Module 3: Plate Tectonics (copy)
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Lithospheric Plates
rigid, outermost layer of the earth’s lithosphere that are fragmented and fit together like a jigsaw puzzle
Plate Boundaries
edges of the lithospheric plates
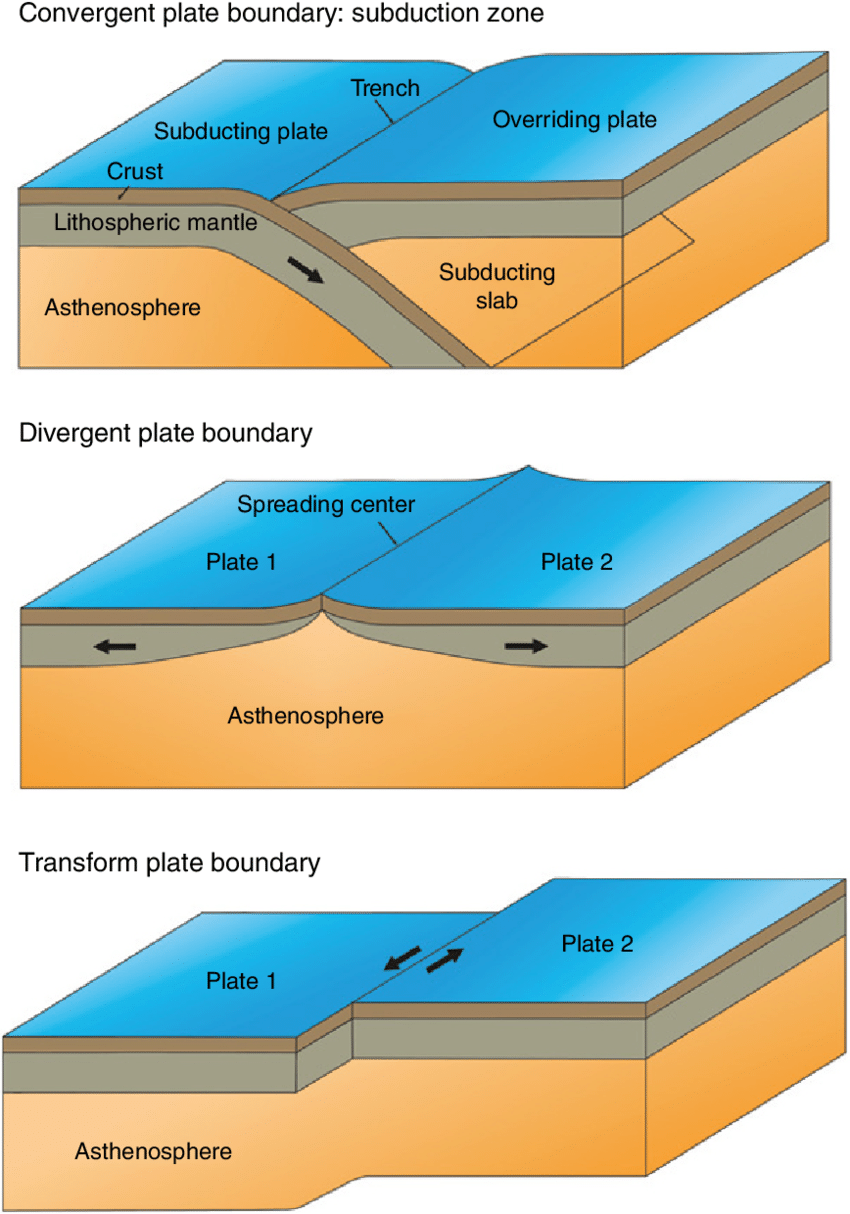
3 Plate Boundaries
convergent
transform
divergent
Tectonics
refers to the structure and deformation of the Earth’s crust, and the processes that lead to the creation, movement, and interaction of the Earth’s lithospheric plates
overall deformations from interactions/movements
Geological Phenomena
any natural events or processes that occur on or within the earth’s crust resulted from the interaction of the plate boundaries
Major Classifications of Earth Layers based on Mechanical Properties
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Mesosphere
Outer core
Inner Core
Lithosphere
crust and uppermost mantle; outermost layer
Consistency of the Lithosphere
rigid; brittle
Asthenosphere
upper-mantle
Consistency of the Asthenosphere
relatively weak; molten (composed of liquid, solid, and some gas → can flow)
Continental Drift Hypothesis
proposed by alfred wegener, who stated that the earth once existed as a whole chunk of a continent (pangaea) and a whole chunk of ocean (panthalassa)
Pangaea
“all land”; the super continent proposed by wegener
period that the Pangaea continent existed
existed 250 million years ago; during Permian period
period that the Pangaea started separating
after Triassic period (~200 million years ago)
2 major supercontinents of the Pangaea
Laurasia (northern pole of the earth)
Gondwanaland (southern pole of the earth)
Current continents that consisted the Laurasia continent
(NEA):
North America
Europe
Asia
Current continents that consisted the Gondwanaland continent
South America,
Africa,
Australia,
Antarctica
Panthalassa
“all sea”; the large body of water that surrounded the Pangaea
Tethys Sea
a smaller sea formed during the triassic period when the pangaea broke into two
4 evidences for the continental drift theory
continental jigsaw puzzle fit
fossil match across continents
rock type and geological features
paleoclimatic evidence
Proof for the Continental Jigsaw Puzzle Fit
Africa and South America fits if Atlantic Ocean is closed;
if you connect the continents, they form a puzzle where their boundaries match
Continental Shelf
the edge of a continent that lies under the ocean
Reason why the continental shelf is used as the boundary for reference in proving the jigsaw puzzle fit theory
edges above the ocean are easily eroded due to exposure to the surface
Proof for the theory on fossil match across continents
Fossils of animals and plants that could not have travelled through the oceans: Mesosaurus, Glossopteris, and Lystrosaurus
