Human Physiology: Respiratory and Digestive Systems Overview
1/333
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
334 Terms
Internal Respiration
Exchange of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues.
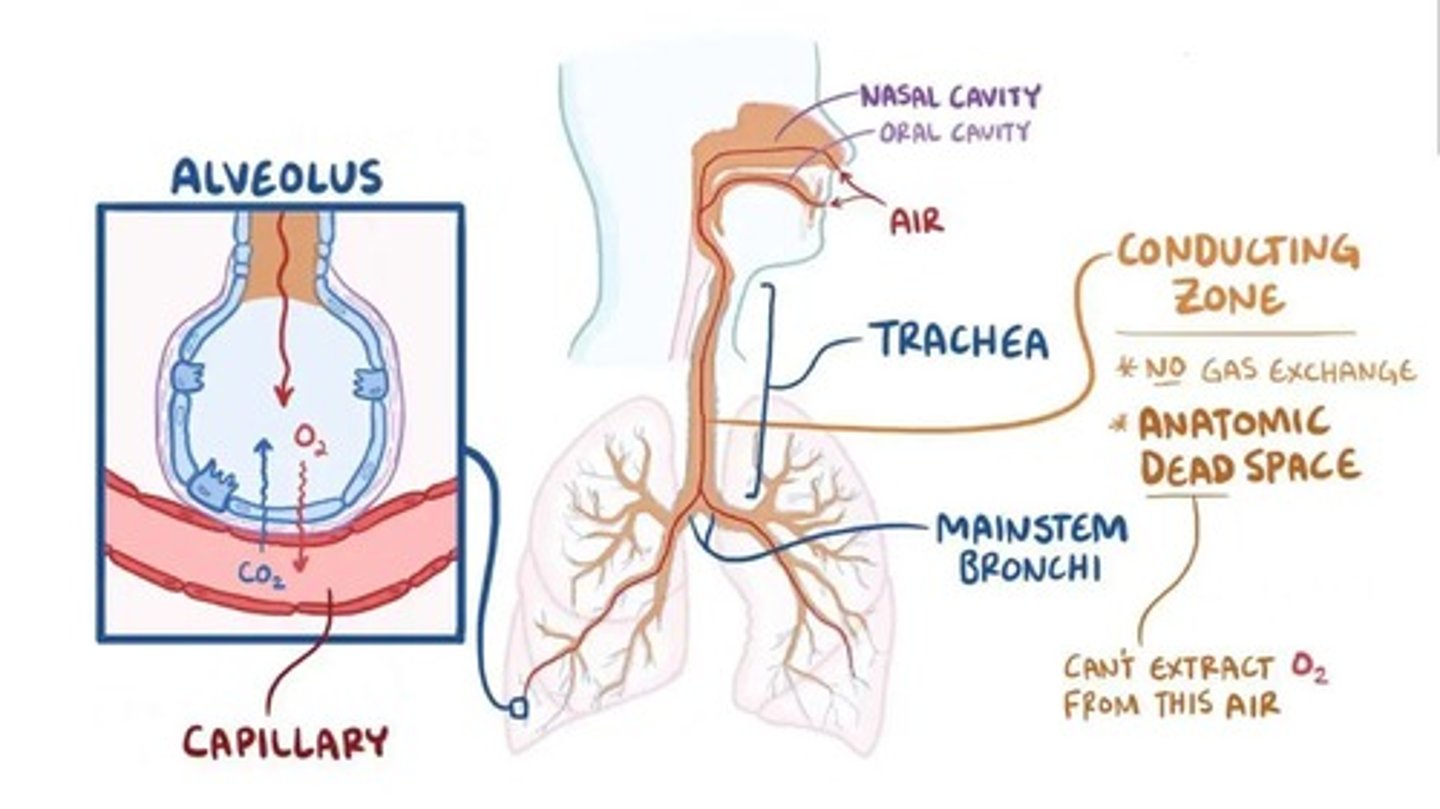
Dead Space
Part of respiratory system not involved in gas exchange.
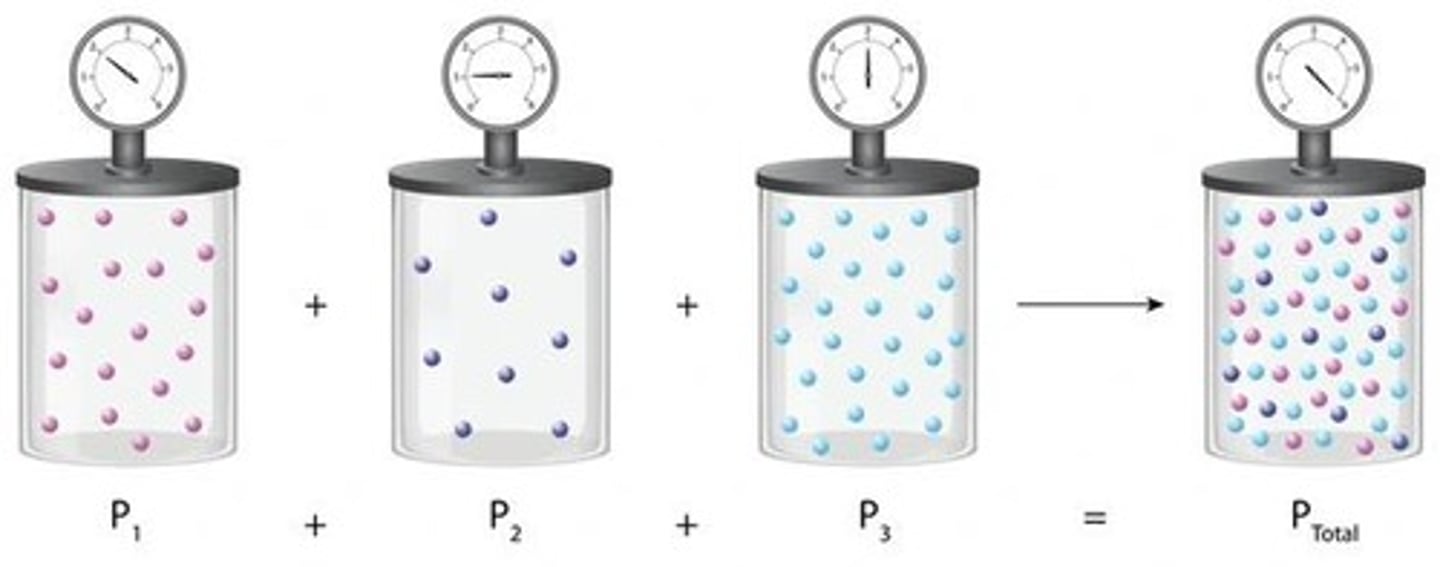
Partial Pressure
Concentration of a specific gas in a mixture.
Blood pH Regulation
Maintains pH between 7.35 and 7.45.
Ventilation
Movement of air into and out of lungs.
Pulmonary Respiration
Exchange of gases between lungs and blood.
Systemic Respiration
Exchange of gases between blood and body cells.
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)
Regulates blood pressure in the body.
