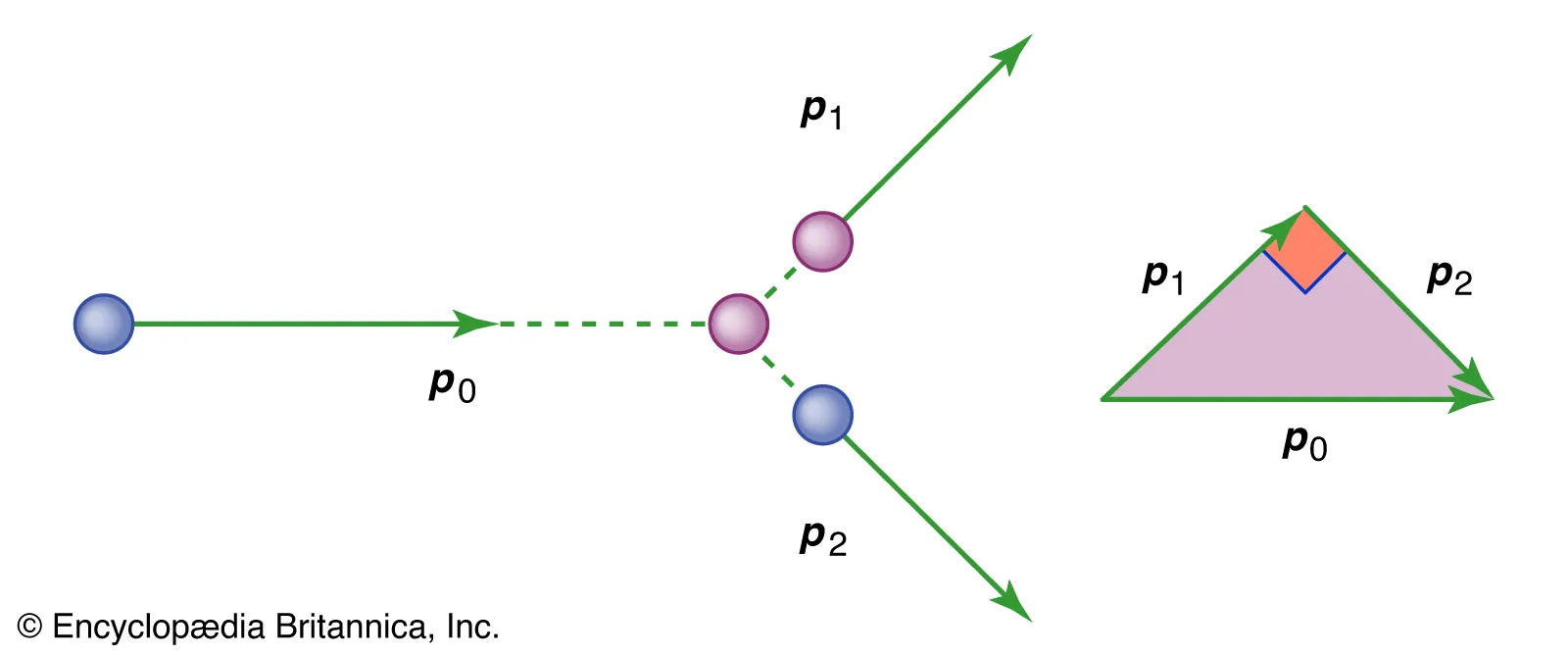
Describe how a Vector Triangle can be applied to solve a 2D Collision.
The vector sum of p1 and p2 (Total final momentum) must be equal to be p (Initial momentum)
Describe how Resolving Vectors can be applied to solve a 2D Collision.
Momentum must be conserved, and must remain the same in the x directions and the y direction
X direction: Total Initial momentum=Total Final momentum →
m1v0 = m1v1cosθ1 + m2v2cosθ2
Y direction: Total Initial momentum=Total Final momentum →
0 = m1v1sinθ1 + m2v2sinθ2