Where the Lystrosaurus was seen
africa, india, antarctica
Where the Glossopteris was seen
South Amrica, Africa, India, Antarctica, Australia
Where the Cynognathus & Mesosaurus were seen
South America & Africa
Reason why the Glossopteris was used in the fossil theory
glossopteris is very big, so it is questionable how it could have travelled
Reason why the Lystrosaurus was used in the fossil theory
it is a terrestrial animal, thus could not cross nor swim water
Reason why the Mesosaurus was used in the fossil theory
it is a marine animal, unsure how it could survive the varying temperature gradient conditions as it swam across the oceans, since salinity conditions across continents are different
Proof for the rock type and geologic feature thoery
Appalachian-Caledonian Mountains
appalachian → north america
caledonian mountains → north eastern europe
Proof for Paleoclimate/Ancient Climate theorem
Coal Seams in North Hemisphere with tropical trees
Glacial till and striations in Southern Africa, South America, Australia, and India
the driving mechanism of alfred wegener on continent movement
Tides, and the gravitational attraction between sun, moon, and earth
debunk of tides as a driving mechanism for continent movement
however, for tidal forces this strong and to cause movement in plate boundaries or continental plates, such equivalent force could also affect overall rotation of earth
Seafloor Spreading
proposed by harry hess, in which it centers on the formation of oceanic crust in a mid-oceanic ridge
Mid Oceanic Ridge
large scale earth feature formed at divergent plate boundaries
Mechanism/purpose of a mid-oceanic ridge
plates move away from the mid-oceanic ridge because of volcanic/mantle activity
new materials from the mantle comes out of this ridge, causing the creation of new oceanic crust along the ridge
Relationship of thickness of sediments and its distance from the mid-oceanic ridge
Thickness of sediments increase as it moves further away from the ridge due to accumulation;
moves faster as it is farther away from ridge
3 Additional Evidences for Plate Motion
Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering
Hot Spot Volcanism
Seismicity and Plate Boundaries
Curie Point
temperature at which a mineral’s magnetic properties change (e.g. magnetite 585ºC)
Paleomagnetism
the record of the magnetic quality of a mineral wherein they “point” toward the position of the magnetic poles at the time of their formation;
Why does paleomagnetism happen
usually when after a mineral melts (reaching curie point), they cool down and become magnetic, and their magnetism freezes once they solidify
Polar Wandering
migration of magnetic poles
How is polar wandering related to moving continents?