Upper Respiratory Tract
Includes external nose, nasal cavity, and pharynx.
Lower Respiratory Tract
Includes trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
Voice Production
Sound made as air moves through vocal cords.
Olfaction
Sensation of smell occurring in the nasal cavity.
Conducting Zone
Area with no gas exchange; air movement occurs.
Respiratory Zone
Area where gas exchange occurs in lungs.
Protection
Prevents microorganisms from entering respiratory system.
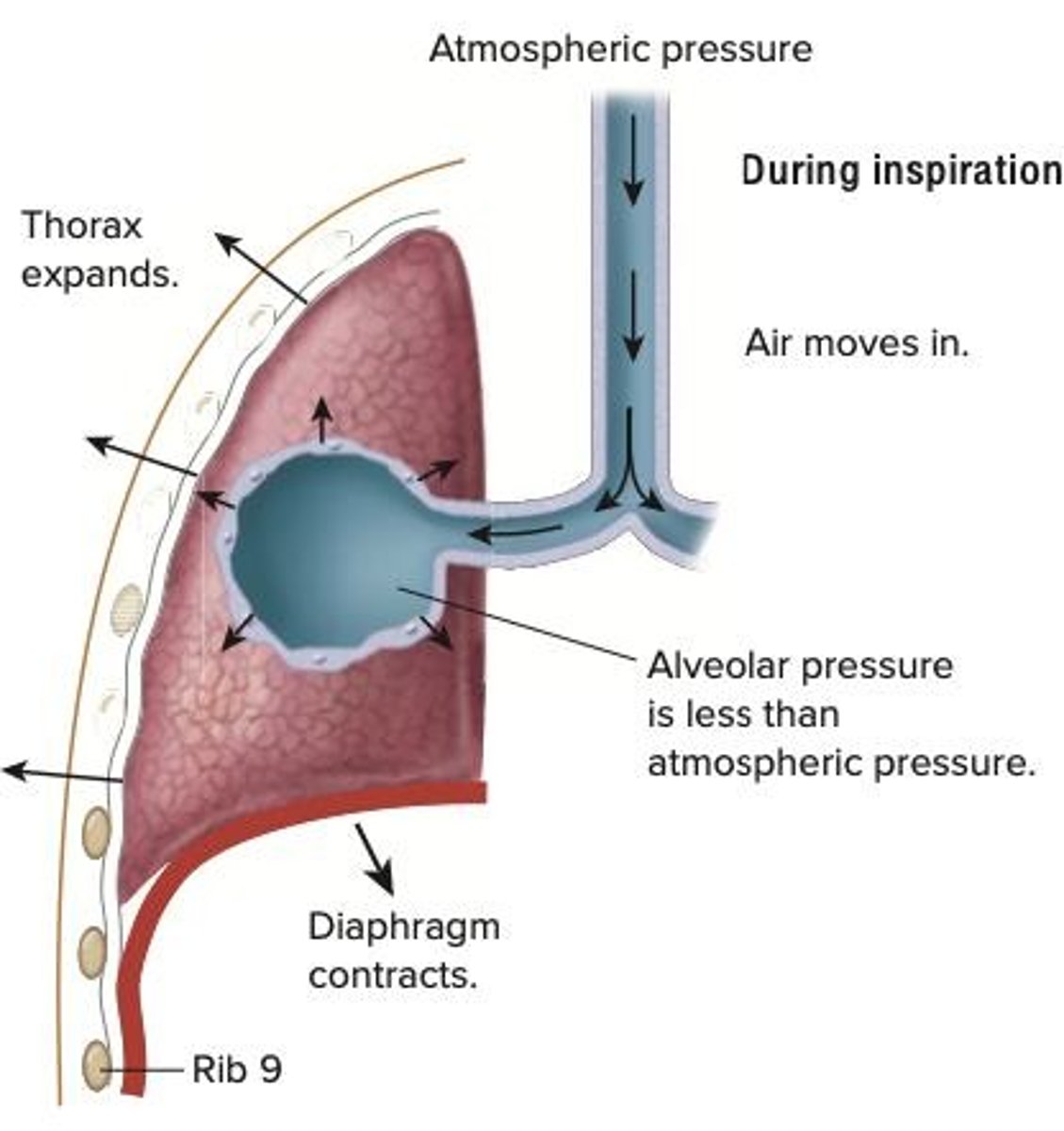
Inspiration
Air flows into lungs due to pressure drop.
Expiration
Air flows out of lungs due to pressure increase.
Gas Exchange Processes
Includes ventilation, external respiration, gas transport.
Boyle's Law
Volume and pressure are inversely proportional.
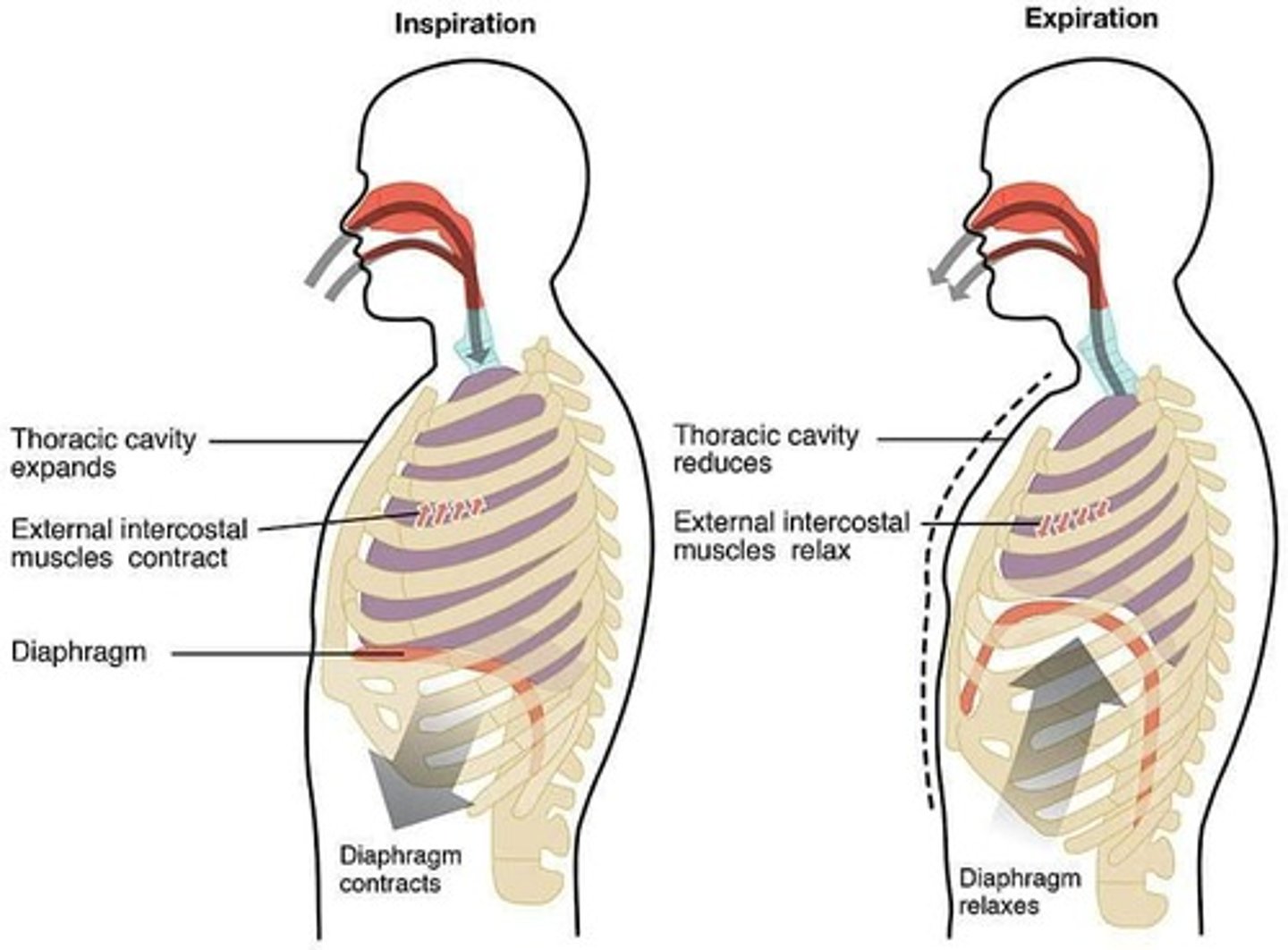
Diaphragm Function
Responsible for 2/3 of lung volume increase.
