UNLV BIOL 251 2.1 & 2.2 Regner
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
Whose work was rediscovered in 1900?
Gregory Mendel's work
What did biologists begin genetic experiments on?
fly, rabbit, guinea pig, corn, tobacco
What was observed during mitosis and meiosis?
chromosomes; however it was unclear how genes and alleles were connected
genotype --> phenotype...
was a mystery
What was found in the nucleus in 1868?
DNA
What was the fibrous called?
nuclein
Two types of nucleic acids
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
RNA contains
uracil and ribose sugar
DNA contans
thymine and deoxyribose sugar
DNA and RNA were present in the ____, had an ____ function, and had no connection btwn ____ acids and ____
nucleus; unknown; nucleic; genetics
What are drosophila?
fruit flies
T.H Morgan's group showed that
genes were carried on chromosomes
Which chromosome has the eye color gene?
X chromosome
Protein(s) complex has ____ amino acids
20
Protein(s) assumed to be _____ material
genetic
DNA was considered
unimportant and uninteresting
scientific name for ear infection
Griffith Streptococcus pneumonia
Types of ear infections
pneumonia, bacteremia, meningitis
do smooth strains produce virulent or avirulent capsules?
virulent
do rough strains produce virulent or avirulent capsules?
avirulent
What was the result when mice were injected with live cells of harmless (R) strain?
Mice live; no live R cells (R cells avirulent) in blood
What was the result with live cells of killer (S) strain?
mice got unalived; live S cells in blood
What was the result when mice were injected with heat-killed S cells?
mice live; no live S cells in blood
What was the result when mice were injected with live R cells + heat-killed S cells
mice unalive; live S & R cells in blood
What did Griffith conclude from this mice experiment?
Griffith concluded that something from the heat-killed S cells transformed the live R cells
What was the debate among scientists about the mice experiment?
debated about what molecule changed the R and S phenotypes
What was the standard assumption about the Transforming Principle?
proteins were responsible for unaliving the mice
What did scientists use that bind specifically to DNA?
dyes
DNA doubles during what phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
"S" phase
Symbol for diploid
2n
Symbol for haploid
n
Diploid and haploid describes the number of ____ and the amount of ____
chromosomes; DNA
After meiosis, games have ____ the amount of DNA
half
What is the Transforming Principle?
DNA, RNA, protein
What are the degradative enzymes?
RNase, Protease, DNase
Diagram of evaluating for the presence of cells
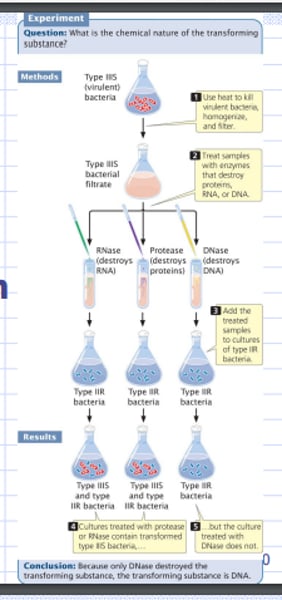
What does RNase and Protease contain?
the both contain Virulent S strain and R strain bacteria
What does DNase contain?
R strain bacteria only
What did the Transforming Principle conclude?
R cells were transformed by DNA from heat-killed S cells
Previous Exam Question:
What happened when Fred Griffith mixed heat-killed smooth (S) and live rough (R) strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
A. mRNA from the heat-killed S cells were translated into lethal proteins by mice cells; inoculated mice died
B. Heat-killed S cells were revived by the R cells; inoculated mice died
C. Some R cells absorbed the DNA from the heat-killed S cells; inoculated mice died
D. There was no change as compared with the control; all survived
E. Capsule from the heat-killed S cells induced a strong mouse immune response; all mice survived
Some R cells absorbed the DNA from the heat-killed cells; inoculated mice died
Most scientists accepted that genes were composed of what?
genes were composed of DNA
What two nitrogenous bases are purines?
adenine and guanine
What two nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines?
