Organizational Behavior: Personality and Cultural Values
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards focus on key concepts related to personality traits, cultural values, and their influence on behavior in organizational settings.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Personality
The structures and propensities inside a person that explain characteristic patterns of thought, emotion, and behavior.
Cultural Values
Shared beliefs about desirable end states or modes of conduct in a given culture.
Conscientiousness
A personality trait characterized by dependability, organization, reliability, ambition, and perseverance.
The biggest influence on job performance of any of the Big Five
Accomplishment striving—a strong desire to accomplish task-related goals
Related to career success, good health.
Agreeableness
A personality trait that reflects being warm, kind, cooperative, and sympathetic.
Communion striving—a strong desire to obtain
acceptance in personal relationships
Not related to performance in all jobs or occupations
Beneficial in service jobs
Extraversion
A personality trait characterized by talkativeness, sociability, assertiveness, and boldness.
Not related to performance across all jobs or occupations
Status striving—a strong desire to obtain power and influence within a social structure
Extraversion correlated with leadership emergence and
effectiveness and with job satisfaction
Positive affectivity—a dispositional tendency to experience
pleasant, engaging moods such as enthusiasm, excitement, and
elation
Neuroticism
A personality trait reflecting emotional instability such as nervousness, moodiness, and insecurity.
Second most important of the Big Five to job performance
• Few jobs benefits from traits associated with neuroticism
• Most jobs benefit from employees who are calm, steady,
secure.
Negative affectivity—tendency to experience unpleasant
moods such as hostility, nervousness, annoyance
Associated with low levels of job satisfaction and happiness in general
Openness to Experience
A personality trait related to being curious, imaginative, and creative.
Beneficial in some jobs but not in others; not related to job
performance across all occupations
Helpful in jobs that are dynamic, creative, opportunities to
learn
Adaptable, good at finding new and better approaches
Big Five Taxonomy
A model summarizing personalities into five broad dimensions: Conscientiousness, Agreeableness, Neuroticism, Openness to Experience, Extraversion.
Status Striving
A strong desire to obtain power and influence within a social structure, particularly associated with extraversion.
Negative Affectivity
A tendency to experience unpleasant moods such as hostility and nervousness, typically associated with high neuroticism.
Locus of Control (Neuroticism)
The degree to which individuals believe they can control events affecting them.
Differential Exposure (Neuroticism)
The increased likelihood of neurotic individuals to perceive situations as stressful.
Differential Reactivity (Neuroticism)
The tendency of neurotic individuals to feel less capable of coping with daily stressors.
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
A personality test categorizing individuals into 16 different personality types based on preferences.
RIASEC Model
A framework summarizing interest in six personality types: Realistic, Investigative, Artistic, Social, Enterprising, Conventional.
Project GLOBE
An ongoing international research effort examining the impact of culture on leadership attributes and behaviors.
Individualism
A cultural value emphasizing individual achievement and autonomy.
Collectivism
A cultural value emphasizing group cohesion and collective achievement.
Situational Strength
A concept suggesting that strong situations have clear behavioral expectations that reduce individual differences.
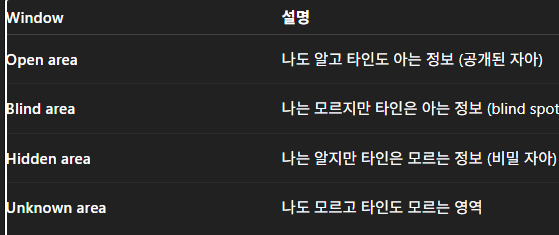
Johari Window (조하리 창)
자신과 타인 간의 인식 차이를 설명하는 모델 (Self-awareness model)
Halo effect
➡ 한 가지 긍정적 특성이 모든 평가를 왜곡하는 현상
예:
“이 사람 말 잘하네 → 전체적으로 유능할 거야”
“잘생김/이쁨 → 성격도 좋을 거야”
반대로 horn effect도 있음
(한 가지 부정적 정보가 전체 평가를 깎아버림)
Pygmalion effect
➡ 높은 기대를 받으면 실제 성과도 올라가는 현상
상사가 “너는 잘할 거야”라고 기대 → 직원이 성과 향상
기대 → 행동 → 실제 성과 → 다시 기대 상승의 선순환
반대 개념: Golem Effect
➡ 낮은 기대를 받으면 성과도 낮아짐
Trait Activation
The idea that some situations provide cues triggering the expression of specific personality traits.
Leadership Traits
Specific characteristics such as ambition, integrity, and self-monitoring associated with effective leaders.
Fiedler Model (Least-Preferred Coworker)
A contingency model of leadership that categorizes leaders as either task-oriented or relationship-oriented.
리더 스타일은 고정(fixed)되어 있고, 상황이 그 리더에게 맞아야 한다.
Low LPC → Task-oriented leader
High LPC → Relationship-oriented leader
Situational Leadership Theory
A theory suggesting that effective leadership depends on the readiness of followers.
Path-Goal Theory
A leadership theory focusing on how leaders can help followers achieve their goals.
Clarify paths & remove obstacles
Transactional Leadership
A leadership style that involves contingent rewards and management by exception.
Focus on transactions
Charismatic Leaders
Leaders recognized for their vision, personal risk, sensitivity to the environment, and unconventional behavior.
Integrity Tests
Assessments used to evaluate a person's predisposition to counterproductive behavior and honesty.
Clear Purpose Tests
Tests that assess attitudes towards dishonesty, including confessions of past dishonesty.
Veiled Purpose Tests
Tests that assess general personality traits associated with dishonesty without revealing their purpose.
Dimensions of Personality
Broad categories used to classify personality traits, often based on adjectives.
Cultural Variations
Differences in cultural values and norms that can influence behavior, particularly in organizational settings.
Leader-Member Relations
The quality of the relationship between a leader and their followers, impacting leadership effectiveness.
Position Power
The amount of power and authority a leader has in a given situation, influencing their leadership style.
Supportive Leadership
A leadership style that focuses on the well-being and personal development of employees.
Low directive, High supportive
Directive Leadership
A leadership style characterized by providing specific guidance and direction to followers.
High Directive Low supportive
Delegative Leadership
Low directive and Low supportive
Coaching Leadership
High Directive and High Supportive
GLOBE Dimensions
Nine dimensions used in Project GLOBE to summarize various cultural attributes.