Microbiology Test 2
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
typical bacterial growth curve
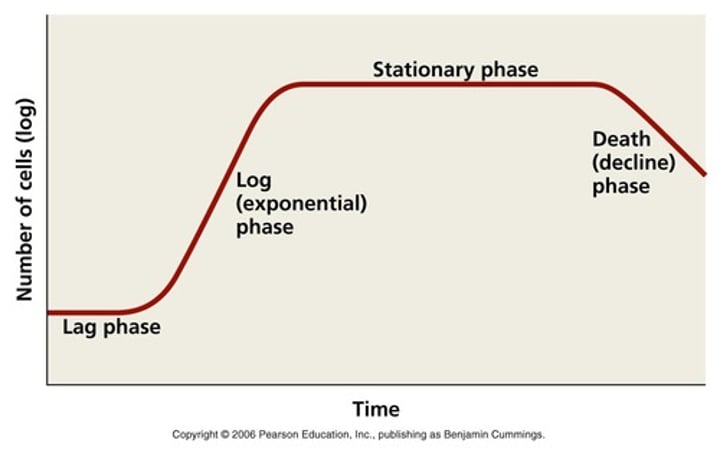
stationary phase
cells are reproducing and some cells are dying at about the same rate, so the overall population numbers stay the same
death phase
when you have bacteria dying at a faster rate than cells are reproducing
lag phase
the bacteria are metabolically active but they are not reporoducing so the cell numbers stay the same
exponential (Log) phase
in a short period of time the bacteria will replicate many times causing a large increase in cell number
bacteria that are grown or cultivated in batches have an _____________ growth phase.
additional
microbial batch growth curve
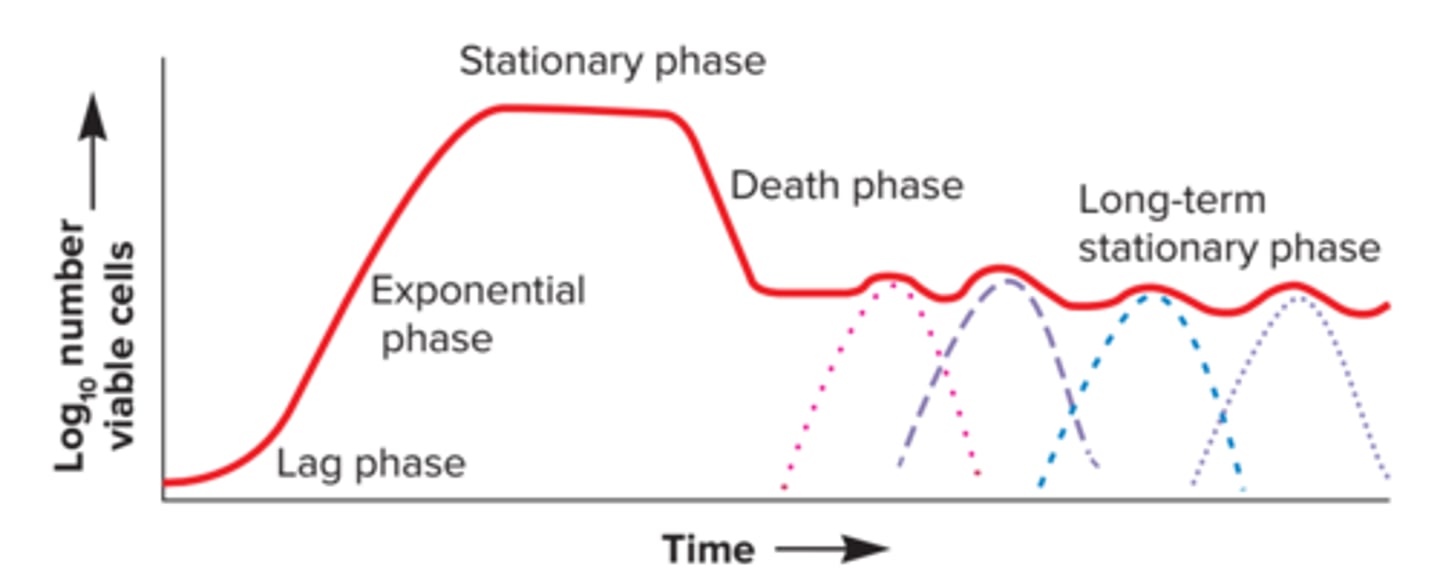
long-term stationary phase
only in the microbial batch growth curve
has a constant input of nutrients and a way to get rid of some waste products
generation (doubling) time
-the time needed for the population to double in size
-varies depending on species of microorganism and environmental changes
in ideal conditions, the generation (doubling) time can occur as quickly as ___ minutes
15
binary fission
-most bacterial cells are divided by this process
-the DNA replicated first & the cytoplasm divides last
most bacterial cells have...
single circular chromosomes
where does DNA replication occur?
