AndyRDH- Anatomy Section
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Articulation
area where the bones are joined to each other
Process
any bony prominence
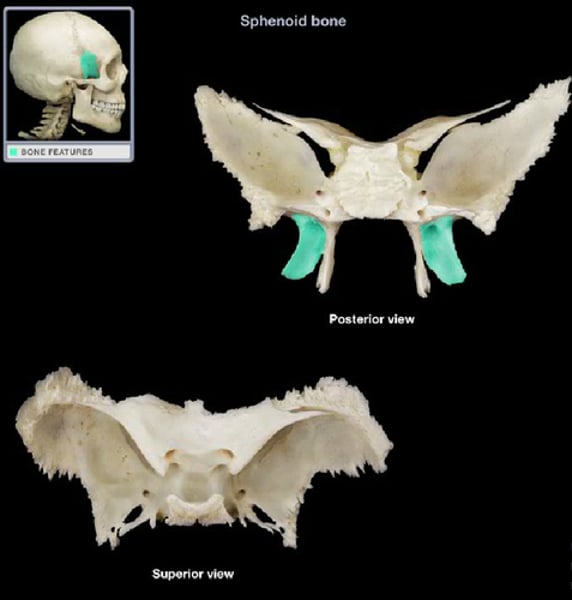
Sphenoid Bone has how many articulations
14
Pterygoid process is part of __________
sphenoid bone
True or false: The mandible is the only moveable bone of the skull at the Temperomandibular joint
True
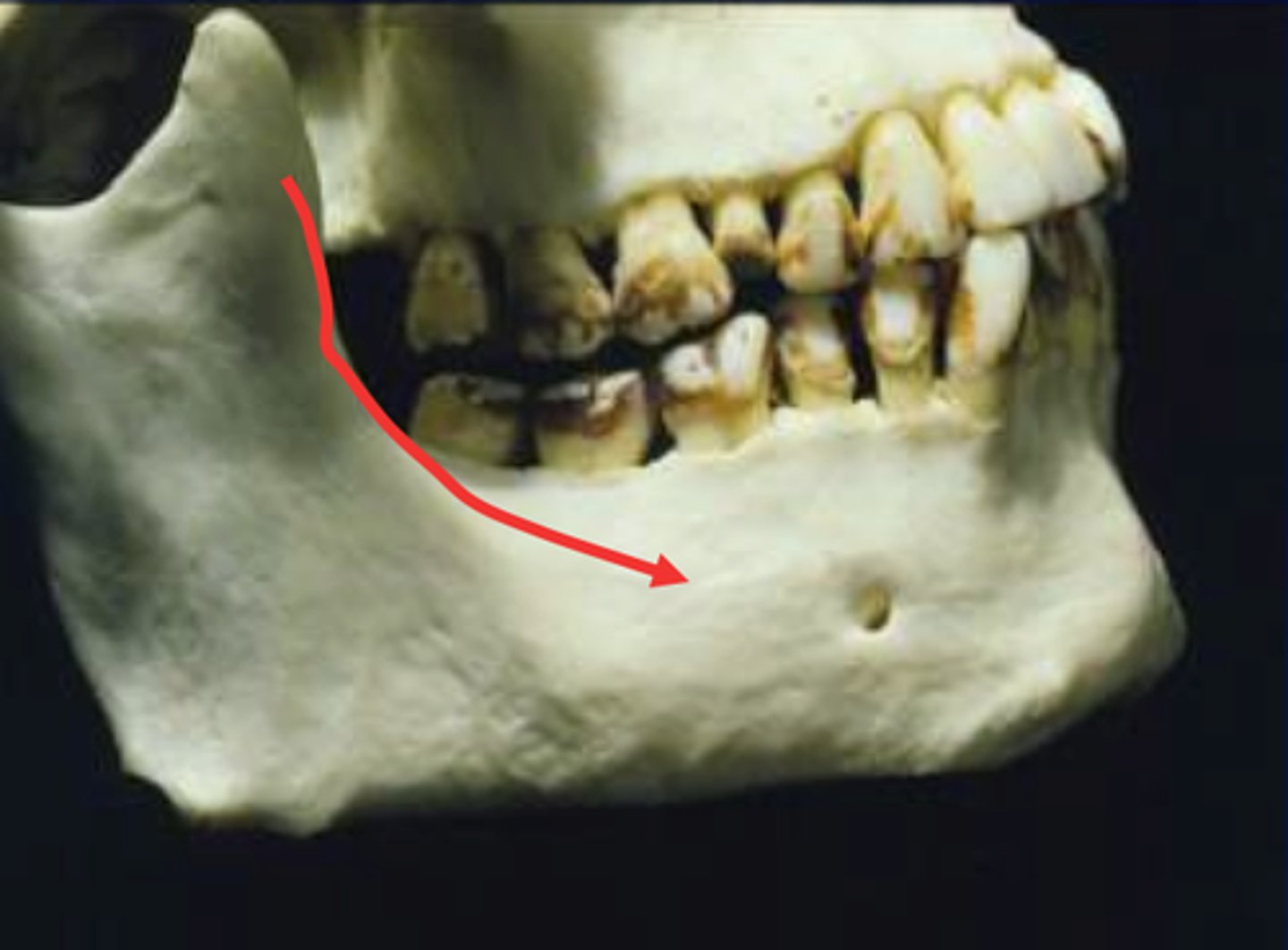
..A radiopaque band extending downward and forward from the anterior border of the ramus of the mandible
External Oblique ridge.
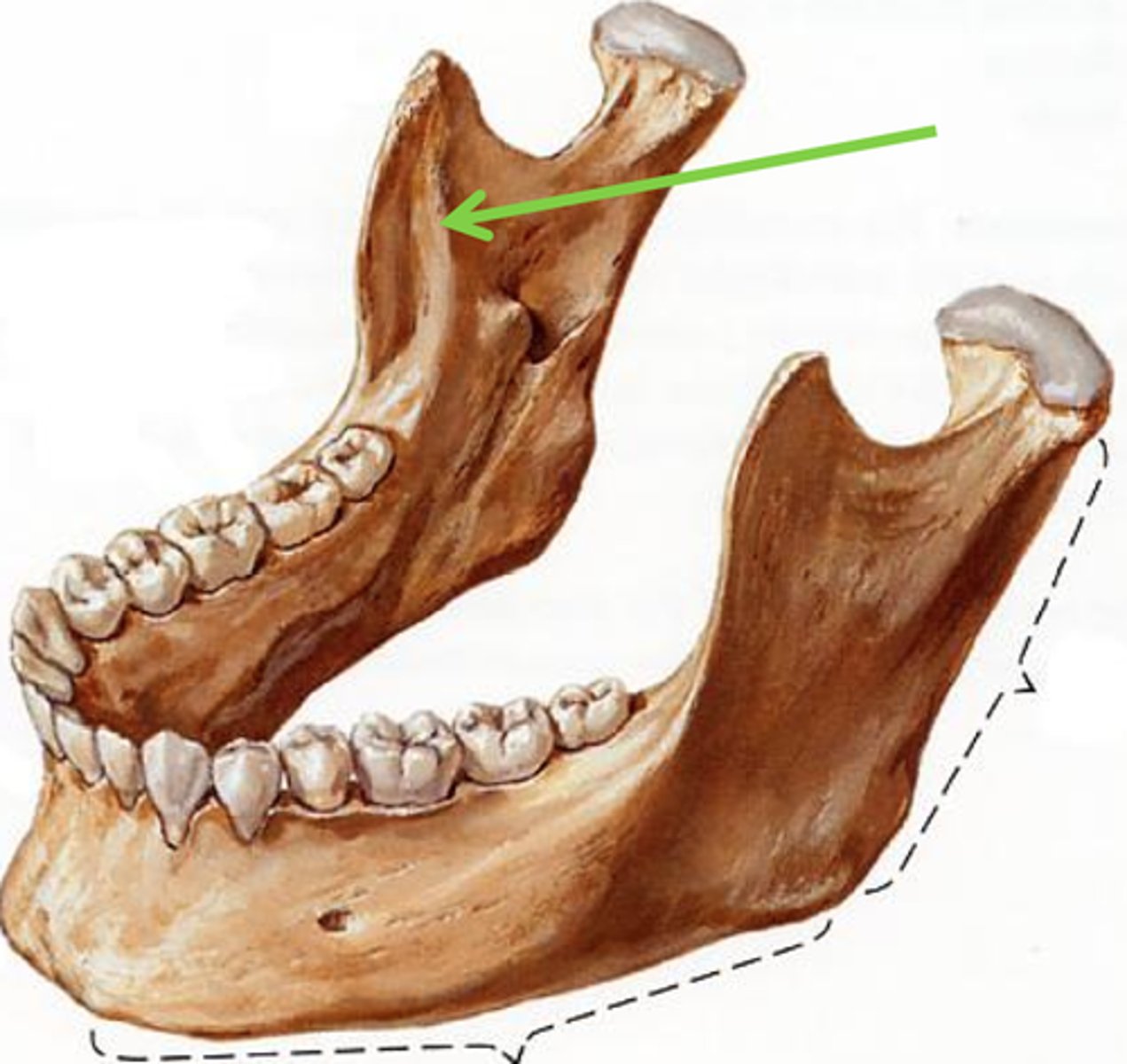
Internal Oblique Ridge
(mylohyoid ridge) follows the inside of the ramus and the body of the mandible.
Condyle articulates with
squamous portion of temporal bone
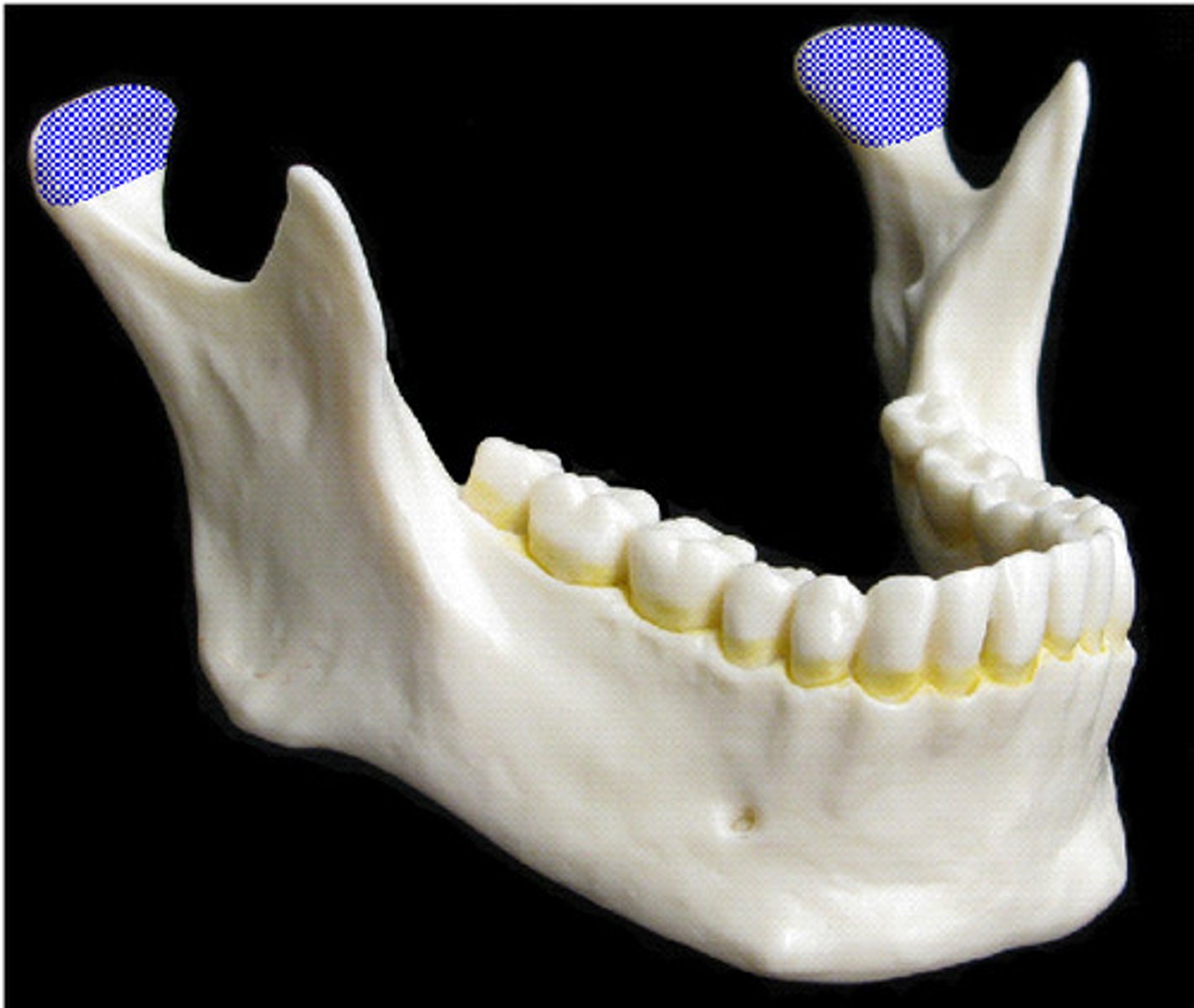
Coronoid process is the attachment point for _________
Temporalis muscle
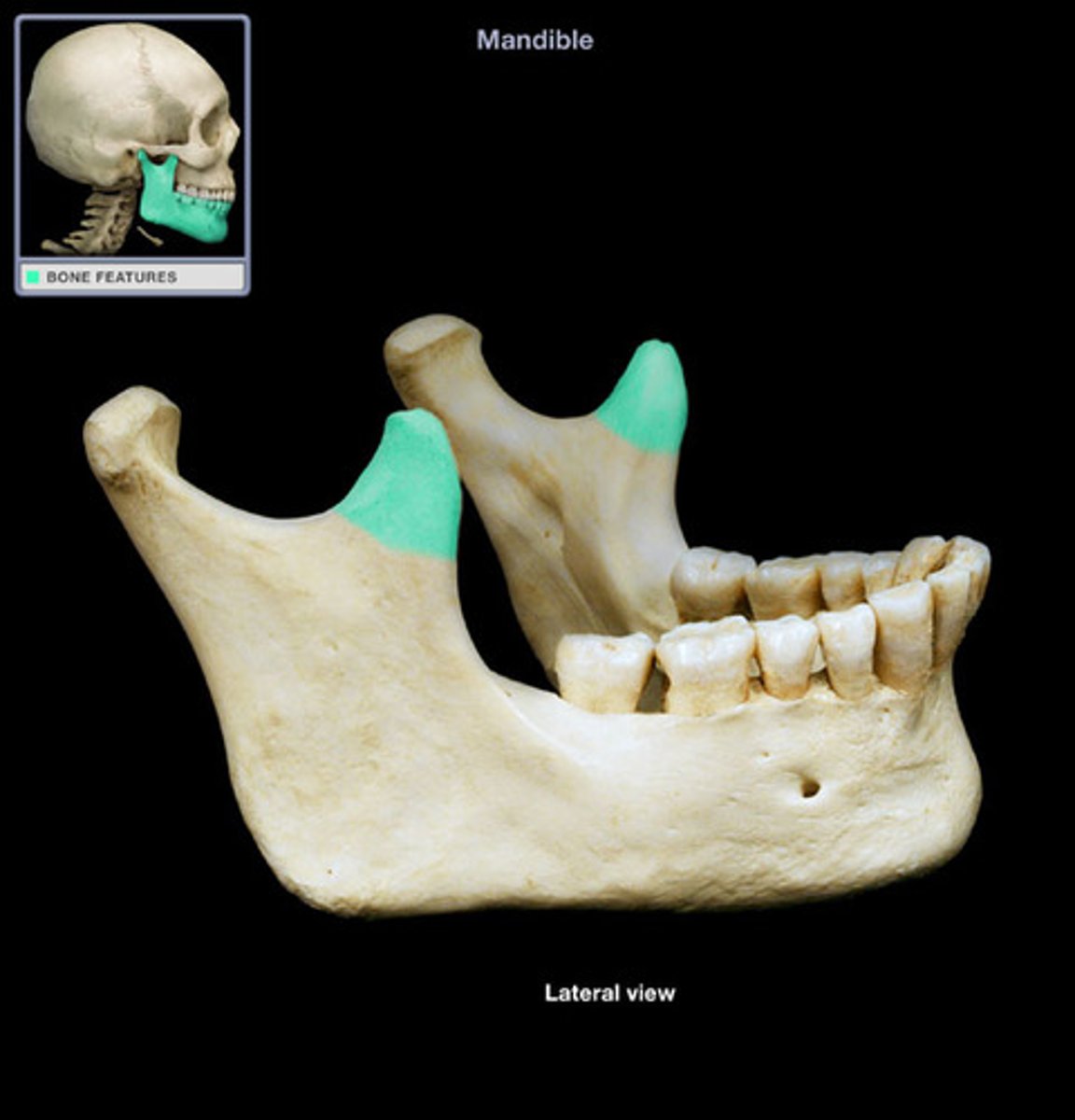
Mandibular notch of mandible
depression between the condylar process and the coronoid process
Origin
Where the muscle orginates; the contraction is TOWARD the origin, the least moveable
Insertion
Where the muscle attaches to the more moveable bone
True or false:
If the name of a muscle is a "combination" the first part is the origin.... the second part is the insertion
True
sternocleidomastoid origin
Medial portion of the clavical and the sternums superior and lateral surfaces
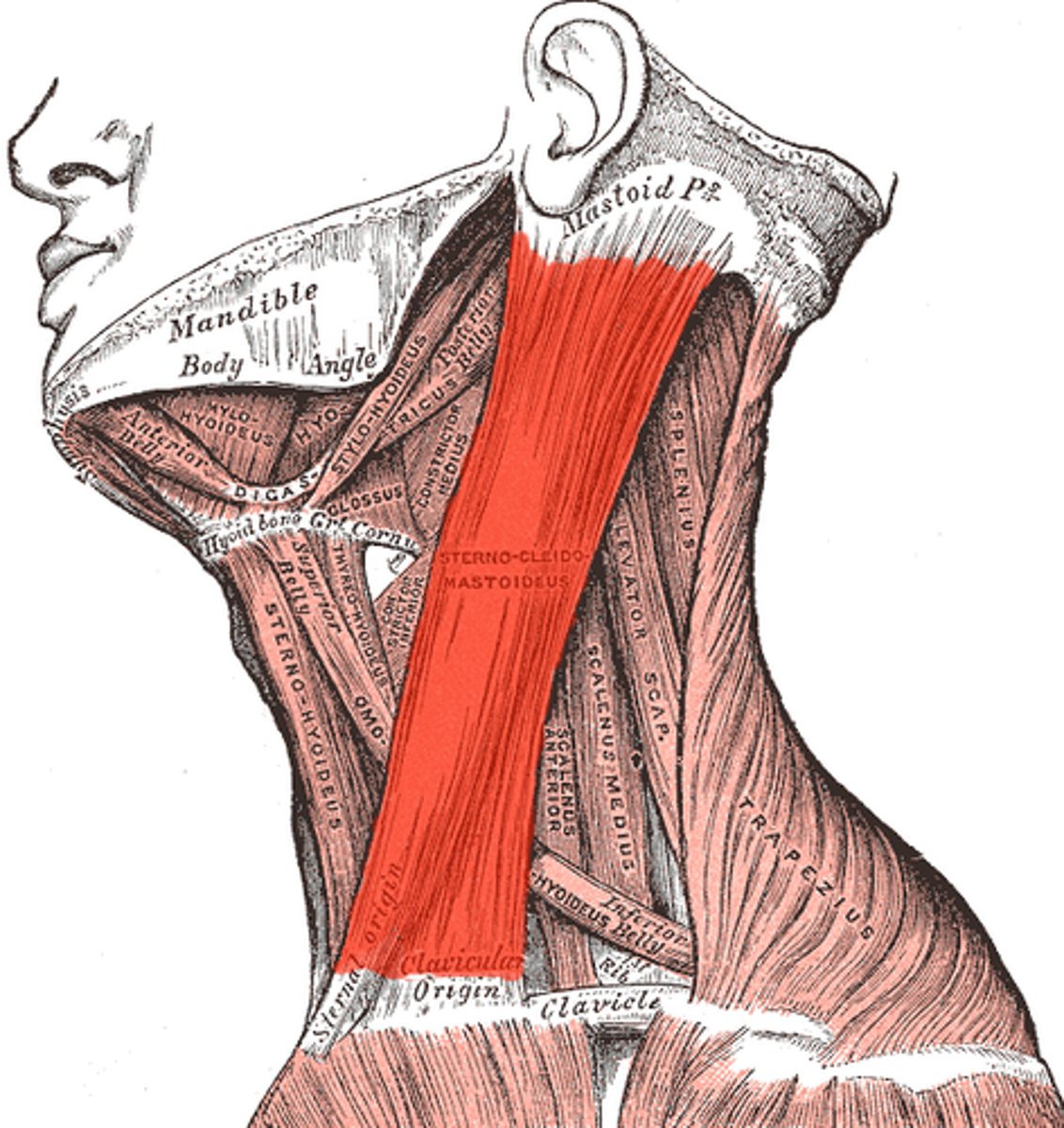
Sternocleidomastoid innervation
