Global Biochemical Cycles
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the phosphorus, sulphur, nitrogen, and carbon cycles, including human influences and anthropogenic disturbances. Also covers related vocabulary.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Biogeochemical cycle
complex systems that involve the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere through a series of inputs and outputs - Dahlgren, 2006
how nutrients are moved
Phosphorus Cycle
Heavily increased since the agricultural revolution in the 1950s. - fertiliser
The main source of phosphorus is the Bodele Depression, which deposits 50 million tonnes of dust loaded with phosphorus in South America per year.
Filippelli, 2008
why is phosphorous important ?
role in biological systems
weathering relates more phosphorus
Filippelli, 2008
Inputs of phosphorus
rate of phospherous flow now 3x more than before agricultural and industrial revolution - Begon et al., 2021
rapid uplift of Himalayan - Tibet Plateau - increased chemical weathering - more phosphorus in oceans - Filippelli, 2008
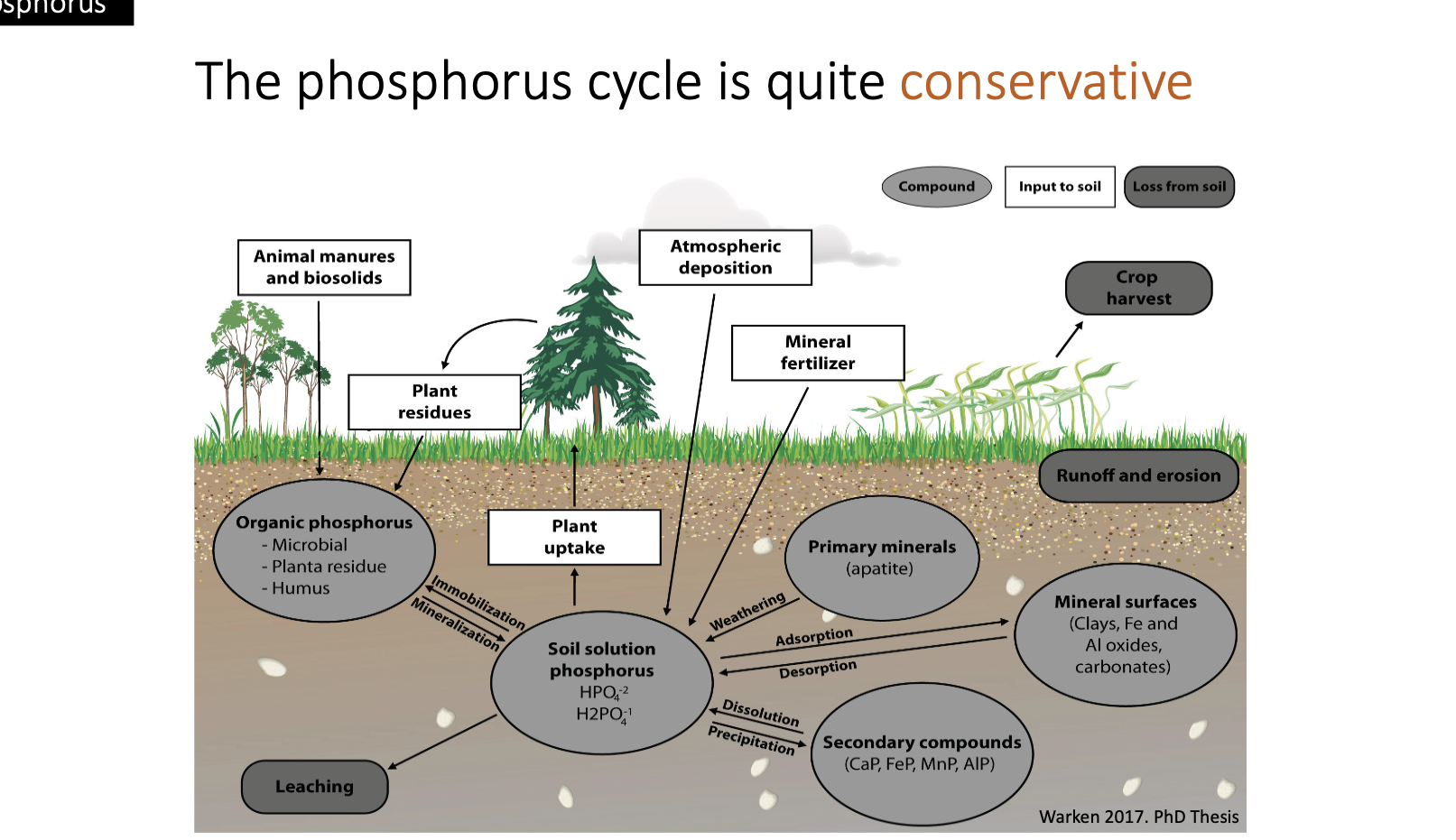
Outputs of phosphorus
loss of phosphorus through leaching and runoff into water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems - Filippelli, 2008.
rivers transports P to oceans - unaltered the oceans - Filippelli, 2008
related during decomposition - Knoops et al., 2002
Impacts from phosphorus cycle
freshwater eutrophication - from runoff and erosion
marine dead zones
loss of plant diversity
P tends to stay in one place - excessive
Filippelli, 2008
Sulphur Cycle
Atmospheric sulphur is coming from smelting and fossil fuel combustion.
