Biochem 406 lecture 3: transport and mobilization of fats
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Where do chylomicrons transport fats (TG and CE)?
From the intestine to other tissues
Why are TAG resynthesized
TAGs are resynthesized from free fatty acid chains that are transported into tissues. By converting free fatty acyl chains to TAG you can create energy for later use
What are lipoproteins?
large complexes of lipids and proteins.
Inside there are TAGs and cholesteryl esters
Outside is a phospholipid monolayer and apolipoproteins
what are apolipoproteins
proteins that target the lipoprotein to specific tissue
what's a key difference in the role of chylomicrons and VLDLs
chylomicrons are assembled in the intestine and VLDLS are assembled in the liver. Both deliver energy to peripheral tissue
What do lipoprotein lipases do
Lipoprotein lipases break down lipoproteins into free fatty acids and glycerol
which class of plasma lipoproteins have the lowest density
Chylomicrons
what are the properties of chylomicrons
Density: <0.95 g/ml (lowest density)
Apolipoprotein: B48, C, E
Role: Transports dietary fat
what are the properties of VLDL
Density: 0.95-1.006 g/ml
Apolipoprotein: B100, C, E
Role: Transports fats made within the body
what are the properties of IDL
Density: 1.006-1.019 g/ml
Apolipoprotein: B100, E
Role: LDL precursor
What are the properties of low density lipoprotein
Density: 1.019-1.063 g/ml
Apolipoprotein: B100
Role: Cholesterol transport (to muscle)
what are the properties of HDL
Density: 1.063-1.21g/ml
Apolipoprotein: A
Role: Reverse cholesterol transport (muscles to liver)
what is the signal for the mobilization of stored fats
Glucagon is the signal for fasting, low energy state. It binds to a GPCR and stimulates cAMP production and PKA activation
How does the glucagon signal initiate fat mobilization
Glucagon signaling activates PKA
Activated PKA phosphorylates perilipins
Phosphorylated perilipins allows HSL to break down TAG in lipid droplets
