OCR A 5.2.3 Redox and Electrode Potentials
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
redox titration
-oxidising agent titrated against reducing agent
-e transferred from 1 species to other
-normally indicators not needed as transition metals naturally change colour when ox state changes
use of redox titration
-used to work out conc of reducing or oxidising agent
potassium manganate (VII) titration agents
-ox agent; manganate (VII) reduced to Mn2+
-red agent; Fe oxidised to Fe3+
-addition of H2SO4; ensure sufficient H+ ions allow reduction of ox agent
choice of acid to acidify mixture
-must not react w/ manganate ions
-dilute H2SO4
-HCl; oxidised to Cl ions by manganate ion
-HNO3; ox agent; oxidise substance being analysed
-ethanoic acid; weak acid insufficient H+ ions
-conc H2SO4; oxidise substance being analysed
potassium manganate (VII) titration procedure to find conc of reducing agent
-standard sol of potassium manganate(VII), KMnO4 is added to burette
-using pipette, add measured vol of sol being analysed to conical flask
-add excess of dilute H2SO4 to provide H+ ions req for reduction of MnO4-
-during titration manganate sol reacts and is decolourised as it is added
-endpoint; first permanent pink colour as this indicates there is an excess of MnO4- ions
-repeat till u get 2 concordant titres
-reverse burette and conical flask to find ox agent
how to read meniscus in manganate titration
-KMnO4 is deep purple colour so difficult to see bottom of meniscus
-so readings taken from top of meniscus is read from
Manganate (VII) titration redox equation
-Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e- (x5)
-MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O
-5Fe2+ + MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O + 5e-
iodine/thiosulphate titration procedure
-measure out a vol of KIO3; produce IO3-
-add excess KI sol
-add this to conical flask
-add Na2S2O3 into burette
-colour changes to pale yellow; dif to see
-add 2cm3 starch; turns from deep blue to colourless
iodine/thiosulphate titration redox reaction
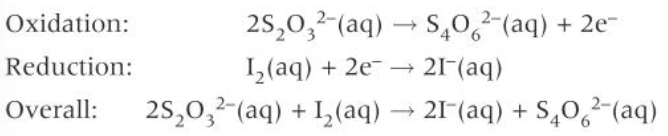
what does electrode potential depend on
-temp
-pressure of gas
-reagent conc
standard condition when comparing electrode potential
-Ion concentration of 1.00 mol dm-3
-temperature of 298 K
-pressure of 100 kPa
electrode potential
-tendency of element to lose e-
-if electrode potential is more negative then it has higher tendency to oxidise
-so flip equation and combine with other
-each half equation rep half call
Mg2+ + 2e- ←→ Mg (-2.3) Al3+ + 3e- ←→ Al (-1.66)
Mg←→Mg2+ + 2e-
Al3+ + 3e- ←→ Al
voltaic cell
-converts chemical energy to electrical energy
-electrical energy results from movement of e from redox reactions
half cell
-one half of an electrochemical cell
-can be constructed of a metal dipped into its ions, or a platinum electrode w/ 2 aq ions
how is voltaic cell made
-by connecting tgthr 2 dif half cells; allows e to flow
-chemicals in half cells must be kept apart; e move in a controlled way
-metal/metal ion or ion/ion half cells
metal/metal ion half cell
-metal rod dipped in sol of its aq metal ion
-