External Intercostal Muscles
Elevate ribs, increasing chest width and depth.
Alveolar Pressure
Pressure inside alveoli; influences air movement.
Thoracic Volume Changes
Increases during inspiration, decreases during expiration.
Diaphragm
Muscle that contracts for inhalation.
Quiet breathing
Passive process relying on lung elasticity.
Thoracic volume
Increases during diaphragm contraction.
Alveolar pressure
Decreases as alveolar volume increases.
External intercostals
Muscles that relax during quiet expiration.
Active Breathing
Forceful expiration using abdominal muscle contraction.
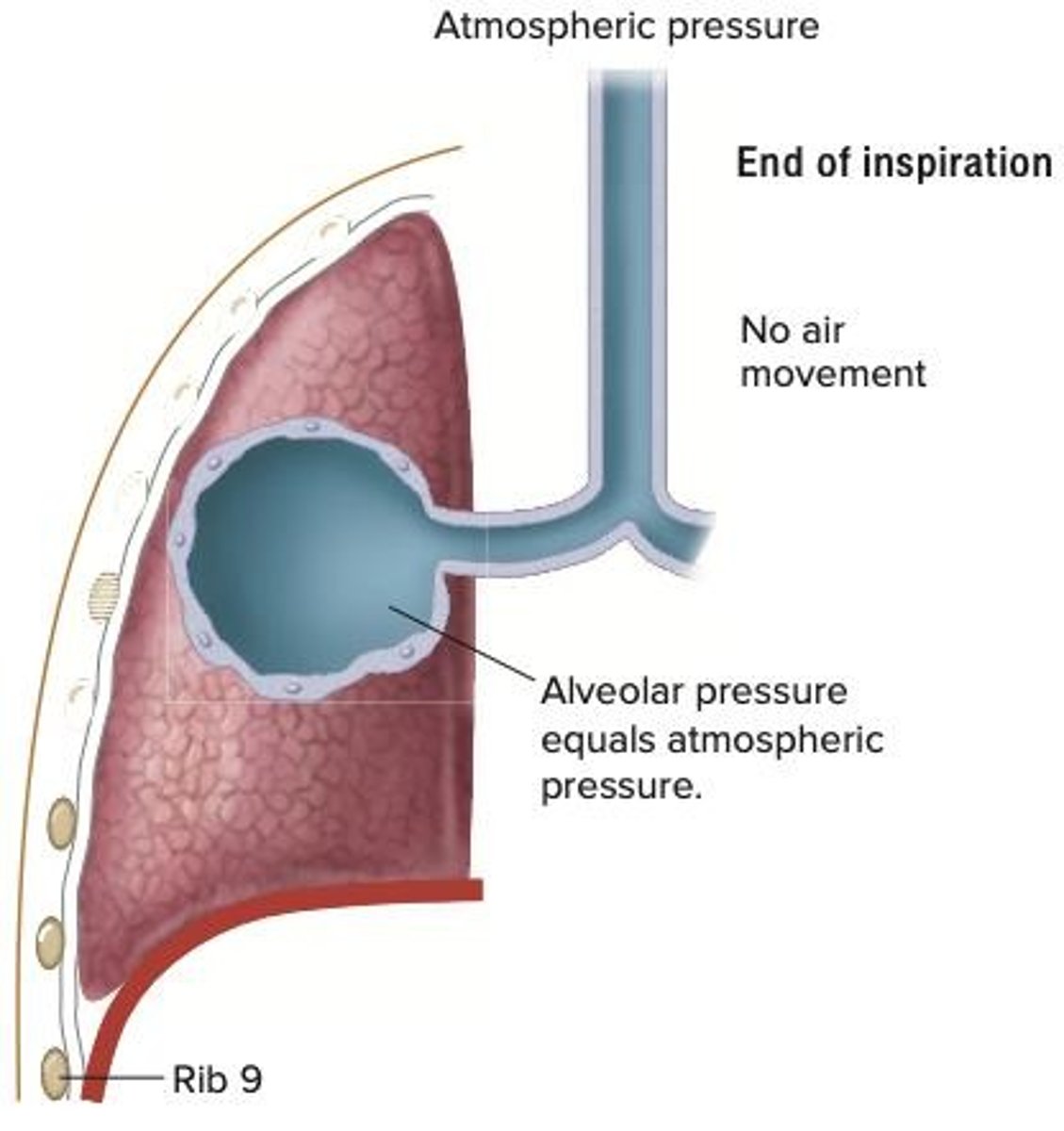
Alveolar Pressure
Pressure inside alveoli equal to atmospheric pressure.
Forced Vital Capacity
Functional measure of lung performance.
Spirometry
Process measuring air volumes in respiration.