What does Serum Albium
once mobilized, fatty acid chains are transported in the blood by binding to serum albium
What are the 3 steps for cells to use fats for energy production
1. Activation to fatty-acyl-CoA
2. Transport into Mitochondria
3. B-oxidation to produce NADH, FADH2, and Acetyl-CoA
How is fatty acid transported to the mitochondria
1. Fatty acid is activated when acyl-coA synthase adds acetyl CoA to fatty Acyl chain
2. Fatty acyl-coA is converted to fatty acylcarnitine by acyltransferase 1 (CAT 1)
3.Acyl carnitine translocase moves fatty acylcarnitine to the mitochondria
4. Carnitine acyltransferase II (CAT II) converts fatty acyl carnitine back to fatty acyl-coA
How many carbons does each round of Beta oxidation remove, and what are products generated
Each round loses two carbons
Produces, 1 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 Acetyl CoA
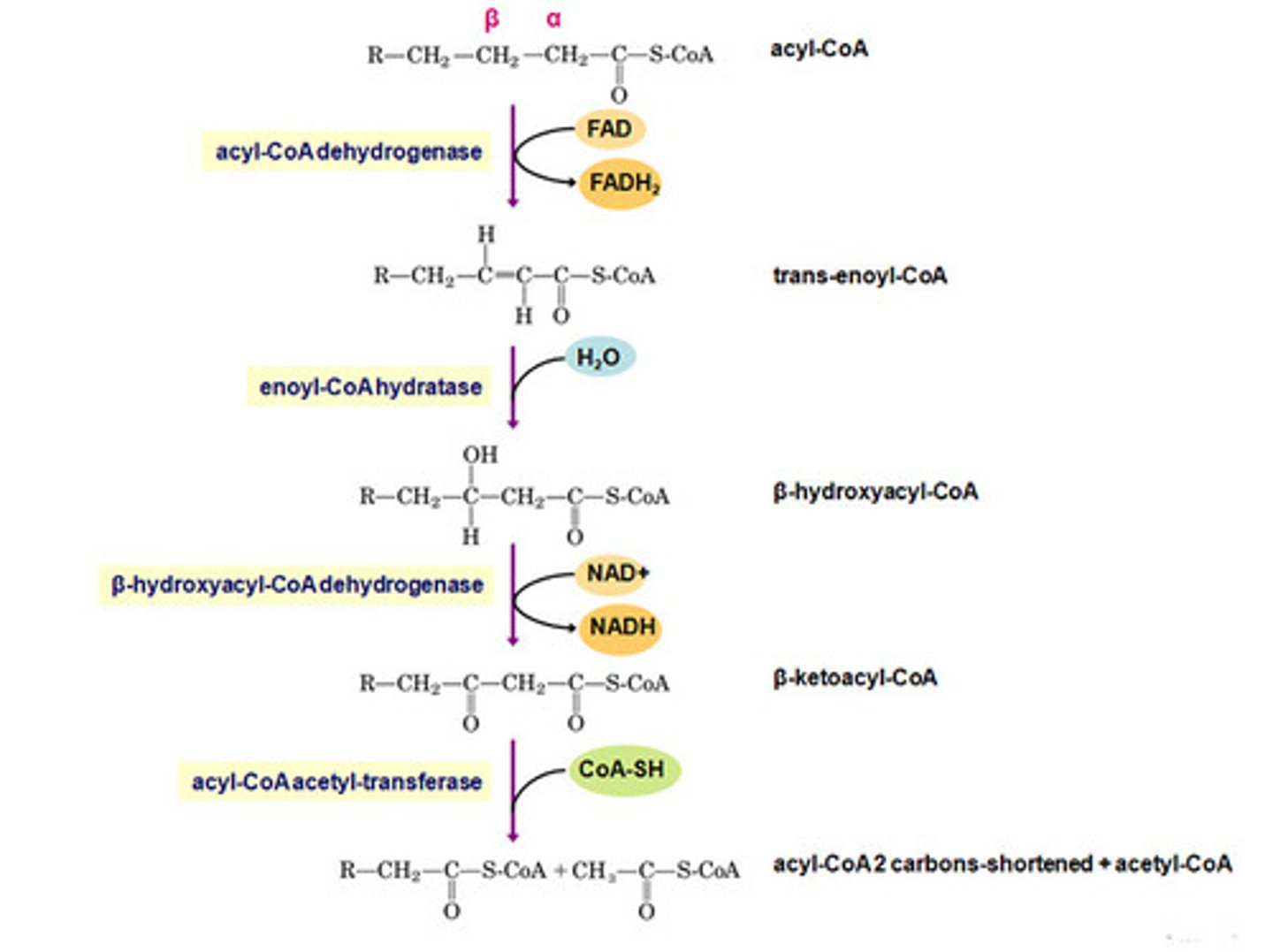
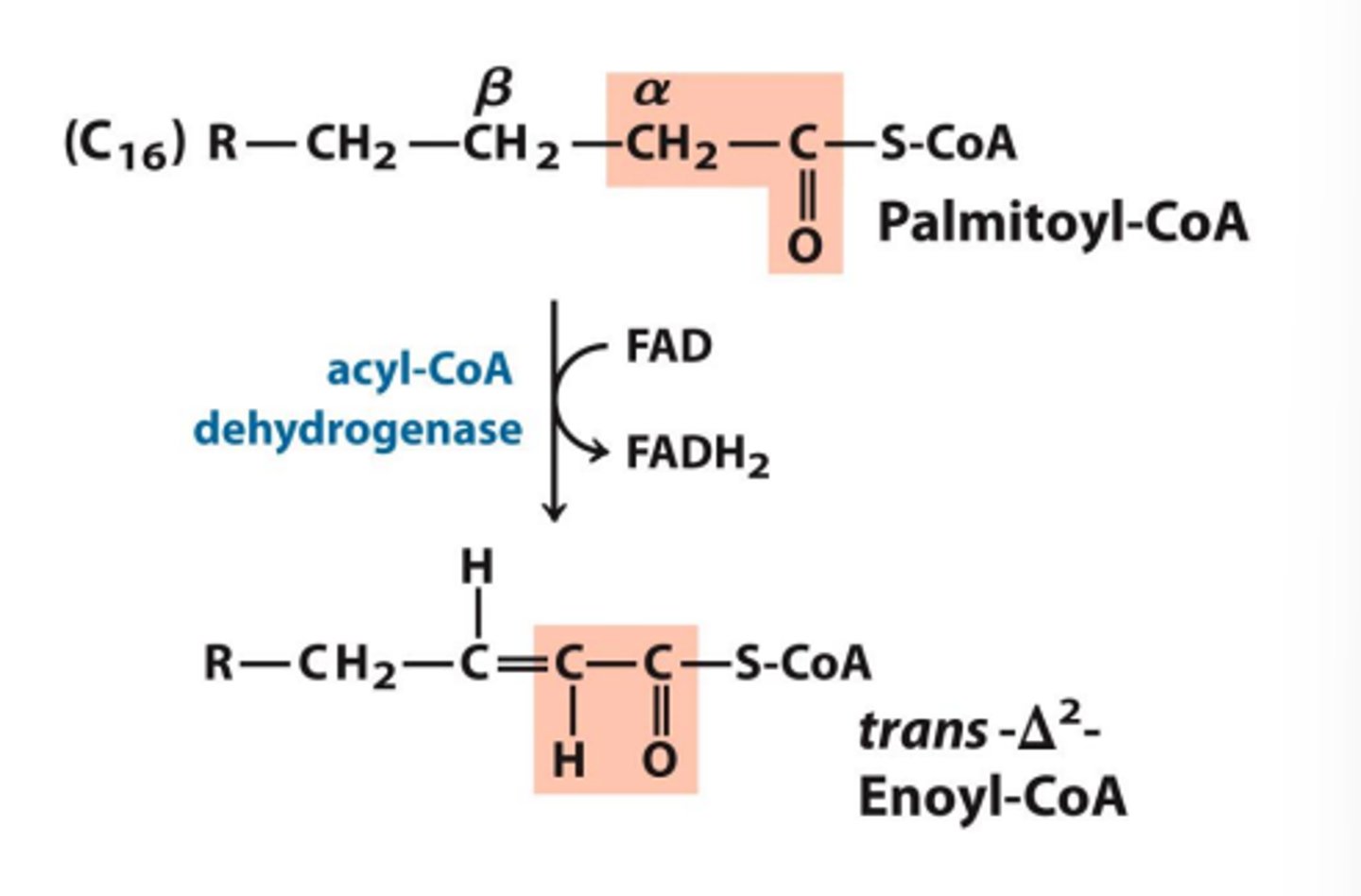
What is step 1 of Beta oxidation
Oxidation converting acetyl-coA to Enoyl-CoA
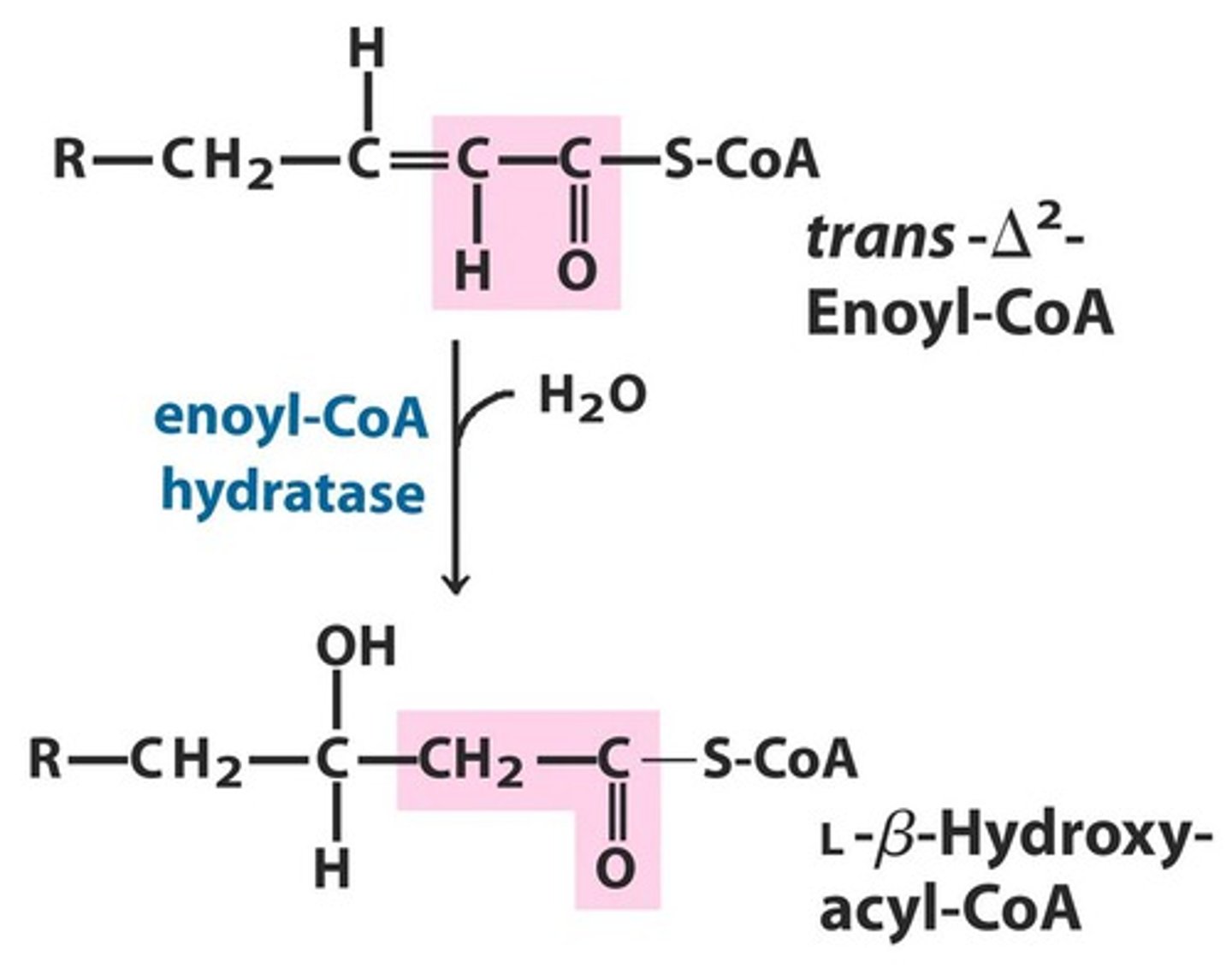
what is step 2 of Beta oxidation
Hydration converting enoyl-CoA to B-hydroxy acyl CoA
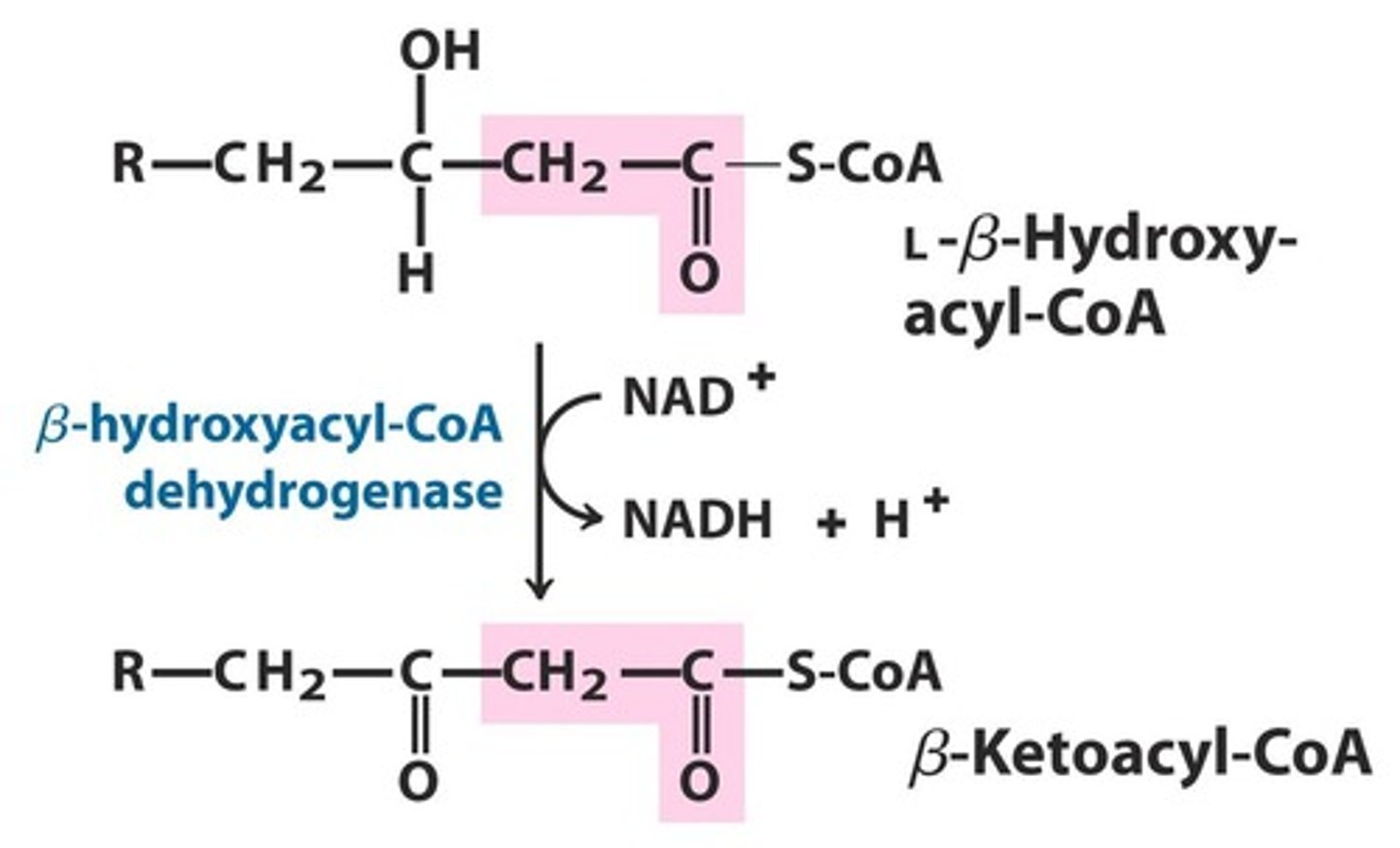
what is step 3 of beta oxidation
oxidation turning the hydroxy group on the beta carbon into a ketone turning B-hydroxy acyl CoA into B-ketoacyl-CoA
