CHPT 17 Functional Organization of the Endocrine System
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary flashcards covering key concepts from the lecture on the functional organization of the endocrine system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Endocrine System
Composed of ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Hormones
Chemical messengers that travel through the blood to target tissues to elicit a response.
Hormonal or Tropic Hormones
Hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands to release their hormones. (i.e. Thyroid stimulating hormones stimulates the production of T3, T4 from the thyroid.)
Half-life
The time required for a quantity of a substance to reduce to half its initial value.
Negative Feedback
A mechanism by which hormone secretion is inhibited by the hormone itself.(i.e.•thyroid hormones inhibit the secretion of their releasing hormones from the hypothalamus and their tropic hormone from the anterior pituitary.)
Synergistic Interactions
Occur when two hormones work together to produce a greater effect. (•Estrogen and progesterone work together to prepare the uterus for pregnancy)
Antagonistic Interactions
Occur when one hormone opposes the action of another hormone.(PTH and calcitonin are each sensitive to blood calcium levels; PTH increases blood calcium, while calcitonin decreases it. )
Upregulation
The process of increasing the number of hormone receptors on a target cell.(•Oxytocin receptors in the uterus during the third trimester of pregnancy)
Downregulation
The process of decreasing the number of hormone receptors on a target cell.(•Drug abuse may result in the down-regulation of dopamine receptors in target cells, which in turn would require more drug to achieve the same effect.)
Water-soluble Hormones
Hormones that cannot pass through the plasma membrane and interact with cell surface receptors. MOVE FREELY,SHORT HALF-LIFE (Large proteins, glycoproteins, polypeptides, epinephrine and norepinephrine)
Lipid-soluble Hormones
Hormones that can pass through the plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptors.LONG HALF-LIFE, TRANSPORTED WITH BINDING PROTEINS(thyroid hormones, testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, aldosterone, cortisol.
Posterior Pituitary Gland
Part of the pituitary that releases hormones produced in the hypothalamus.
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Gland that is regulated by hypothalamic hormones and releases its own hormones into the bloodstream.
Humoral Control
The action of a substance other than a hormone influencing endocrine gland activity.(i.e Parathyroid hormone is secreted based on calcium levels in blood.)
Neural Control
Control of hormone secretion by the nervous system.(i.e. Adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine upon neural stimulation)
Membrane-bound Receptors
Receptors located on the surface of a cell that bind to water-soluble hormones.
Short-Half life
water soluble hormones, regulate activities of rapid onset and short duration/ quick response by target cell and then eliminated from blood stream
Long Half life
lipid soluble hormone, reach more slowly and stay in the blood longer sue to transporter protein
Autocrine
Secreted by cells in a local area; influences the activity of the same cell from which it was secreted