thymine and cytocine
Chargaff's Rule
distinguishing between which two nitrogenous bases were either purines or pyrimidines
What did Rosalind Franklin analyze at King's College?
analyzed DNA with X-ray crystallography
Franklin's results
Helical molecule
Turn every 3.4 nm
Diameter of 2.0 nm
X-ray crystallography diagram
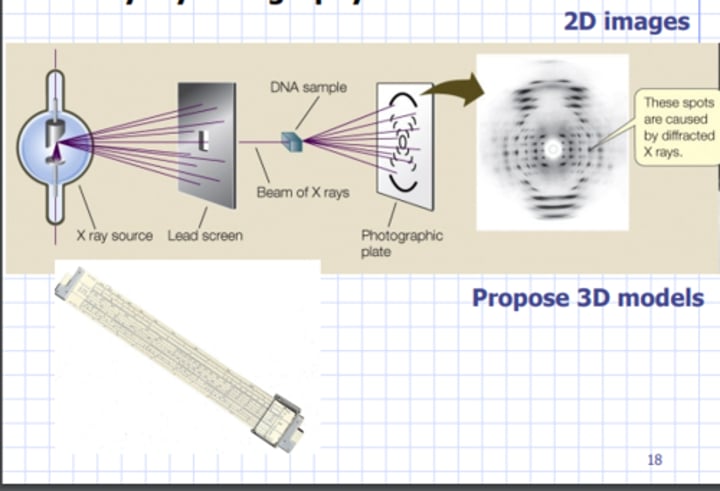
Watson & Crick determined what with DNA?
DNA was a double helix without performing any independent experiments
What data did Watson & Crick use to build models of DNA helix?
alpha helix, width & no. bases per turn, purine = pyrimidines
How did knowing 3D structure of DNA help biologists?
understand DNA replication and transcription
How did purine and purine fit together?
wide fit
How did pyrimidine and pyrimidine fit together?
narrow fit
What were purine and pyrimidine consistent with?
consistent with X-ray diffraction data
How many rings did pyrimidines have?
1-ring
How many rings do purines have?
2-rings
DNA is ____ chains of nucleotides
2 chains

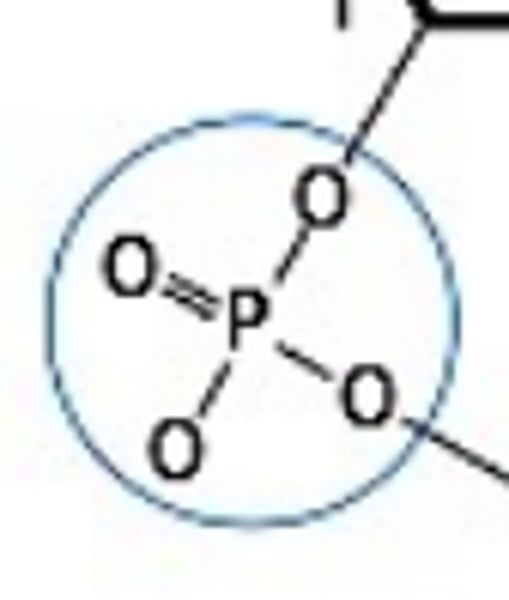
Structure of DNA
Pentose sugar, phosphate group, base
How is DNA synthesized?
connecting the sugars of one nucleotide to the phosphate of the next
How do the sugars connect when DNA is being synthesized?
connects via phosphodiester link/bond
Is Uracil a purine or pyrimidine
pyrimidine
Does DNA contain thymine or uracil?
thymine
Does RNA contain thymine or uracil?
uracil
What bonds are used to pair nitrogenous bases?
H bonds
Which nitrogenous base pairs with thymine?
adenine
Which nitrogenous base pairs with cytosine?
guanine
What are antiparallel strands?
two strands of DNA that run in opposite directions
5' to 3'
3' to 5'
Who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology of Medicine in 1962?