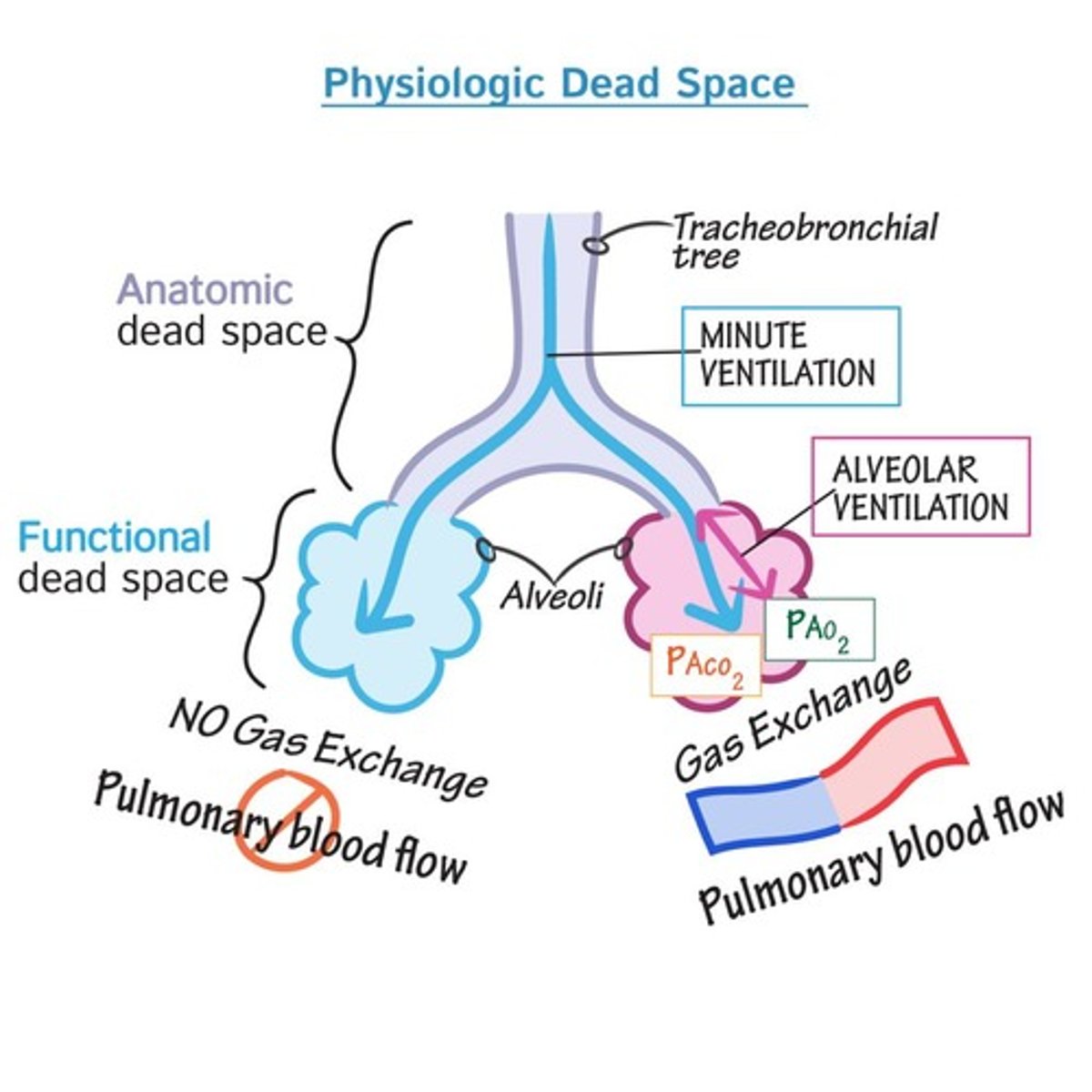
Alveolar Ventilation
Volume of air available for gas exchange.
Spirometer
Device measuring pulmonary volume per minute.
Tidal Volume (TV)
Air volume inspired and expired during quiet breathing.
Dead Space
Area where no gas exchange occurs.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
Air that can be forcefully inspired after normal inspiration.
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
Air that can be forcefully expired after normal inspiration.
Residual Volume (RV)
Air remaining in lungs after maximal expiration.
Anatomical Dead Space
Upper and lower respiratory tract structures without gas exchange.
Physiological Dead Space
Combination of anatomical dead space and poorly exchanging alveoli.
Pulmonary Capacities
Sum of two or more pulmonary volumes.
Inspiratory Capacity
Maximal air inspired after normal expiration.
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
Air remaining in lungs after normal expiration.
Vital Capacity
Max volume expelled after maximum inspiration.
Total Lung Capacity
Sum of all lung volumes.
Lung Recoil
Lungs' tendency to decrease in size after stretching.
Partial Pressure (P)
Pressure exerted by a specific gas in a mixture.
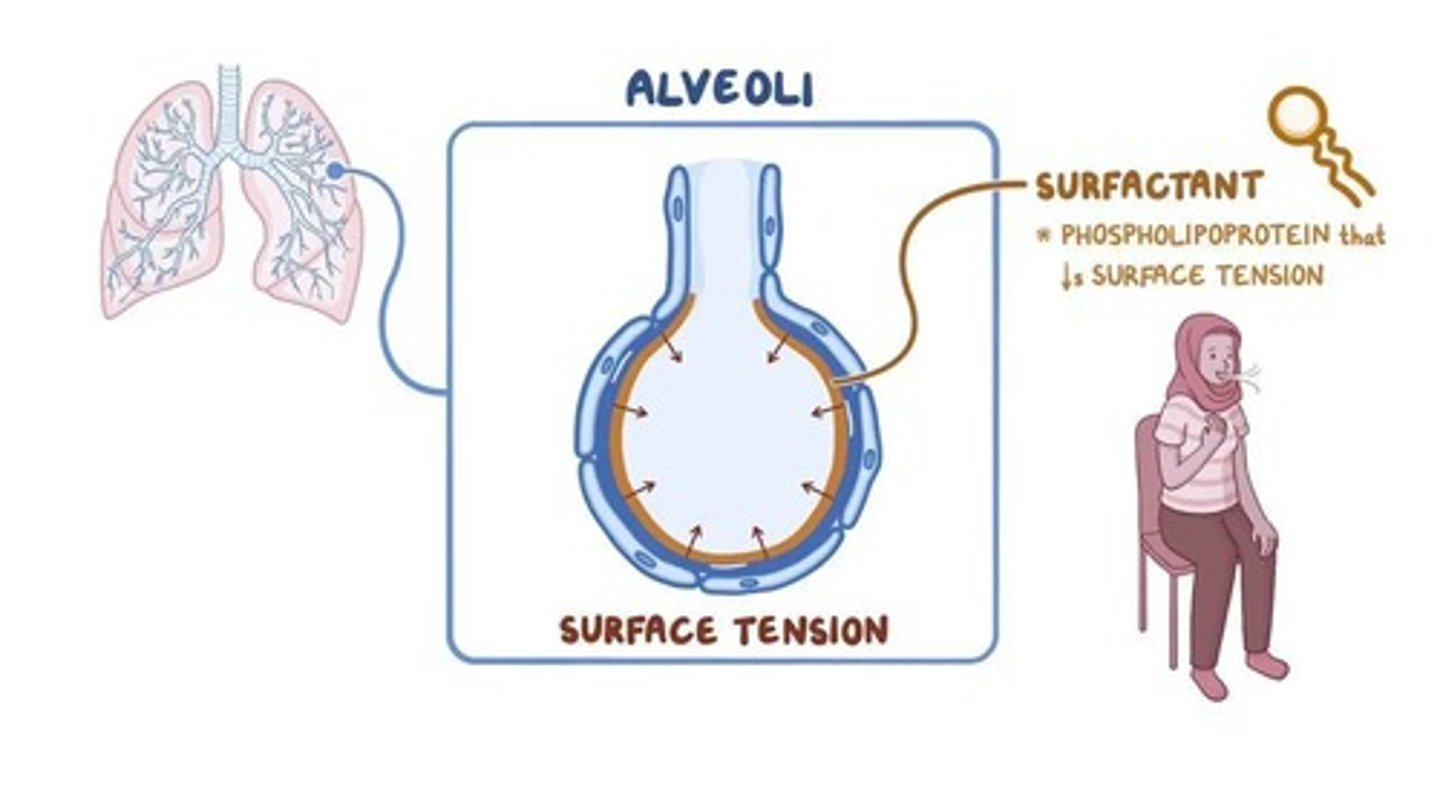
Surfactant
Lipoprotein mixture reducing alveolar surface tension.
