Flower Dissection
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Know the parts of a flower.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
How many Whorls make up a flower?
4
Name the 4 whorls
Sepal
Petal
Stamen
Carpel
Is the sepal a sexual or asexual part of the plant?
Asexual
True or false: all flowers have a sepal
False
What is the function of a sepal?
Protects the flower, especially the petals
True or false: Petals are a sexual part of the flower
False
What is the function of the petals?
Attract pollinators
Landing pad
Is the stamen sexual or asexual part?
Sexual
What sex is the stamen?
Male
What structures make up the stamen?
Filament
Anther
What’s the job of the filament?
To hold the anther
What’s the job of the anther?
Make pollen
What is pollen?
Sperm/male gamete
What is the carpel?
Female organ
What structures make up the carpel?
Stigma
Style
Ovary
What is the job of the stigma?
Sticky for pollen
What does pollen do after attaching to the stigma?
Makes a pollen tube
What does the pollen tube do?
Release sperm into an egg
The style is the ____ of the carpel.
Neck
What important thing does the ovaries hold?
Ovules that hold eggs
A matured ovary is known as a
Fruit
Once an ovule is fertilized it becomes a
seed
What are the flower types?
Complete
Incomplete
Perfect
Imperfect
Monoecious
Dioecious
Define a complete flower
Has all the whorls
Define an incomplete flower
Is missing one or more whorls