Heavily connected to acidification of the ocean. Though volcanoes are a natural source, their emissions are tiny compared to human emissions.
Changes in soil pH due to sulphur levels can drive massive changes in plant community composition.
Begon et al., 2021
why is sulphur useful
most organisms need a small amount
high sulphur = major changes
humans now use it for fuels to produce energy
Begon et al., 2021
Sulphur inputs
originated from burning coal + volcanoes
Begon et al., 2021
Sulphur outputs
occurs as acid rain
Begon et al., 2014
impacts from sulphur
freshwater acidification
forest dieback
loss of plant diversity
reduced sulphur emissions have led to an increase in PH
Higher PH = lower plant diversity
Begon et al., 2021
Nitrogen Cycle
The most active cycle, with most nitrogen coming from fertilizers.
Human nitrogen fixation is twice as much as natural fixation.
Fowler et al., 2021
Why is nitrogen important
Nitrogen inputs
elevation and topography have an impact on soil characteristics - affects nitrogen cycling - Bohlen et al., 2001
Acacia invasions influence nitrogen cycling - Knoops et al., 2002
herbivores slow down nitrogen cycling by eating plants - Knoops et al., 2002\
Fixation - N enters the soil
Fowler et al., 2013
Nitrogen outputs
Denitrification - nitrogen leaves as nitrogen oxide
Ammonification - debris proteins get broken and metabolised to ammonium
Nitrification - ammoinia —> nitrogen dioxide —> Nitrate
Fowler et al., 2013
Nitrogen stores
in biomes - wetlands and soils that are waterlogged - Begon et al., 2021
higher litter fall of nitrogen may increase nutrient cycling
Most nitrogen in decomposition not released - in soil - Knoops et al., 2002
Forests 70% of terrestrial nitrogen - Townsend et al., 2011
Geologic nitrogen store - 20% - Dahlgren, 2006
Nitrogen impacts
ocean dead zones with loss of biotic diversity
stream and lake eutrophication - agal blooms
nitrogen deposition that changes community deposition
toxic nitric oxide compounds in atmosphere with carcinogenic effects
Fowler et al., 2013
Nitrogen deposition changes biotic communities
N deposits soil PH increases affecting plant community diversity and composition
Field et al., 2014
Carbon Cycle
When productivity is higher than respiration, an ecosystem acts as a carbon sink.
Increased CO2 in the atmosphere can lead to CO2 fertilization, allowing plants to grow more.
Mycorrhizal fungi provide nitrogen and phosphorus to plants. The growing season is becoming earlier each year, allowing plants to store more carbon.
Luyssaert et al., 2008
Why is carbon important
for plant growth - photosynthesis - Huggett, 2004
carbon inputs
higher plant diversity - increases C input - Lange et al., 2015
concentration increase due to burning of fossil fuels ( combustion) - Begon et al., 2021
deforestation - Begon et al., 2021
terrestrial ecosystems as carbon sinks
Land abandonment increases carbon sequestration
forests grow —> primary productivity exceeds ecosystem respiration
respiration may = primary productivity
poorter et al., 2016
carbon outputs
warm ocean water releases C, cold absorbs it - Begon et al., 2021
Carbon storage
soils store most of it - Lange et al., 2015
C soluble in water - Begon et al., 2021
warming temperatures increase C storage - Keenan et al., 2014
sink dynamics affect C storage more N or P = higher primary productivity = more Caron storage
Old growth forests accumulate C
Luyssaert et al., 2008
Carbon impacts
co2 has fertilising effect
higher concentration - increases rates of primary productivity
response varies in magnitude
Terrer et al., 2016
more C02 = warmer temperatures - Keenan et al., 2014
Water and nutrient cycling
water solvent - transport agent
nutrient cycling large impacts on lake productivity
lake metamophic features reduce nutrient losses
streams - cycling - controlled by the ability of particulates to sequester nutrients + dissolved nutrients to travel downstream
lakes - controlled by processes of remineralisation from particulates
Essignton and Carpenter, 2000
Eutrophication
Excessive richness of nutrients in a lake or other body of water, frequently due to runoff from the land
causes a dense growth of plant life and death of animal life from lack of oxygen.
fowler et al., 2013
Mycorrhizal fungi
help plants grow
terrer et al., 2016