if the magnetic poles remain stationary, their apparent movement is produced by continental drift
connection of magnetic pole to geographic poles according to polar wandering
the positions of magnetic poles (averaged over thousands of years) correspond closely to the positions of the geographic poles
proof of polar wandering and its connection to continental drift
of north america and europe are moved back to pre-drift positions, their wandering paths coincide (but separated by the atlantic ocean)
magnetic reversal
phenomenon wherein the earth’s magnetic field periodically reverses polarity, wherein the north magnetic pole becomes the south magnetic pole, and vise versa
normal polarity
when rocks exhibit the same magnetism as the present magnetic field
reverse polarity
when rocks exhibit the opposite magnetism
connection of magnetic reversals to seafloor spreading
alternating, equal mirror strips of high and low intensity magnetism mapped out that arose from underlying crustal rocks in the mid-oceanic ridge
hot spot volcanism
localized; long-lasting hot regions below the lithosphere that originated from the core mantle boundary, wherein magma plumes move upward and cause pacific plates around the plumes to move
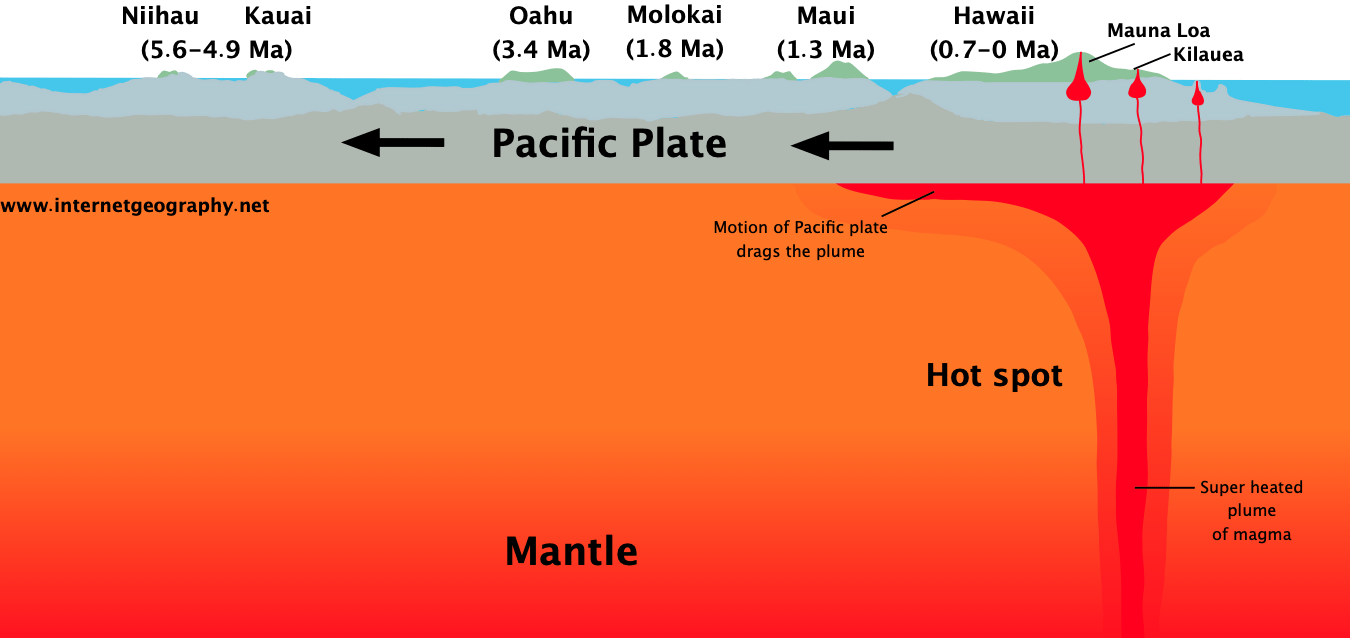
where are hot spot volcanisms formed
magma plumes beneath the lithospheric plates
implication on age of volcano relative to distance from mantle plume
as a volcano/island moves further away from plumes, it implies it is older in age and more dense
example on proof of hot spot volcanims
islands of hawaii, where the hawaii island is more active given that it is under a hot spot volcanism, and niihau and kauai (which are further from the plume) are dormant (no magnetic materials created beneath island)
Seismicity and Plate Boundaries
areas of shallow earthquakes: regions of rifting
Wadati-benioff zone
anar zone of seismicity corresponding with the down-going slab in a subduction zone
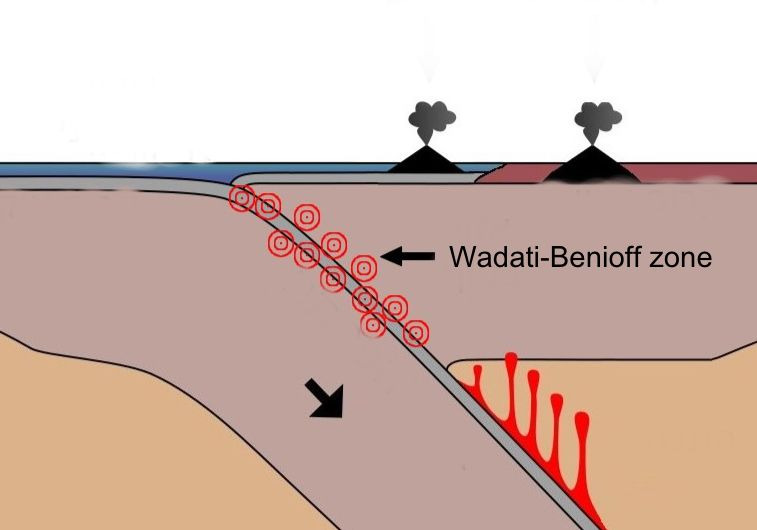
areas if sub-ducting plate relative to the wadati-benioff zone
on top (along conversion boundaries): seismicity is concentrated
below: weak and negligible seismicity
relationship of seismicity and plate boundaries
plate boundaries are the edges of lithospheric plates and where plates interact, and it is where seismic activity (earthquakes) are seen
debunk of seafloor spreading
“If new materials are create along mid oceanic ridge, that means that new crust created along MOR, does it mean that the earth is expanding?”