At the origin site of replication
Terminus
site at which replication of DNA is terminated, located opposite of origin
Mesosomes
-look like loop-like structures of the plasma membrane
-they help to pull the chromosomes to the opposite pole of the cell to ensure that the daughter cells will each have a chromosome
what happens during cell replication?
-the septum begins to grow inward as the chromosomes move towards opposites ends of the cell via mesosome
-the septum is synthesized completely through the cell centers creating two separate cell chambers (aka daughter cells)
-some species separate completely while others remain attached.
What is the cell wall composed of?
1/2 cell wall is newly synthesized peptidoglycan and the other 1/2 is an old cell wall hemisphere and a peptidoglycan
some bacteria reprodcue by methods other than binary fission such as....
budding (ex. yeast) and multiple fission
Ftsz determines the site of _____________ growth
cell wall
How does cell wall synthesis work?
-peptidoglycan synthesis starts in the cytoplasm with the attachment of uridine diphosphate (UDP) to the sugar n-acetylglucosamine (NAG)
-NAM is transferred from UDP to bactoprenol (a carrier embedded in the plasma membrane)
-NAG is then attached to NAM: generating a NAM-NAG; the NAM-NAG units are available for insertion
-in order for NAM-NAG unites to become part of the cell wall, you need to have Autolysins degrade bonds in the existing peptidoglycan-> this permits the insertion of new NAM-NAG units
What are some environmental factors that affect microbial growth?
pH, temperature, oxygen, biofilms
What is pH?
measure of the relative acidity of a solution
acidophiles
pH 0 and 5.5
neutrophiles
pH 5.5 and 8
alkaliphiles (alkalophiles)
pH 8 and 11.5
What are some mechanisms that maintain a neutral cytoplasmic pH?
-exchange potassium for protons
-pump protons out
-synthesize acid and heat shock proteins
-change the pH of their habitat by producing acidic or basic waste product
temperature effects
bacteria have a range in which they will grow, the range varies for different types of bacteria
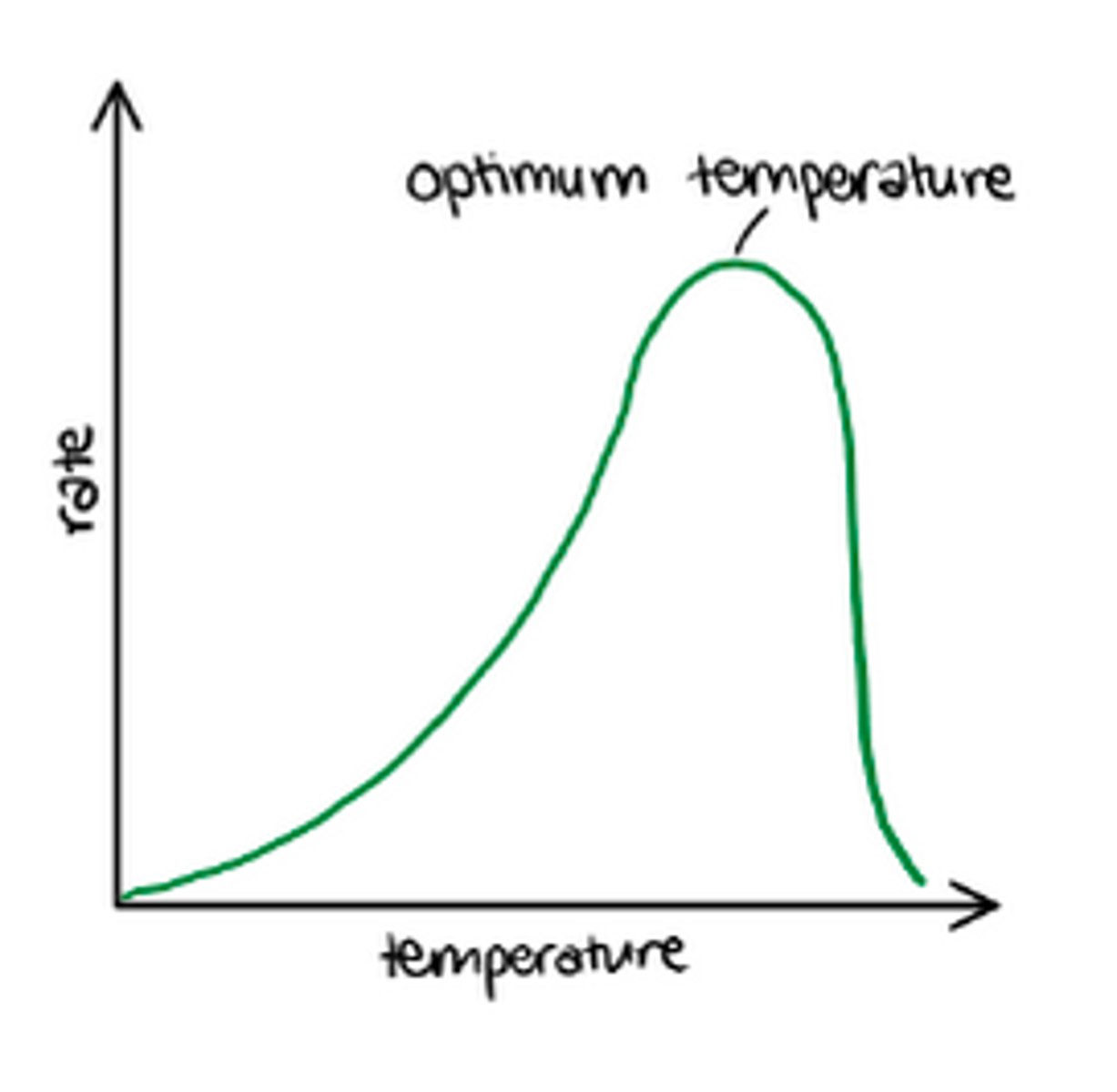
psychrophiles
cold loving
0-20 degrees celsius
pyschotrophs