Define a perfect flower
Has both sexual organs
Define a imperfect flower
has one sexual organ
Define a monoecious flower
Plant has both sexual organs on the same plant
Define a Dioecious flower
Plant has the sexual organs on separate plants
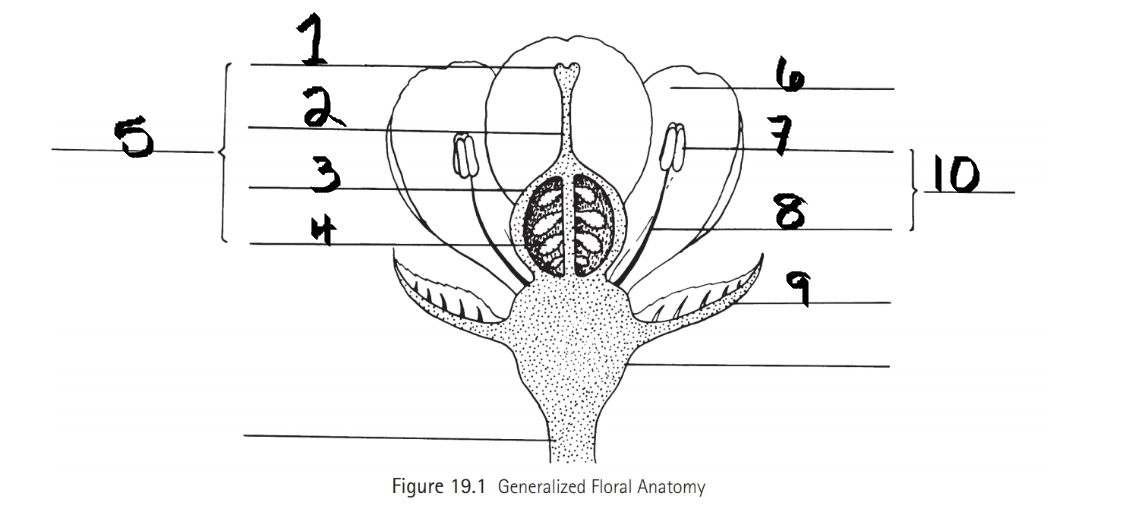
Identify 1
Stigma
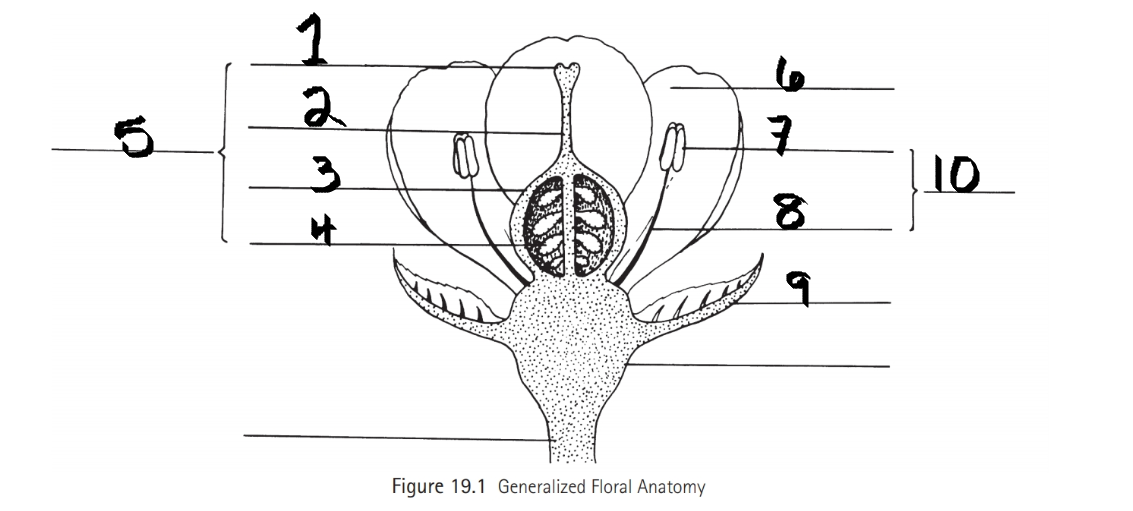
Identify 2
Style
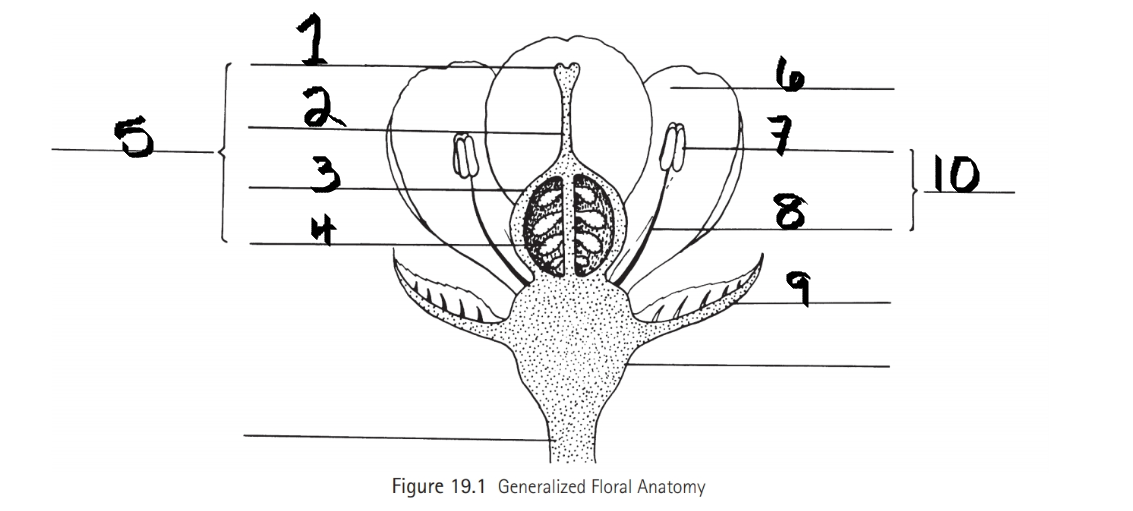
Identify 3
Ovary
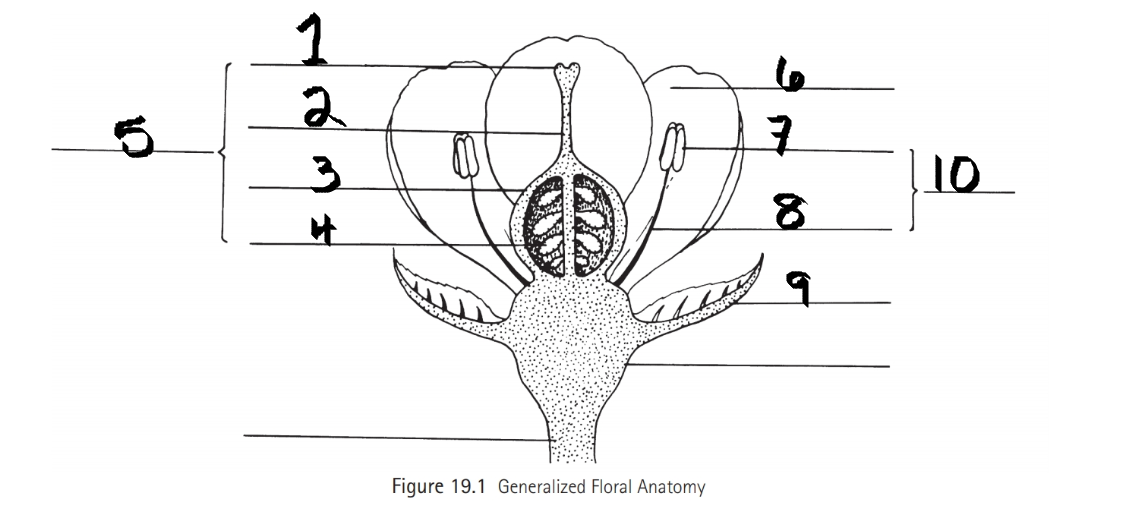
Identify 4
ovule