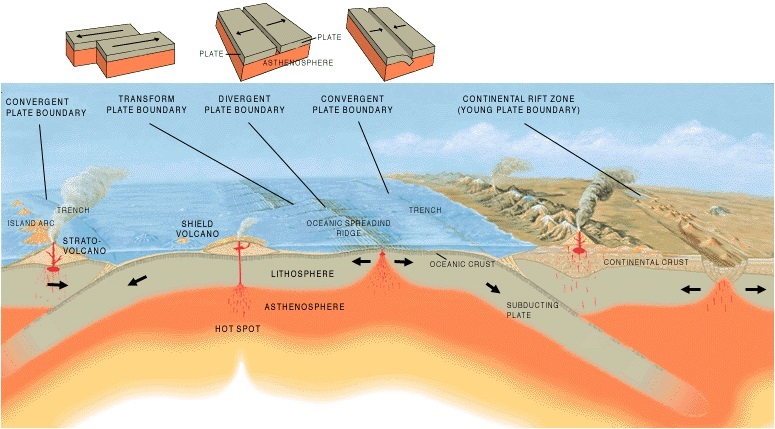
Plate Tectonics Theory
unifying theory of geology; states that the lithosphere is composed of segments (tectonic plates) and that plates are in constant motion relative to one another
3 classifications of plate boundaries
major plate boundaries
minor plates
micro plates
7 major plate boundaries
North American
South American
Pacific
Eurasian
Australian
Indian
Antarctic
another name for convergent boundary
destructive boundary
convergent boundary
where two plates move together forming either arcs or mountain systems, forms subduction zones when oceanic lithosphere is involved
tectonic featured formed from two oceanic plates converging
island arcs
how are island arcs formed
when the older, denser, and colder oceanic plate sub-ducts beneath the younger, less dense oceanic plate
example of a tectonic feature of two oceanic crusts converge
mt. pinatubo
tectonic feature created from an oceanic and continental crust converging
continental volcanic arc
how are continental volcanic arcs formed
when the dense oceanic crust sub-ducts under the continental crust
example of tectonic feature from continental and oceanic converge
andes mountains
tectonic feature created when two continental plates converge
mountain ranges
how are mountain ranges formed
continental crusts crumple upwards; do not subduct
example of tectonic feature when continental plates converge
mt. everest
another name for divergent boundaries
constructive boundary
divergent boundary
where two plates move apart, leading to the formation of new oceanic crusts as seafloor
tectonic feature formed when oceanic crusts diverge
mid-oceanic ridge
example of mid-ocean ridge
mid-atlantic ridge that cuts iceland into 2 parts
tectonic feature formed when continental crusts diverge
rift vally
example of a rift valley
east african rift zone
example of where a triple junction is formed
african plate, arabian plate, indian plate moving away from each other
triple junction
when there are three continental plates diverging away from each other
phenomenon that takes place when divergent plates do not progress to form rift valleys
in tensional forces when plates move away from each other, the others just form a depression or basin, and overtime may discharge of water where it creates lakes (i.e. lake victoria)
another name for transform boundaries
conservative boundaries
transform boundaries
where two plates grind past each other; connects oceanic ridge systems into a continuous network
tectonic feature formed from transform boundaries
strike-slip faults
direction of strike slip faults relative to divergent plate boundaries
forms perpendicular lines with respect to the boundary
example of a strike slip dextral fault
san andreas fault
types of strike slip faults
dextral
sinistral
dextral faults
right lateral strike-slip faults
sinistral faults
left lateral strike-slip faults
mantle convection
movement of mantle in mantle plumes and active hotspot volcanisms, wherein warmer materials tend to rise up, cooler material tend to sink
processes involved in mantle convection
ridge push & slab pull
ridge push
process in which mantle plumes are extruded to the surface causing rifting (divergent plate boundary)
slab pull
process in which density and gravity differences further strengthens the subduction process (convergent plate boundary)
Type of tectonic feature of the Philippines
island arc system
How the philippines was created
created from the convergent boundaries of 2 oceanic plates (south china sea and philippine sea plate) that are moving toward each other
trenches of the philippines that subduct in the east direction (but are west geographically)
manila trench and sulu negros trench
trenches of the philippines that subduct in the west direction (but are east geographically)
east luzon trough & philippine trench
result of the net forces created by subduction zones (in the PMB area)
philippine fault zone
type of strike slip of the philippine fault zone
left-lateral strike slip