0-35 degrees celsius
known for food spoilage in fridges
mesophiles
20-45 degrees of celsius
human pathogens are classed as ________________.
mesophiles
thermophiles and hyperthemophiles are found in _______________.
hydothermal vents in the ocean.
oxic zone
area where O2 is available
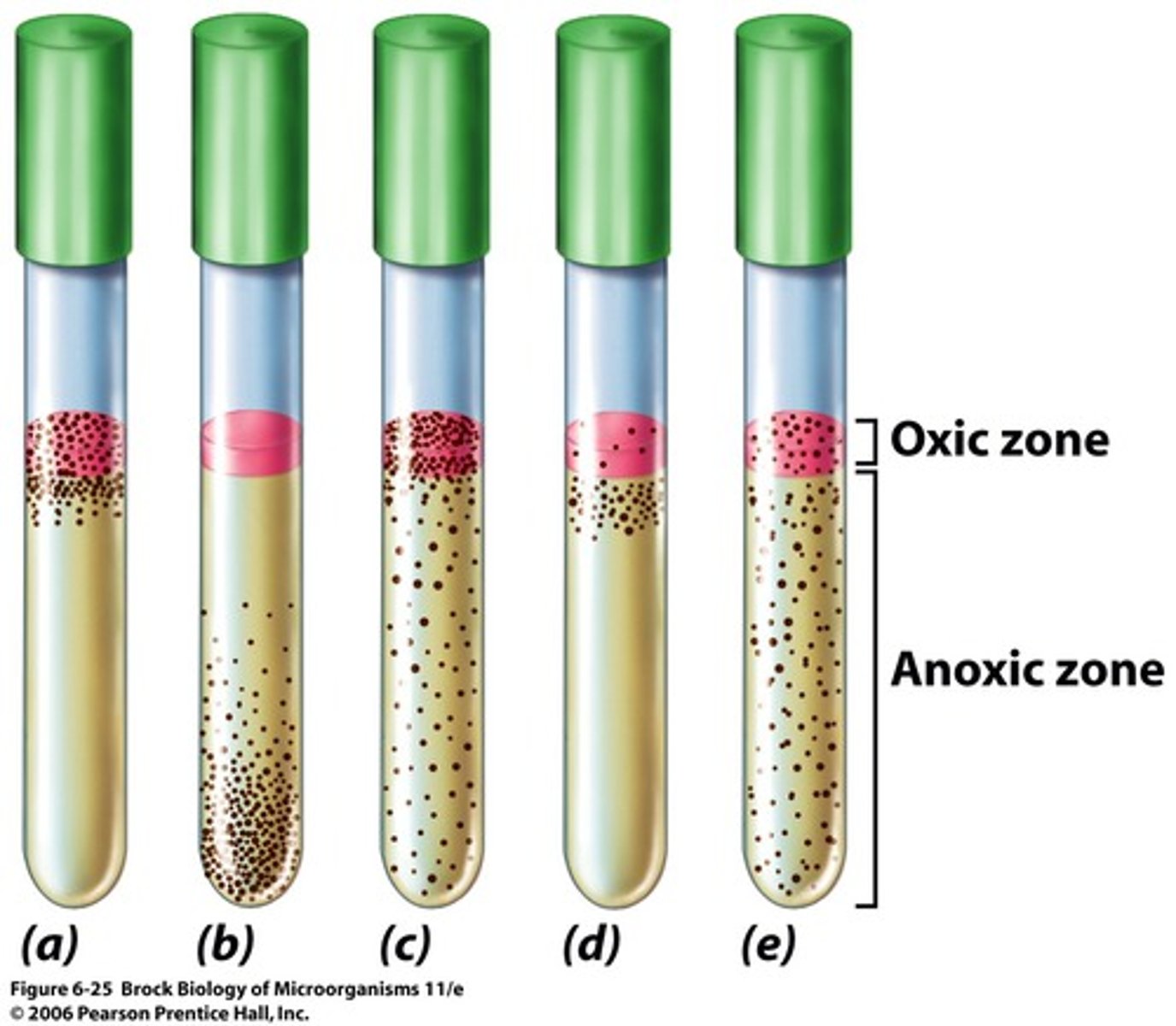
anoxic zone
where there is no O2
aerobe
requires oxygen
anaerobe
does not require oxygen, could potentially die in its presence.
obligate aerobe
requires O2
microaerophile
requires low levels of O2
facultative anaerobes
do NOT require O2 but grow better in its presence
aerotolerant anaerobes
grow with or without O2
Growing anaerobic microbes in anaerobic jar
-water is added to gas peak (gas generator envelope) to generate H2 and CO2
-carbon dioxide promotes more rapid growth of microbes
-oxygen is removed with hydrogen to form water
-this reaction is catalyzed by the palladium pellets
-the anaerobic indicator stirp methylene blue becomes colorless in absence of O2

quorum sensing
bacterial cells in biofilms communicate in a density dependent manner
what is a quorum sensing system?