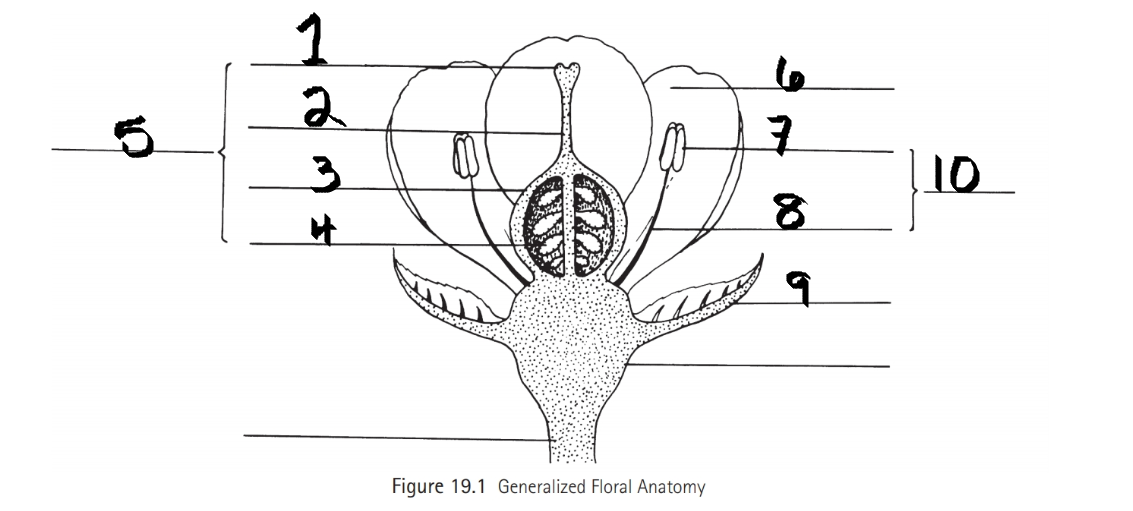
Identify 5
Carpel
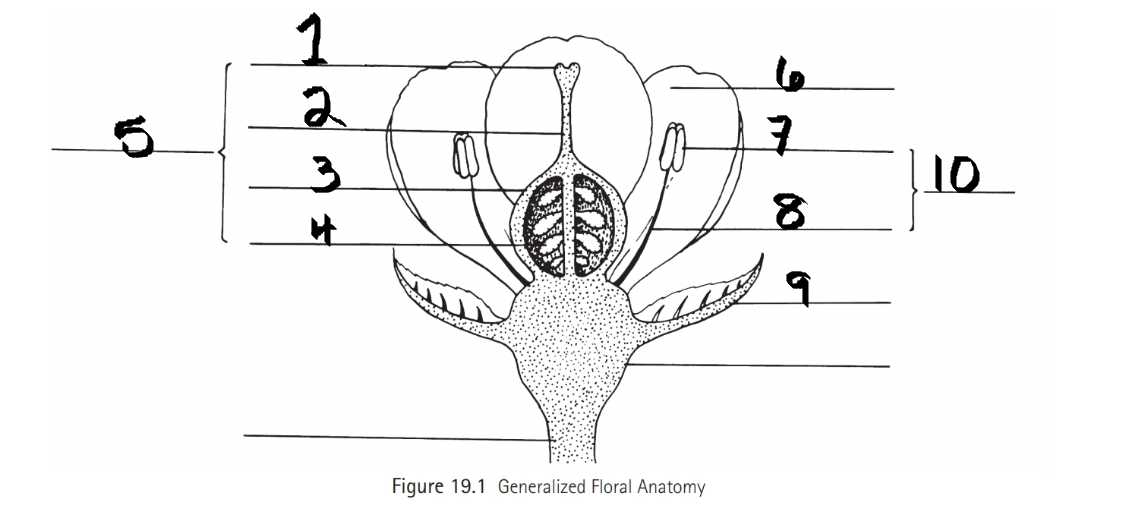
Identify 6
Petal
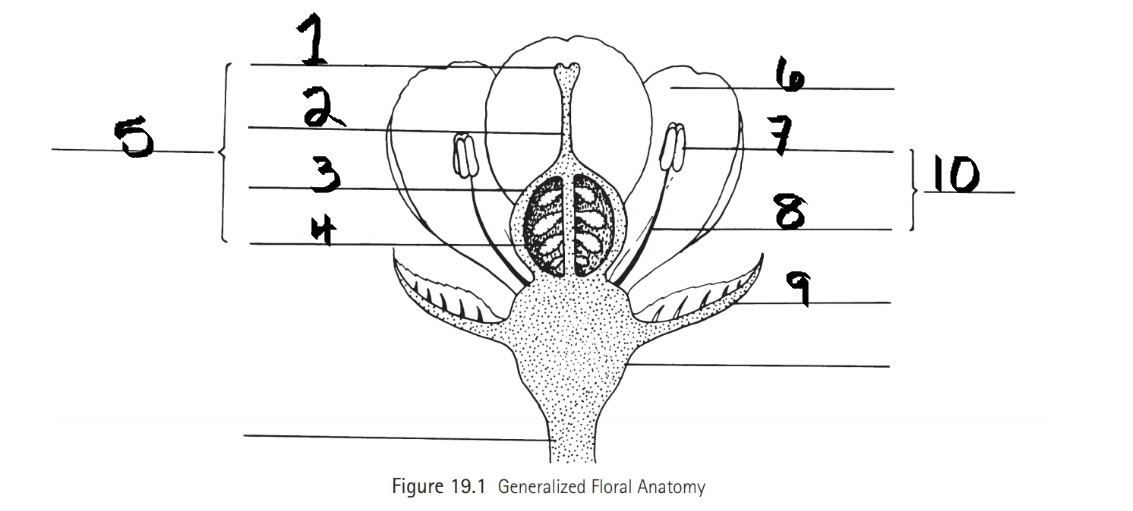
Identify 7
Anther
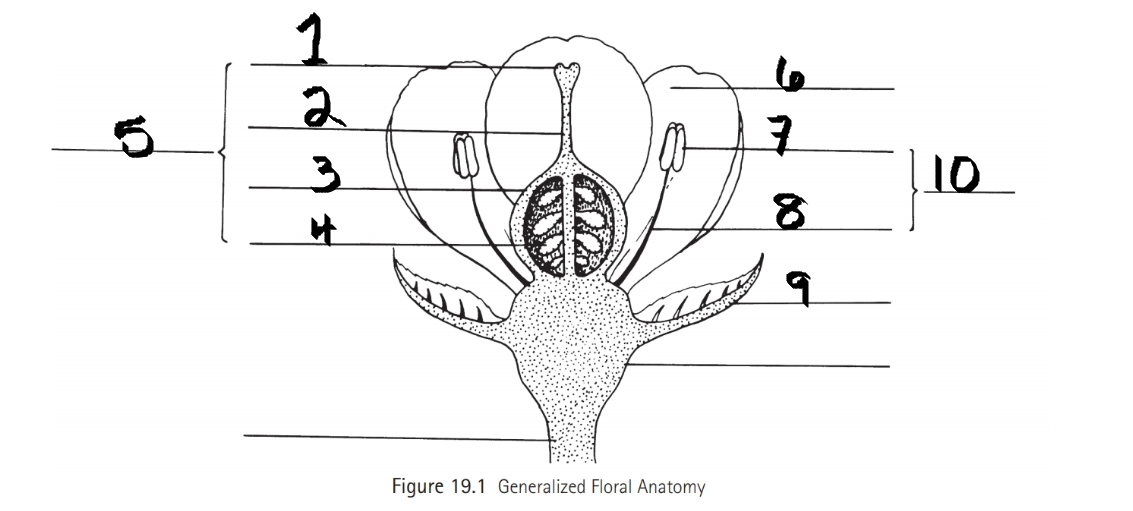
Identify 8
Filament
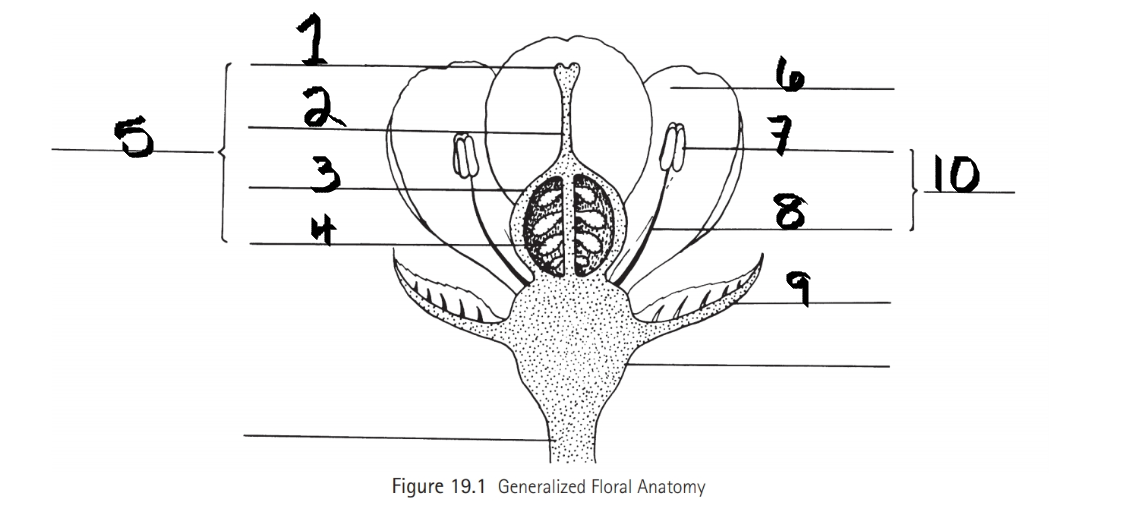
Identify 9
Sepal
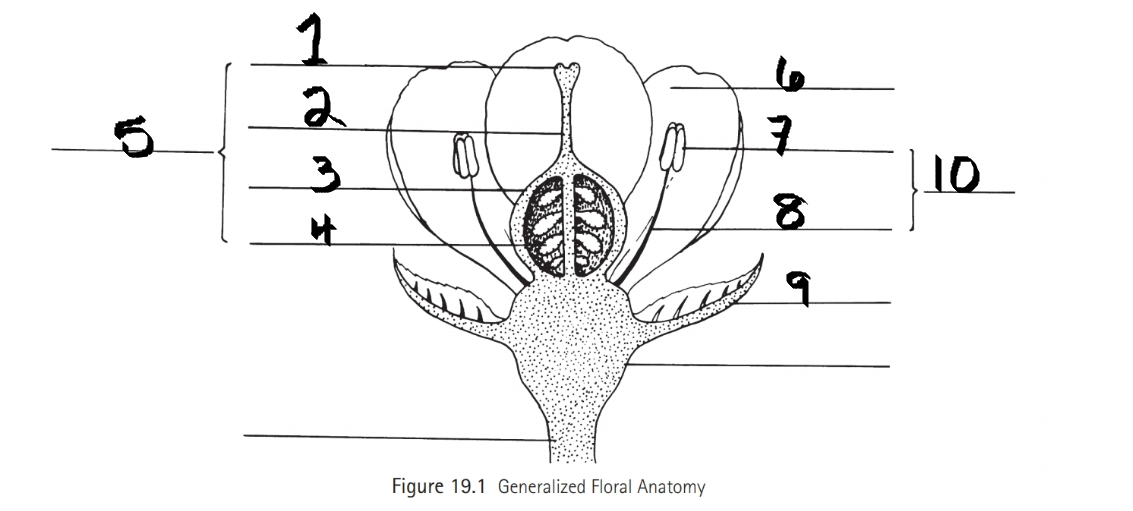
Identify 10
Stamen
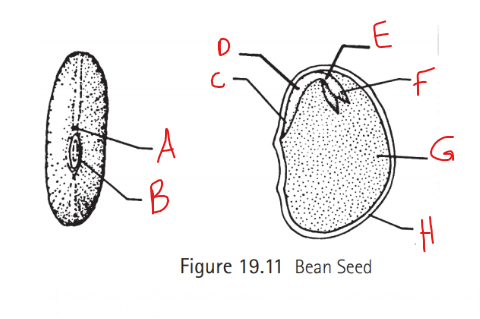
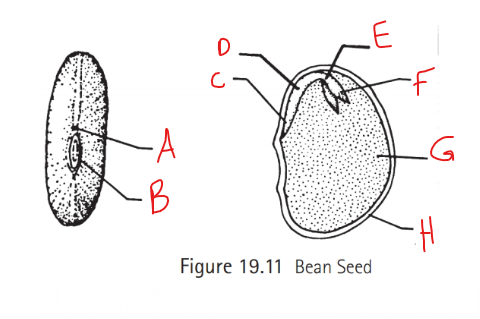
Identify A
Micropyle
What is the function of the micropyle?