Eleveneth (XII) cranial nerve or accessory nerve
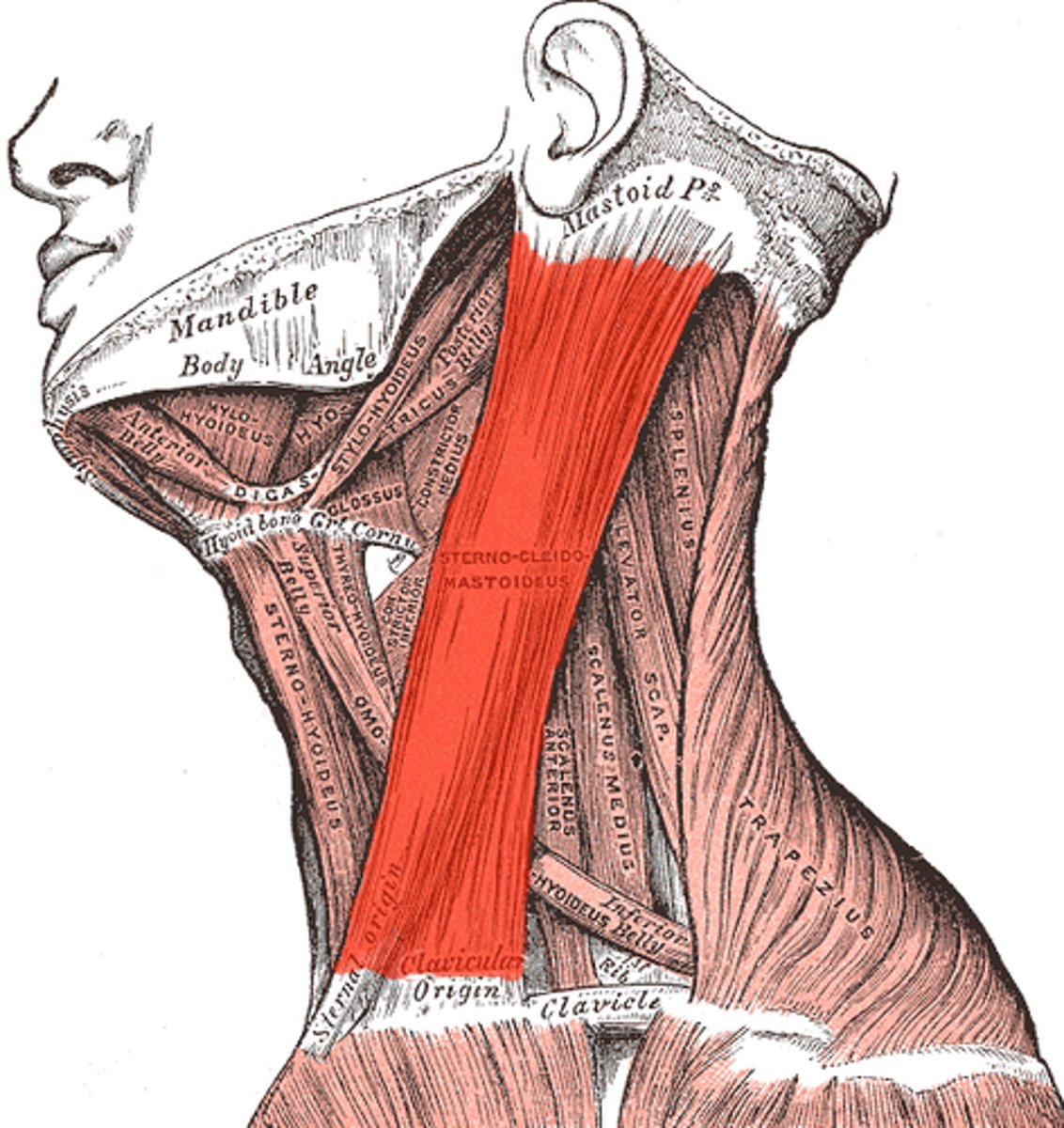
Sternocleidomastoid insertion
Mastoid process of temporal bone
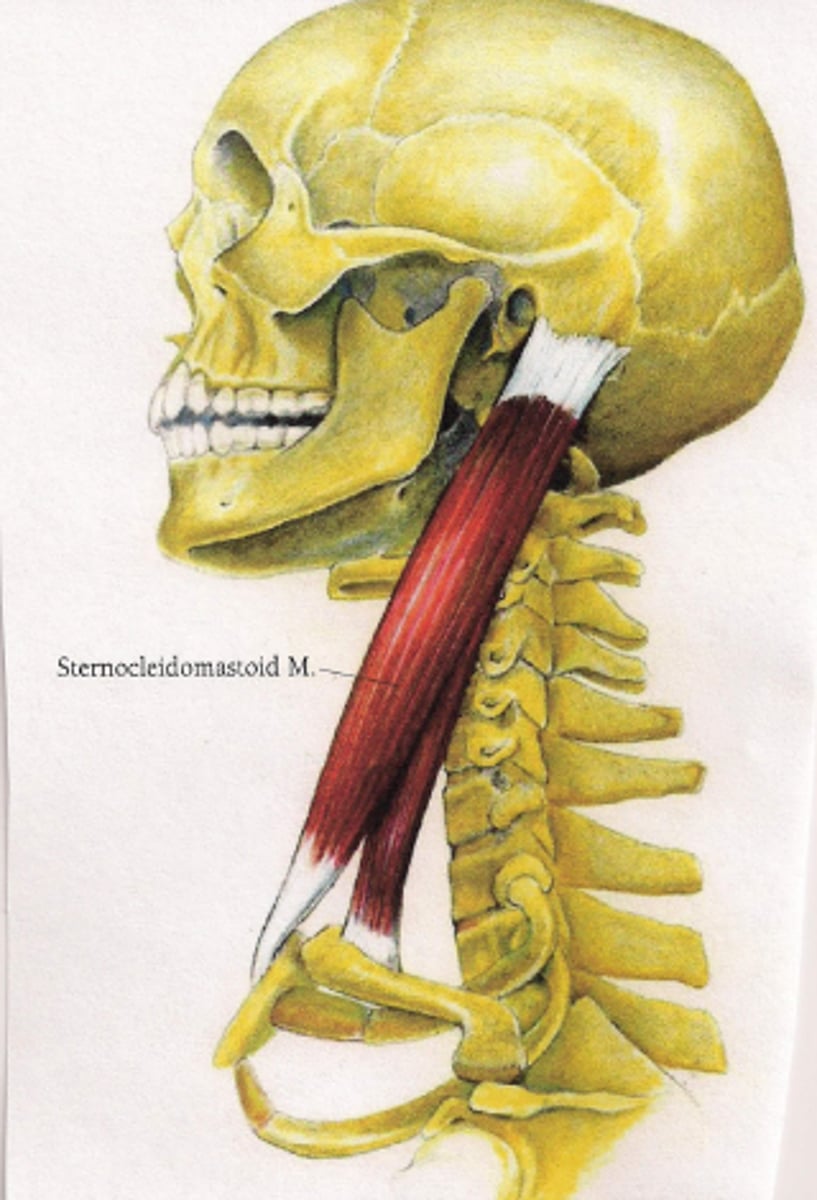
Sternocleidomastoid movement
tilts and rotates head and neck; flexing of neck; stabilize neck
Trapezius origin
External surface of the occipital bone and the posterior midline of the cervical and thoracic regions
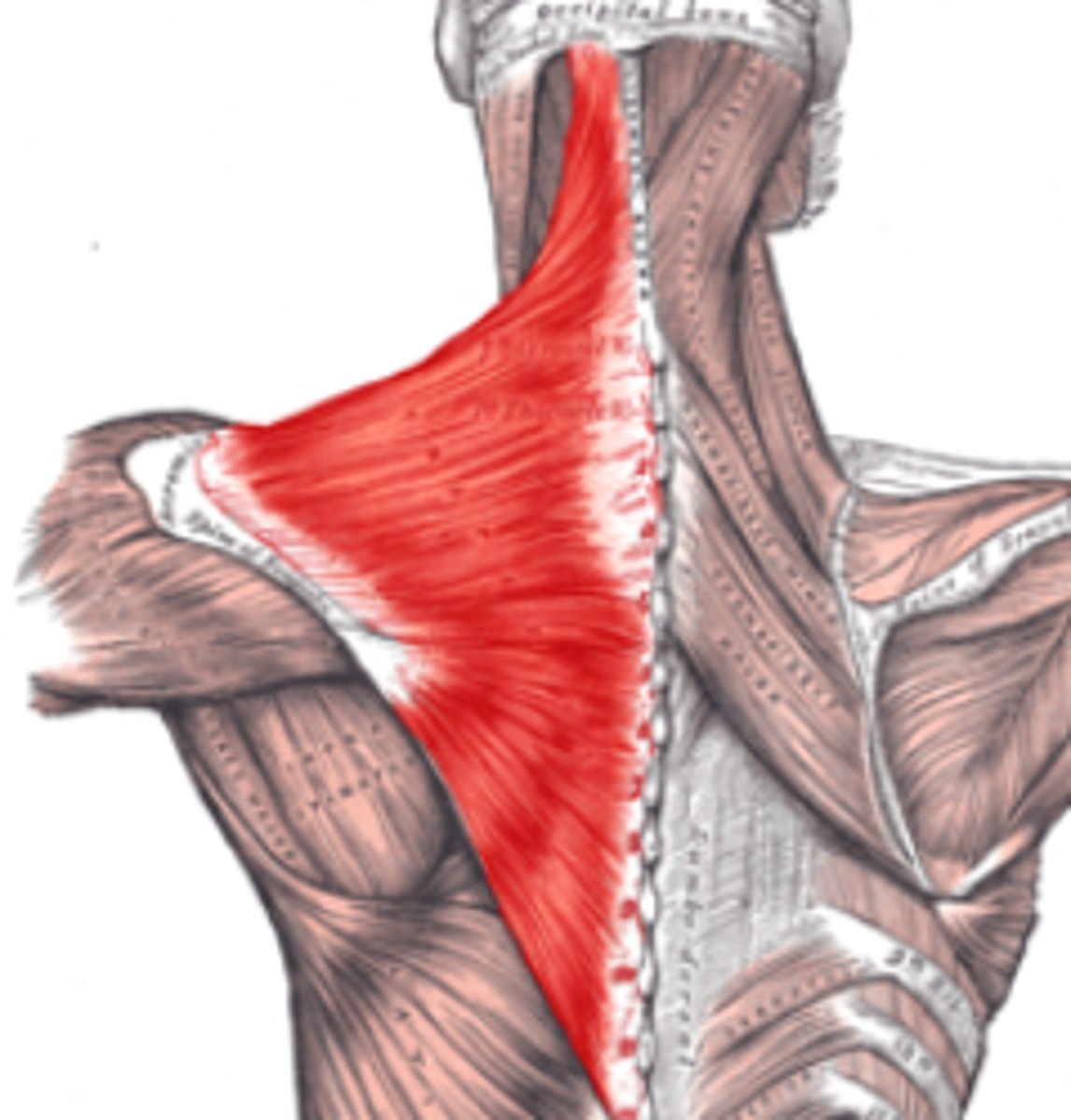
Trapezius Innervation
Eleventh (XII) cranial nerve or accessory nerve
and Third and fourth cervical nerves
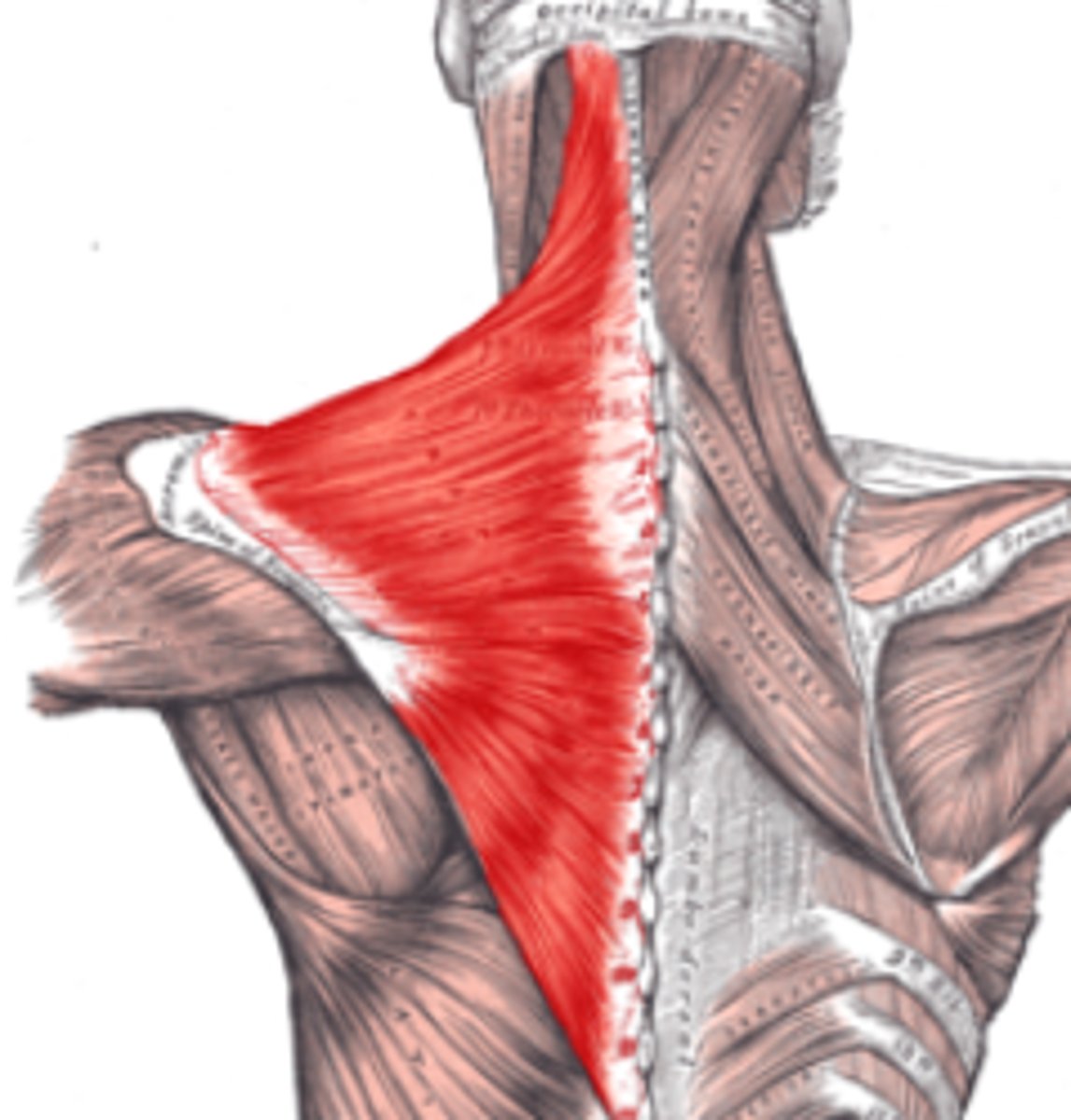
Trapezius Insertion
Lateral one third of the clavicle and parts of the scaapula
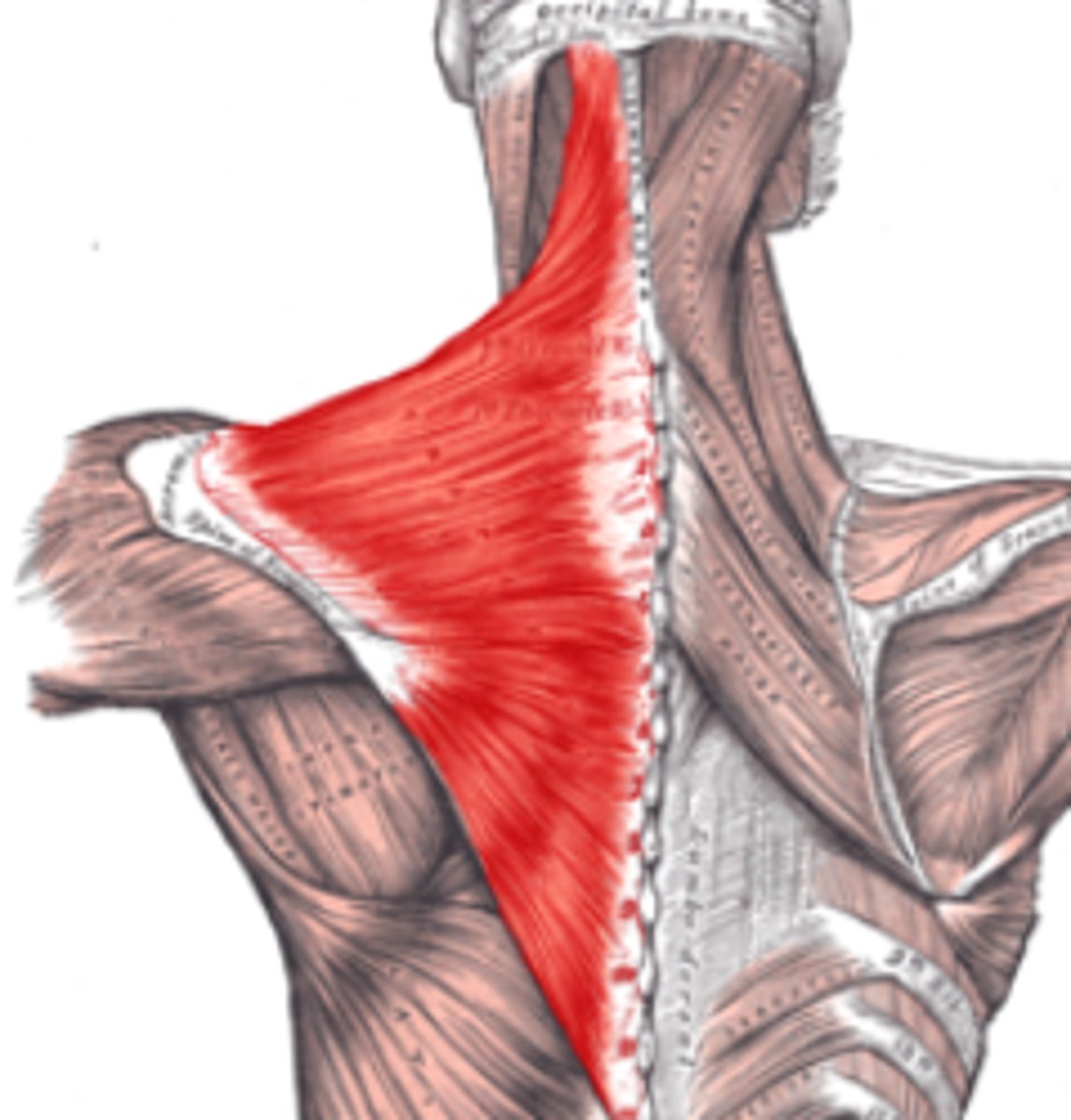
Trapezius Movements
Lifts and rotates the shoulders; dorsal flexion of the head; twist head
Muscles of facial expression
Orbicularis oris
Buccinator
Risoris
Zygomaticus
Levator anguli oris
Depressor anguli oris
Orbicularis Oris origin (muscle of facial expression)
encircles of the mouth
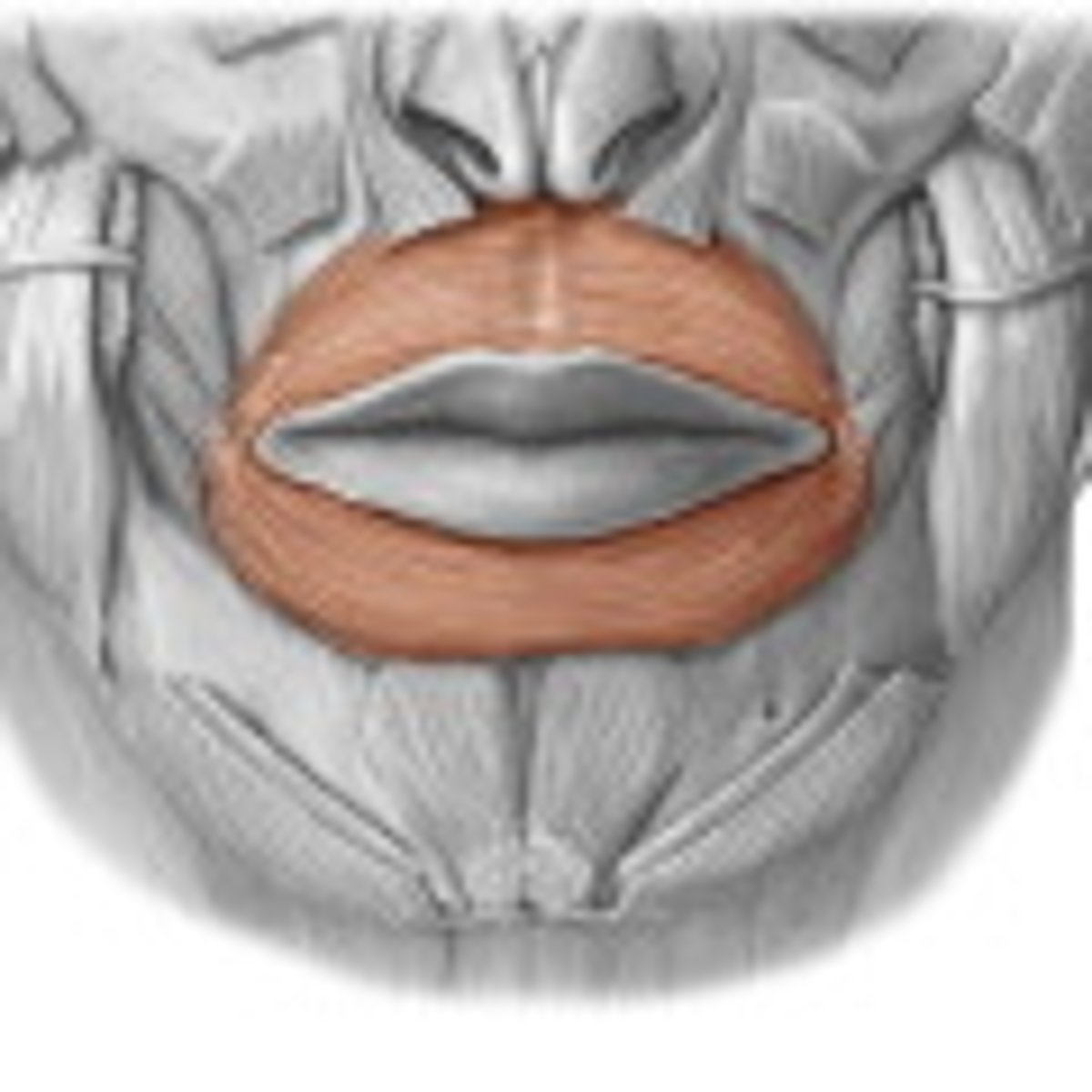
Orbicularis oris insertion (muscle of facial expression)
Angle of the mouth
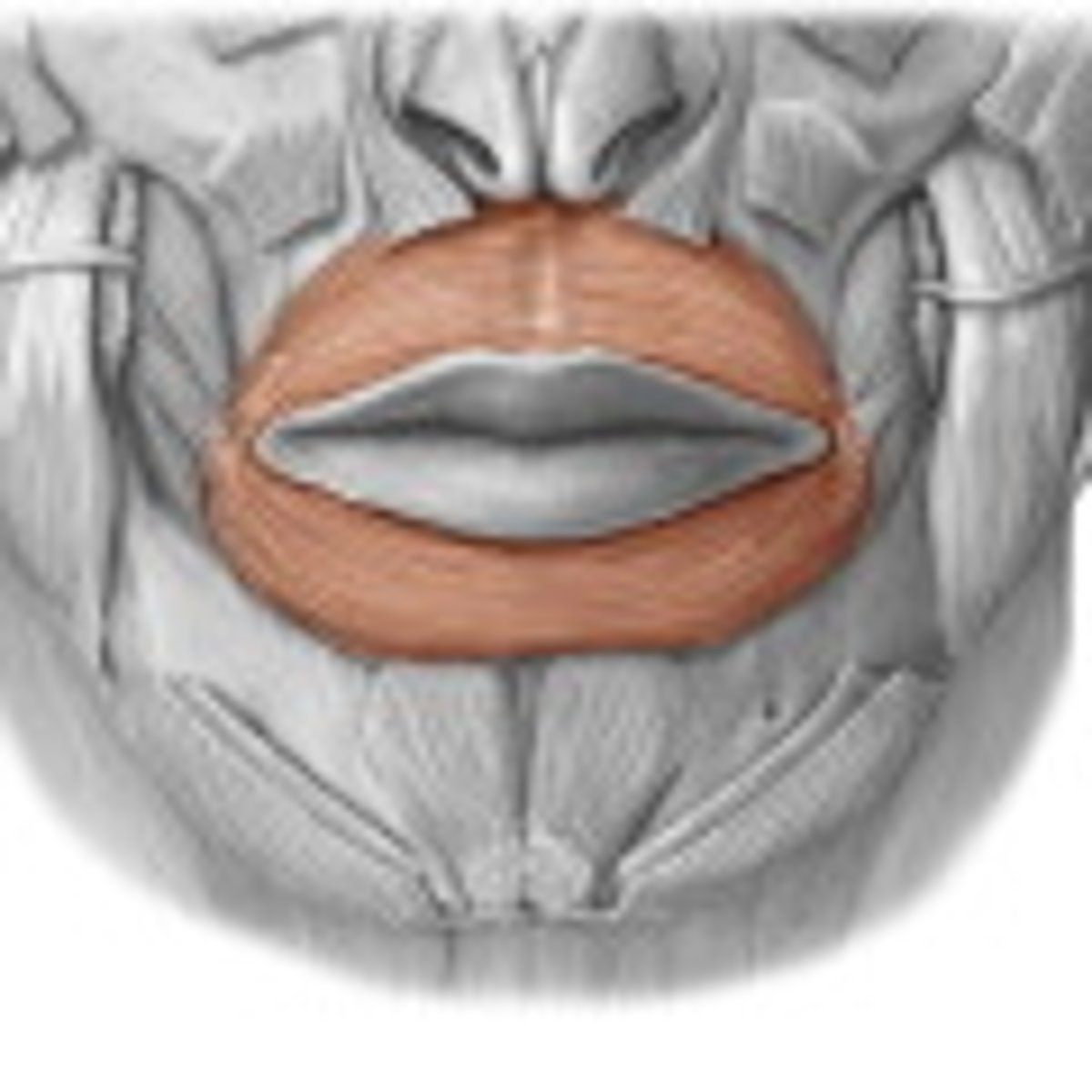
Orbicularis oris expression (muscle of facial expression)
closing or pursing lips
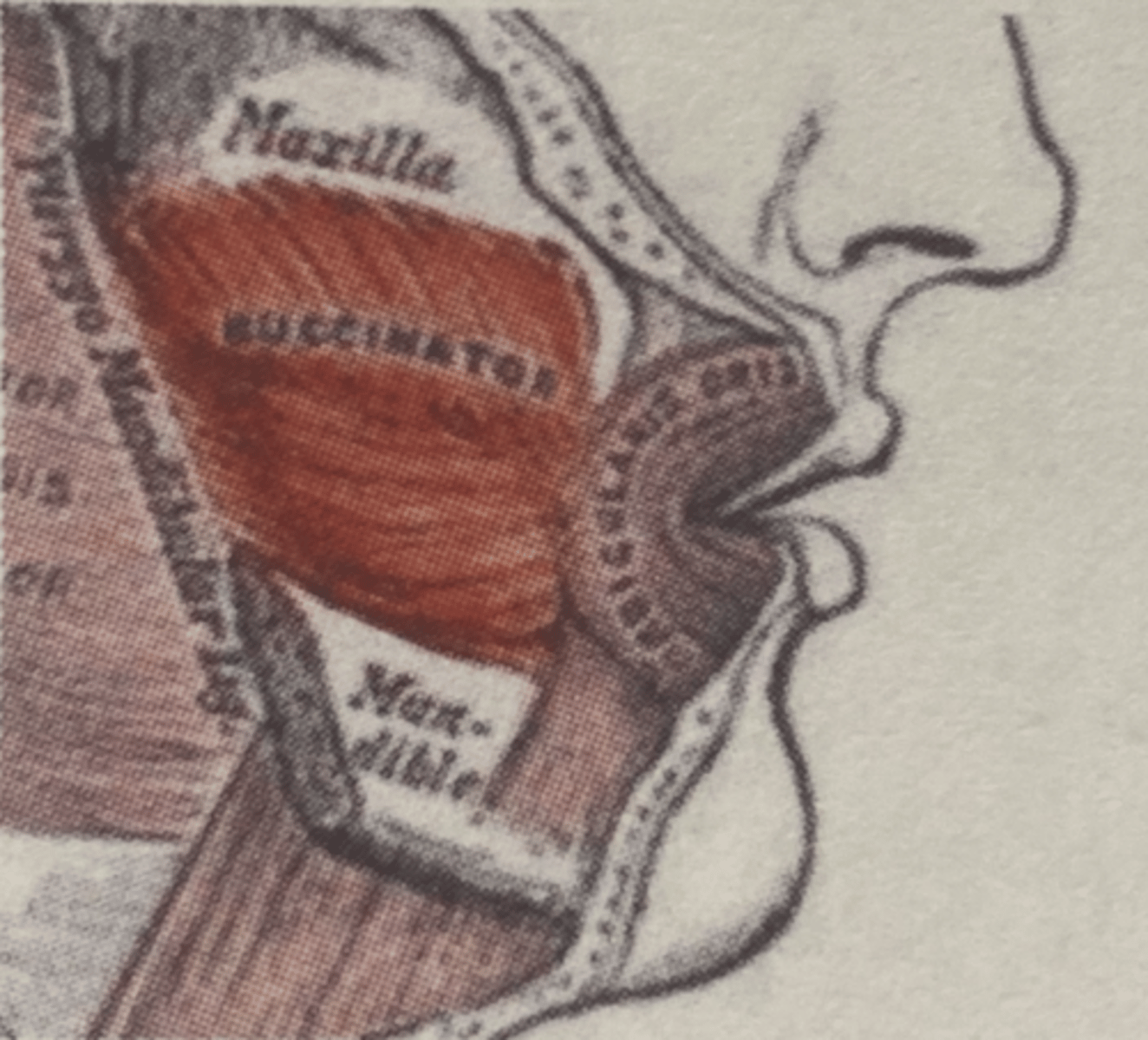
Buccinator origin (muscle of facial expression)
Maxilla, mandible, and pterygoid raphe
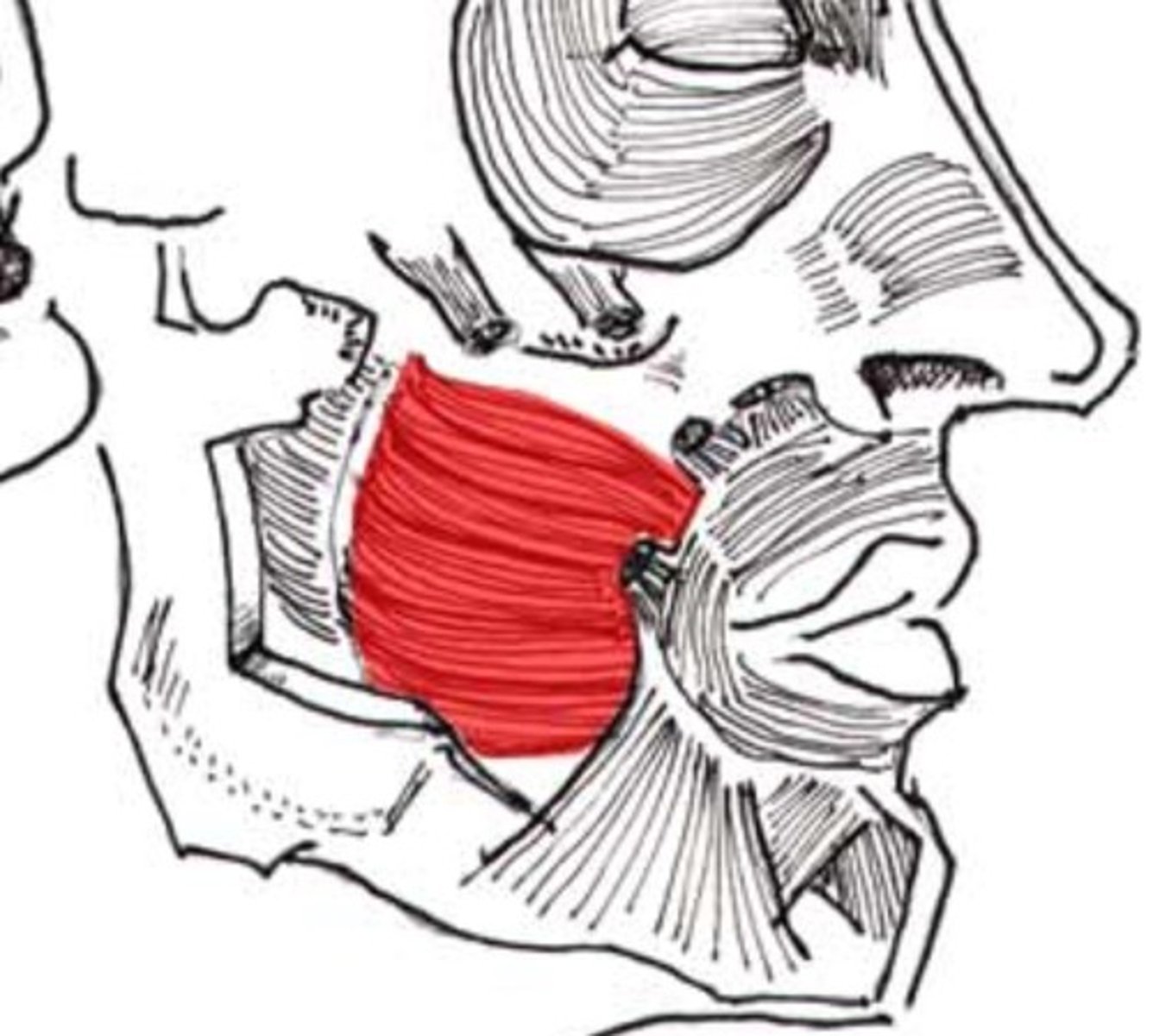
Buccinator insertion (muscle of facial expression)
angle of mouth, orbicularis oris
Buccinator expression (muscle of facial expression)