Francis Crick, James Watson, Maurice Wilkins
What year did Rosalind Franklin die?
1958
Which antiparallel are DNA sequences always written?
5' to 3'
What did Hershey and Chase discover?
Bacteriophage T2
What was the function of Bacteriophage T2?
Infects E. coli
What were the two groups of phage?
protein and DNA
How was protein labeled in Bacteriophage T2?
labeled with (superscript) 35S
How was DNA labeled in Bacteriophage T2?
labeled with (superscript) 32P
What did the Henry Chase experiment conduct?
to see which part of the phage (DNA or protein) serves as the genetic material and is transmitted to phage progeny?
What was the result of the Henry Chase experiment?
DNA is genetic material in bacteriophages
What was determined in the life cycle of the T2 bacteriophage?
DNA is the molecule of inheritance. Bacteriophage was put into the E.coli, the virus spread within the E. coli, then virus busted out of E. Coli.
Paradigm Shift (merriam webster)
An important change that happens when the usual way of thinking about or doing something is replaced by a new and different way
Paradigm shift (Cambridge Dictionary)
A time when the usual and accepted way of dong or thinking about something changes completely
What was the role of bacterial cells in the Henry Chase Experiment?
role = pellet
What was the role of the phage in the Henry Chase Experiment?
role = supernatant
100s of thousands of ____ are available at the Joint Genome Institution
genomes
Define Genome
the entre set of DNA found in a cell
What is inside a genome?
chromosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, prokaryotic extrachromosomal elements
What is within prokaryotic extrachromosomal elements
plasmids, transposons, integrons, borgs
How many bacterial and archaeal genomes have been sequenced?
Have these 200k microbes been grown in the lab?
no
What percentage of all prokaryotic genomes have been sequenced?
2.1%
How many bp & genes does E. coli have?
E. coli has 4,641,652 bp and 4419 genes
There's a lot of ____ in the prokaryotic world
diversity
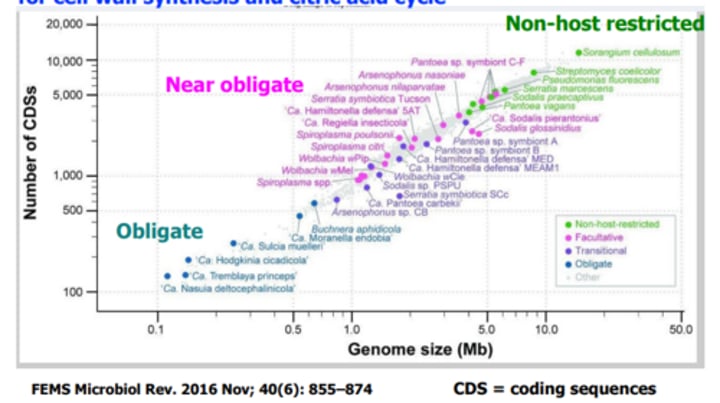
Prokaryotic genome size varies tremendously
490,000 bp (smallest) - 9,105,828 bp (largest)
# of genes varies too
480 (smallest) - 9600 (largest)
What do smaller prokaryotic genomes associate?
obligate symbionts, near-obligate and obligate parasites have smaller genomes
Nanoarchaeum lives within or ____ to Ignicoccus, another archaeon
adjacent
How many bp and genes do Nanoarchaeum have?
Nanoarchaeum has 491000 bp and 536 genes
How many bp and genes do Ignicoccus have?
Ignicoccus has 1297583 bp and 1434 genes
Chlamydia trachomatis (chlamydia) and Treponema pallidum (syphilis): cannot ____ without a host in nature
survive
bp and gene of Chlamydia
Chlamydia has 1,042,519 bp and 902 genes
bp and gene of Treponema (syphilis)
Syphilis has 1,138,011 bp and 1082 genes
Obligate symbionts, near-obligate and obligate parasites are missing genes and are dependent upon host for common components:
lipids, amino acids, nucleotides, vitamins, enzymes for cell wall synthesis and citric acid cycle