symbiosis- Vibrio fischer and bioluminescence in squid
peptones
protein
extracts
aqueous extracts, usually of beef or yeast
agar
polysaccharide solidifying agent
selective media
-allow the growth of particular microorganisms, inhibiting the growth of others
-mannitol salt agar- staphylococcus
differential media
-distinguish among different groups
-blood agar- hemolytic bacteria
-EMB- lactose fermenters
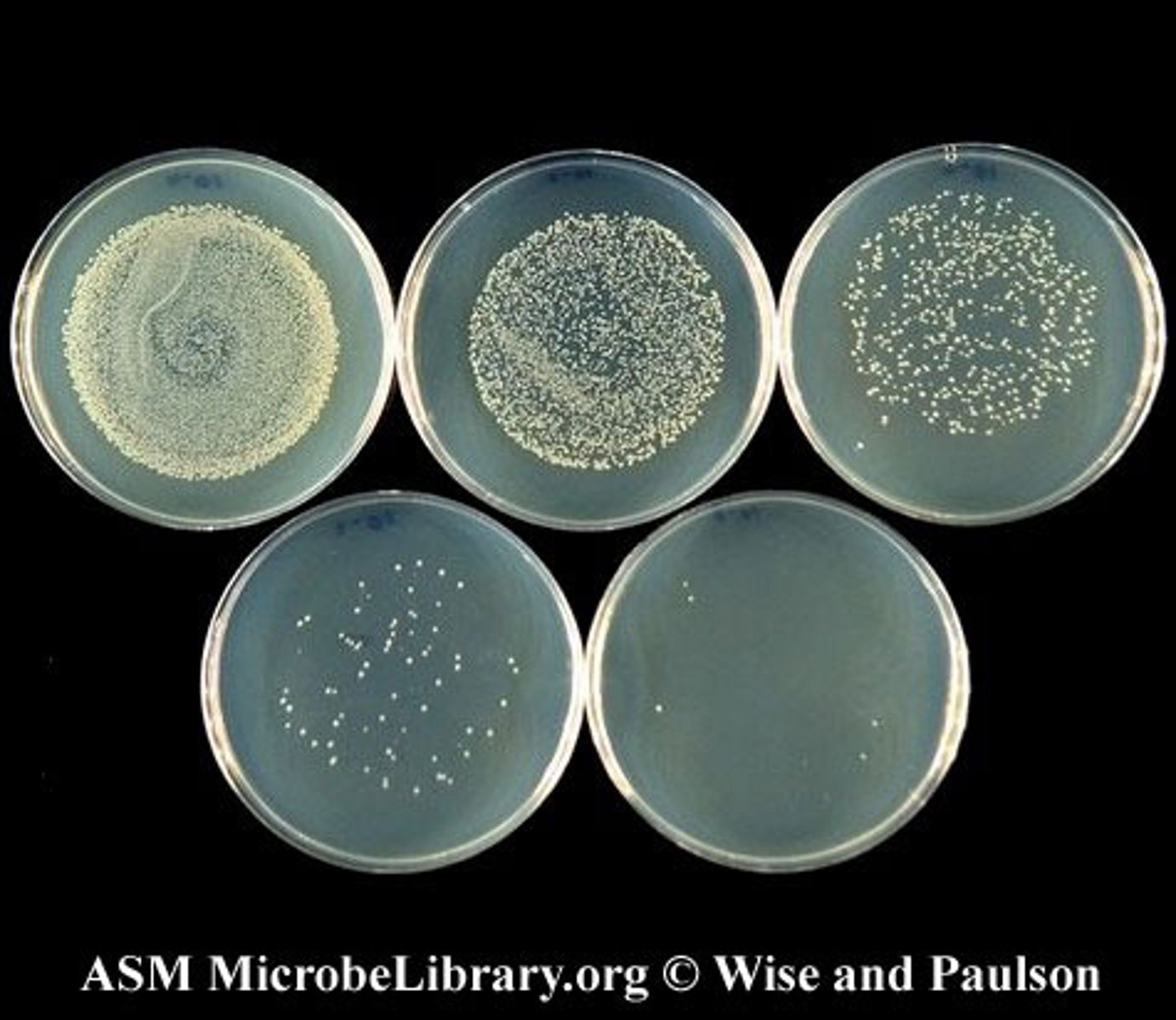
Describe counting cell numbers by the spread plate
After incubation the numbers are determined by counting the colonies.
Results expressed as colony forming units (CFU) ideally approximately 25 to 250 colonies per plate.