Flattens cheek/ assists in chewing; assists the muscles of mastication (MMTL)
Risorius origin (muscle of facial expressions)
Fascia superficial to masseter muscle
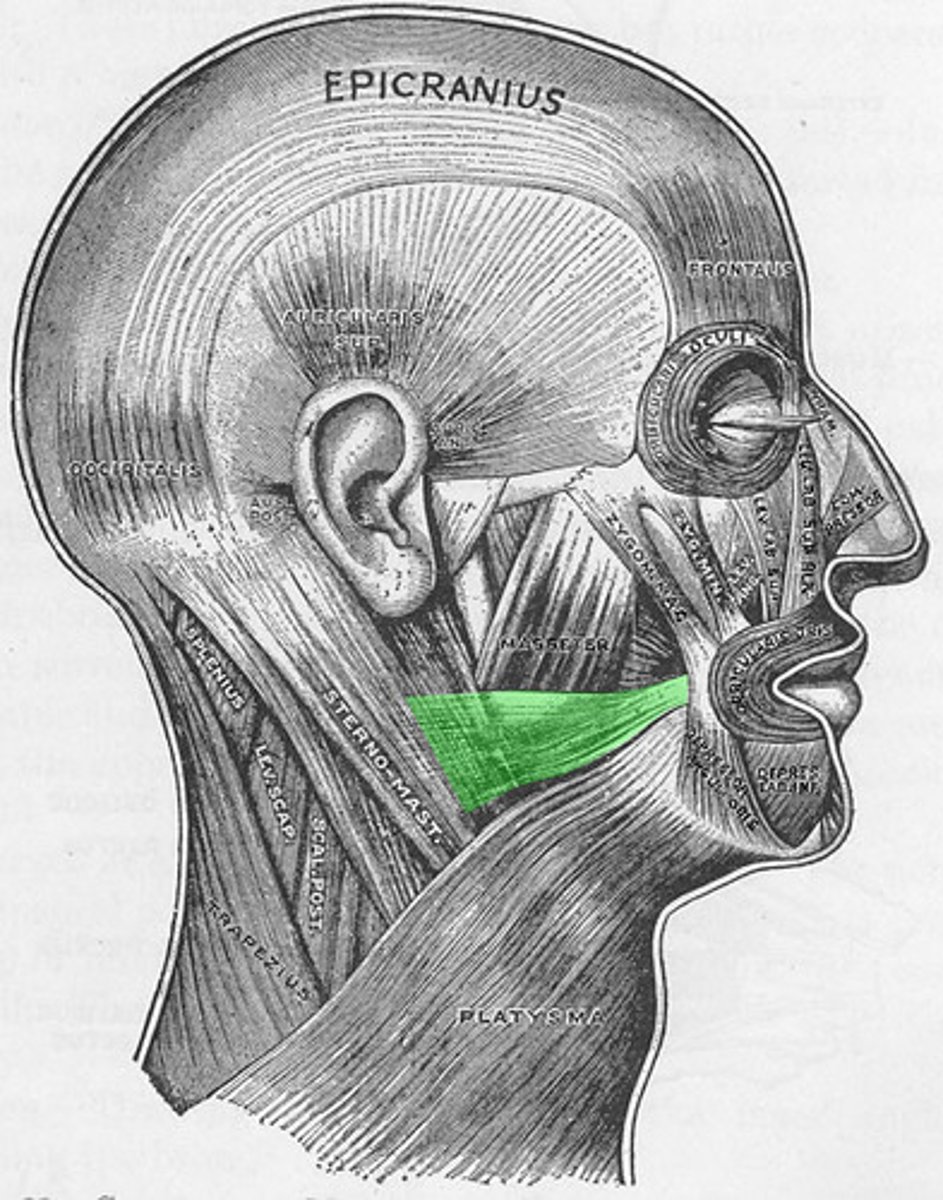
Risorius Insertion (muscle of facial expression)
Angle of mouth
Risorius expression (muscle of facial expression)
smiling widely

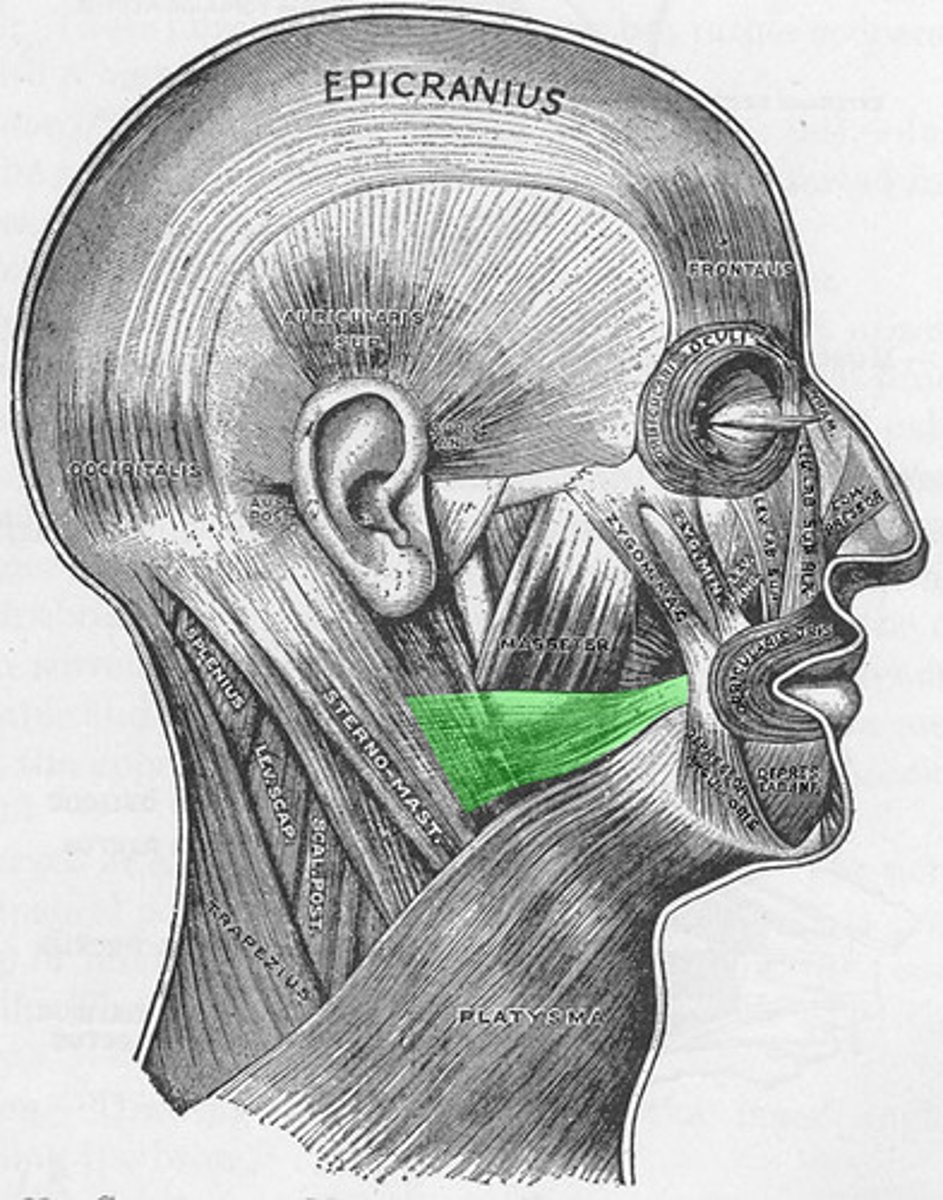
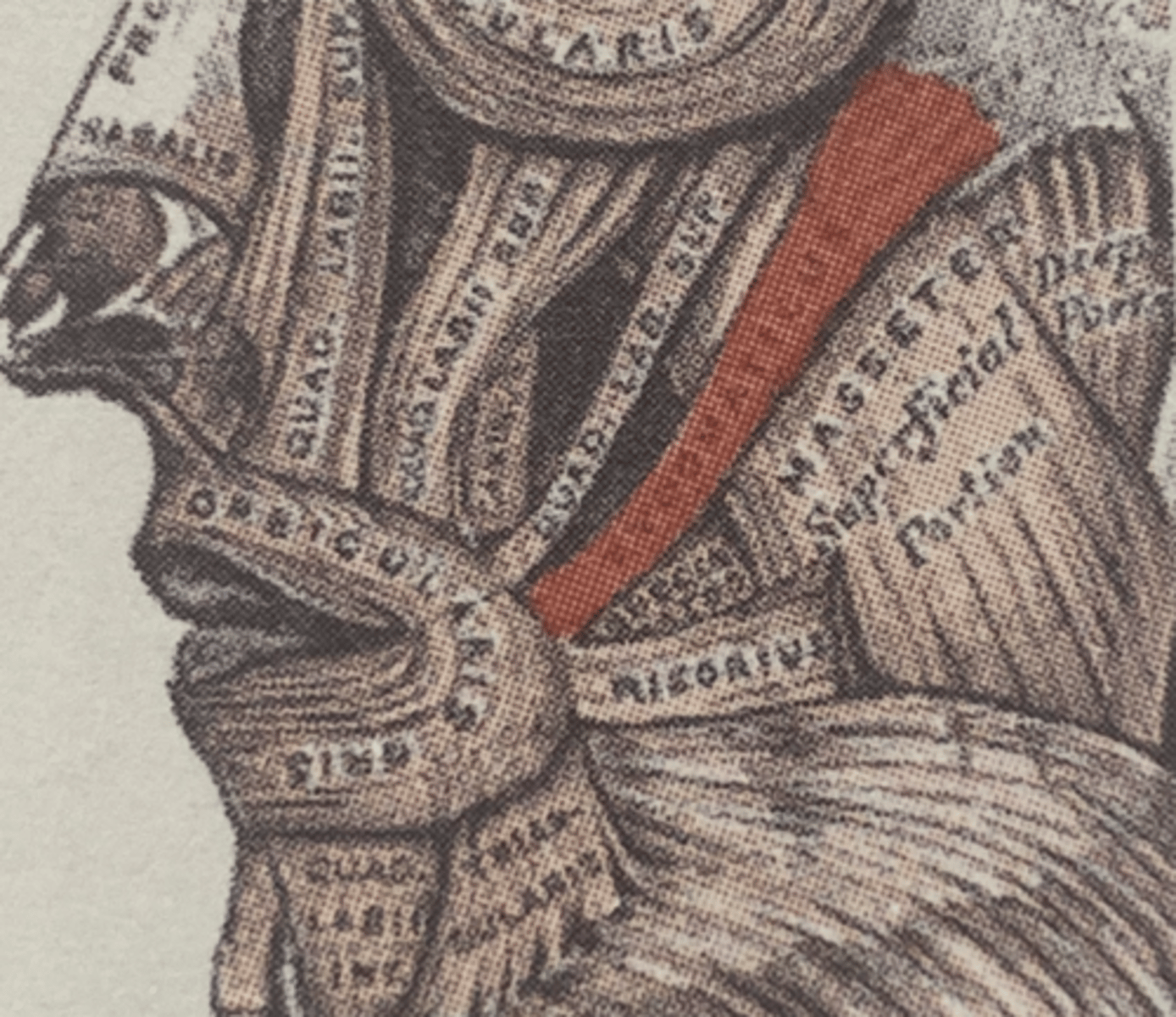
Zygomaticus Origin (muscle of facial expression)
zygomatic bone
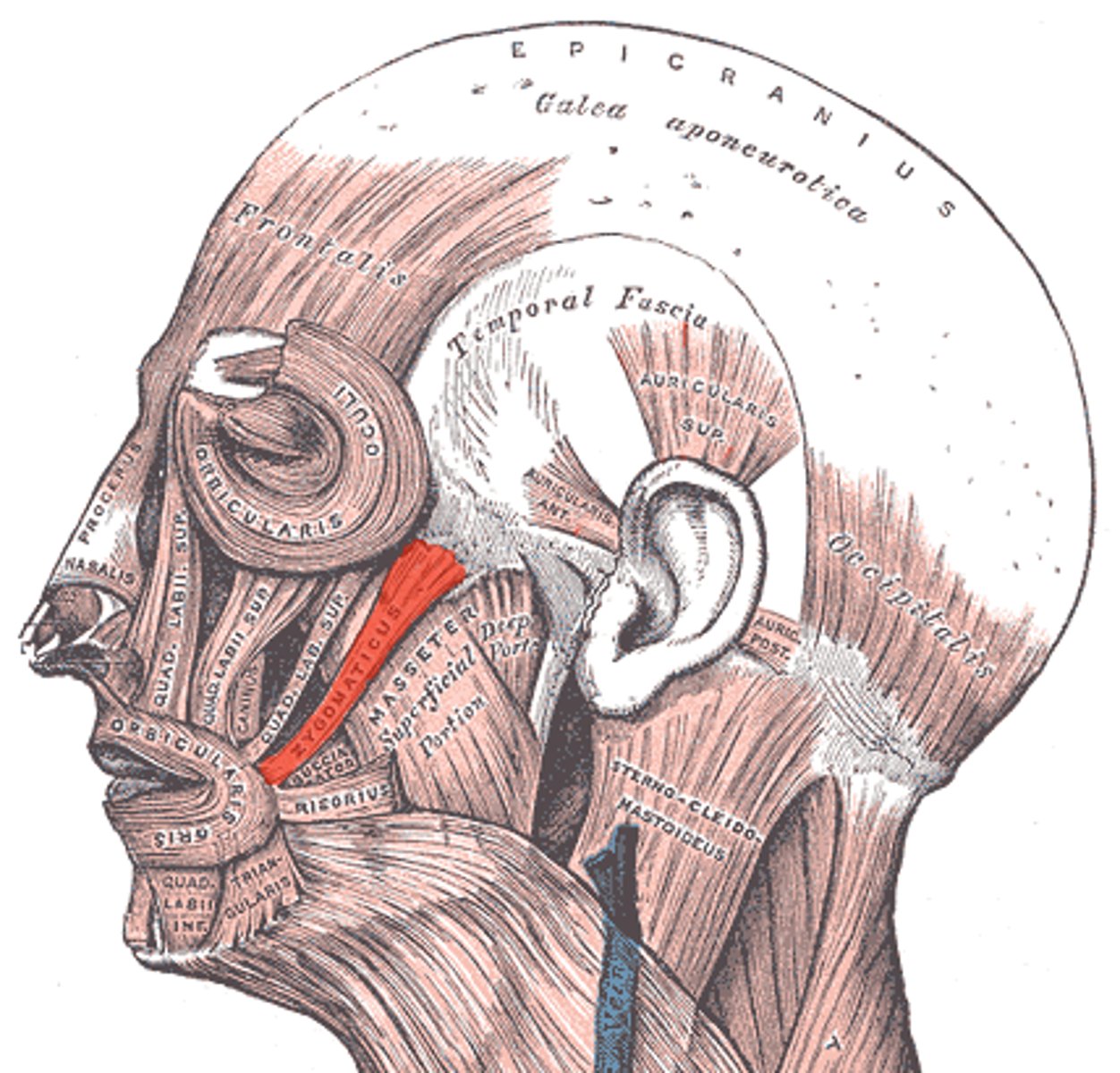
Zygomaticus Insertion (muscle of facial expression)
Major: Angle of mouth
Minor: Upper lip
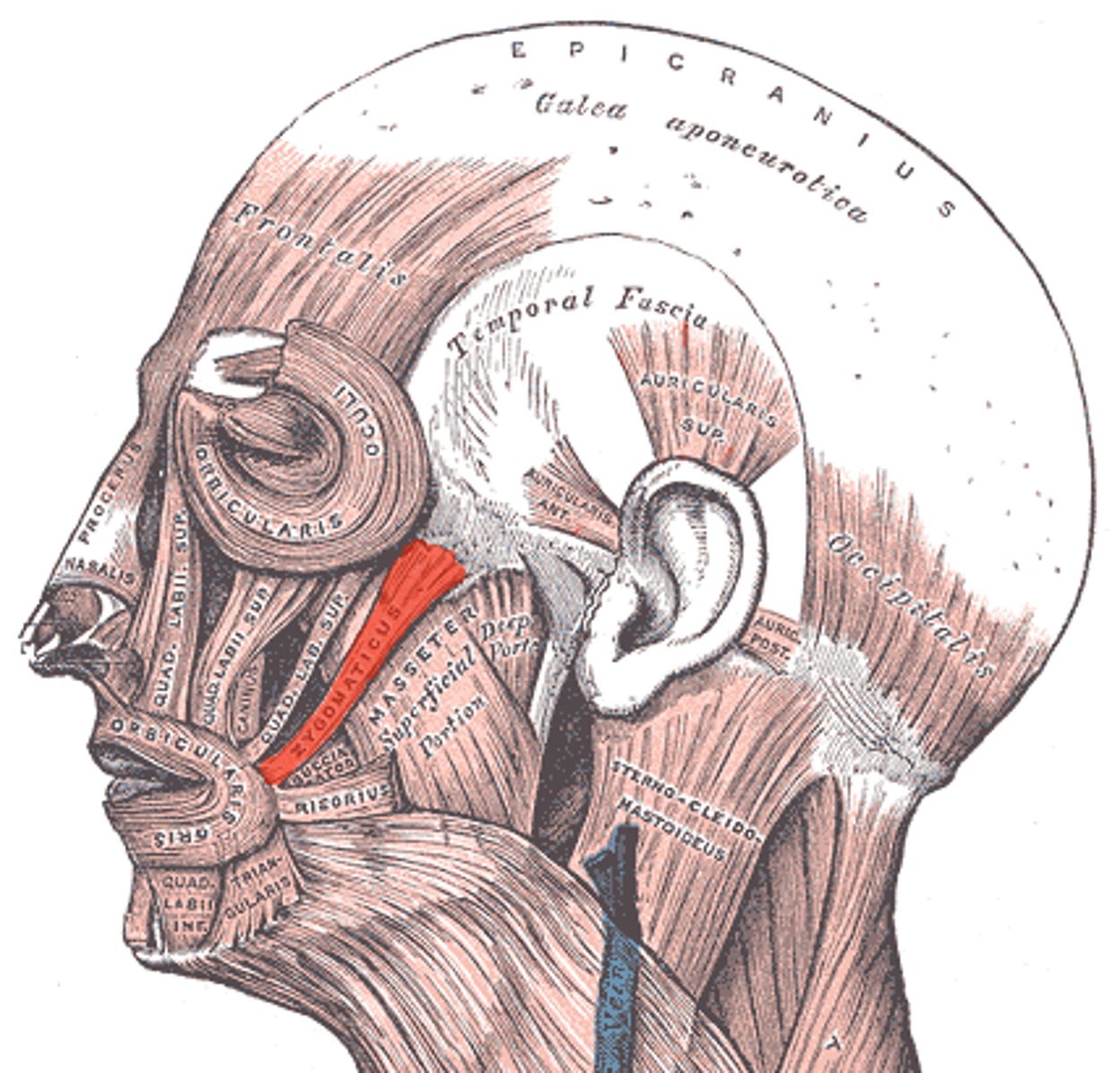
Zygomaticus Expression (muscle of facial expression)
smiling and raising upper lip
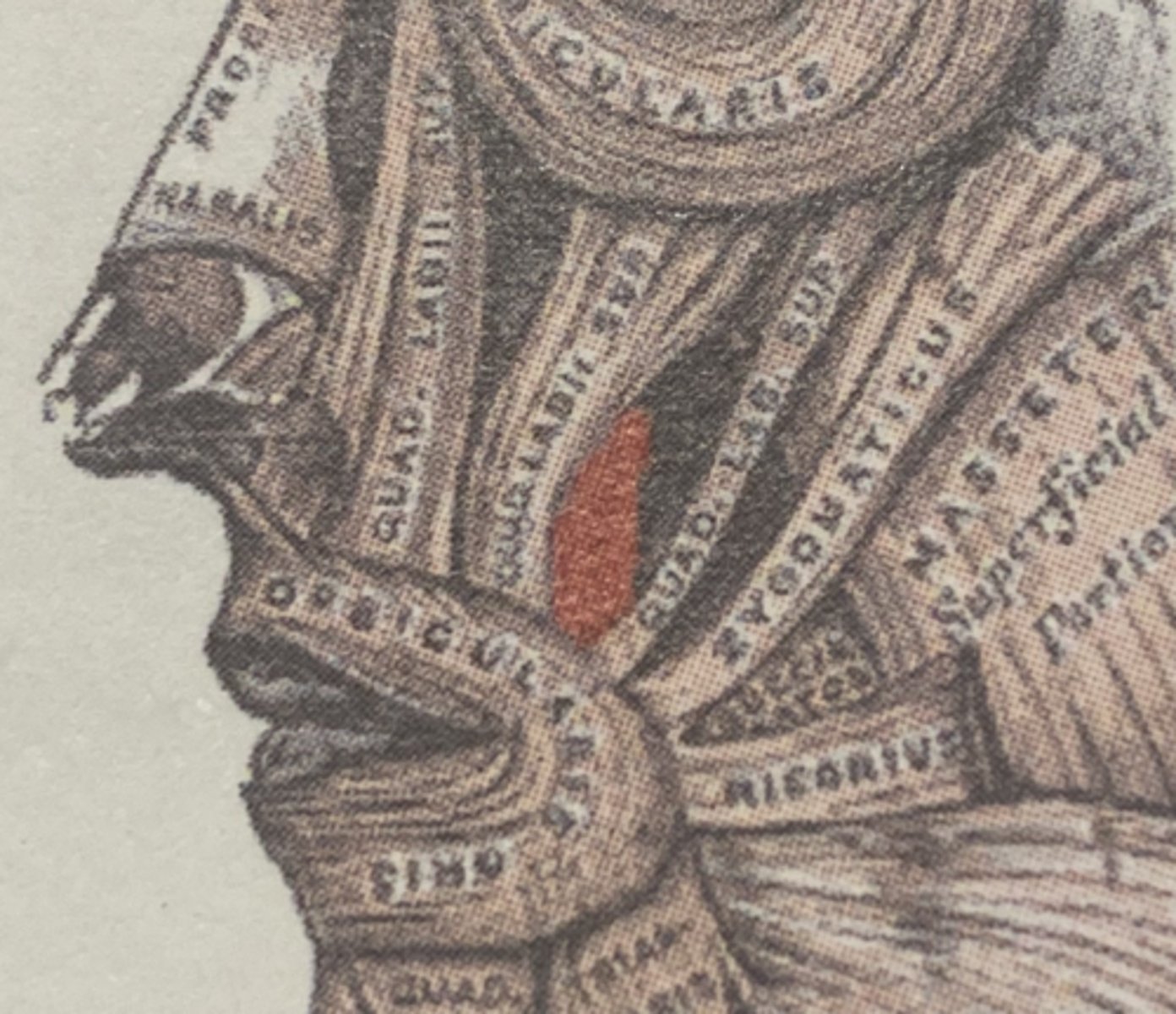
Levator anguli oris origin (muscle of facial expression)
canine fossa of maxilla
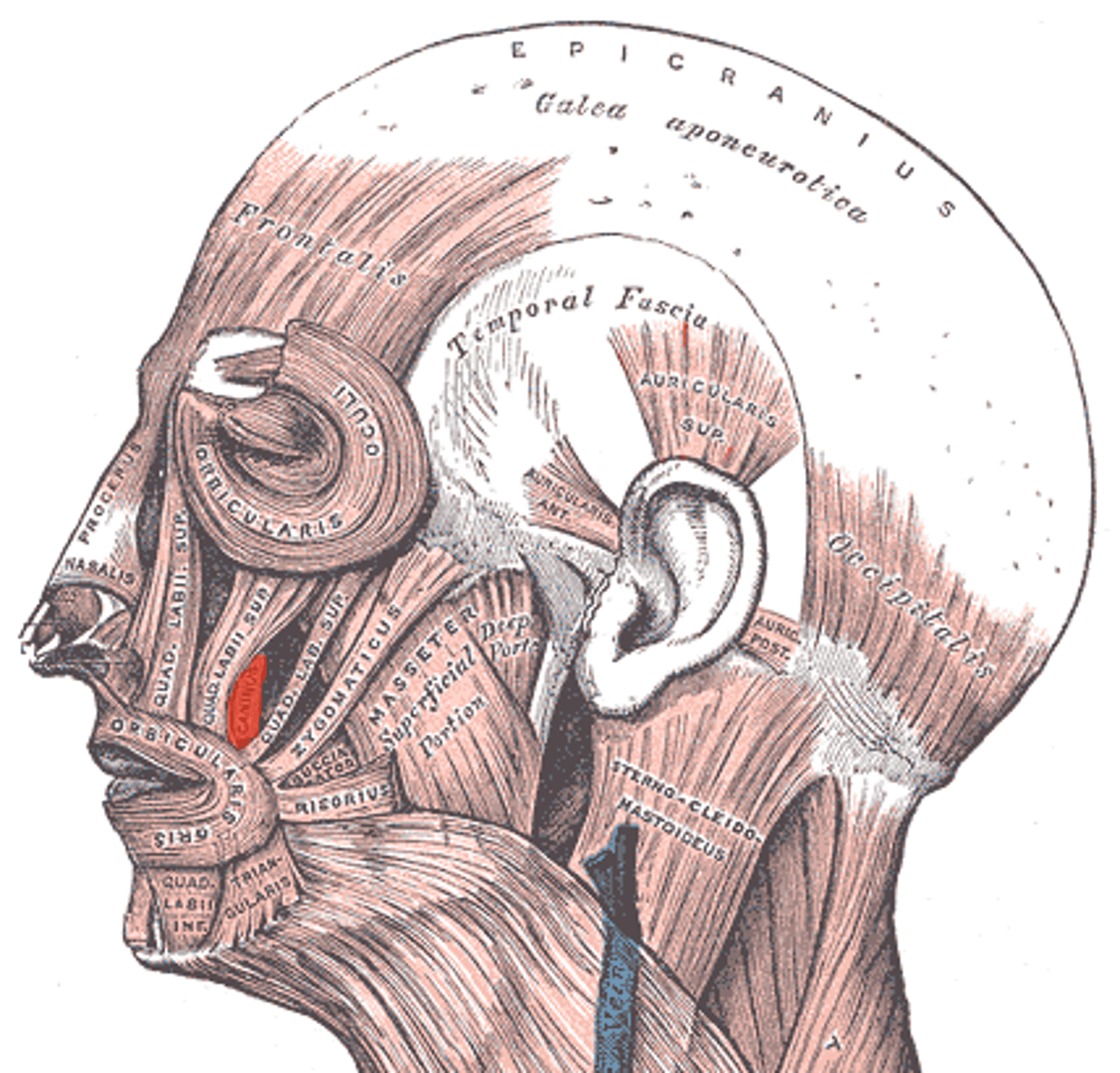
Levator anguli oris insertion (muscle of facial expression)
angle of mouth
Levator anguli oris expression
smiling
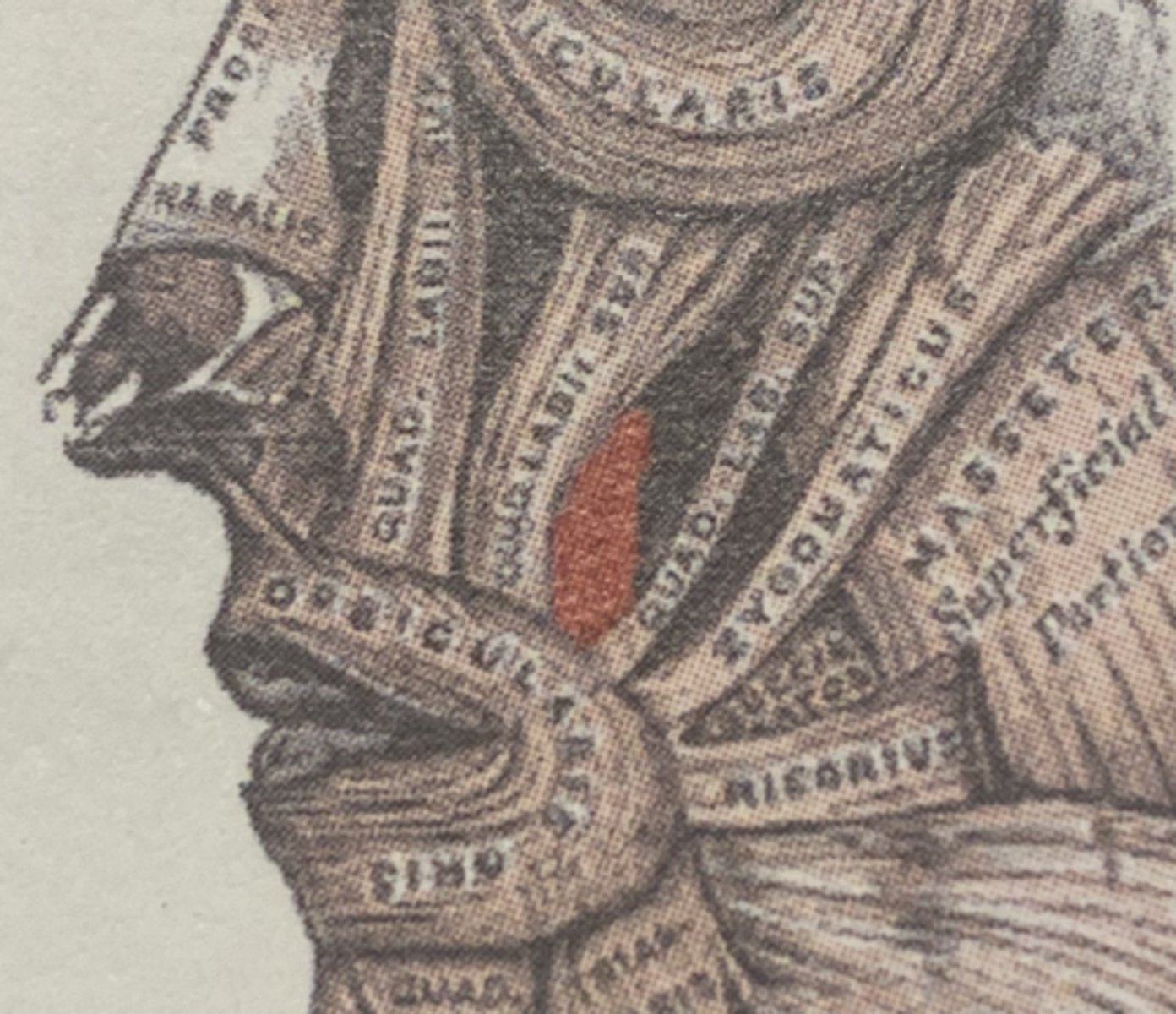
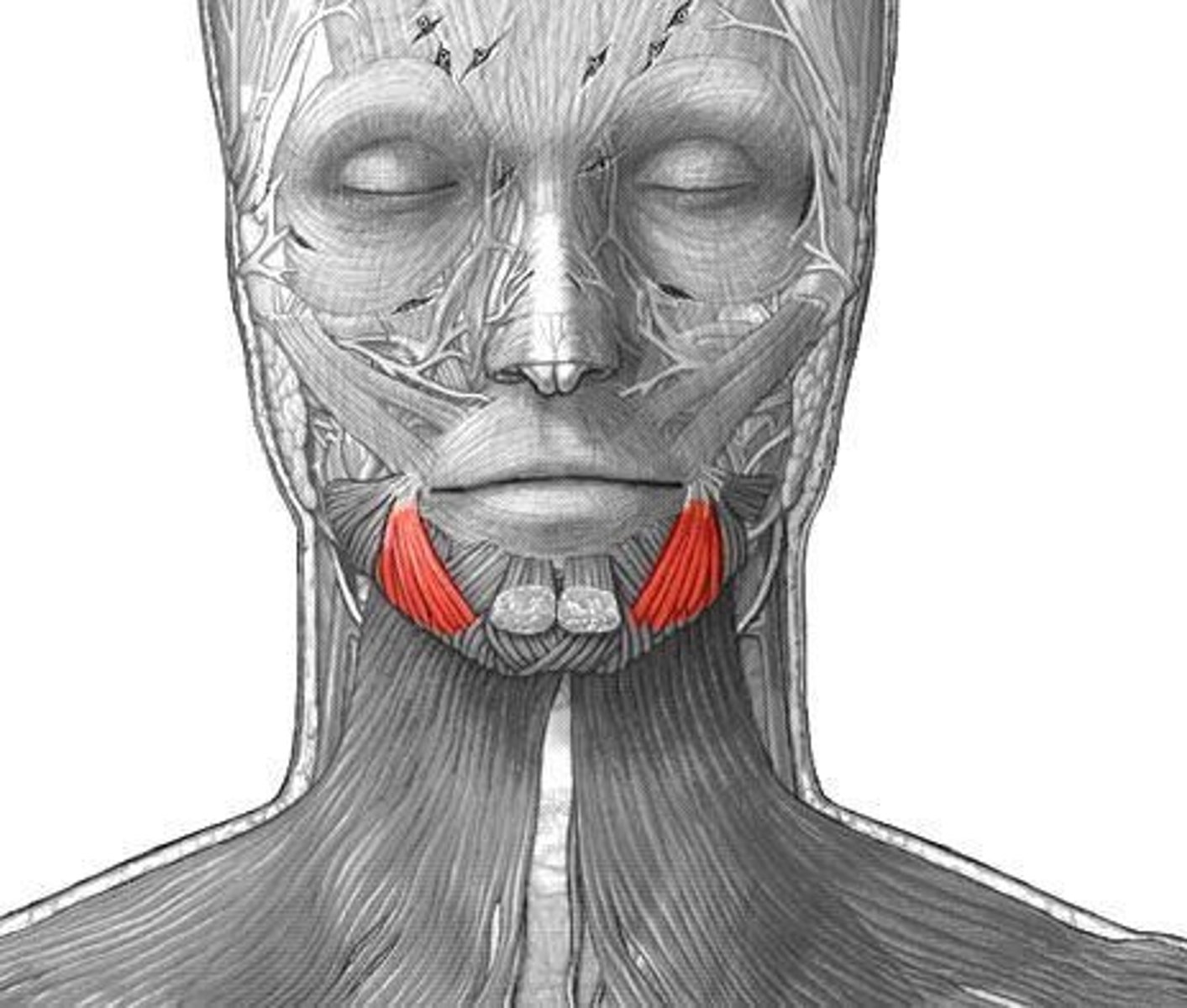
Depressor anguli oris origin (muscle of facial expression)
mandible
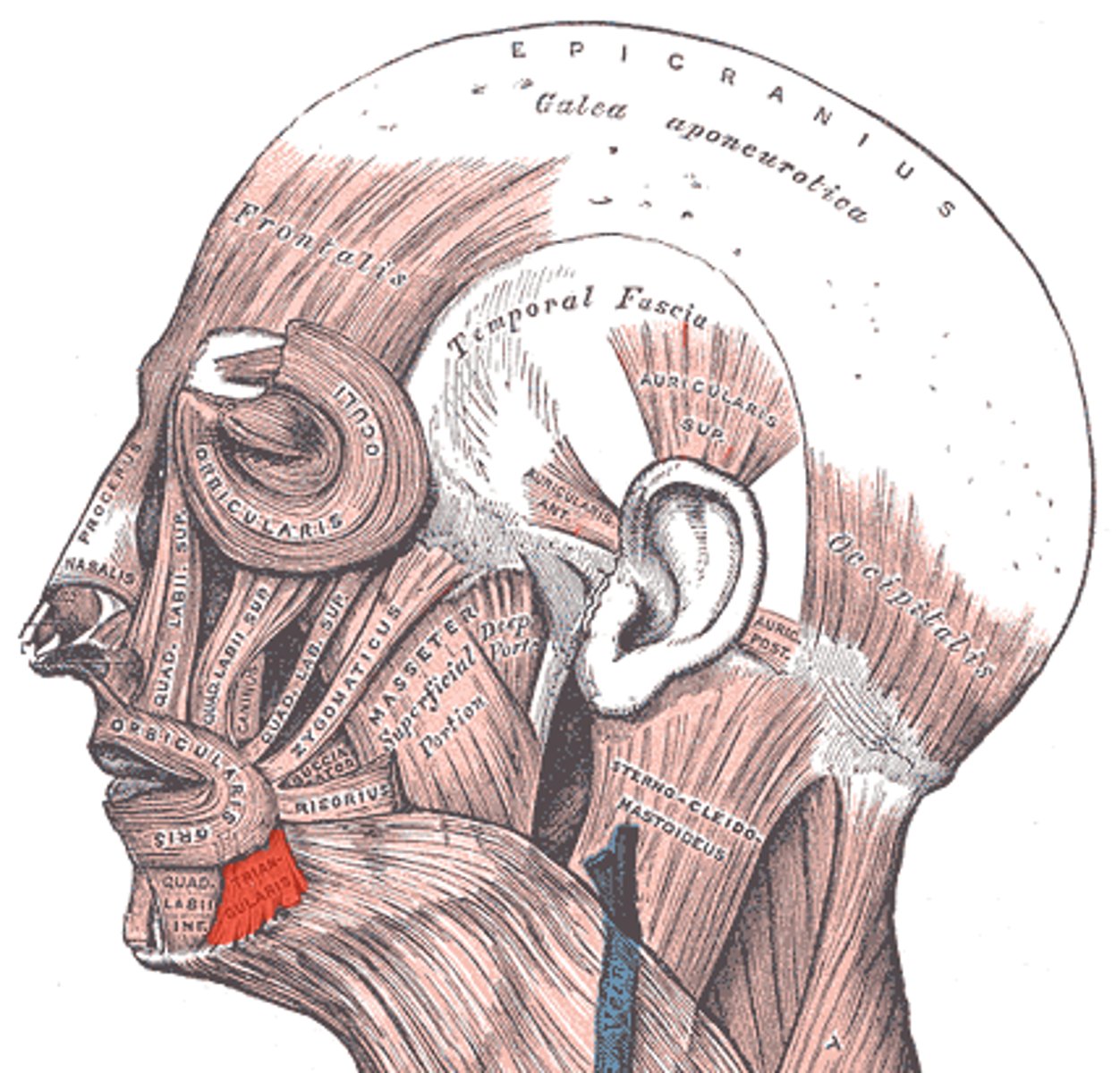
Depressor anguli oris Insertion (muscle of facial expression)
angle of mouth
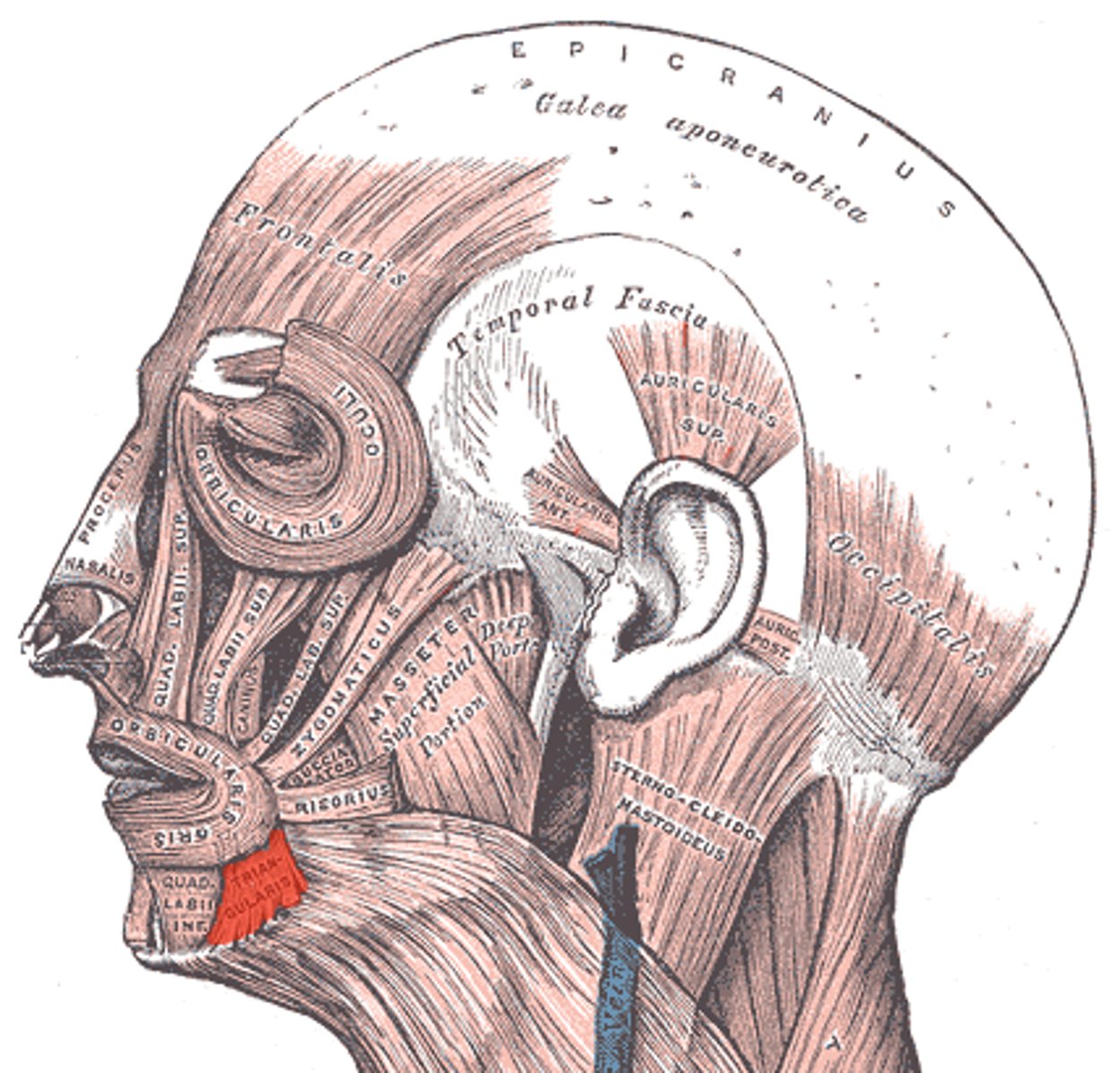
Depressor anguli oris expression (muscle of facial expression)
Frowning
True or false:
All facial muscles are innervated by the Seventh (VII) cranial nerve or facial nerve
True