Pleural Pressure
Pressure in pleural cavity, less than alveolar pressure.
Gas Diffusion Factors
Conditions affecting oxygen diffusion across respiratory membrane.
Partial Pressure Gradient
Gas moves from high to low pressure.
Respiratory Membrane Thickness
Thicker membranes reduce gas diffusion rate.
Respiratory Membrane Surface Area
Larger area increases gas diffusion rate.
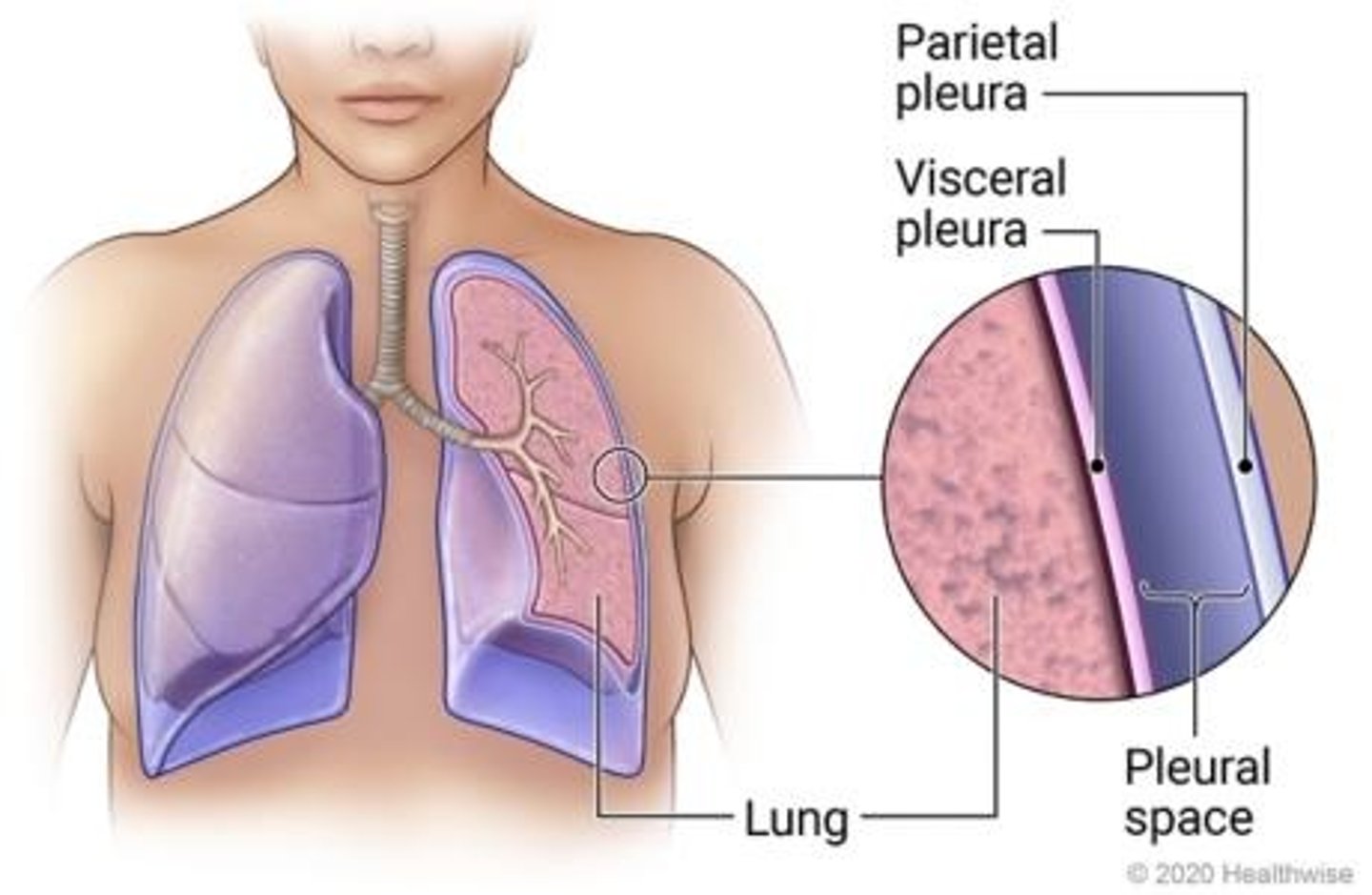
Pleural Space
Contains fluid that maintains pleura attachment.
O2 Diffusion
O2 moves from alveoli to blood.
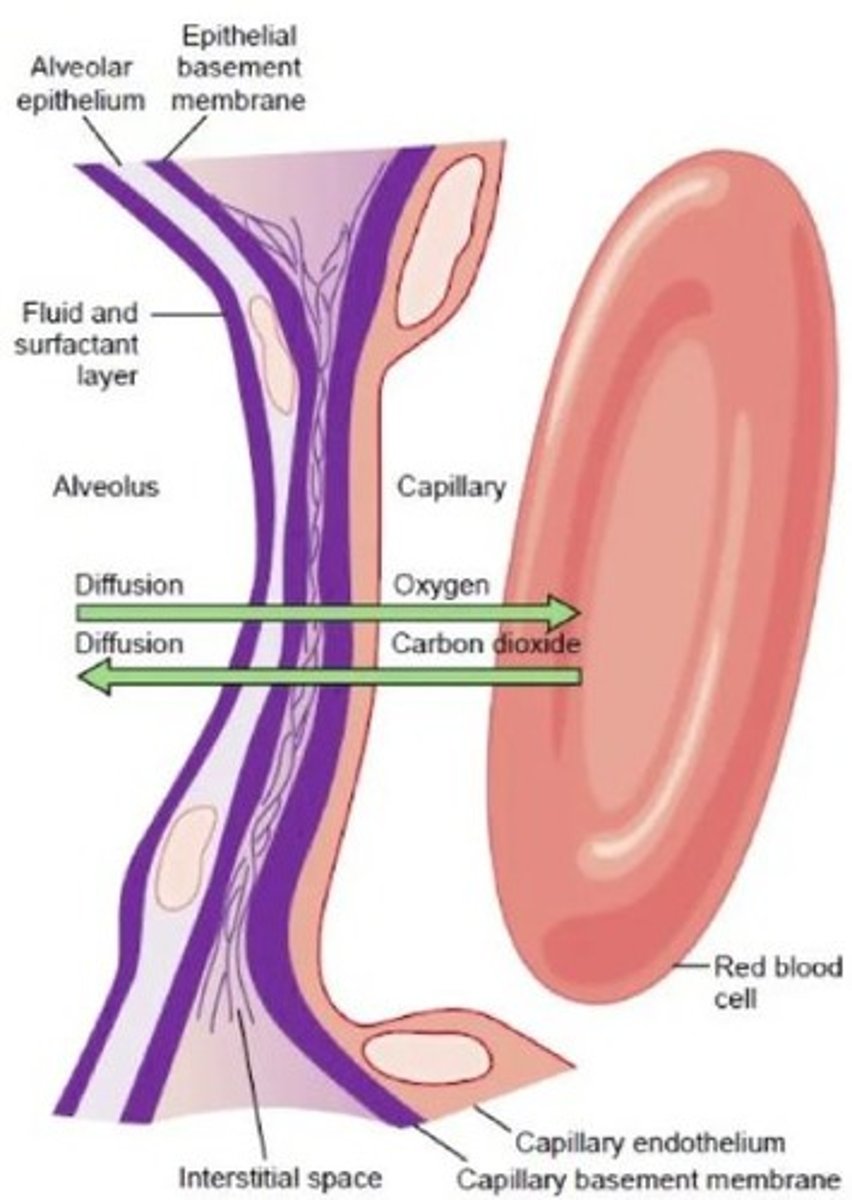
CO2 Diffusion
CO2 moves from blood to alveoli.