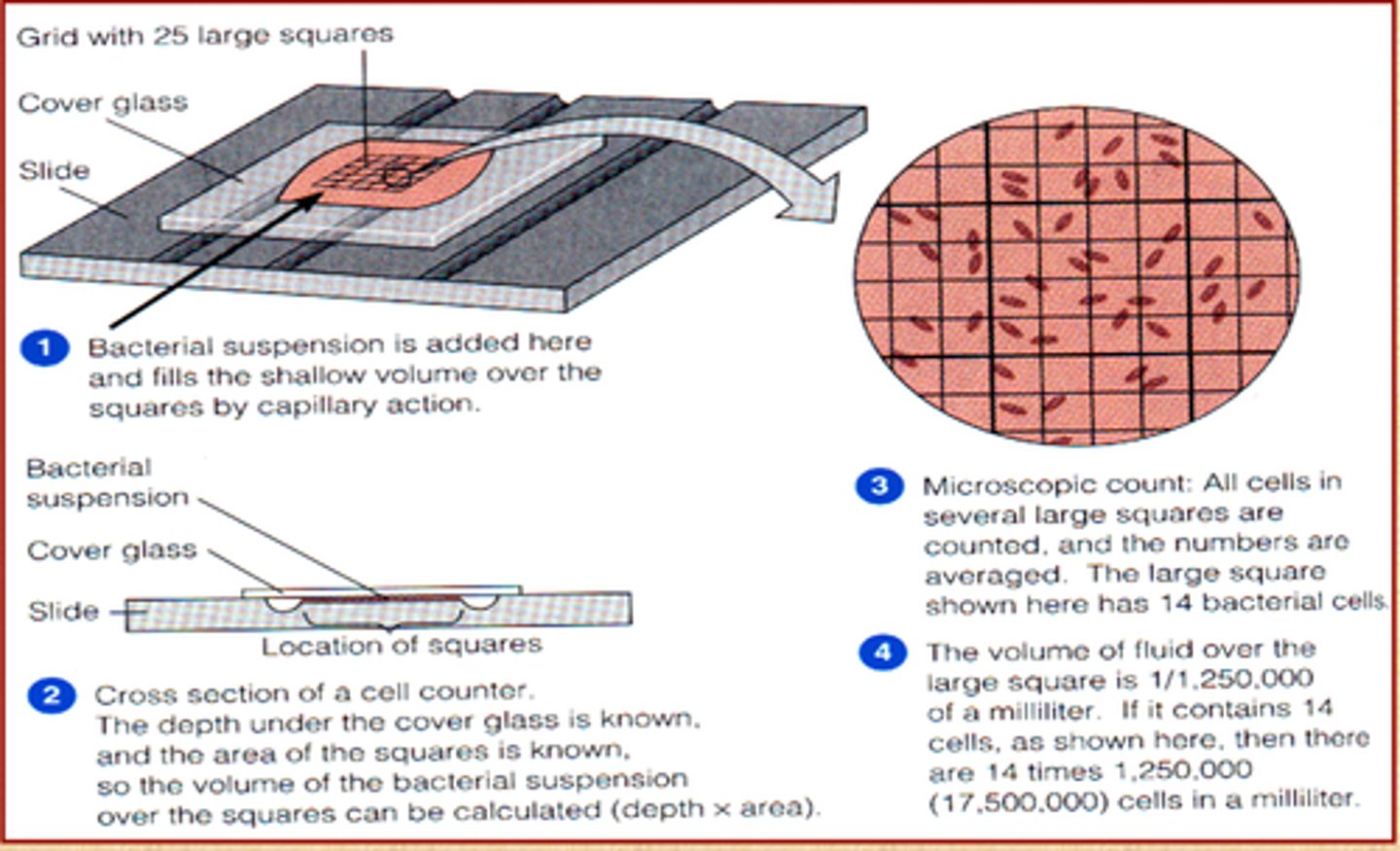
Petroff-Hauser chamber
-a type of counting chamber
-used often to determine the Grade of milk
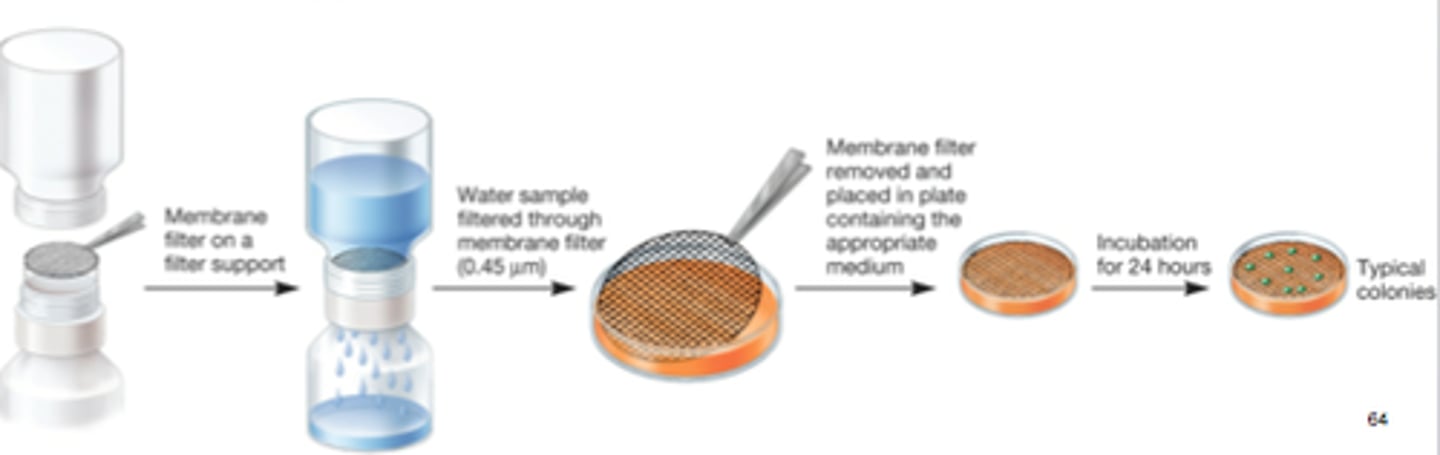
membrane filter technique
-bacteria from aquatic samples are trapped on membranes
-colonies grow on membrane
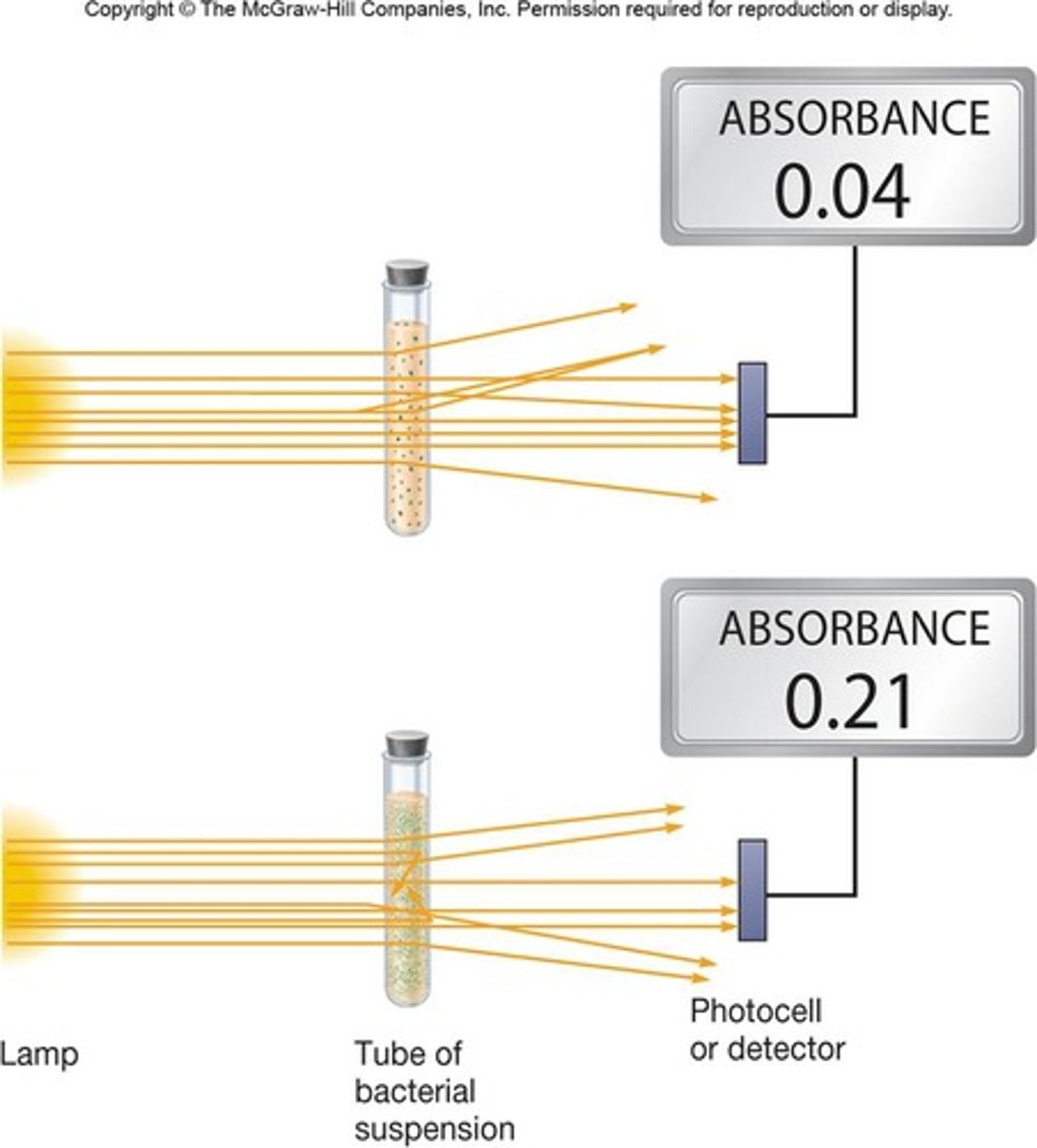
turbidometric measures
-light scattering
-quick, easy, sensitive
-spectrophotometer
metabolism
total of all chemical reactions in the cell
catabolism
breakdown/ degrade large molecules
anabolism
build/ synthesize large molecules
metabolism pathways can be varied
-linear
-cyclin
-branching
Catabolic reactions _______ ATP molecules.