Example: Eicosinoids
Paracrine
Produced by a wide variety of tissues and secreted into extracellular fluid; has a localized effect on nearby tissues
Example: Histamines
Endocrine
Secreted into the blood by specialized cells; travels to target tissues (anywhere in the body); Example: Insulin, GH etc
Neurotransmitter
Produced by neurons; secreted into a synaptic cleft by presynaptic nerve terminals; travels short distances; Example: Acetylcholine
Permissive Interactions
Hormone 1 helps out Hormone 2 (epinephrine and norepinephrine on the heart for heart rate, stoke volume, and contractility)
Agonist
•a drug with similar structure of a specific hormone that can bind to a hormone receptor and activate it.(i.e. drugs in asthma inhalers mimic epinephrine to cause smooth muscles in the lung to relax)
Antagonist
•a drug that can bind to a hormone receptor and inhibit its action.(i.e.anti-stroke drugs will inhibit the action of epinephrine to prevent epinephrine-stimulated platelet aggregation)
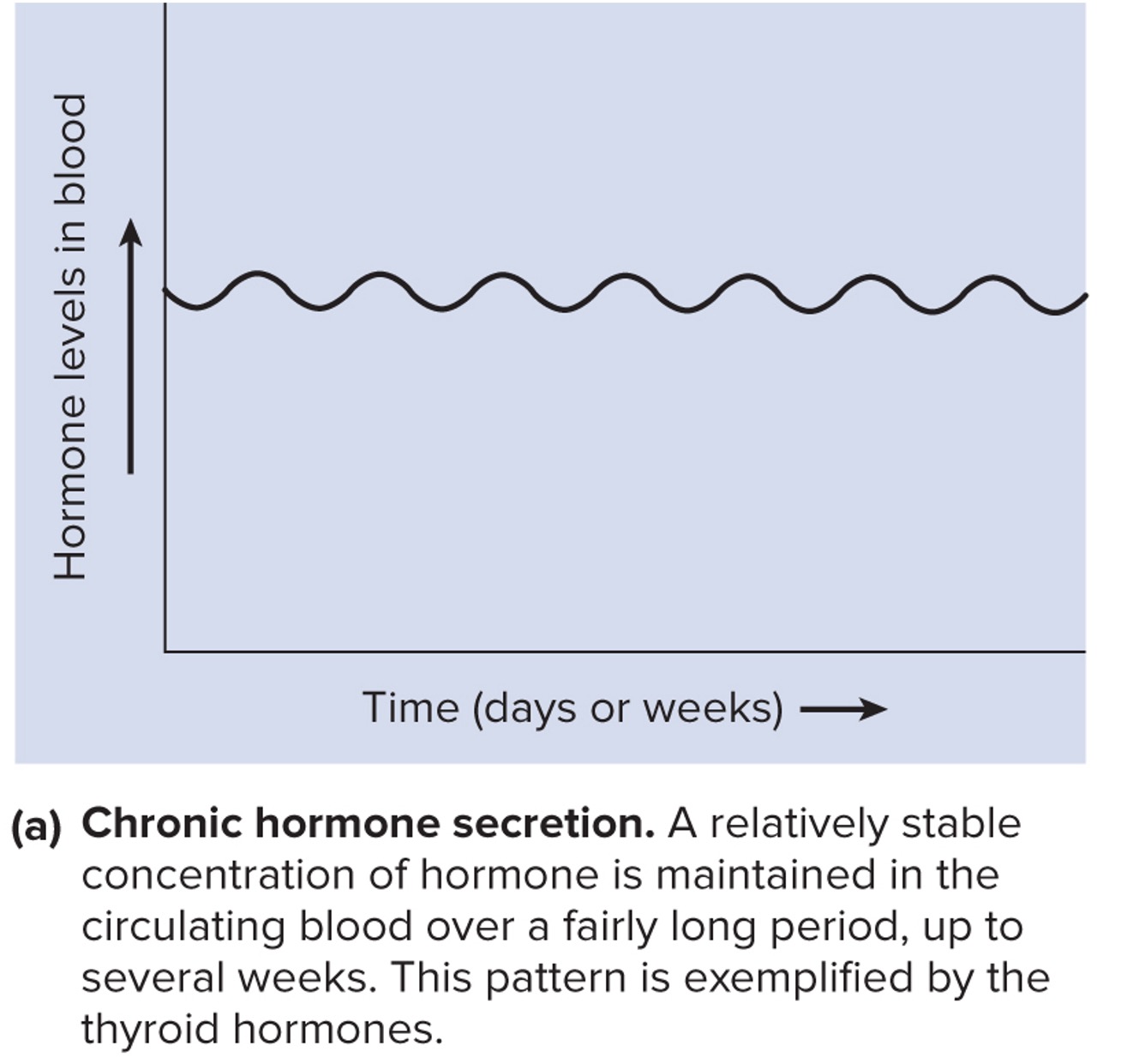
Chronic Hormone Secretion
Relatively constant blood levels of hormone over long periods of time:
Thyroid hormones
Acute Hormone Secretion
Hormone’s concentration changes suddenly and irregularly, and its circulating levels vary at each stimulus:
epinephrine

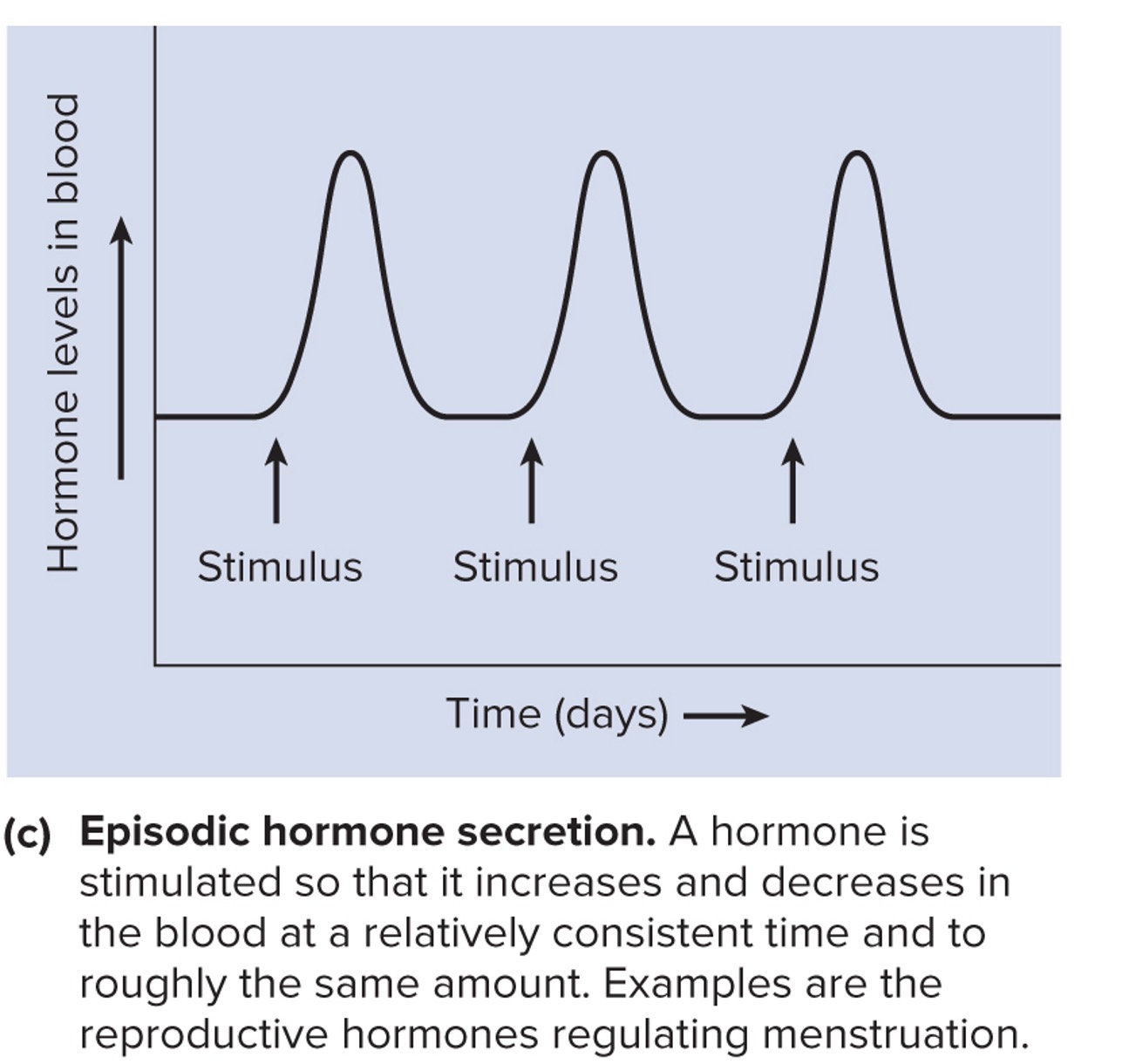
Episodic Hormone Secretion
Hormones are secreted at fairly predictable intervals and concentrations:
Reproductive hormones
Positive Feedback
the hormone’s secretion is stimulated by the hormone itself; self-perpetuating(i.e.•: oxytocin from the posterior pituitary gland during labor)