Seventh (VII) cranial nerve is also called
Facial nerve
True or false:
In general, facial muscles have origins with bone and insertions in skin tissue
True
Muscles of mastication
-Mom Makes Tasty Lasagna
Masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid
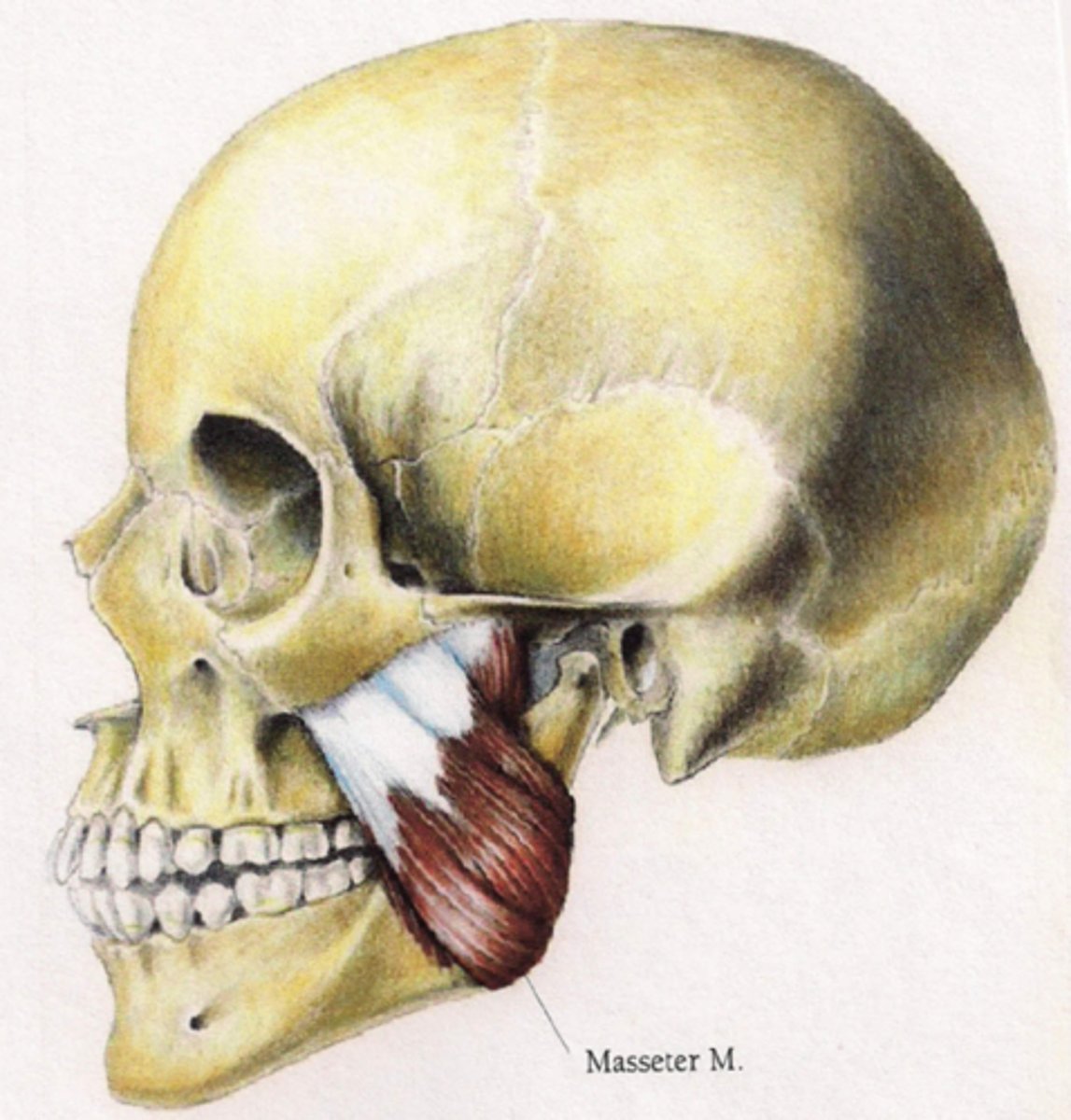
masseter origin (muscle of mastication)
Superficial head: Anteriror 2/3 of the lower boarder of the zygomatic arch
Deep head: posterior 1/3 and medial surface of the zygomatic arch
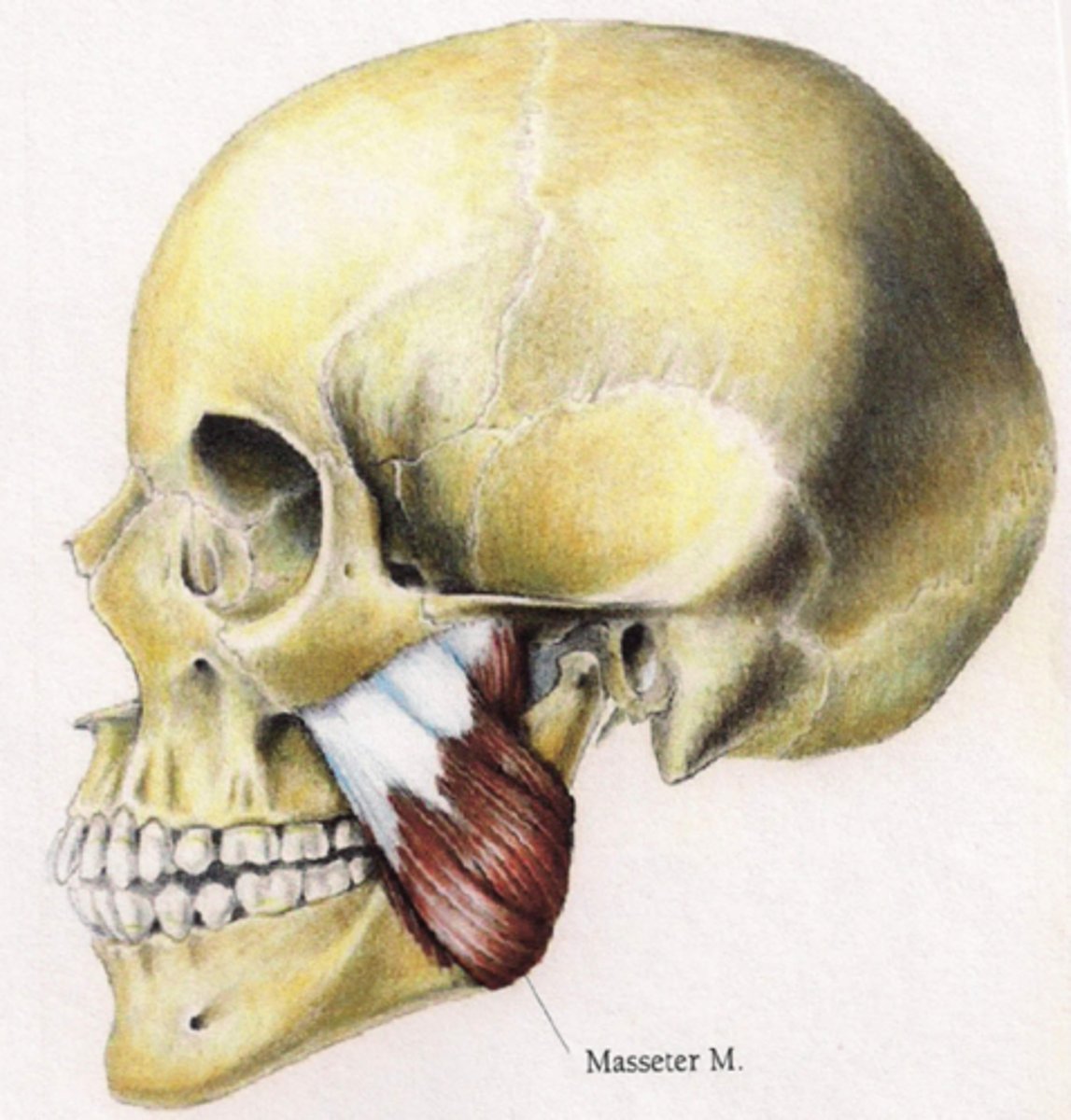
True or false: Masseter muscle can become enlarged in patients who habitually clench or grind (bruxism)
True
Masseter insertion (muscle of mastication)
Superficial head: angle of the mandible
Deep head: upper half of ramus of and as high as the coronoid process of the mandible
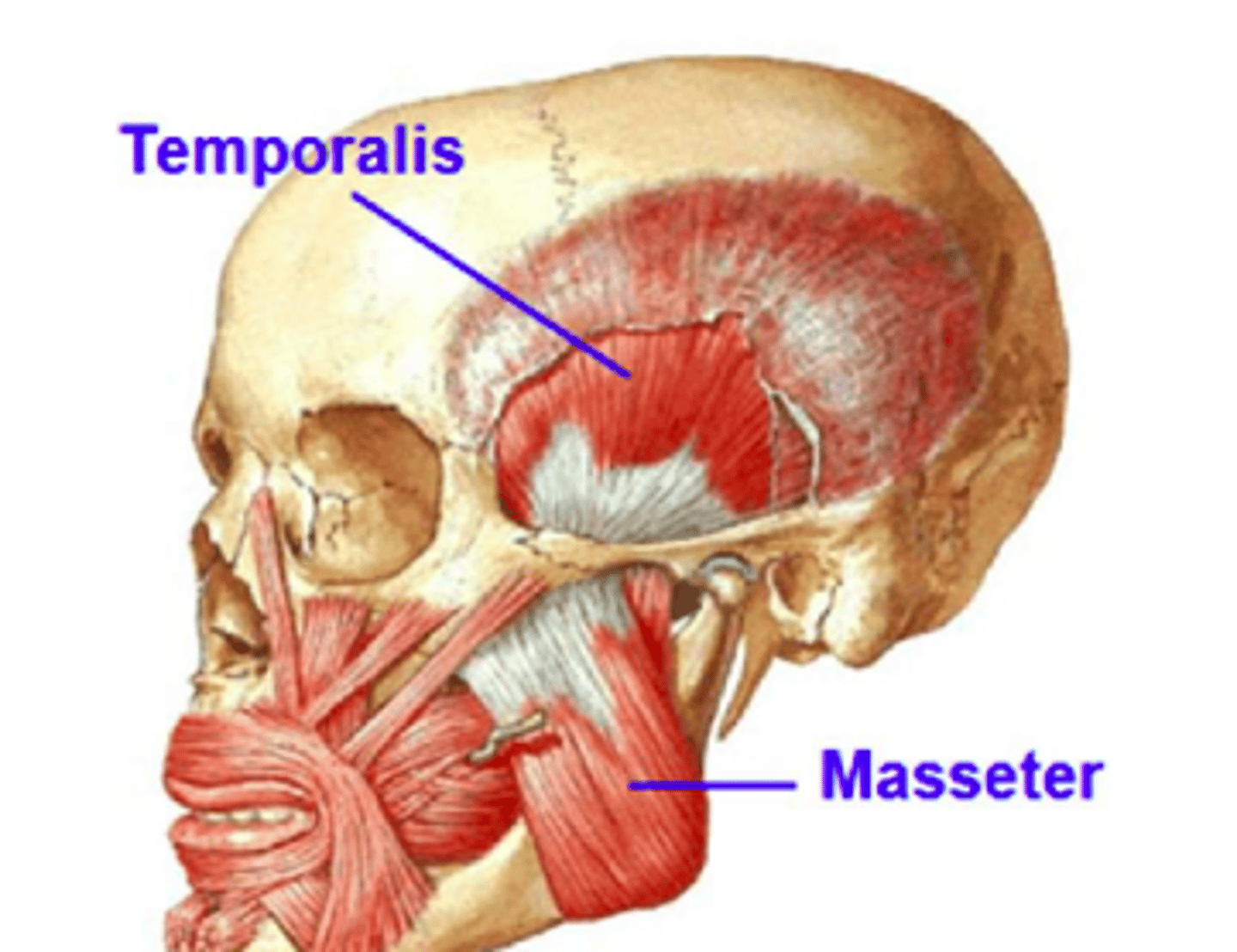
Masseter Movement (muscle of mastication)
Elevation of mandible during jaw closing
Temporalis origin (muscle of mastication)
Temporal fossa
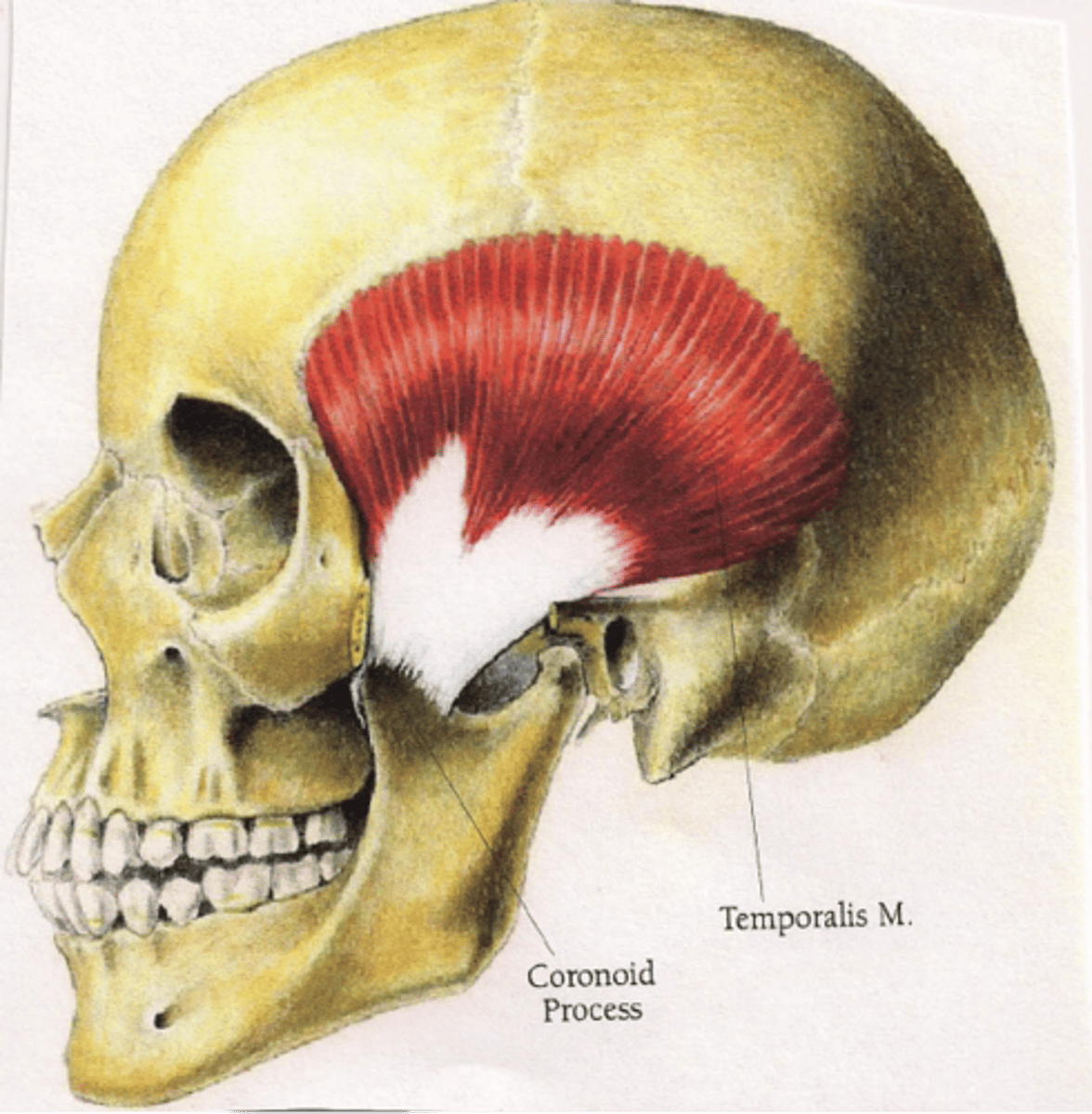
Temporalis insertion (muscle of mastication)
coronoid process of mandible
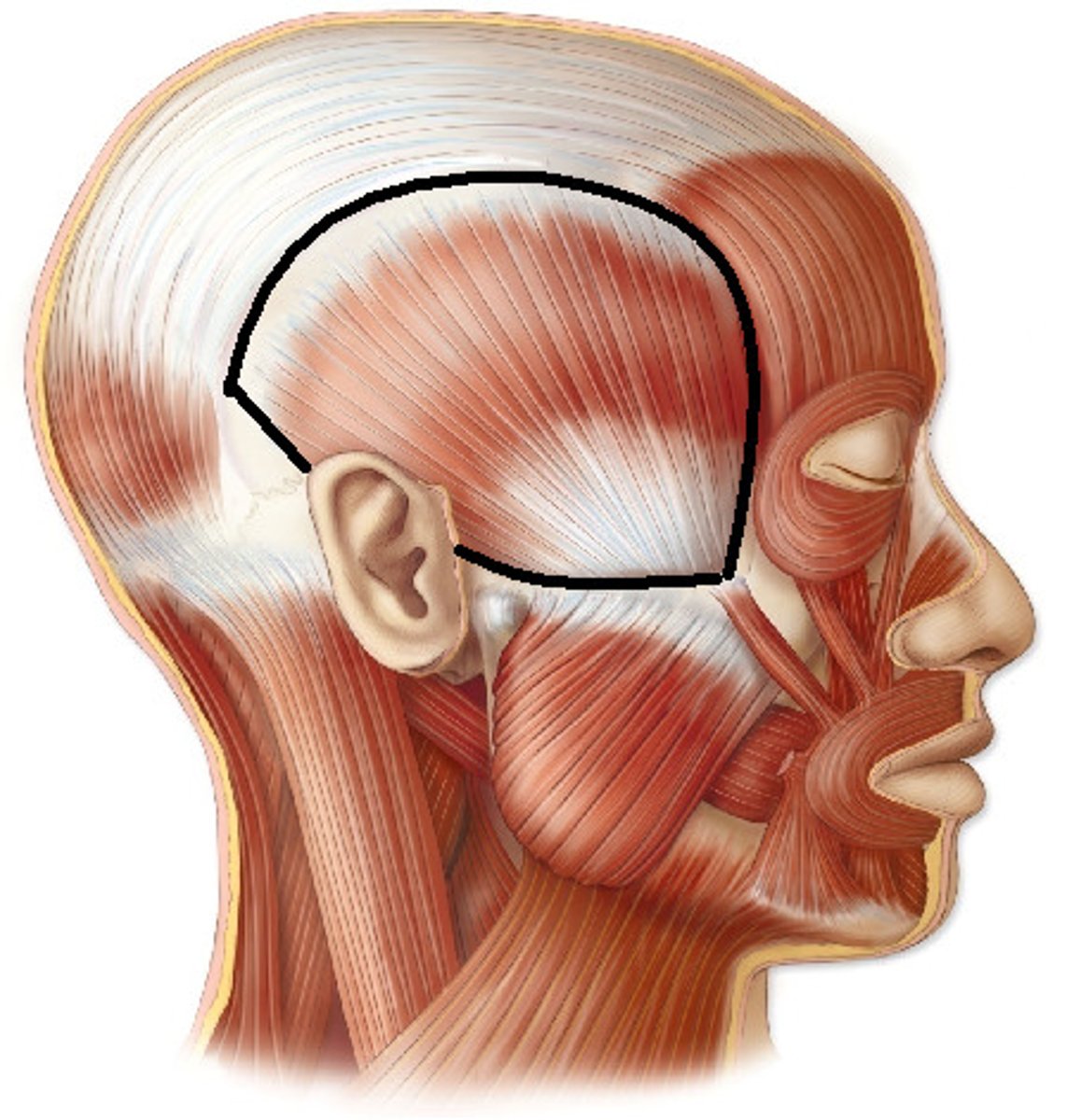
Temporalis movement (muscle of mastication)
Elevation of mandible during jaw closing
Retraction of mandible (lower jaw backward)
Medial Pterygoid origin (muscle of mastication)
Pterygoid fossa of Sphenoid Bone
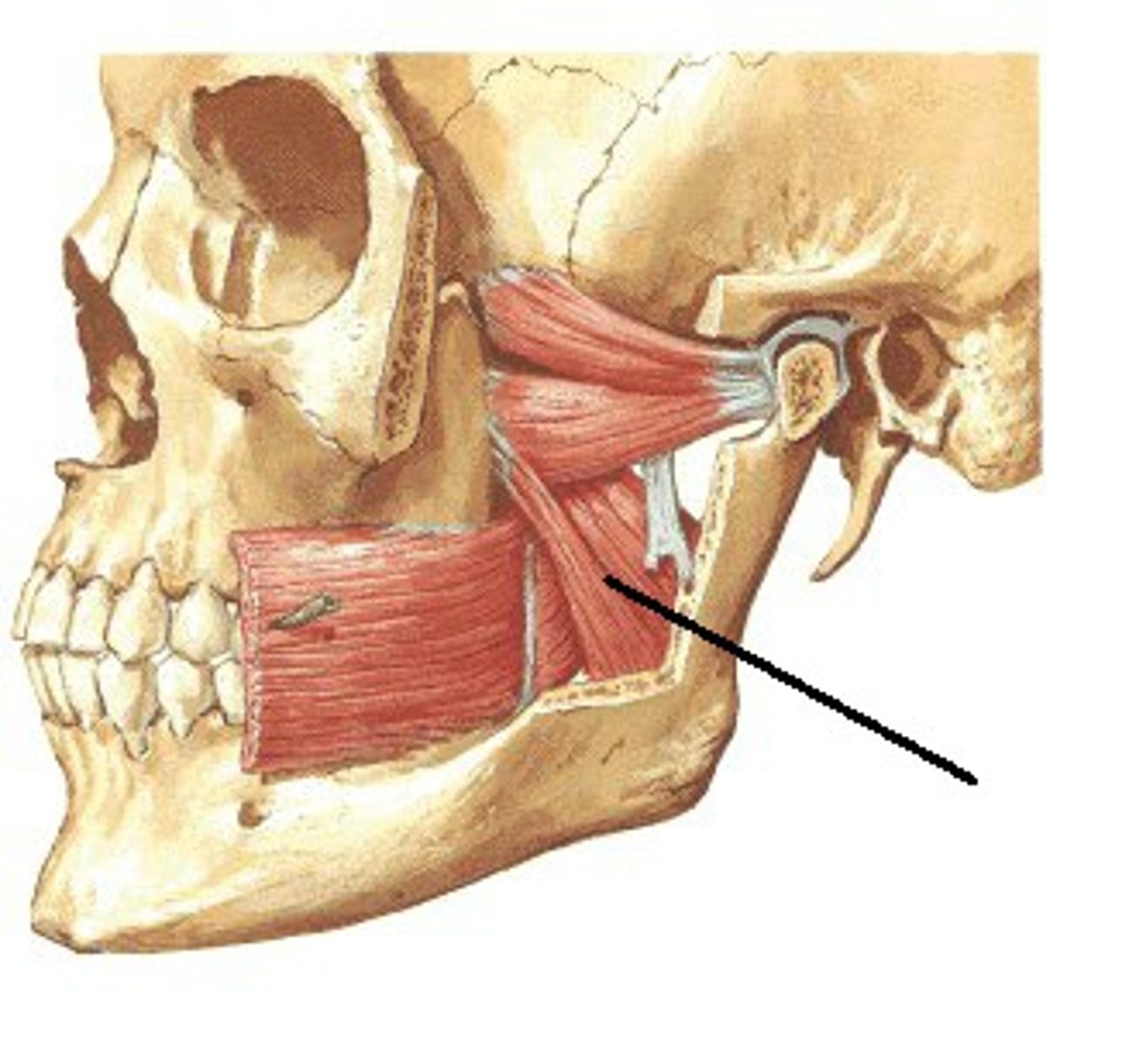
Medial Pterygoid Insertion (muscle of mastication)
Angle of mandible
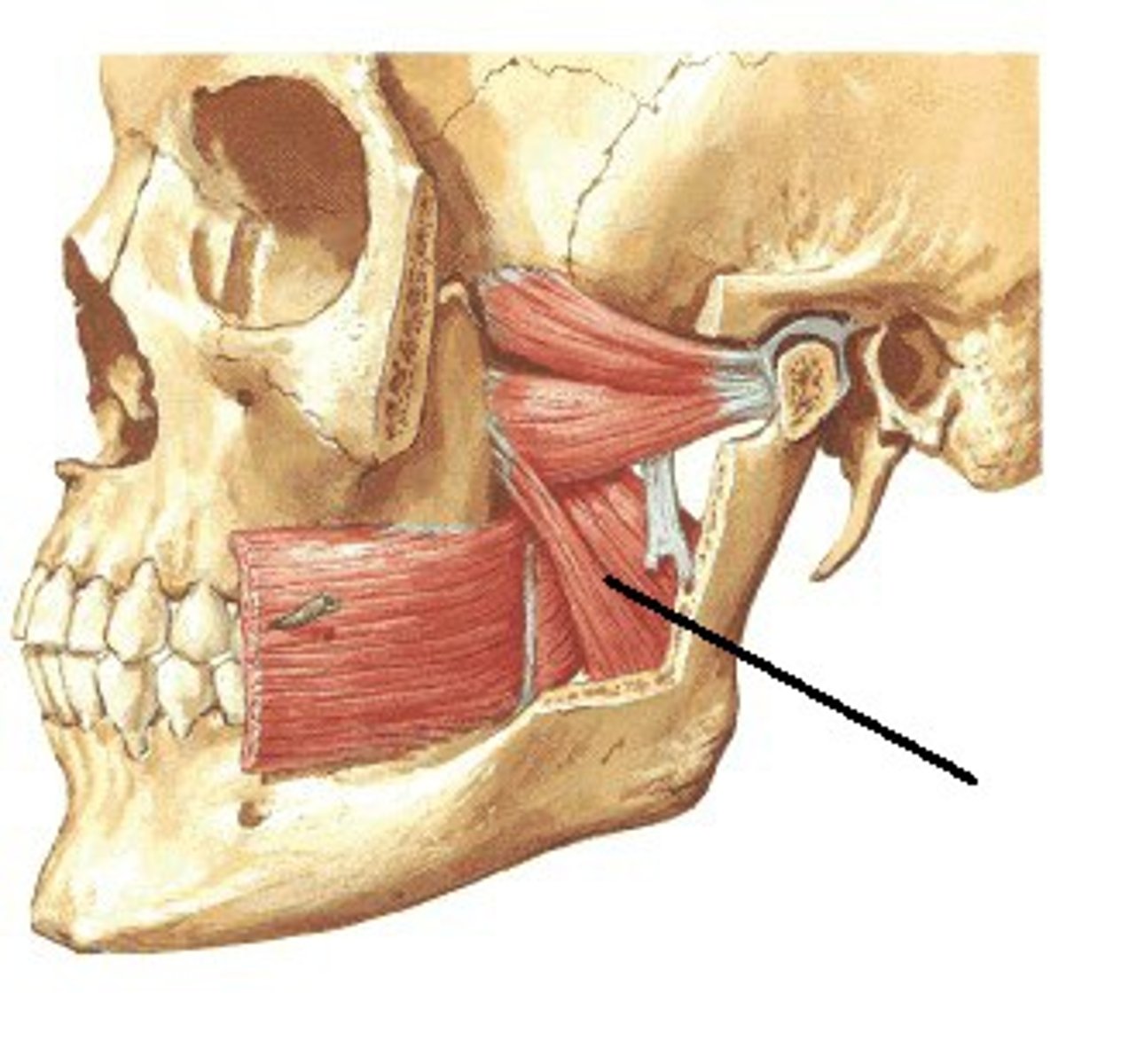