Entrance for sperm
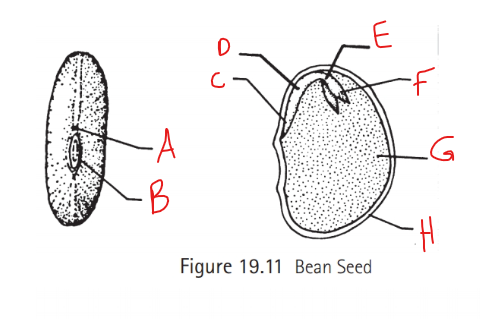
Identify B
Hilum
What does hilum do?
attaches seed to ovary
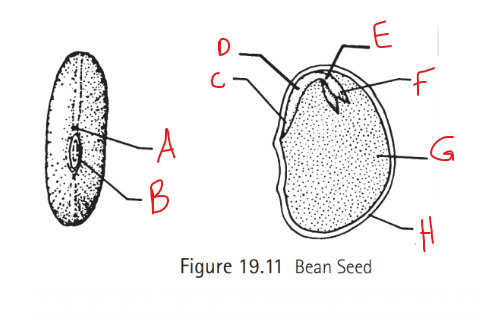
Identify C
Radical
What does the radical create?
The first primary roots
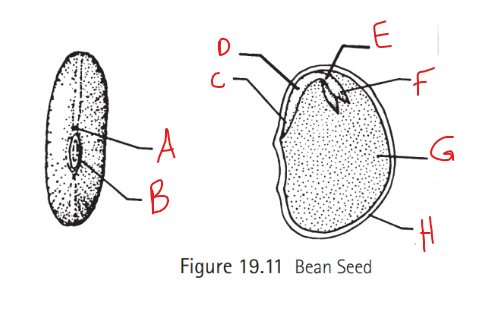
Identify D
Hypocotyl
What does the hypocotyl turn into?
roots
stems
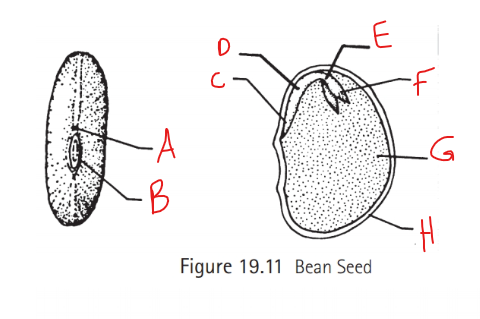
Identify E
Epicotyl
What does the epicotyl turn into?
Shoots
leaves
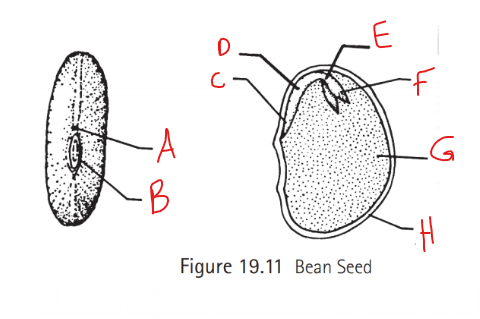
Identify F
Plumule
What does the plumule become?
forms the first leaves
Identify G
Cotyledon
What is cotyledon referred to as? What happens to this structure?
Seed leaves
It falls off
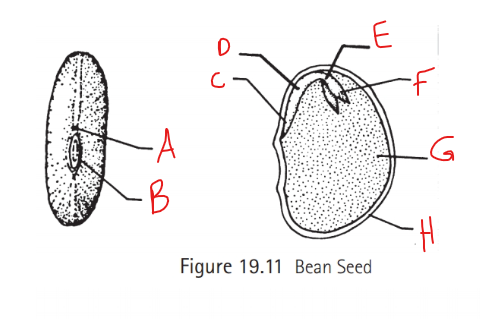
Identify H
Seed coat