what is step 4 of beta oxidation
Thiolysis forming acetyl CoA and a shortened acyl-coA
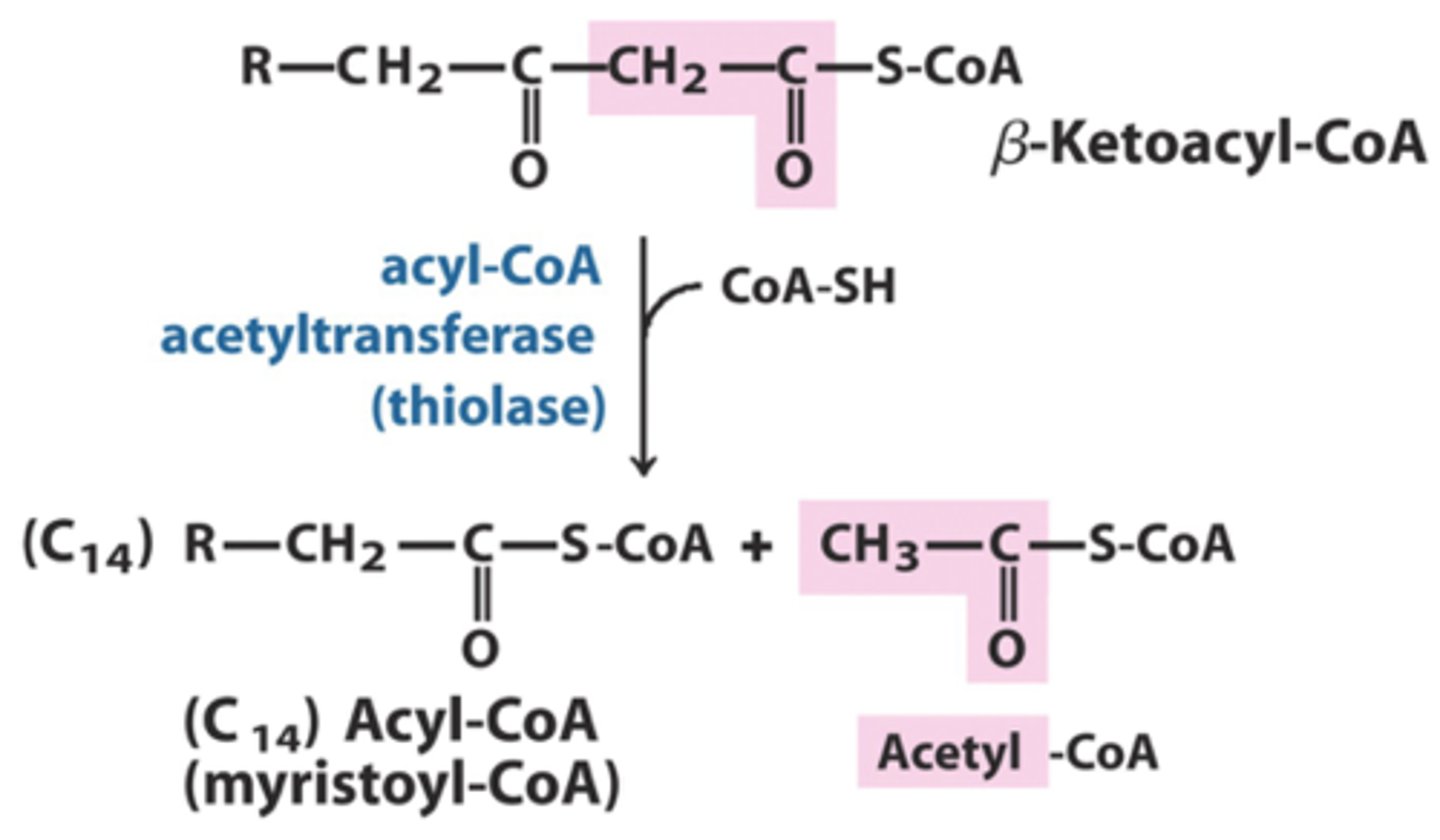
For 1 molecule of Palmitoyl-CoA how many acetyl-CoA would be produced for TCA
8 acetyl-coA
What are the key enzymes for B-oxidation of fatty acid for poly unsaturated fatty acids
2,4, Dienoyl-CoA reductase and enoyl-CoA isomerase (which turns cis to trans bonds)
What enzymes are additionally need for odd chain fatty acids
Propionyl CoA carboxylase (+biotin cofactor) adds a CO2 to remaining acetyl coA
Methyl malonyl CoA mutases (+B12 cofactor) rearranges the C-C bonds to make succinyl CoA