Medial Pterygoid Movement (muscle of mastication)
Elevation of mandible during jaw closing
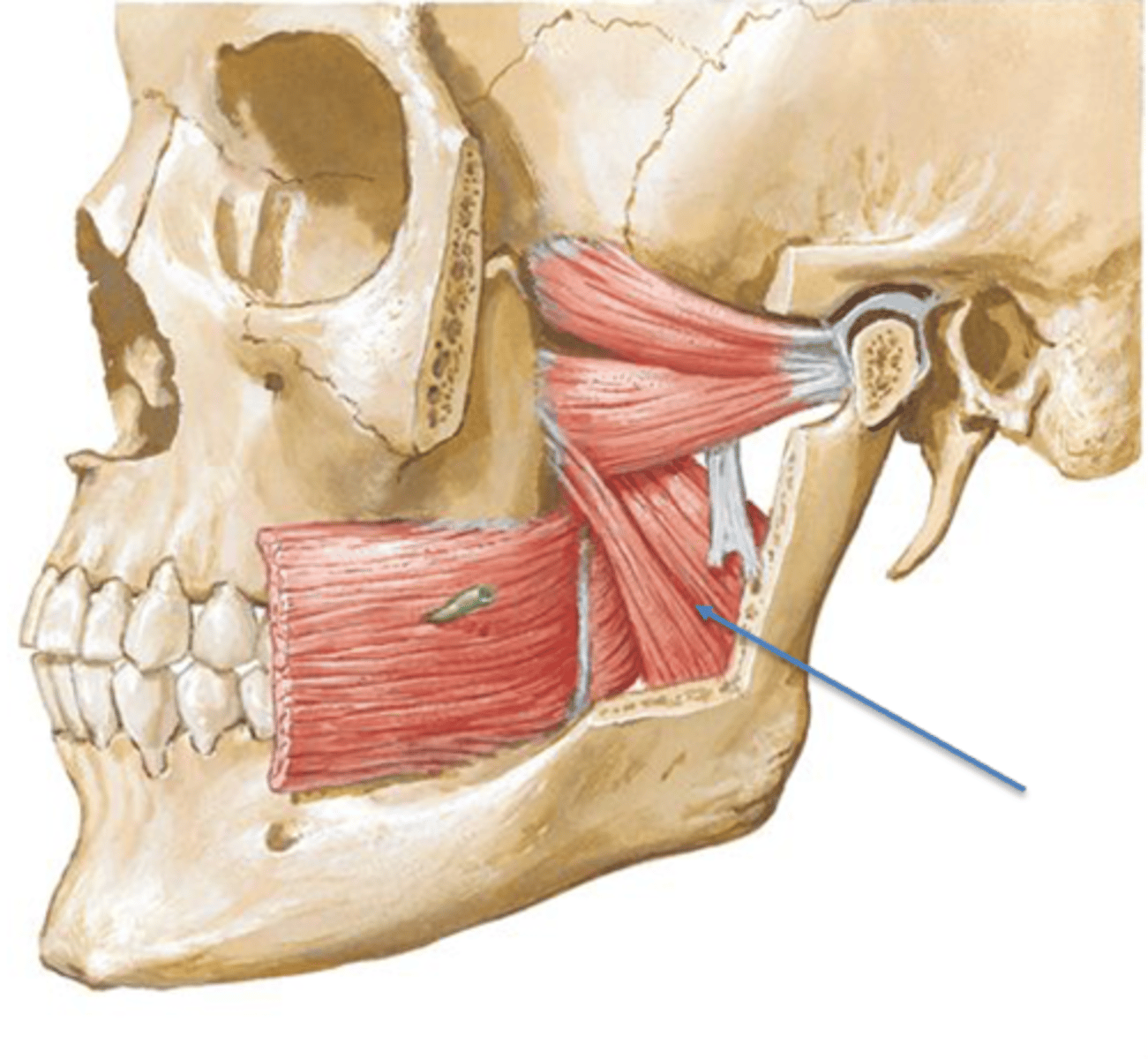
Lateral Pterygoid Origin (muscle of mastication)
Superior head: Greater wing of Sphenoid bone
Inferior head: Lateral pterygoid plate from sphenoid bone
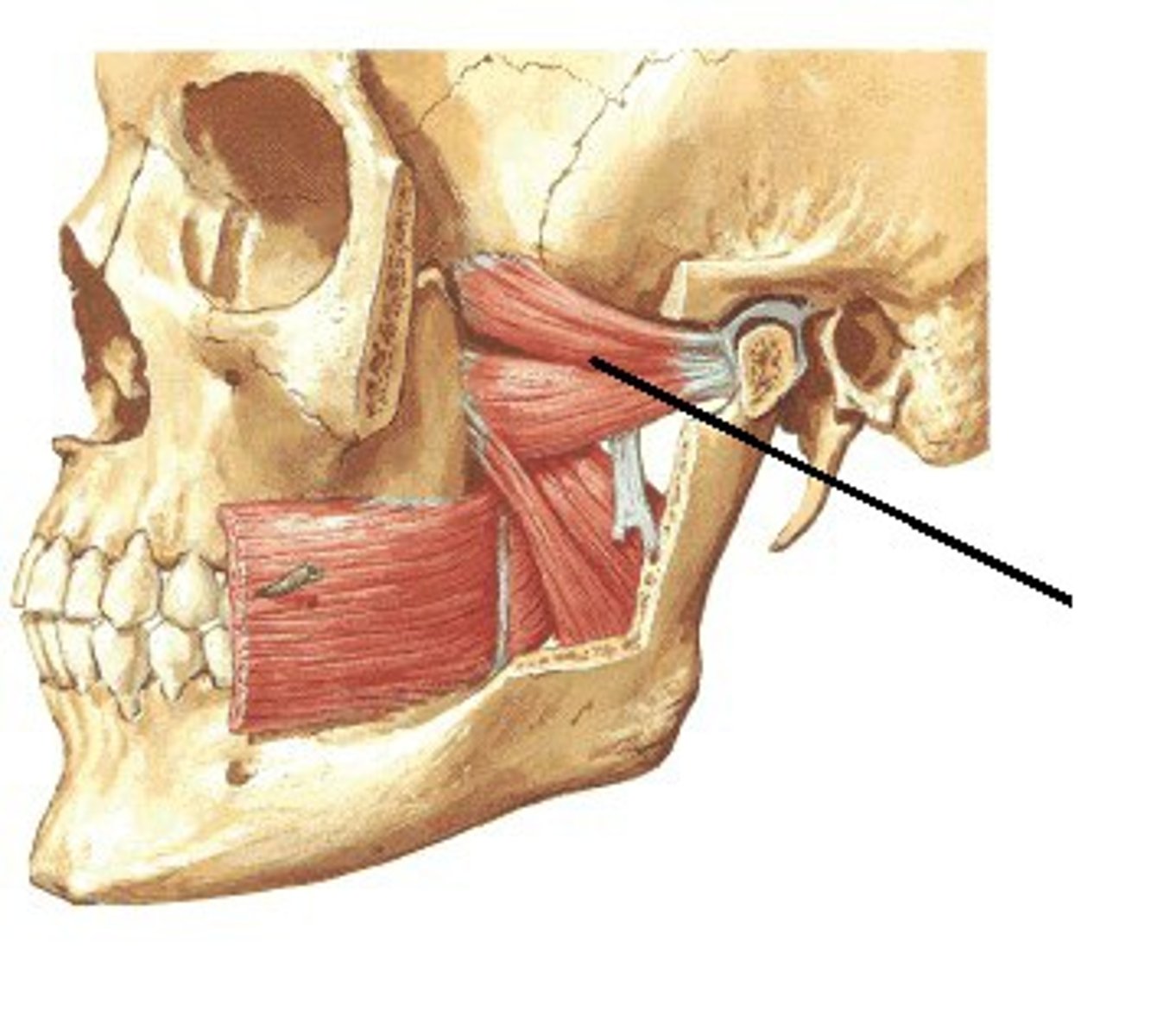
what muscle of mastication is most likely affected by direct trauma to the TMJ?
Lateral Pterygoid
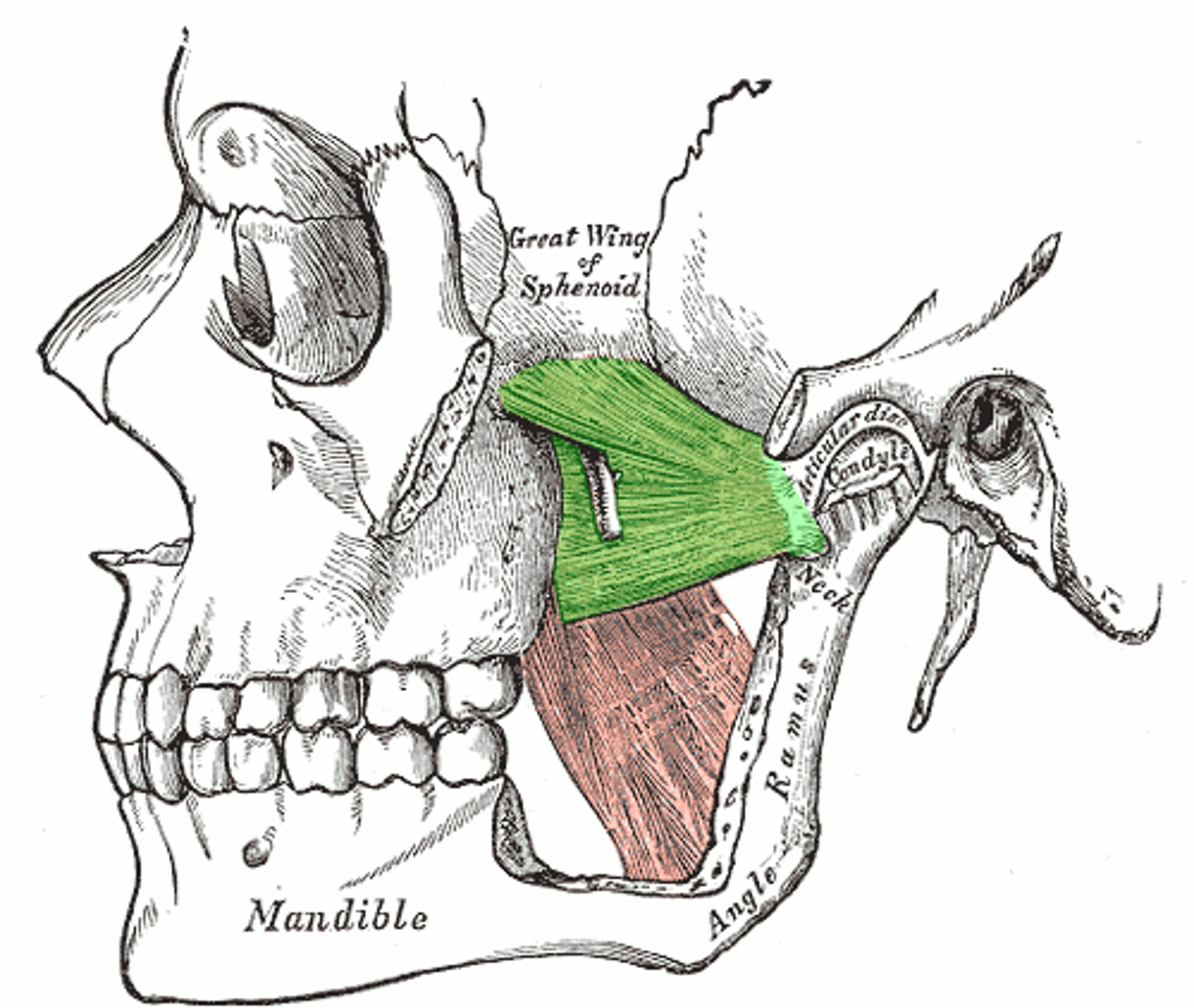
Lateral Pterygoid Insertion (muscle of mastication)
Both heads: pterygoid fovea of mandible below condyloid process of mandible and intra-articular cartilage (articular disk) of TMJ
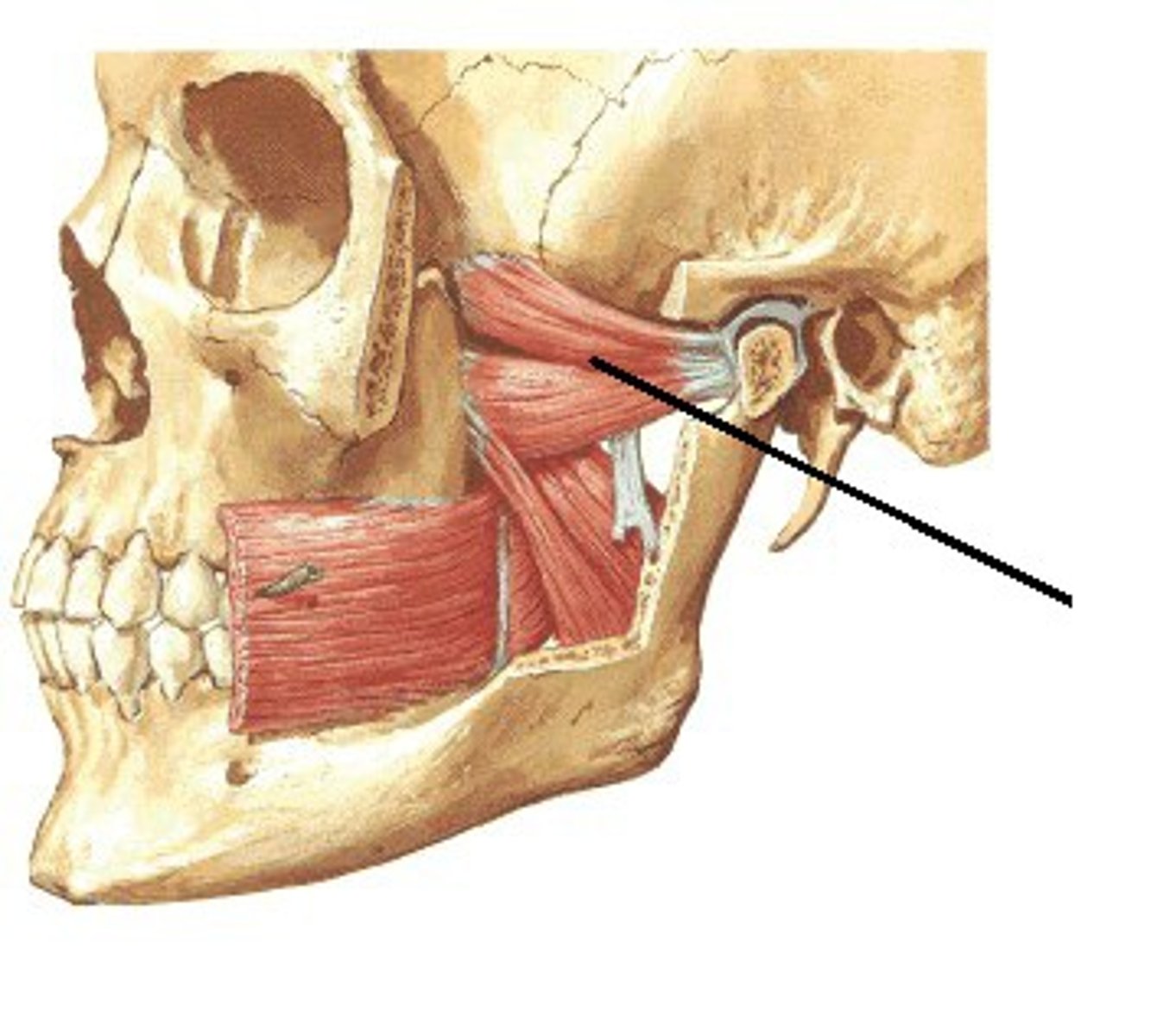
Lateral pterygoid movements (muscle of mastication)
Inferior Heads: Slight depression of mandible during jaw opening
One muscle: lateral deviation of mandible (shift lower jaw)
Both muscles: Protrusion of mandible (lower jaw forward)
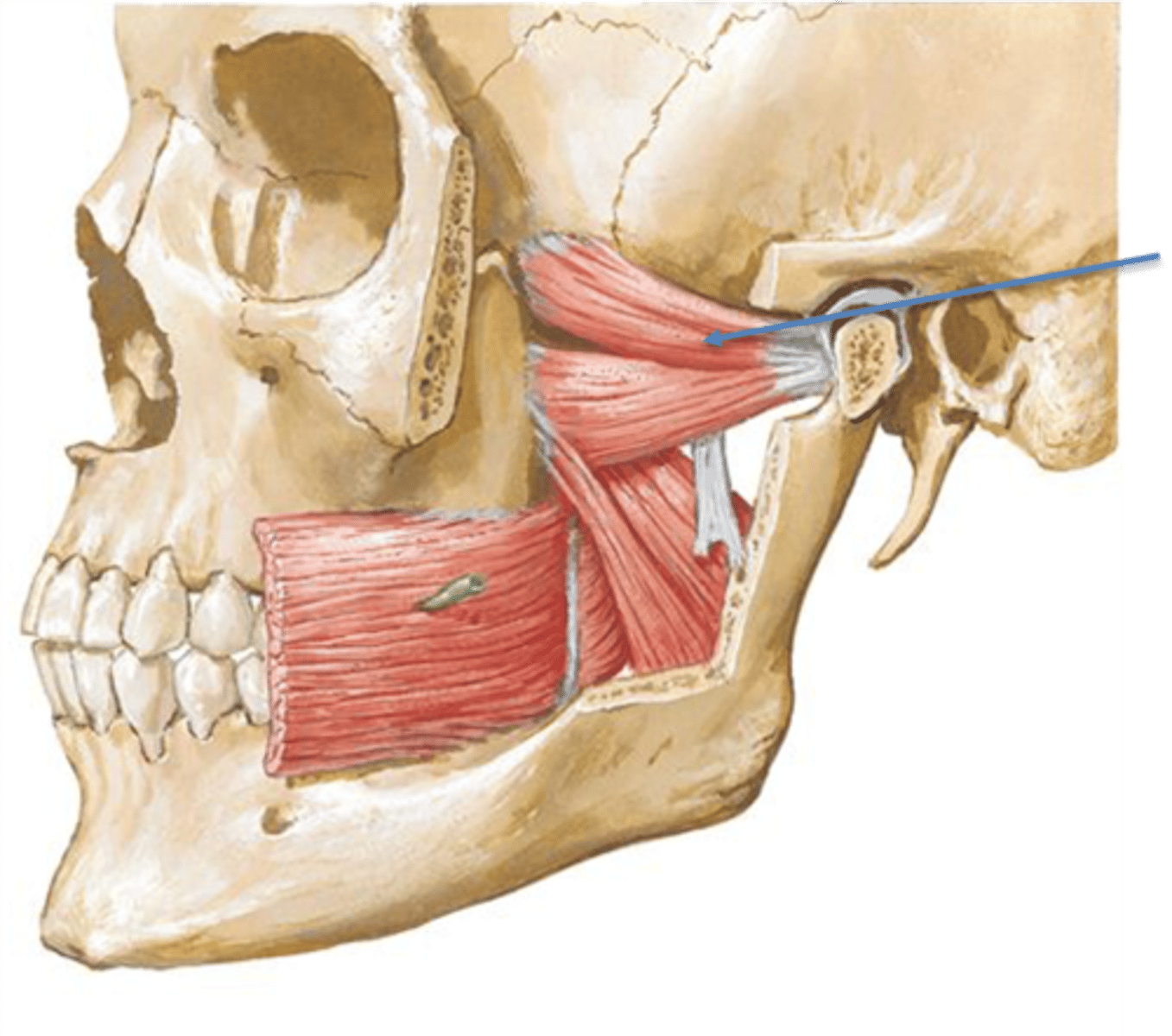
True or false:
All muscles of mastication are innervated by the mandibular division of the fifth cranial or trigeminal nerve (v3)
True
true or false:
Blood is supplied by the maxillary artery (branch of the external carotid artery) to all muscles of mastication
True
True or false:
All muscles of mastication insert on the mandible
True
True or false:
All muscles of the hyoid insert on the hyoid bone
True
Hyoid muscles assist in _________
mastication and swallowing
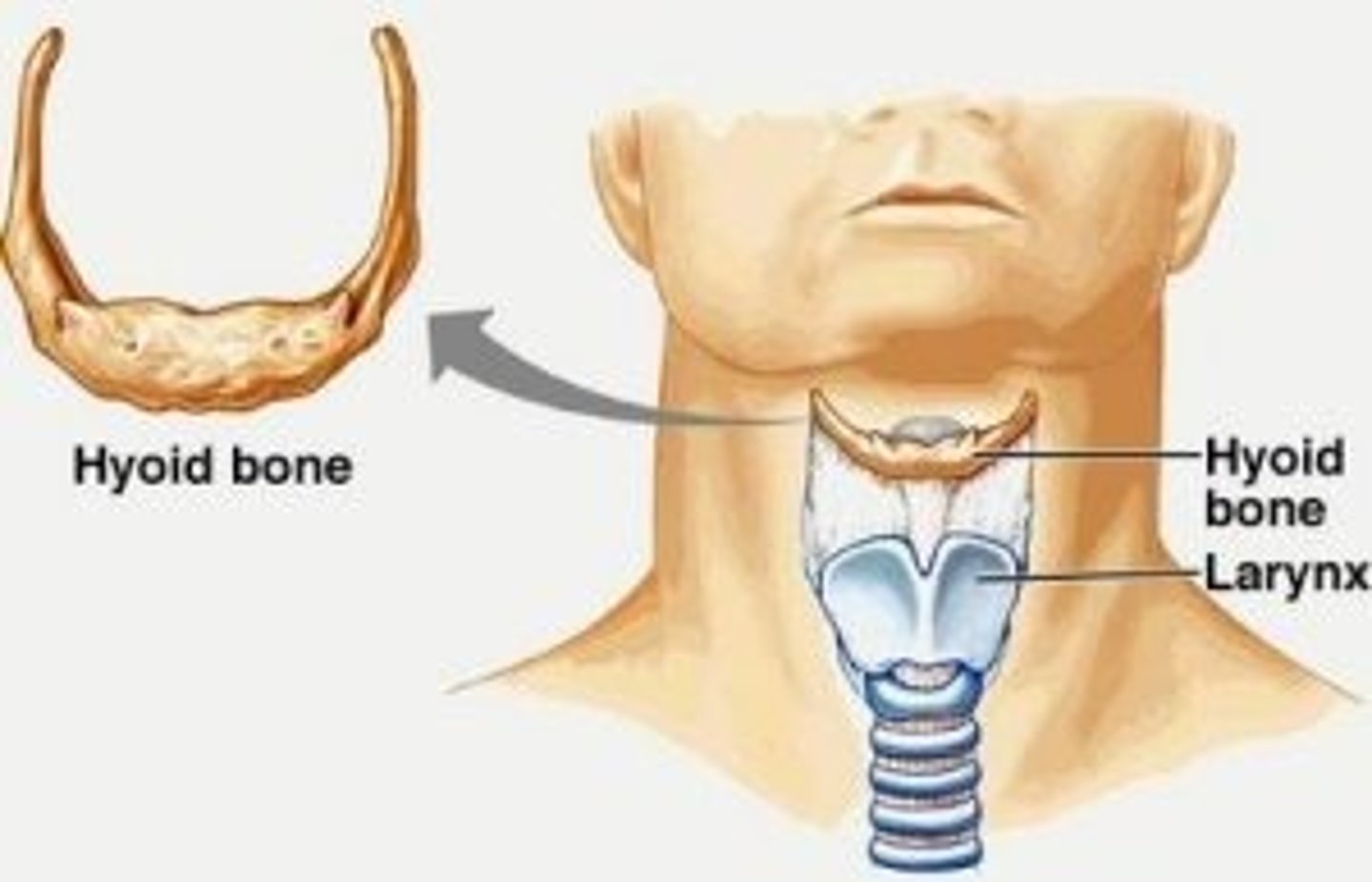
What bone does not articulate with any other bone?