Pulmonary Edema
Thickening of membrane decreases gas exchange.
Emphysema
Enlarged air sacs reduce surface area.
O2 Transport in Blood
98.5% O2 binds to hemoglobin.
CO2 Transport in Blood
CO2 interacts with blood components for solubility.
Carbonic Anhydrase
Enzyme converting CO2 and H2O to carbonic acid.
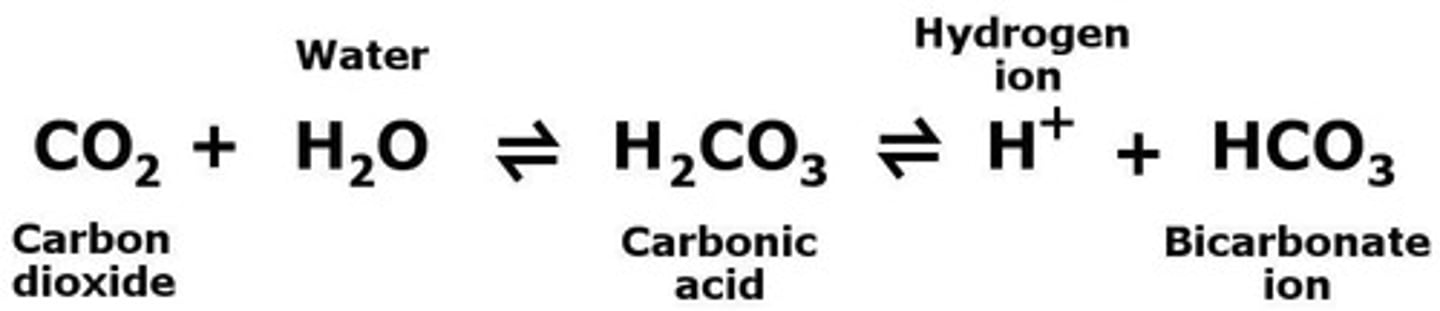
H2CO3
Carbonic acid formed from CO2 and water.
H+ Ion Production
Increased H+ lowers blood pH.
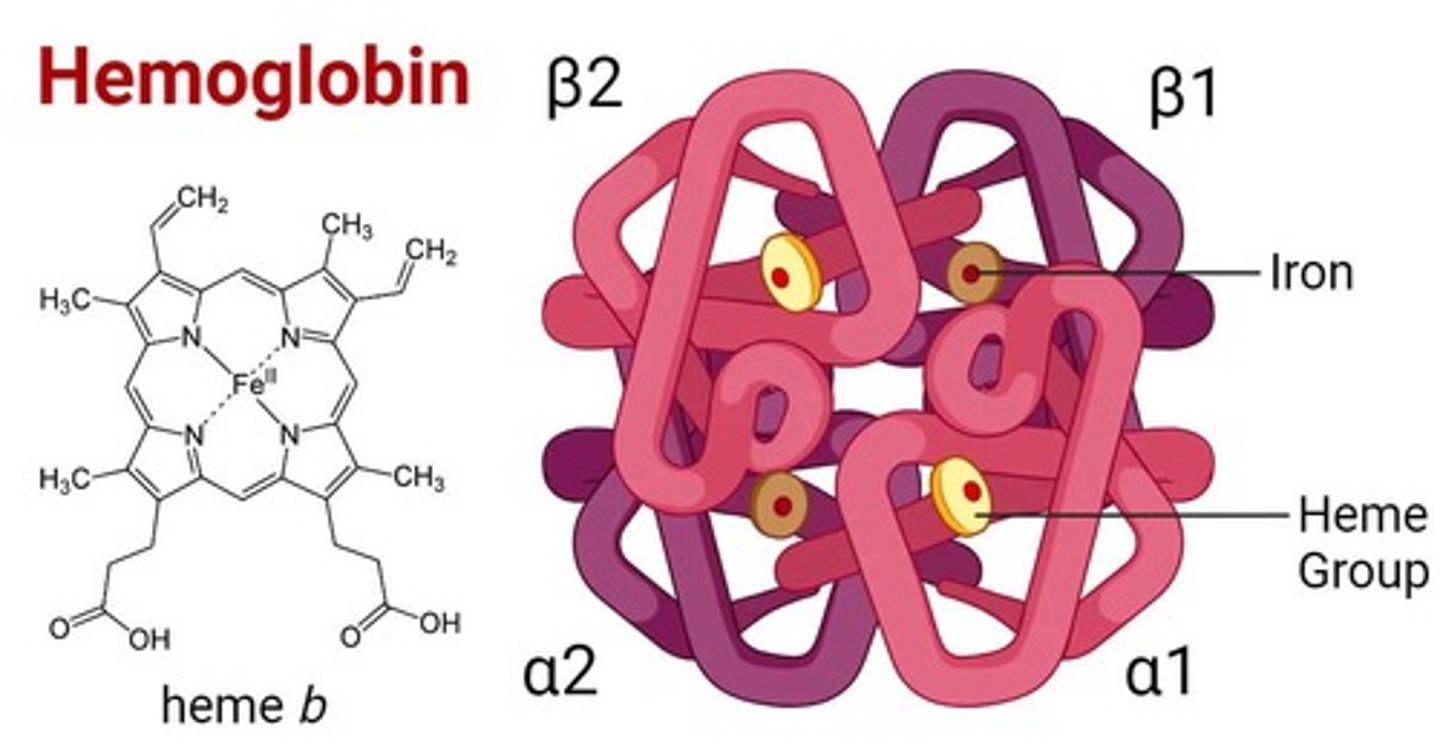
Hemoglobin Structure
Complex protein with 4 iron-containing heme groups.