form
anabolic reactions use ATP to _________________________.
build larger molecules
What are three ways to generate ATP?
1. substrate level phosphoylation
2. oxidative phosphorylation
3. photophosphoylation
Molecules needed for metabolism:
electron carriers picks up high energy electrons and carry them to electron transport systems
enzymes help to carry out each step in metabolic pathway.
NAD
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
an electron carrier
NADP
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
(typically used in anabolic pathways)
an electron carrier
FAD
electron carrier
flavin adenine dinucleotide
FMN
-flavin mononucleotide
-riboflavin phosphate
coenzyme Q (CoQ)
electron carrier, also called ubiquinone
cytochromes
electron carriers
used iron to transfer electrons
electron transport chain (etc)
electron carriers organized into ETC
enzymes
-lower activation energy of rxns
-speed up rate
-not changed during reaction
-binds to substrates
-some enzymes are composed more than one polypeptide
apoenzyme
protein portion of enzyme
coenzyme or cofactor
non-protein portion of enzyme
holoenzyme
apoenzyme & coenzyme
active site
where it binds to substrate
Each enzyme has specific pH and temperature optima, deveiation from optimum will __________________________.
slow enzyme activity
denaturation
loss of enzymes structure and activity when temperatures rises too much above optima
microorganisms have different sources for getting ______, ___________, and __________.
energy, electrons, and carbon
auto-
self
hetero-
from an "other" source
photo-
light
chemo-
chemicals
litho-
inorganic
-troph
feeding or eating
photolithoautotroph
carry out photosynthesis, get their energy from light and carbon from carbon dioxide
chemoorganoheterotroph
most human pathogens!
most respiration involves the use of an _____________________________.
electron transport chain
aerobic respirations final electron acceptor is _________________.
oxygen
femernation has no _________________.
electron transport chain
How many steps does aerobic respiration in prokaryotics have?
4 steps
what is the formula for glucose
C6 H12 O6
isomer of glucose is ______________.
fructose
Aerobic respiration produces ATP by.....
substrate level phosphorylation & oxidative phosphorylation
The Embden-Meyerhof Pathway
-commonly called glycolysis
-occurs in cytoplasmic matrix
-this is the most common pathway for glucose degradation
-it can function in the presence or absence of O2
How does glycolysis work?
1. addition of phosphates "primes the pump"
2. oxidation step- generates NADH
3. High-energy molecules used to synthesize ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation
What is the summary of glycolysis?
glucose + 2ADP + 2P + 2NAD-> 2 pyruvates + 2 ATP + 2NADH + 2H+
The tricarboxylic acid cycle is also known as.....
citric acid cycle, TCA cycle, and Krebs cycle
bacteria and archaeal electron transport chains are found in the ___________.
plasma membrane
bacterial and archaeal ETCs are different from mitrochondrial ETC because.......
they have different molecules and they may be shorter
in bacteria and archaea, for each NADH+H, ____ ATP are made.
3
In bacteria, ______ NADH always results in ______ATP produced at the ETS
1, 3
In bacteria, _____FADH2, results in _____ATP produced at the ETS.
1,2
What is generated at the ETS?
most of the ATP of carbohydrate catabolism (aerobic respirtation)
the atp is produced by the process of oxidative phosphorylation