hyoid bone
Mylohyoid makes up the
floor of the mouth
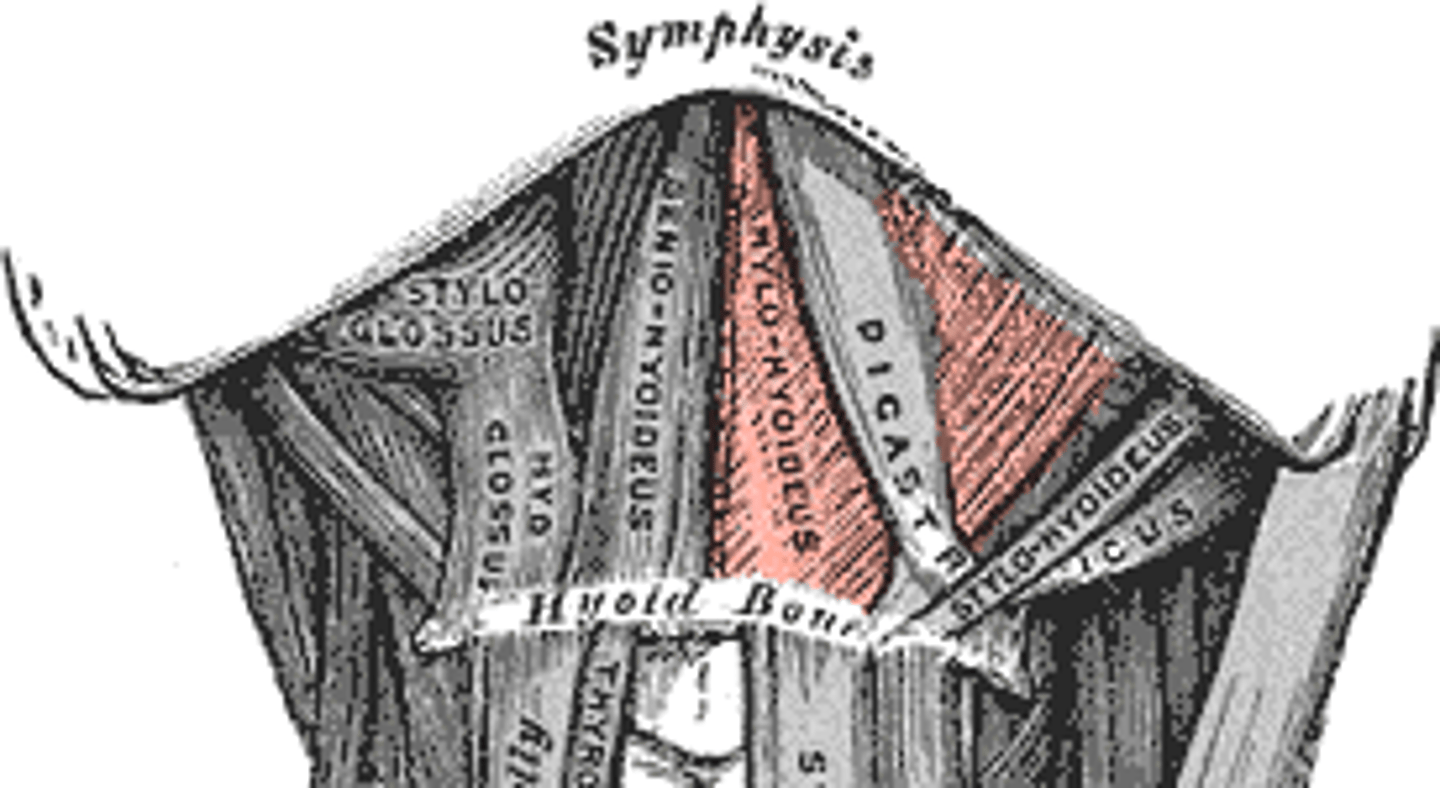
Mylohyoid is innervated by
V3 (fifth cranial or trigeminal nerve)
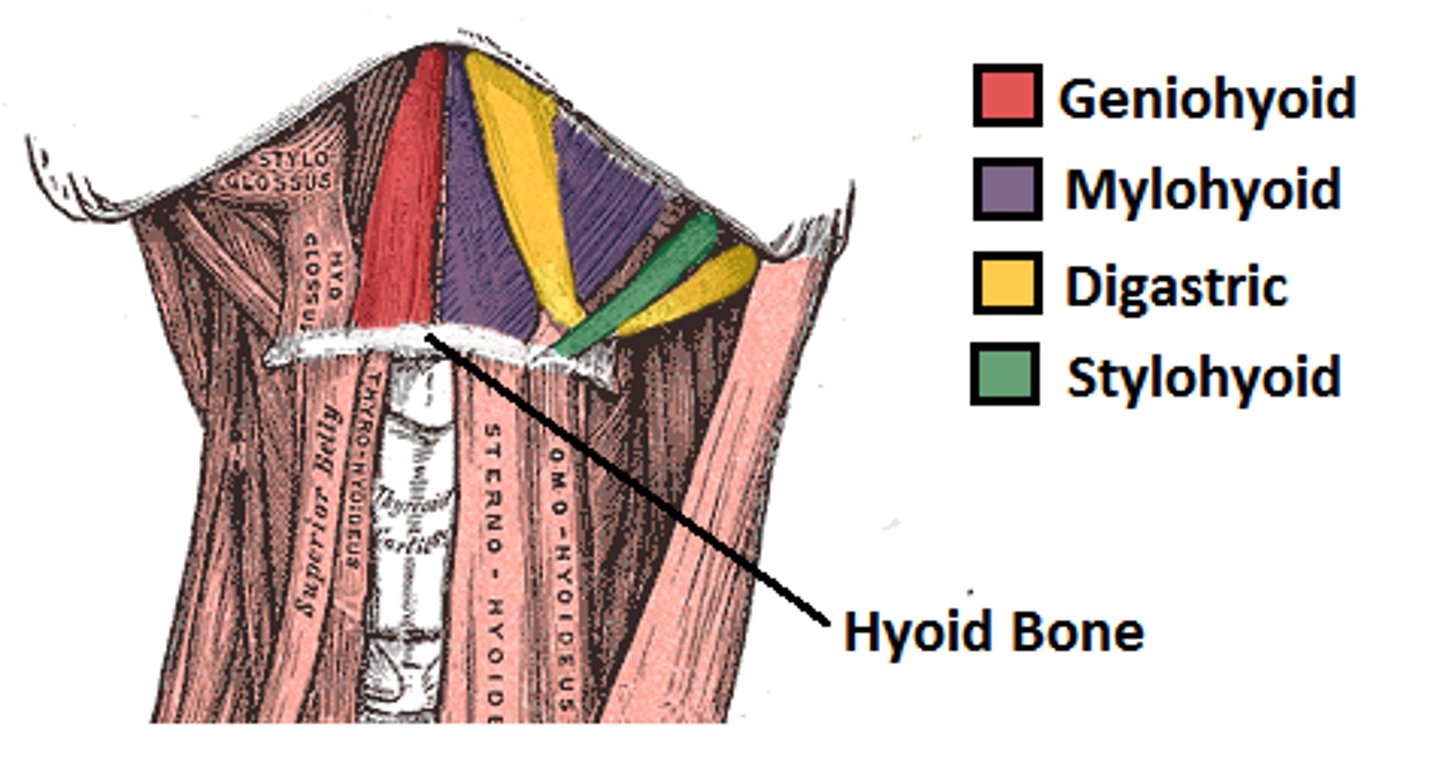
Suprahyoid movement (includes the mylohyoid)
Depression of mandible
Suprahyoid Action (includes the mylohyoid)
Swallowing
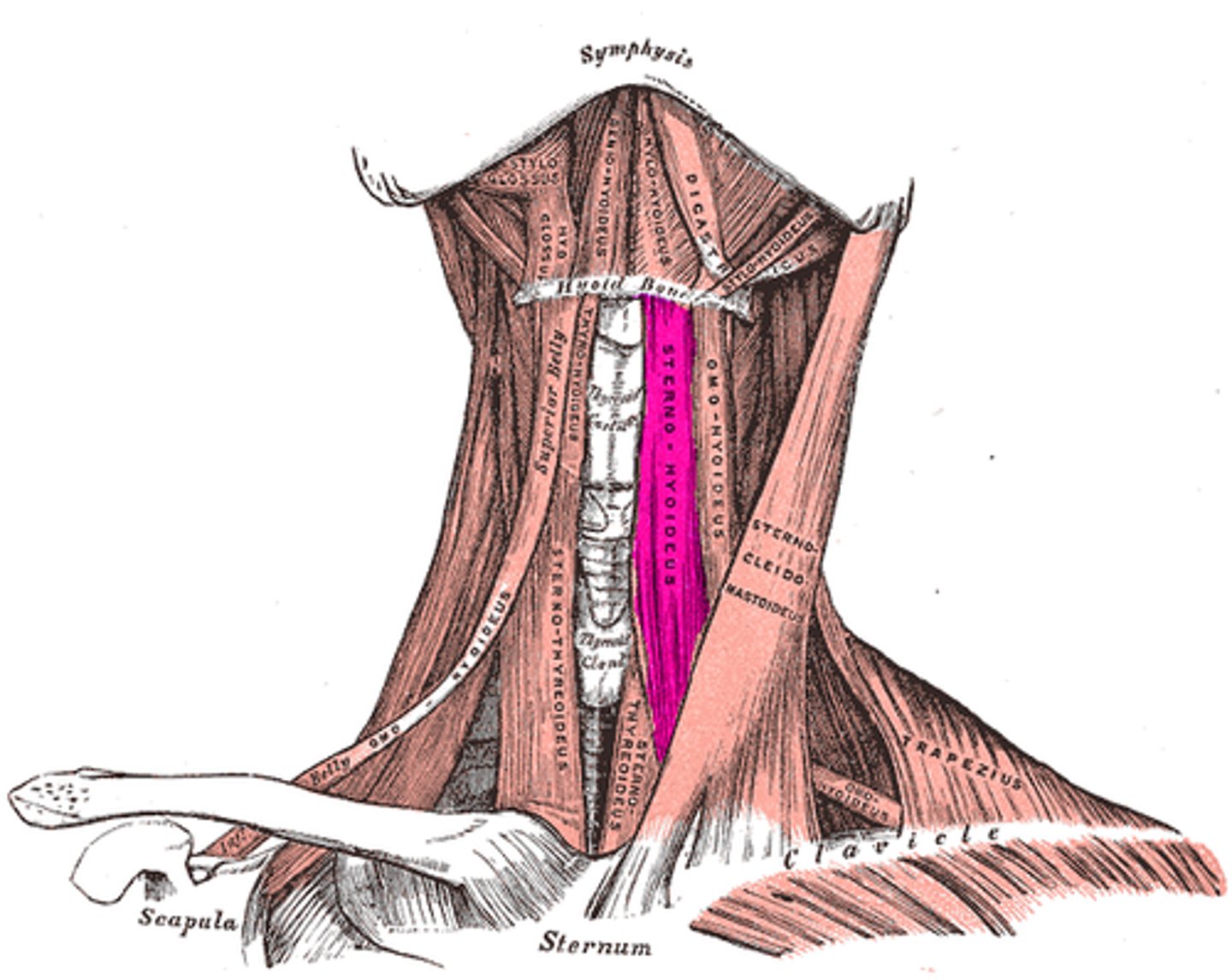
Infrahyoid movement
Stabilize hyoid bone
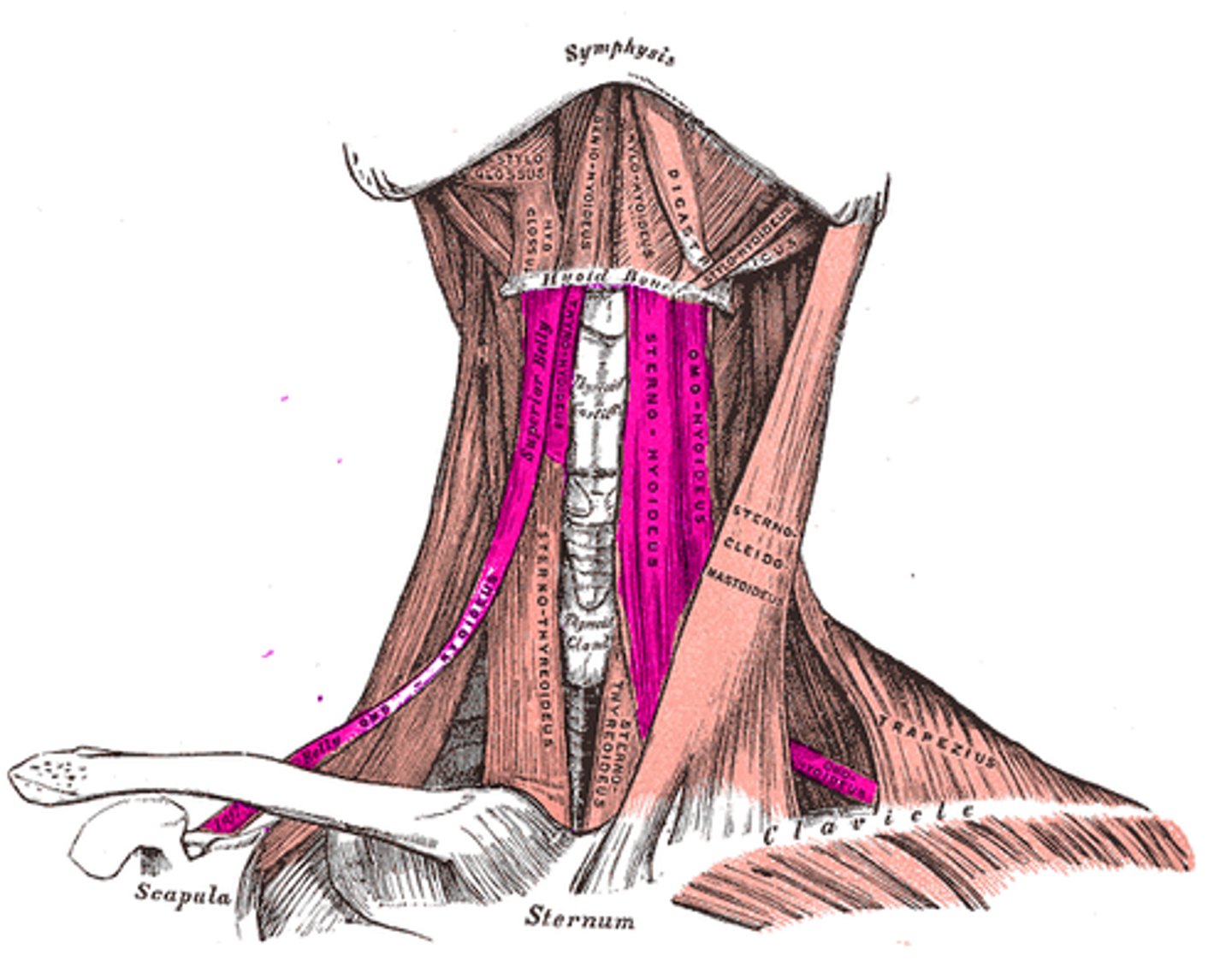
Infrahyoid Action
Swallowing and speech
True or false:
Muscles of the pharynx are involved in speaking, swallowing, and middle ear function
True
what muscle of the soft palate initiates swallowing?
Palatoglossus muscle
Palatoglossus muscle elevates the_________of the tongue and depresses the ___
base; soft palate
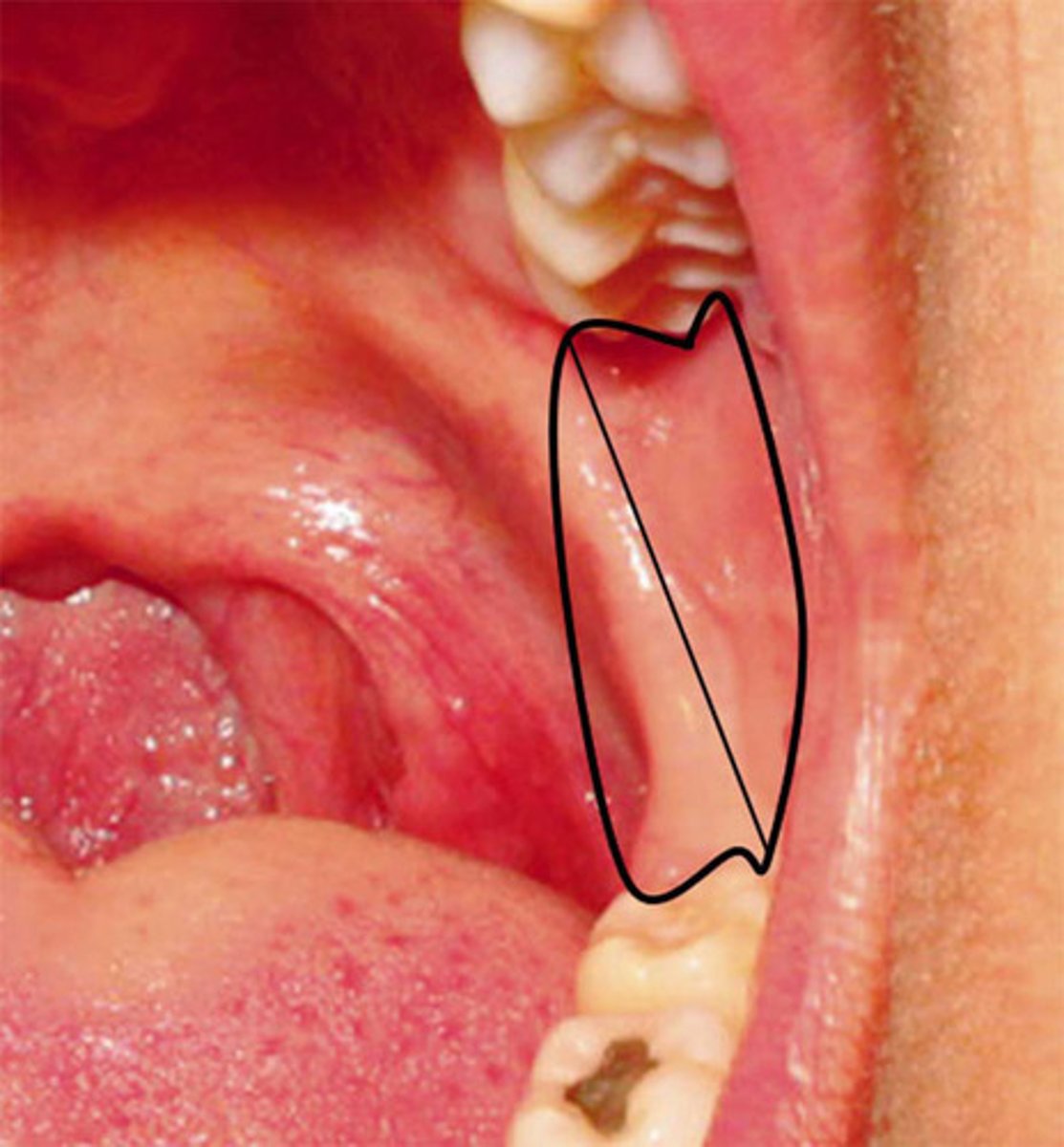
tissue that extends from the junction of the hard and soft palates down to the mandible (distal to the last tooth) and stretches upon opening (Referred to as raphe)
Pterygomandibular fold
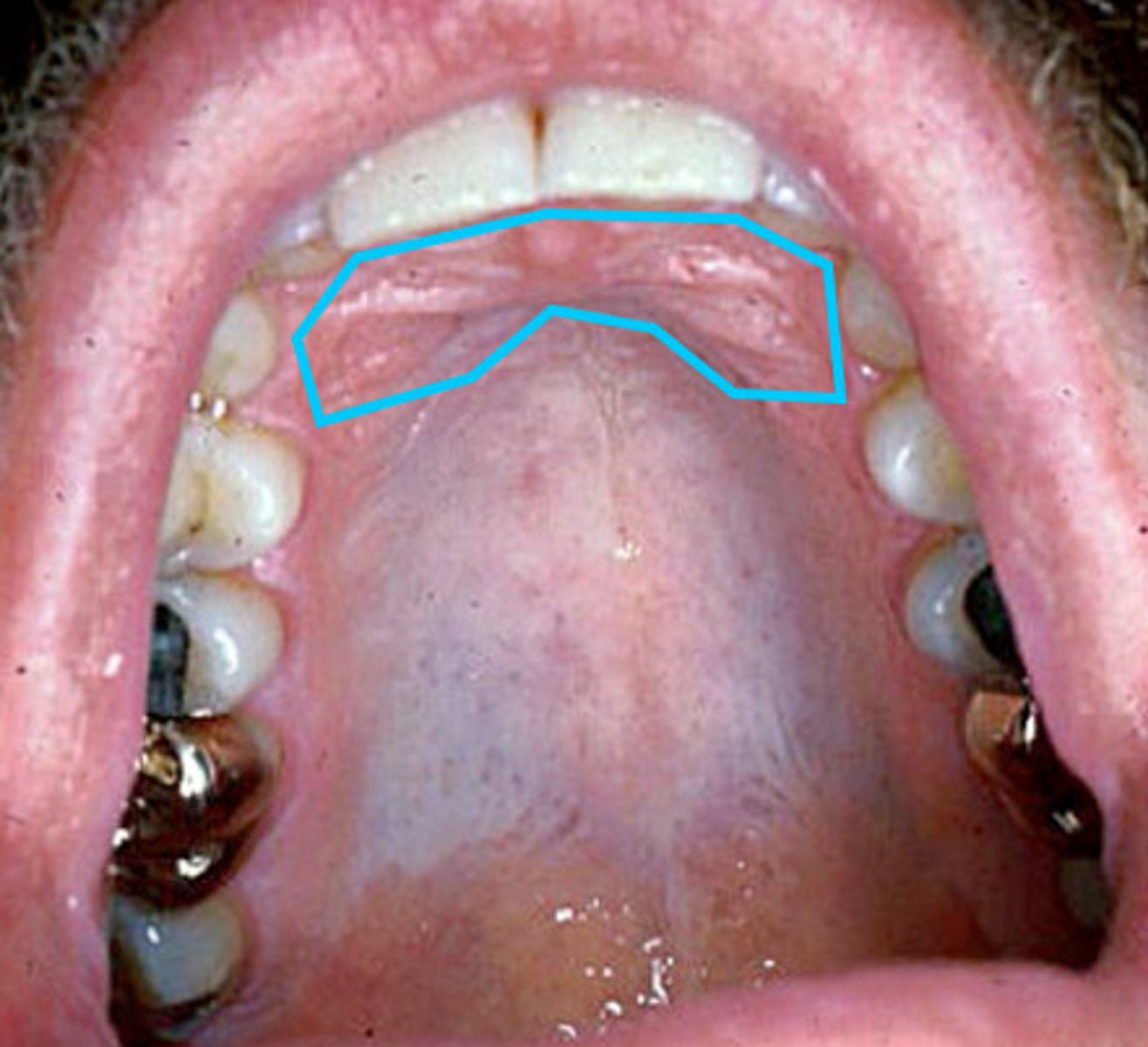
palatine rugae
the ridges that run horizontally across the hard palate behind the incisive papilla
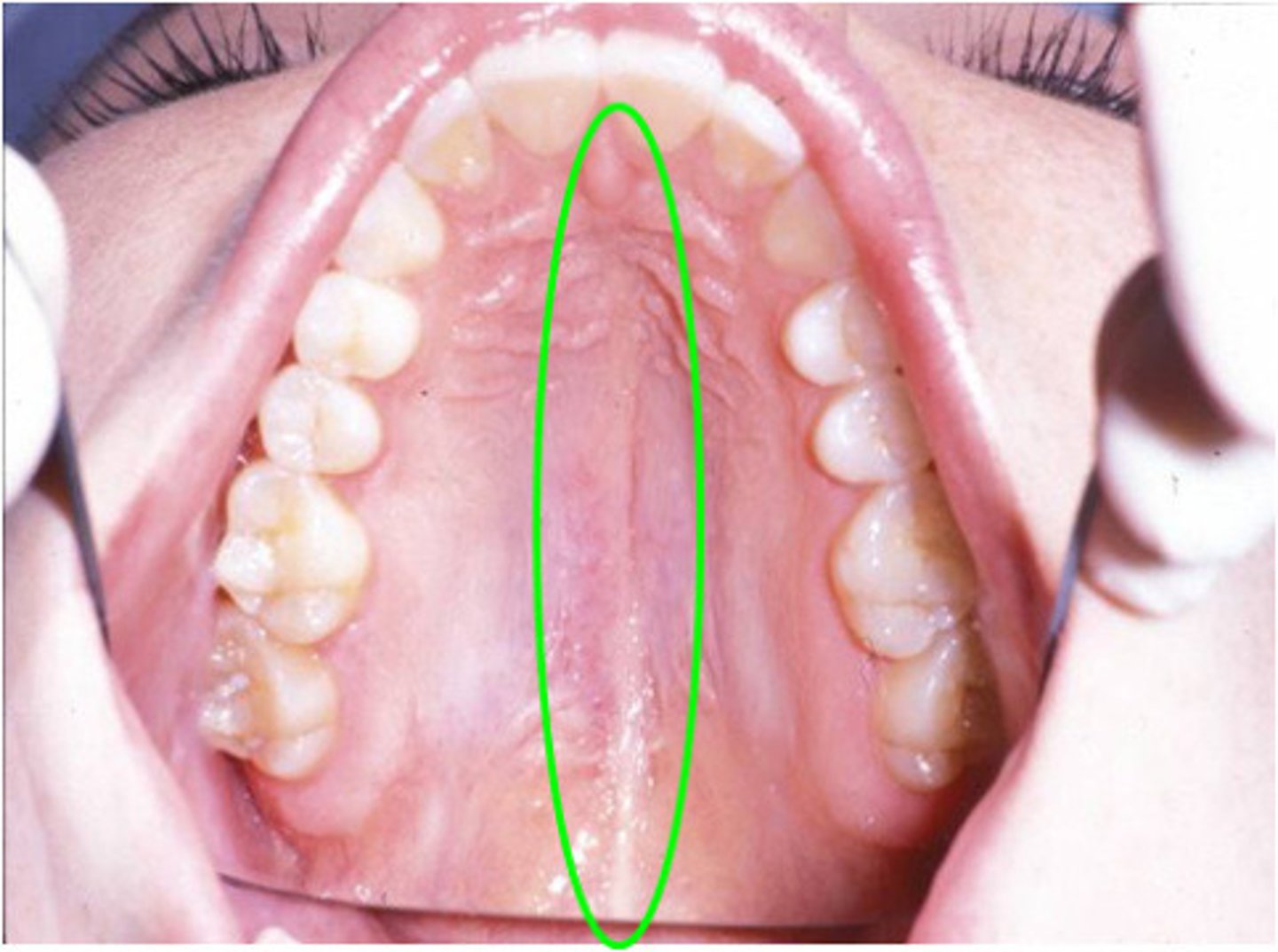
Median palatine raphe
A midline ridge of tissue on the hard palate, which runs from the uvula to the incisive papilla
Floor of the mouth is located inferior to the ventral surface of the tongue and includes:
Lingual frenum
Sublingual folds (pilca siblingualis)
Sublingual caruncle