O2 Affinity
Hemoglobin's affinity for O2 increases with binding.
CO2 Effect on Hemoglobin
CO2 binding decreases hemoglobin's O2 affinity.
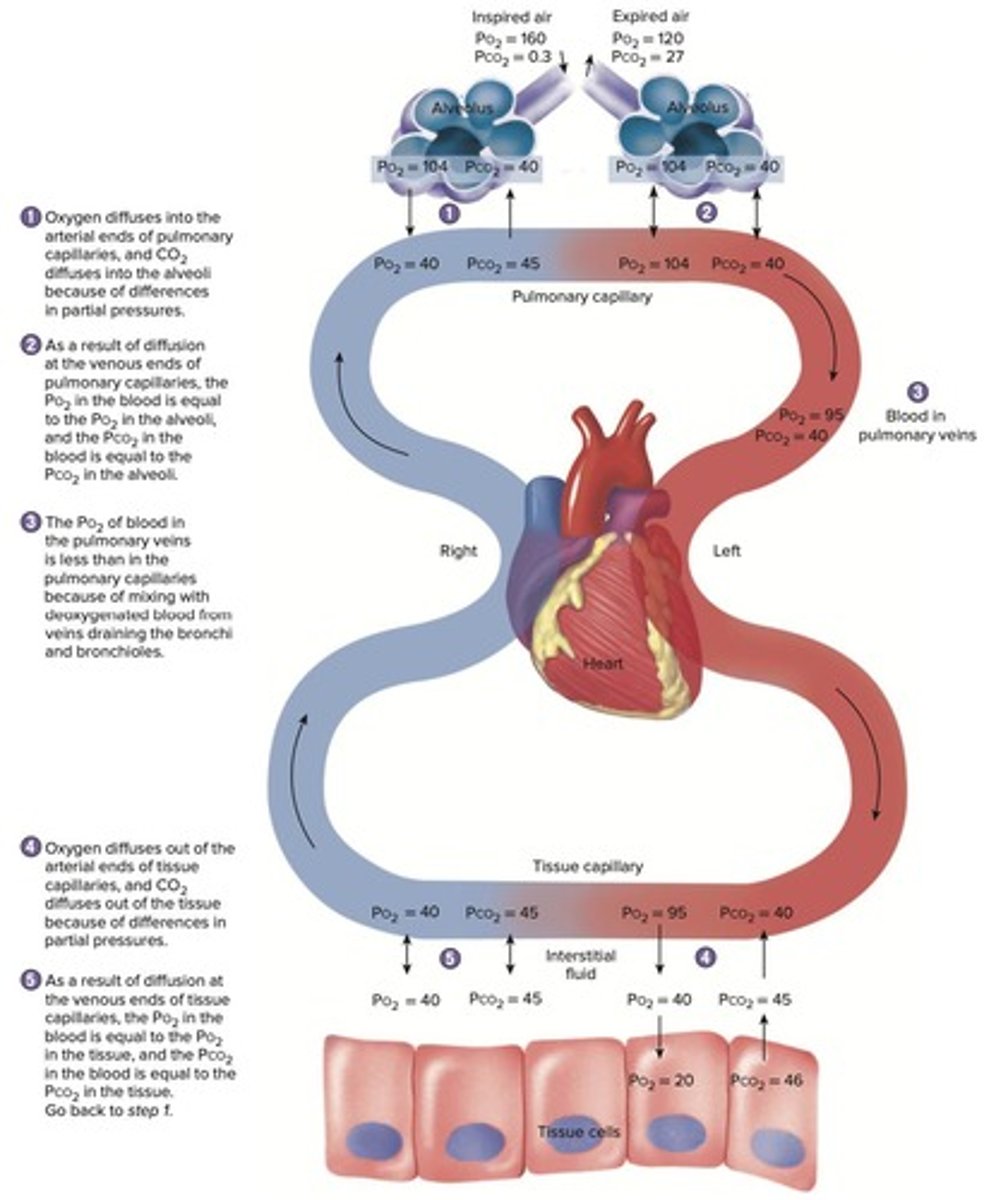
Alveolar PO2
Partial pressure of O2 in alveoli.
Capillary PO2
Partial pressure of O2 in pulmonary capillaries.
Tissue PO2
Partial pressure of O2 in body tissues.
Alveolar PCO2
Partial pressure of CO2 in alveoli.
Capillary PCO2
Partial pressure of CO2 in pulmonary capillaries.
Tissue PCO2
Partial pressure of CO2 in body tissues.
Gas Exchange Process
O2 and CO2 exchange between blood and tissues.
Carbonic Anhydrase
Enzyme speeding up CO₂ and H₂O reaction.
Carbonic Acid
Formed from CO₂ and water in blood.
Bicarbonate Ion
HCO₃⁻, product of carbonic acid breakdown.
Hydrogen Ion
H⁺, released during carbonic acid dissociation.
Chloride Shift
Exchange of bicarbonate and chloride ions in blood.
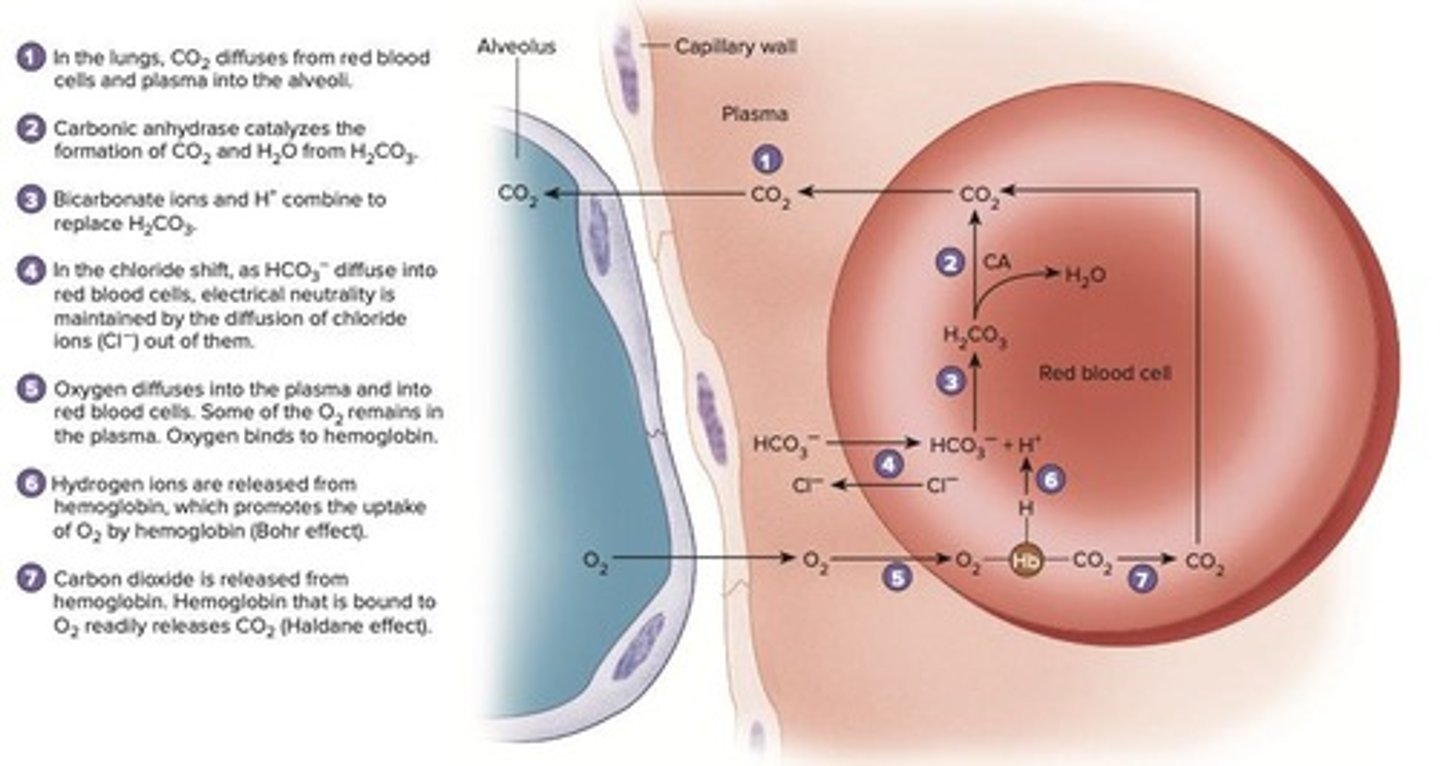
Bohr Effect
H⁺ ions enhance oxygen release from hemoglobin.