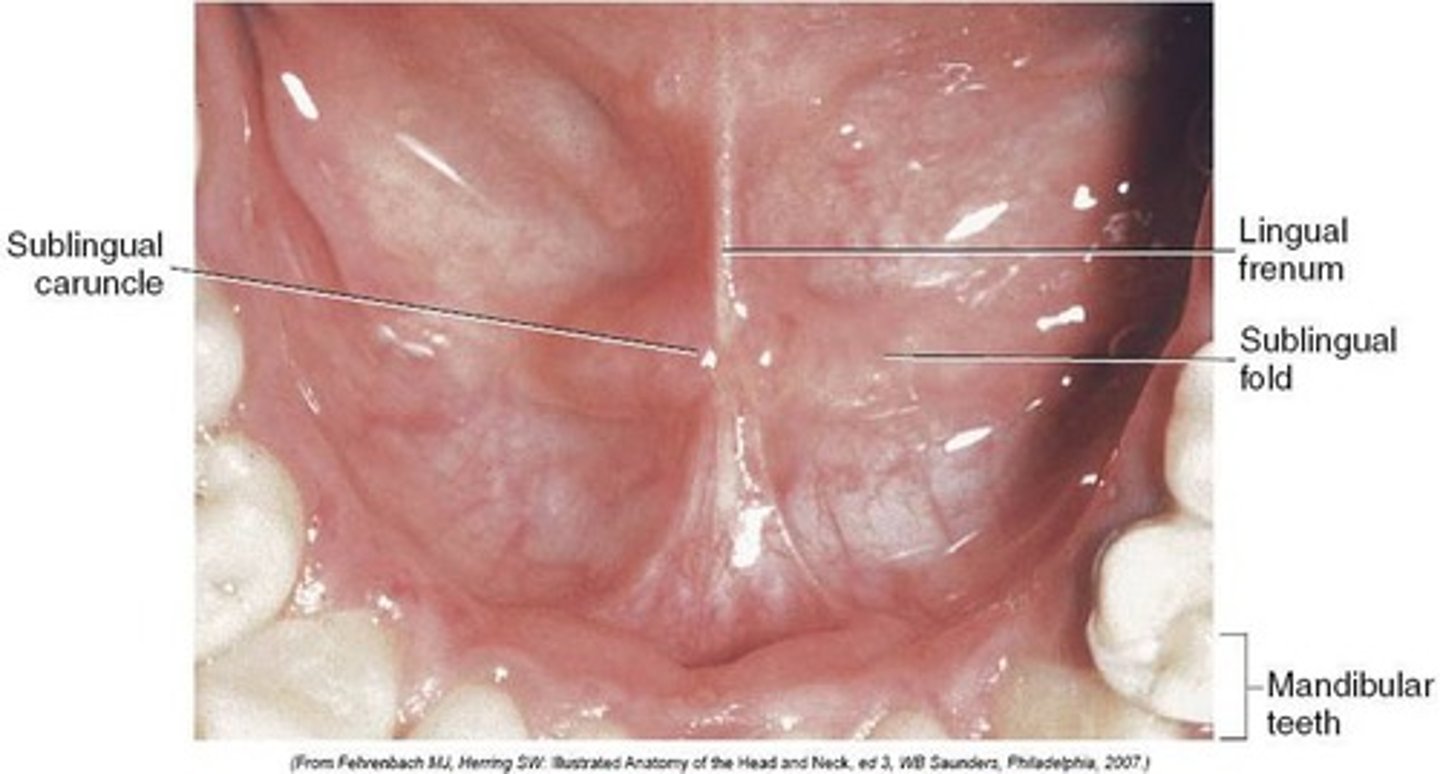
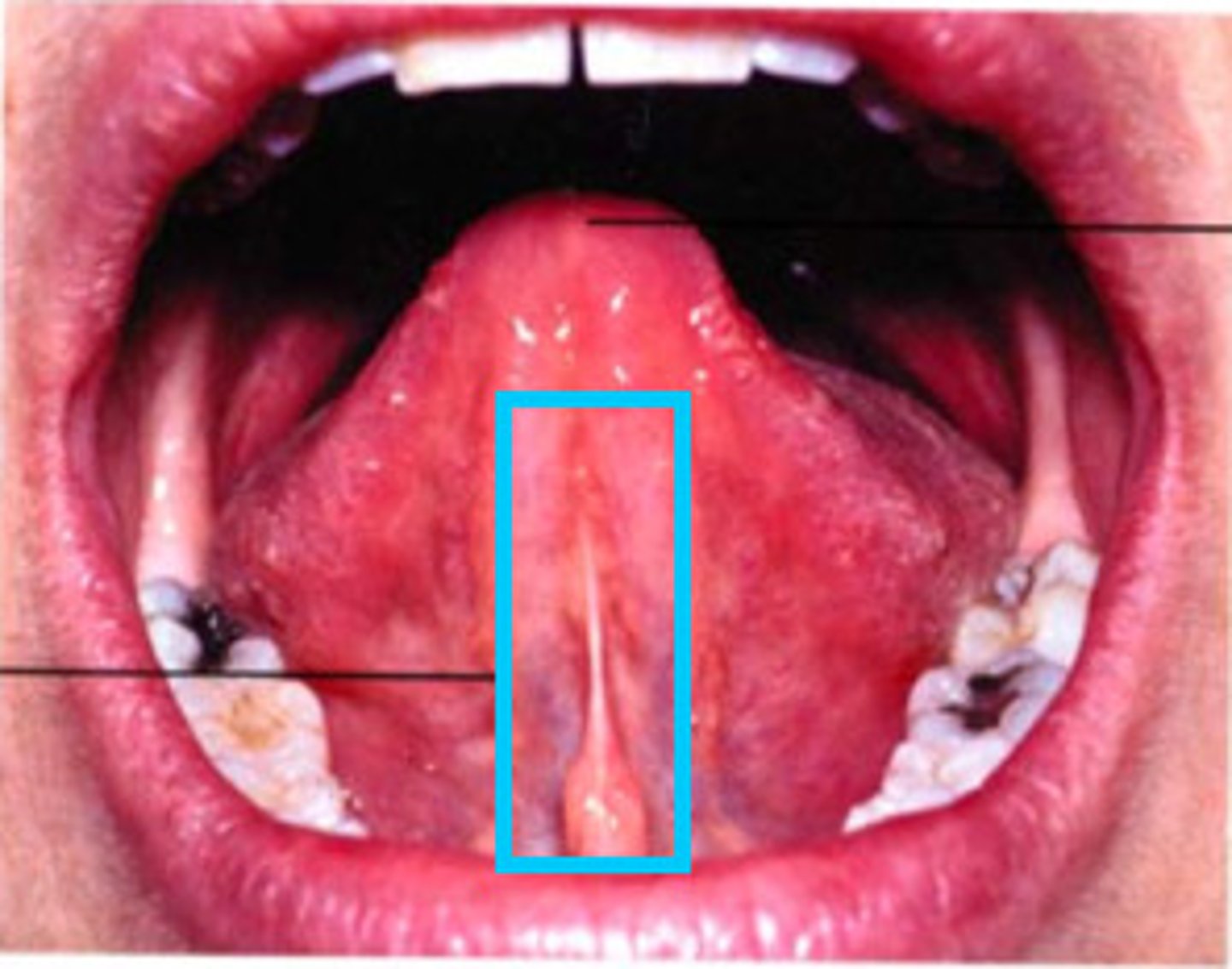
Lingual frenum
midline fold of tissue between the ventral surface of the tongue and the floor of the mouth
Sublingual fold (plica sublingualis)
a 'v' shaped ridge of tissue on each side of the frenum, which empty the sublingual glands
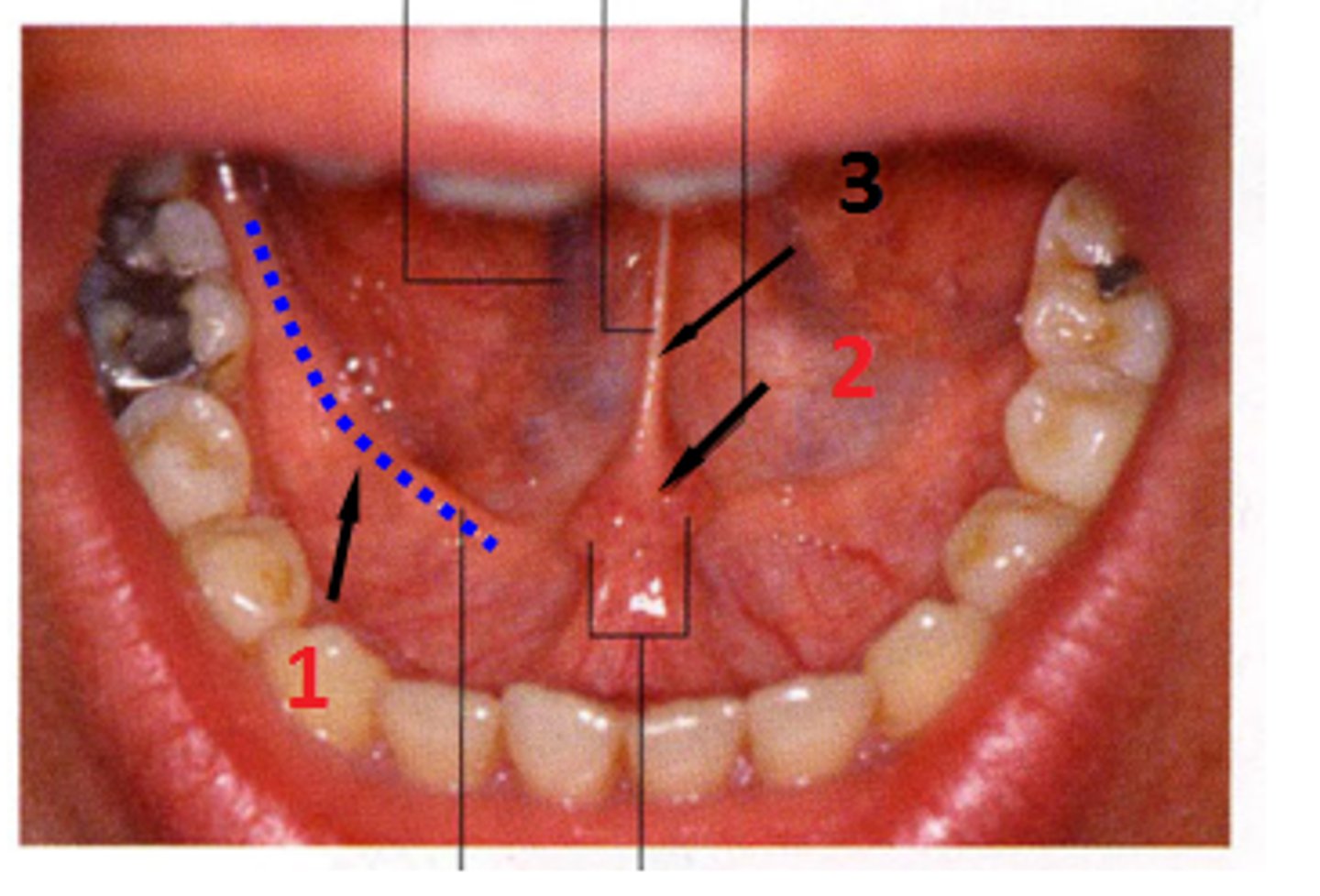
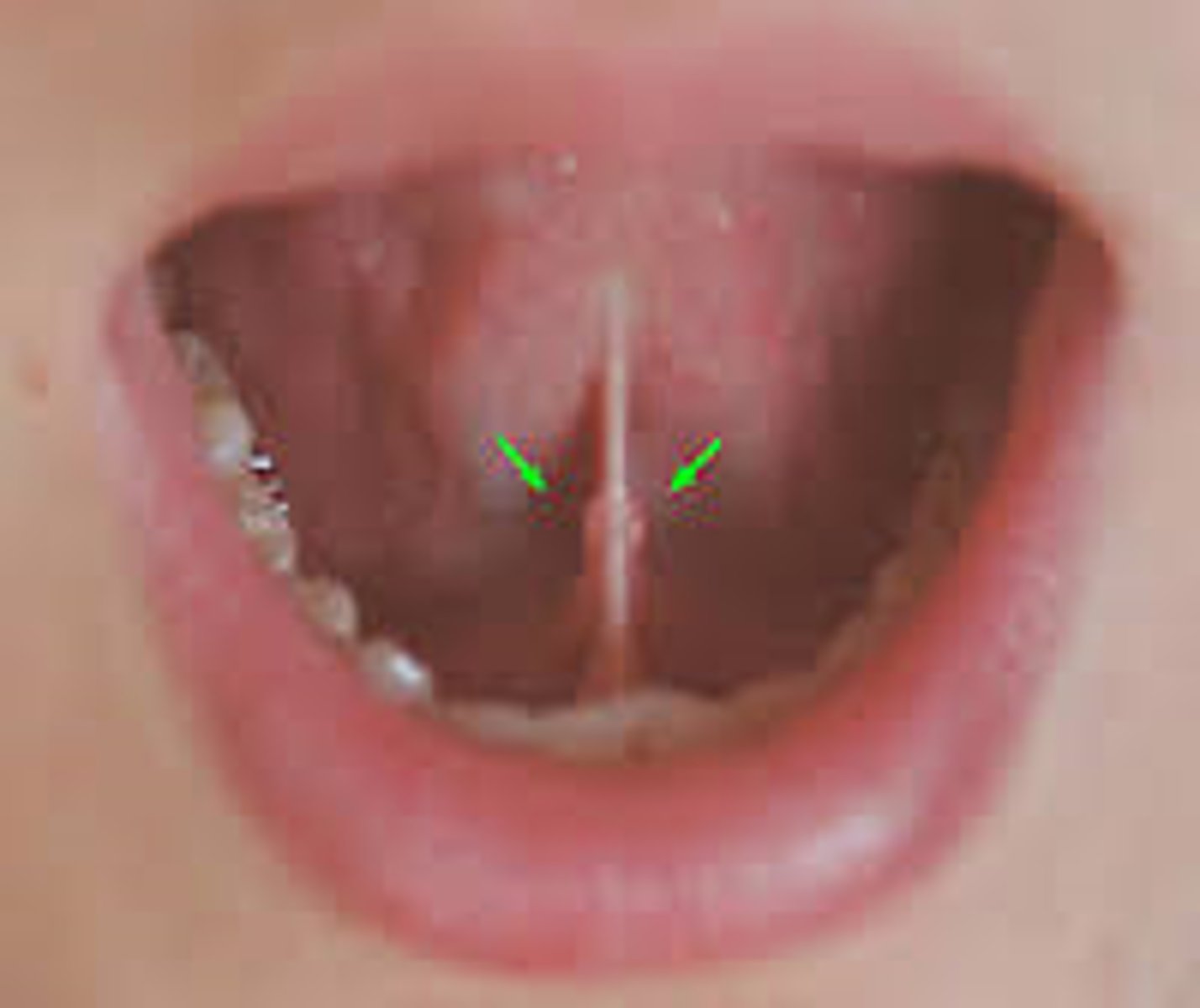
Sublingual caruncles (Wharton's duct openings)
A pair of papillae under the floor of the mouth extending from the first molar on either side of the lingual frenum. Each papillae contains an opening of the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands.
Anterior 2/3 of the tongue muscles are innrevated by:
lingual nerve (v3) and chorda tympani
Posterior 1/3 of the tongue muscles are inervated by:
IX (glossopharyngeal nerve)
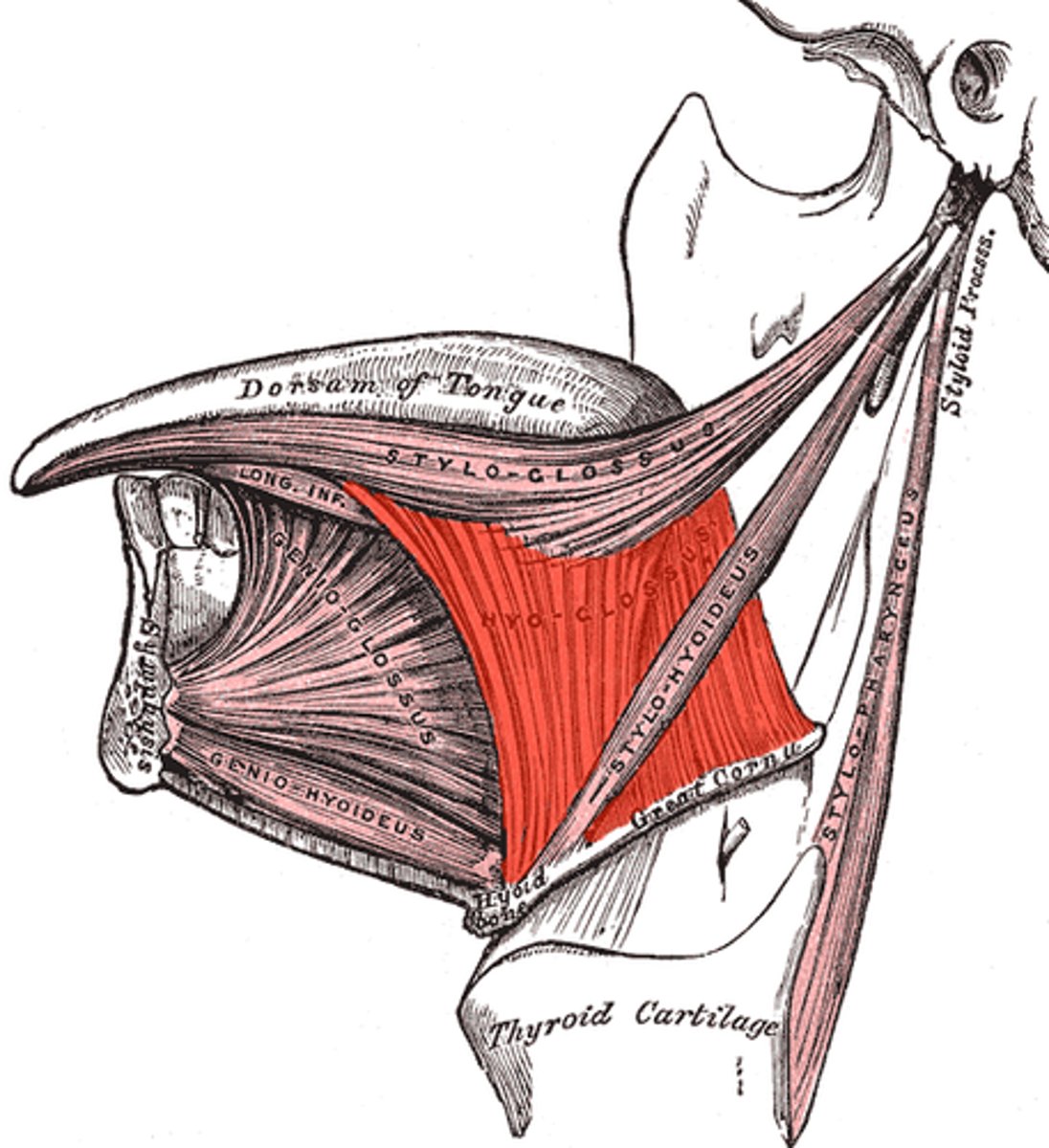
Extrinsic muscles of the tongue
genioglossus, styloglossus, hyoglossus
Genioglossus (extrinsic muscle of tongue)
Protrudes tongue (sticks tongue out)
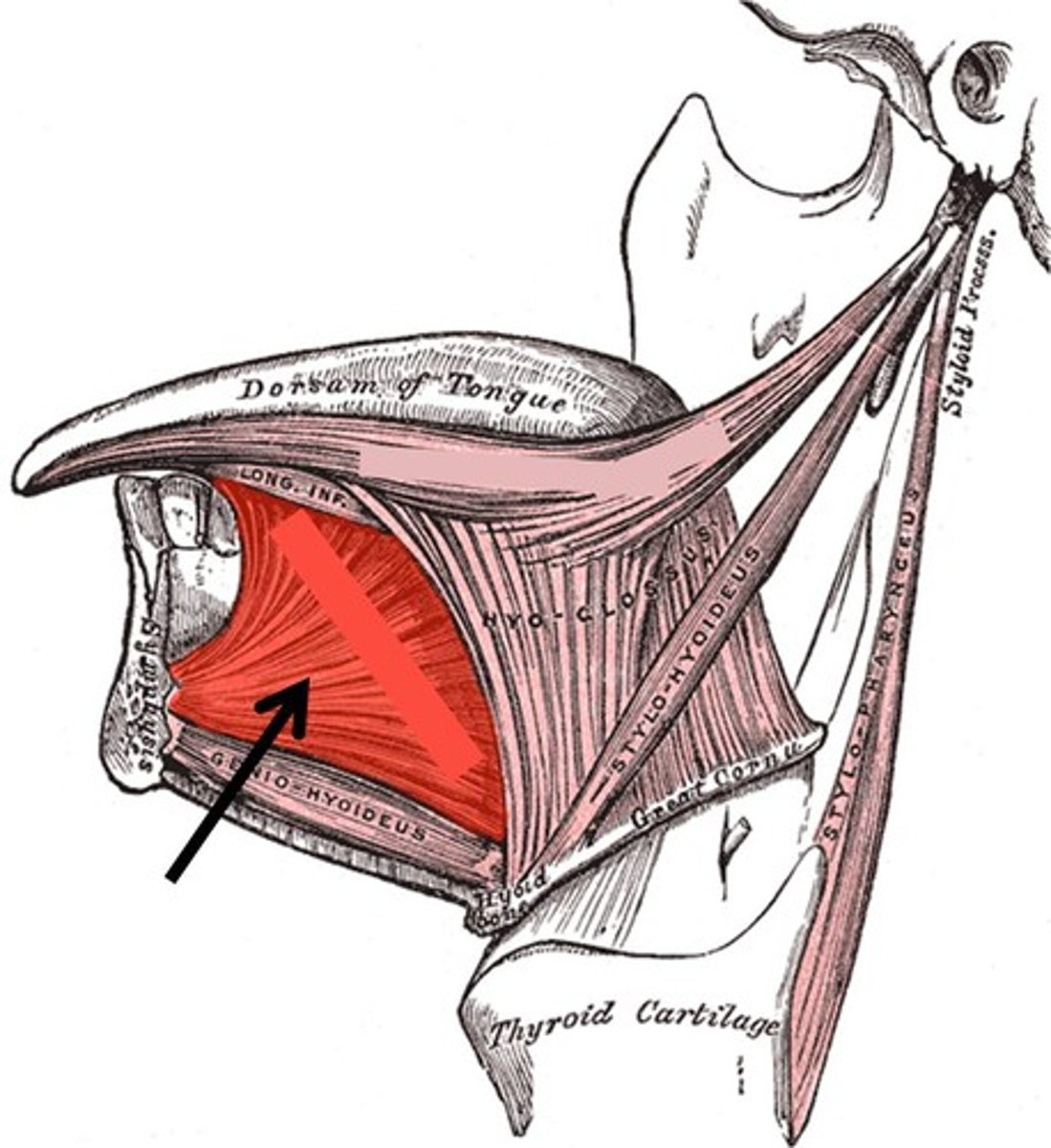
Styloglossus (extrinsic muscle of the tongue)
Retracts the tongue (has style, doesnt stick tongue out)
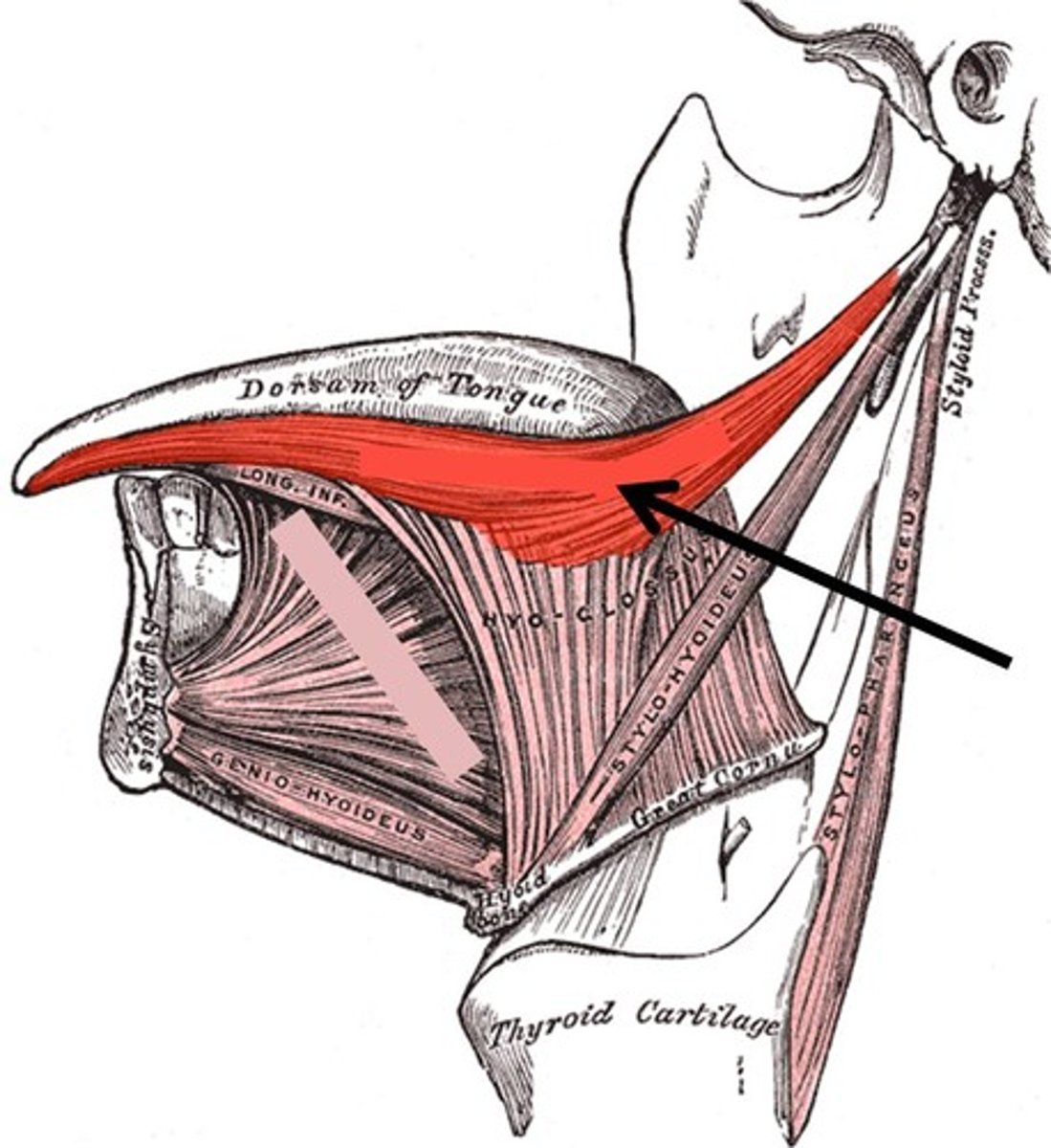
Hyoglossus
depresses tongue
True or false:
Extrinsic muscles of the tongue move/control position of the tongue
True
Extrinsic muscles of the tongue get their blood supply from the
Lingual artery
Contain taste buds (red in color)
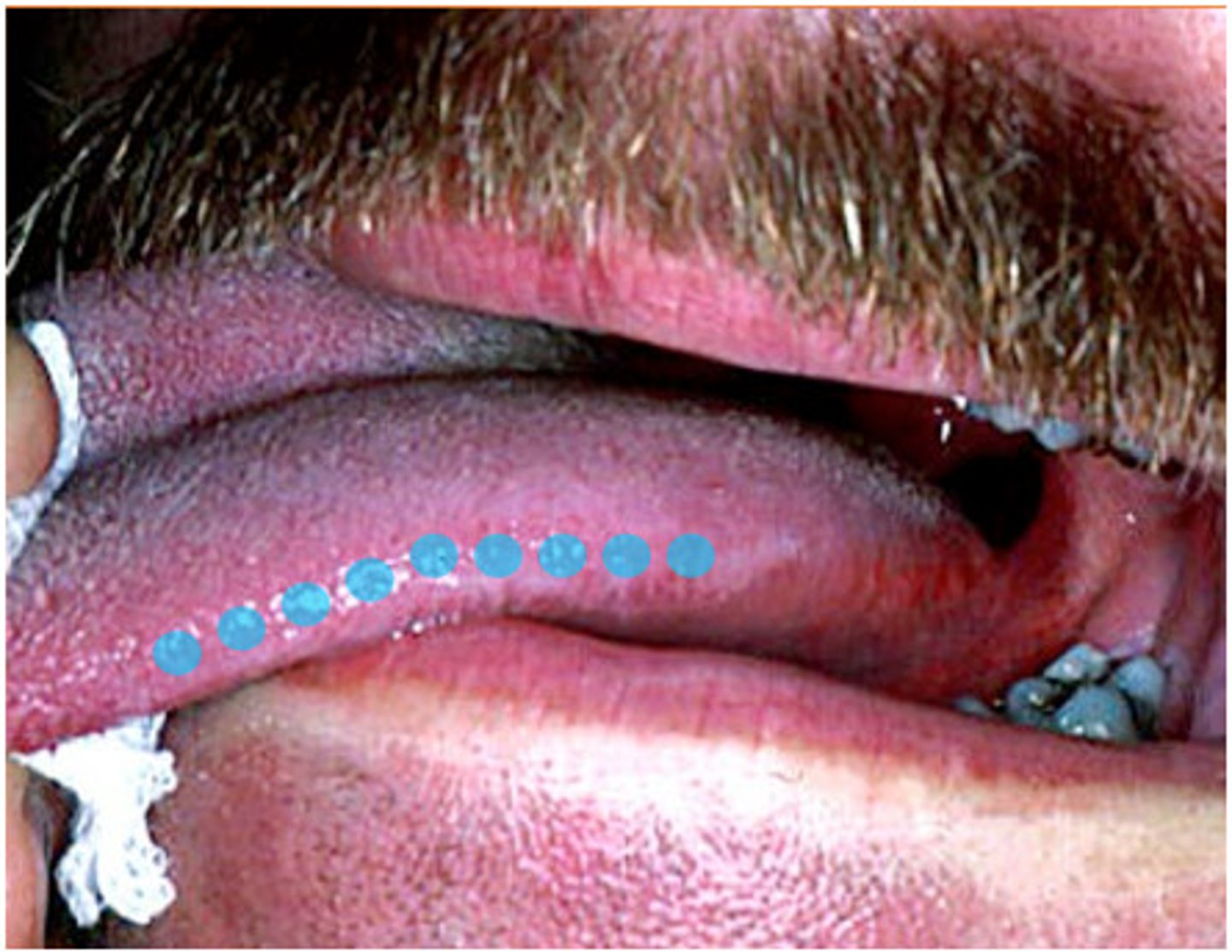
foliate papilla
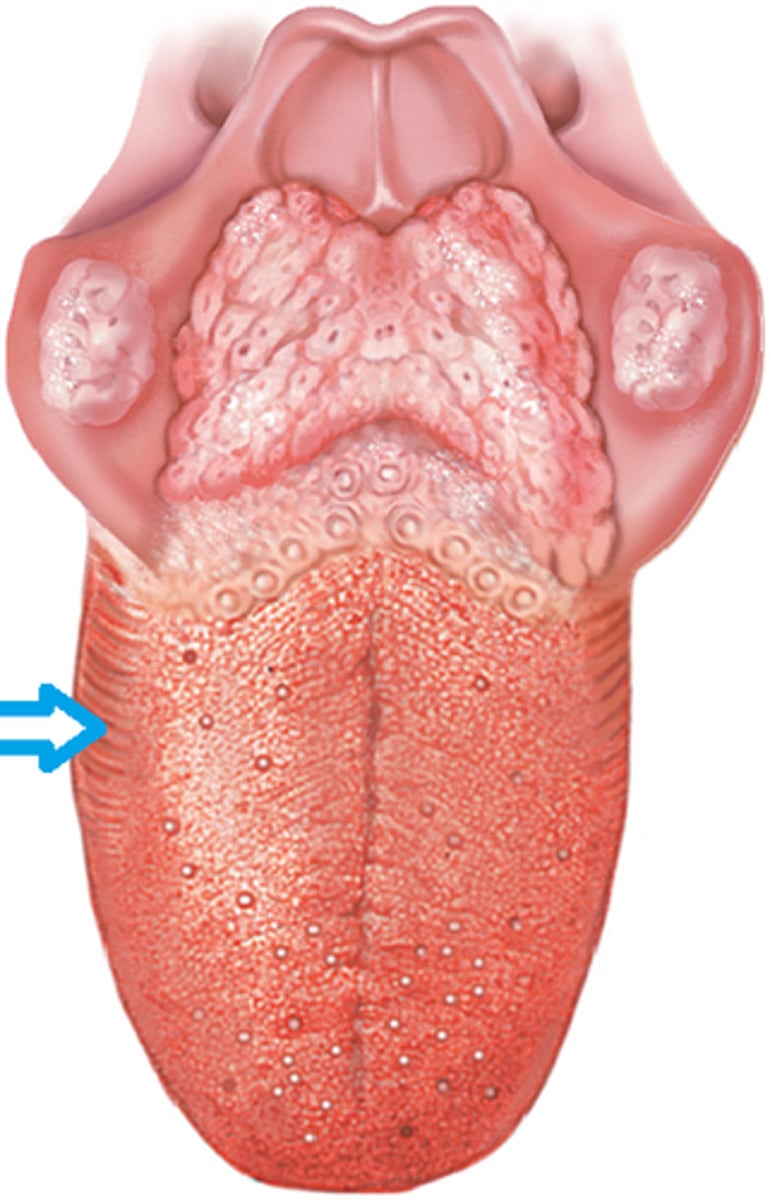
10 to 14, contains taste buds and associated with ducts of Von Ebner's glands, large
Circumvallate papilla
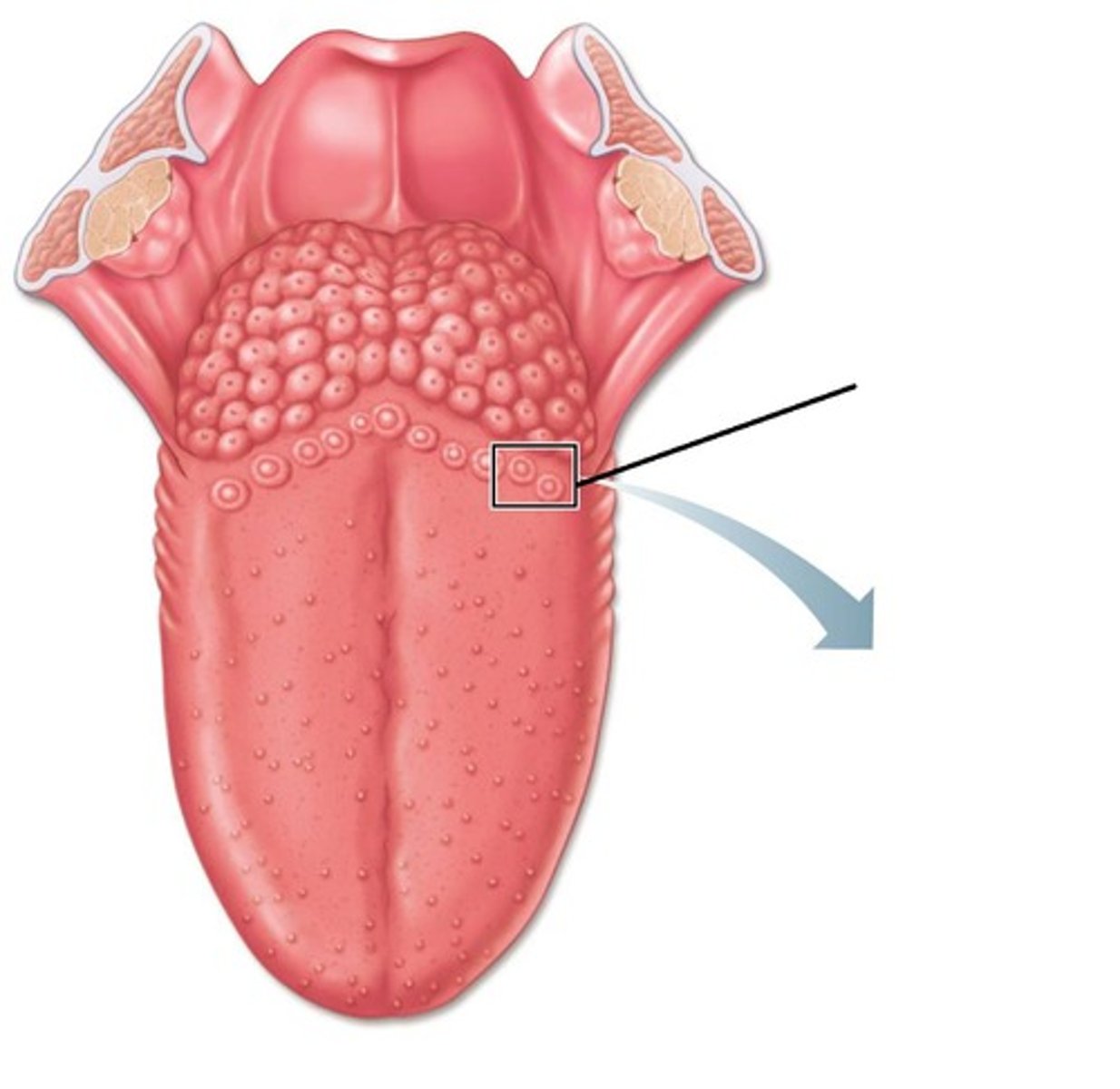
Fewer, Contain taste buds, red, mushroom shaped
fungiform papilla
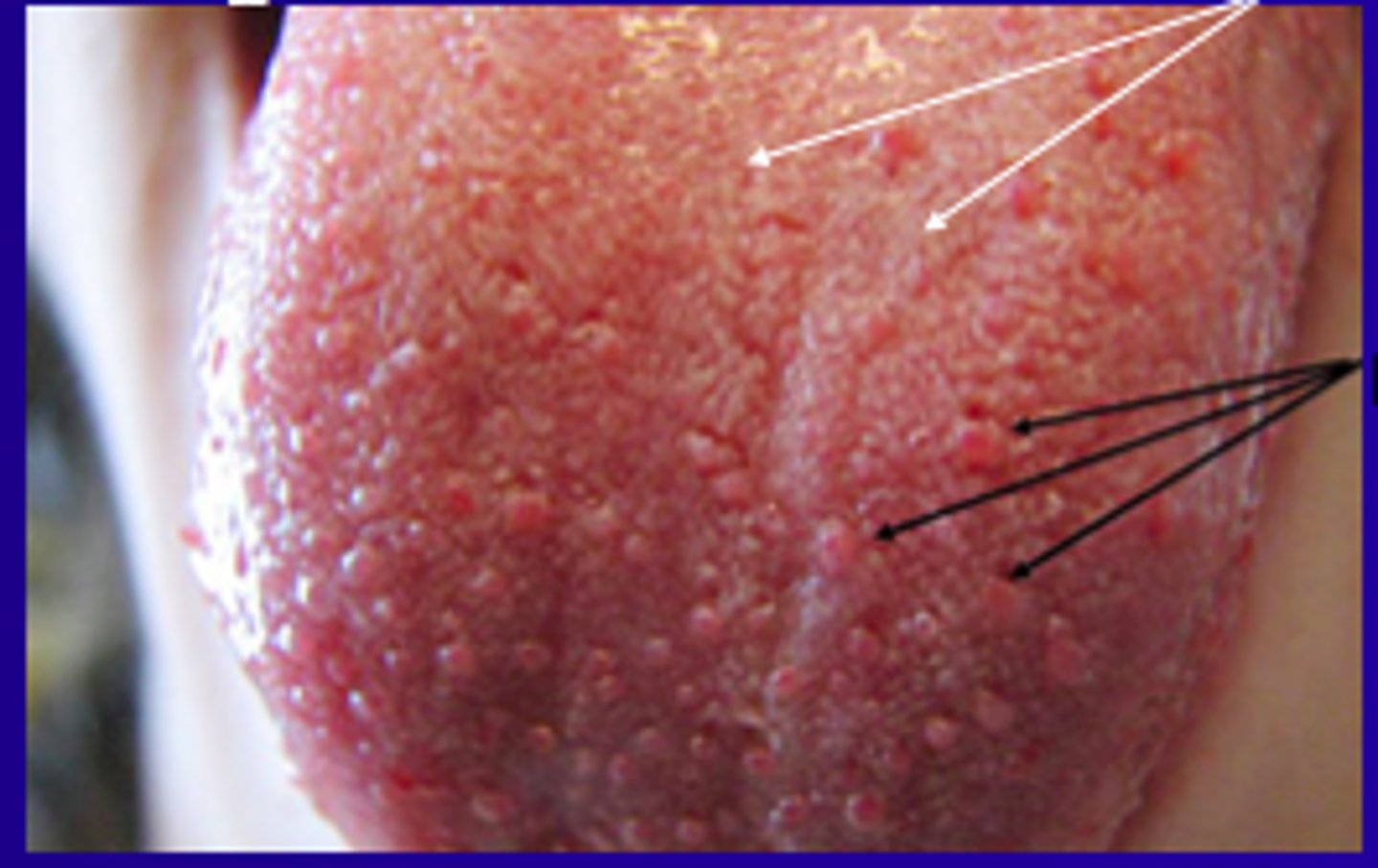
the most numerous but do not contain taste buds, keratinized tissue give tongue a velvety texture; associated with geographic tongue and hairy tongue (whitish tint in color)
Filiform papilla
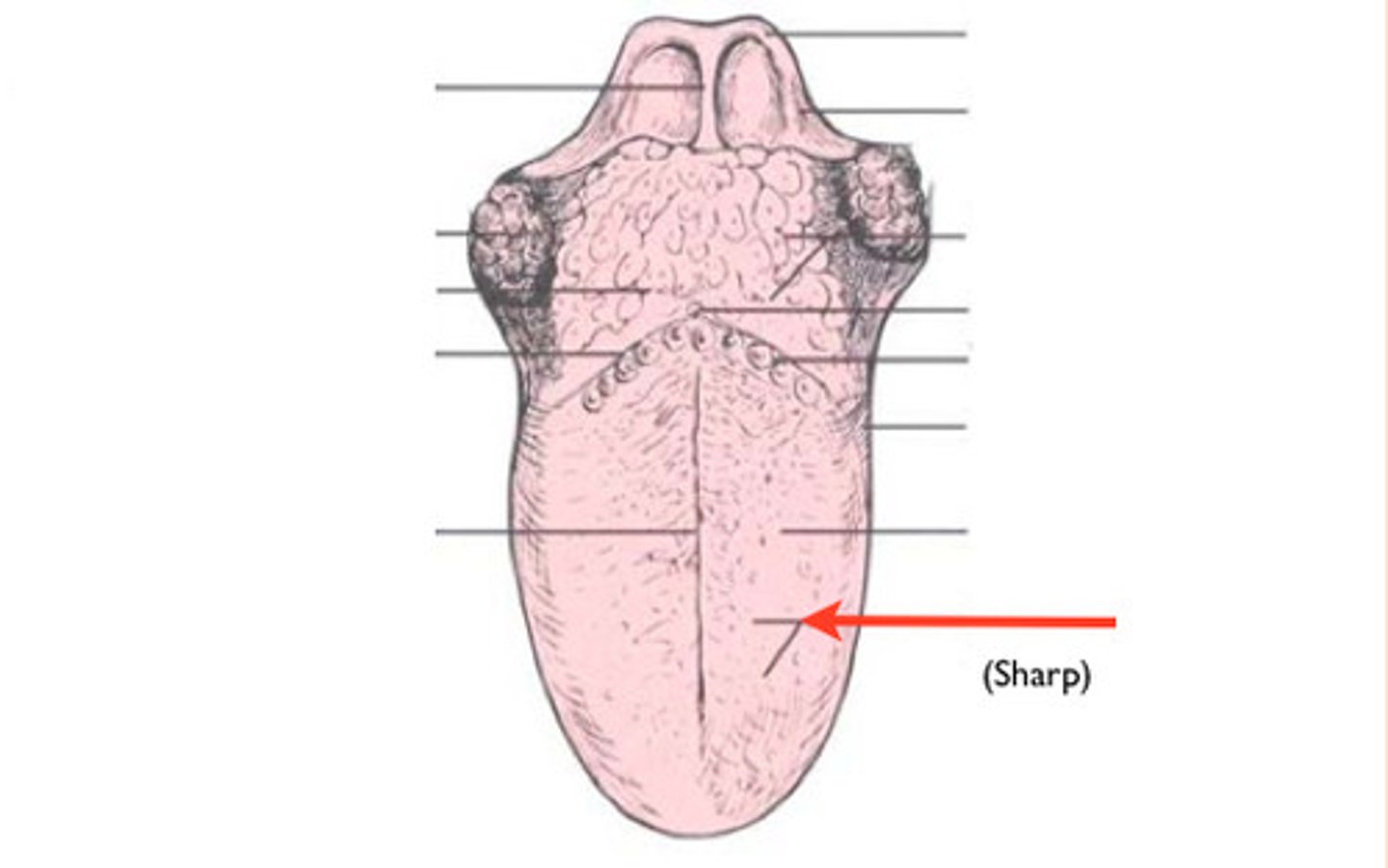
Foliate lingual
Located on lateral surface (side) of tongue, some contain taste buds
Sulcus terminalis of tongue
V shaped shallow groove separating anterior 2/3 of body from posterior 1/3 of base
What joint is the hinge and sliding joint?
TMJ
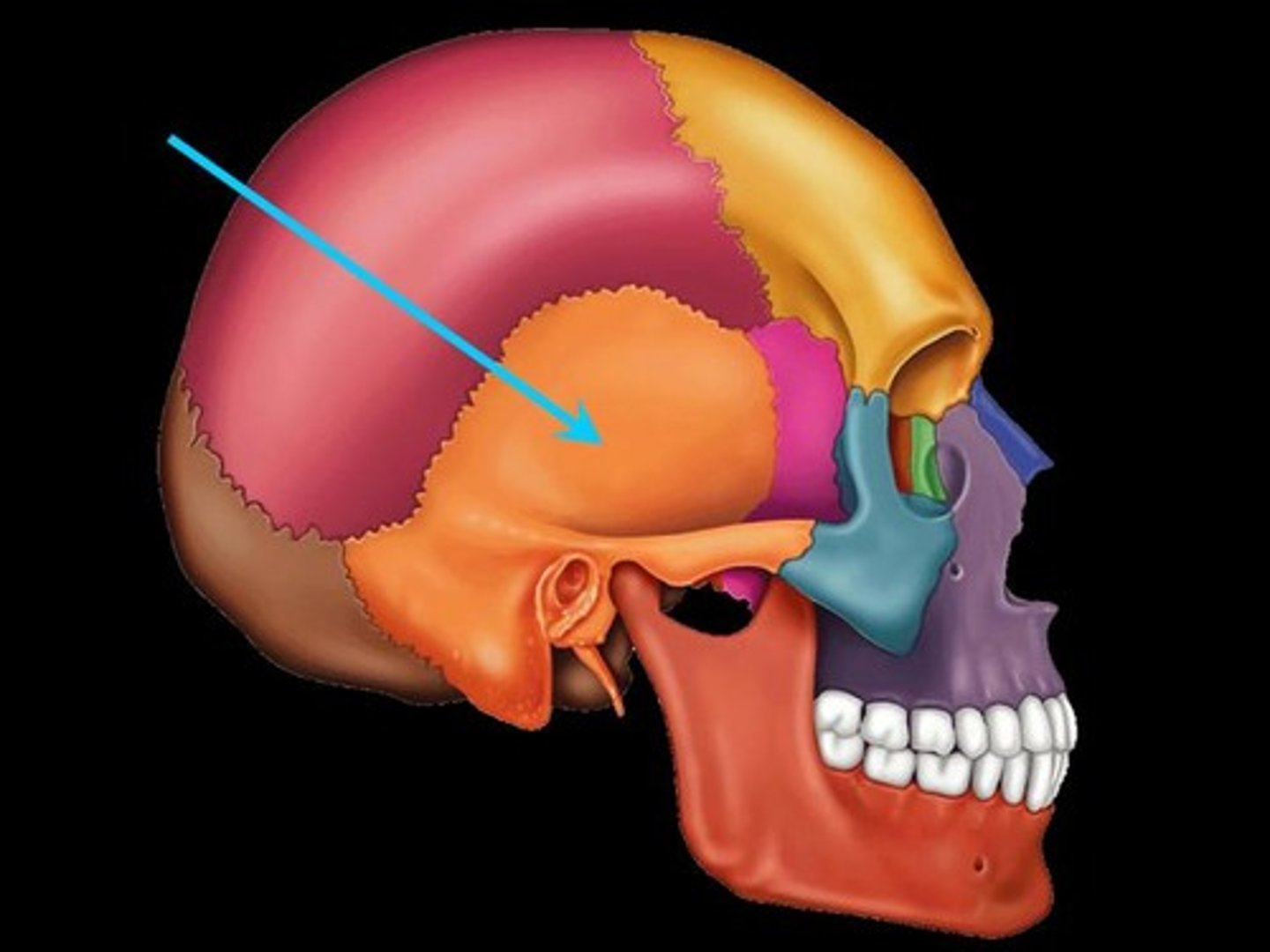
What bone includes the articular eminence (articular tubercle), articular fossa (mandibular fossa), and postglenoid process?
Temporal bone
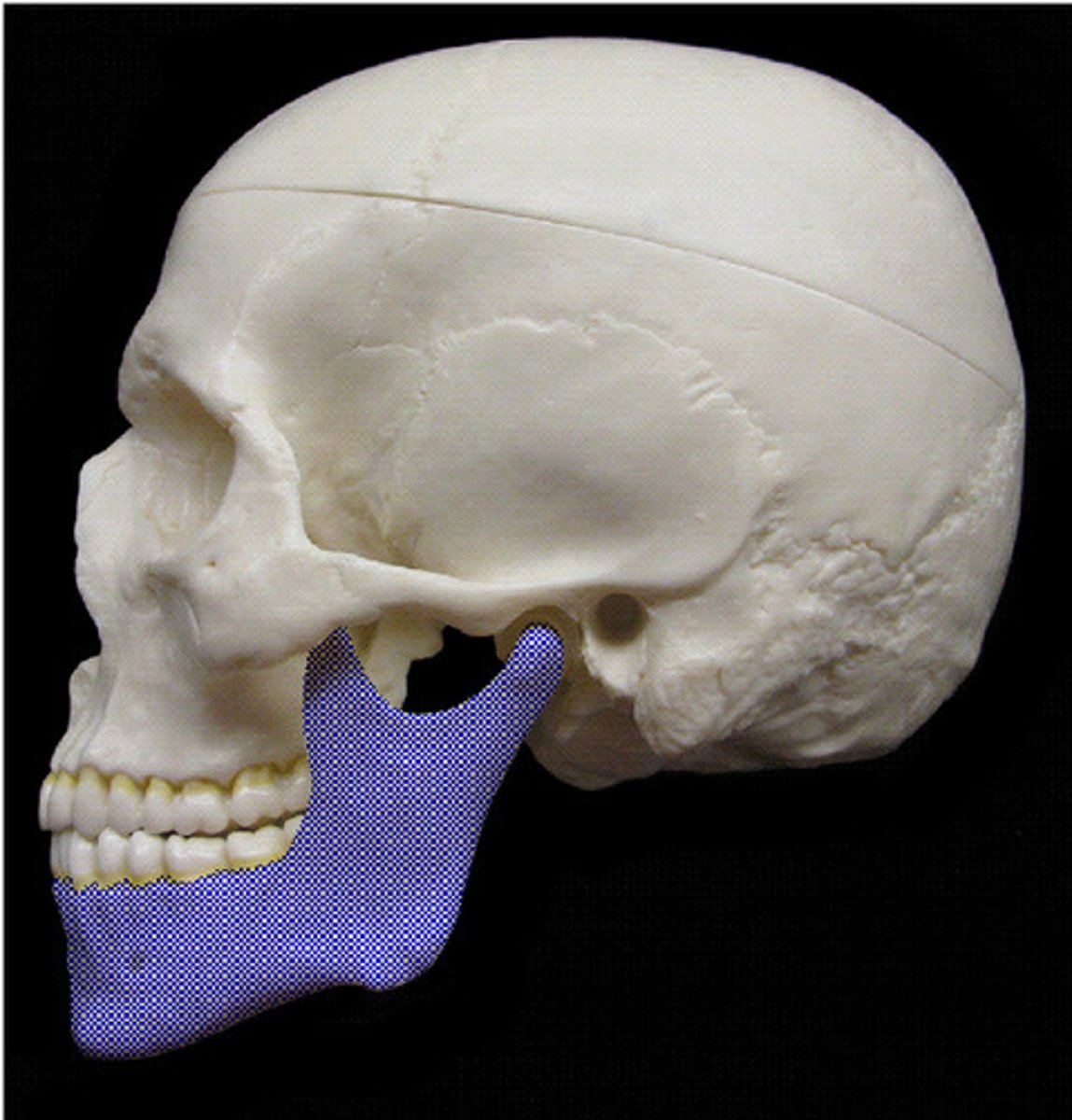
what bone includes the condyle of the mandible, the coronoid process and the mandibular notch?
Mandible
Contains synovial fluid to lubricate the TMJ, divides the TMJ into two compartments called synovial cavities
Articular disc
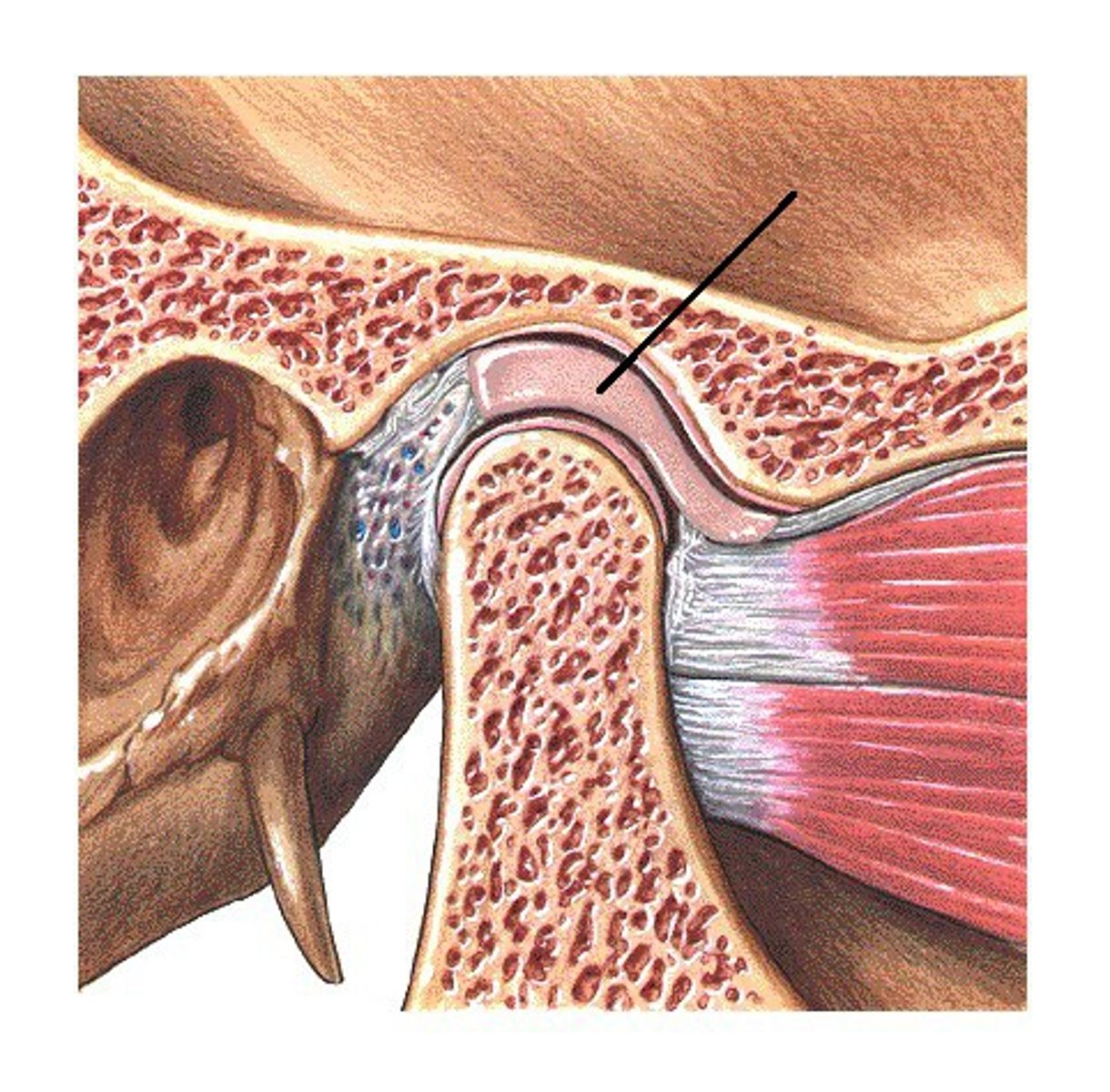
what kind of connective tissue are articular disc's of tmj made out of?
Fibrous, dense, connective tissue
TMJ ligaments
TMJ ligament, sphenomandibular ligament, stylomandibular ligament