Haldane Effect
Deoxygenated hemoglobin carries more CO₂.
Oxygen Release
Hemoglobin releases O₂ to tissues from blood.
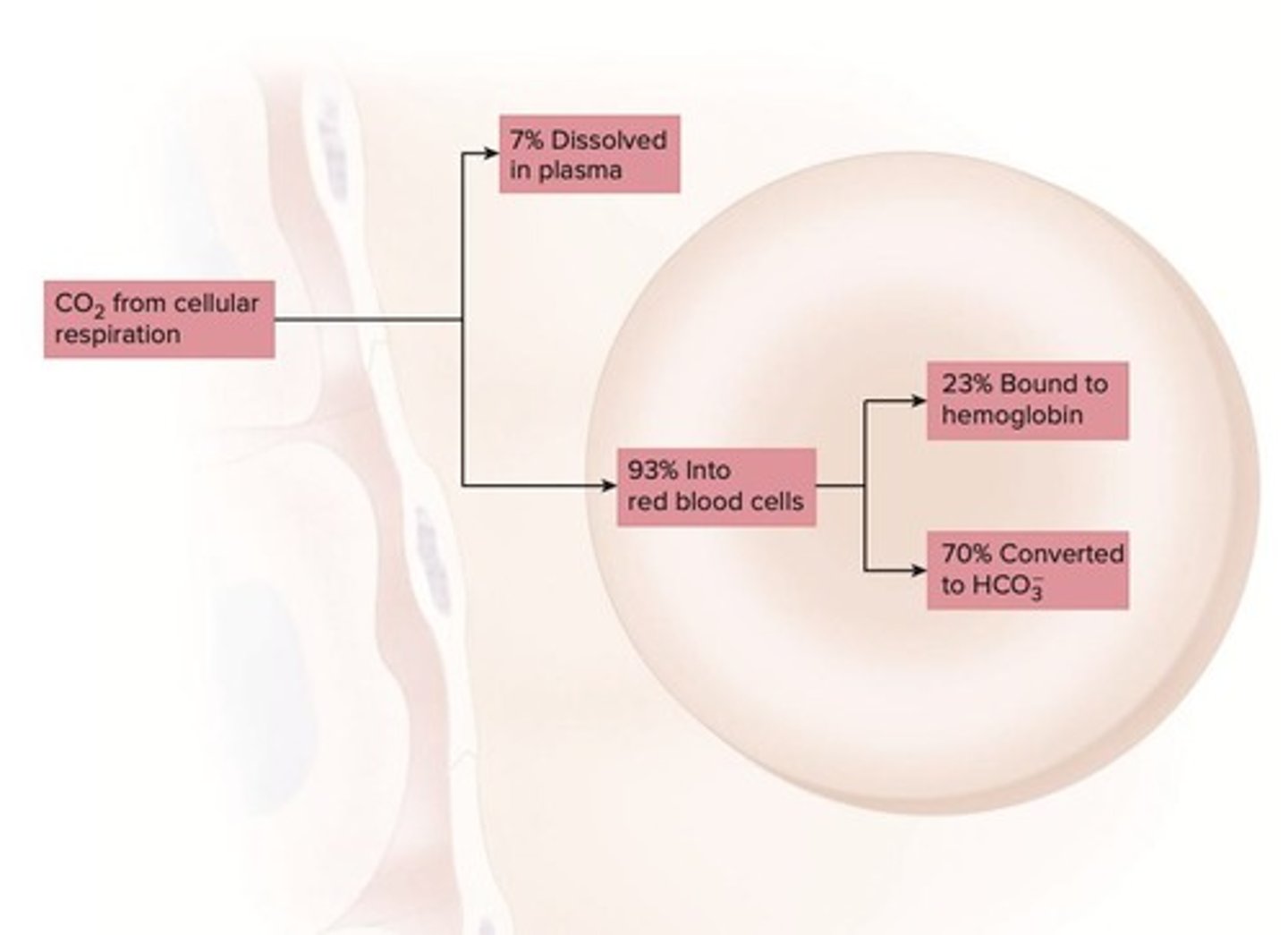
CO₂ Transport Methods
CO₂ transported as dissolved gas, bicarbonate, or bound.
Dissolved CO₂
7% of CO₂ is directly dissolved in plasma.
Hemoglobin Binding
23% of CO₂ binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Bicarbonate Transport
70% of CO₂ is transported as bicarbonate ions.
Respiratory Rate Regulation
Maintains blood gas concentrations within normal limits.
Sensitivity to CO₂
Body reacts to changes in CO₂ and blood pH.
Neurons in Brainstem
Control respiration; sensitive to blood gas levels.
CO₂ Exhalation
CO₂ moves from blood to alveoli for exhalation.
Reversal of Reaction
Bicarbonate and H⁺ convert back to carbonic acid.
O₂ Uptake
O₂ enters red blood cells from the lungs.
Alveoli Function
Site where CO₂ is exhaled and O₂ absorbed.
Carbonic Acid-Bicarbonate Buffer
Regulates blood pH by balancing CO₂ and bicarbonate.
Blood pH Regulation
Maintained through carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system.
Hemoglobin
Protein that binds oxygen in red blood cells.
Haldane Effect
Oxygen binding enhances CO₂ release from hemoglobin.
Bohr Effect
H⁺ release improves hemoglobin's oxygen binding.
Medullary Respiratory Center
Neurons controlling basic respiratory rhythm.
Dorsal Respiratory Group
Neurons primarily responsible for inspiration.