matrix-vector multiplication
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
for every point p (a1, a2, …, an) there is a corresponding vector
(0,0,…,0) to p, denoted (see image)
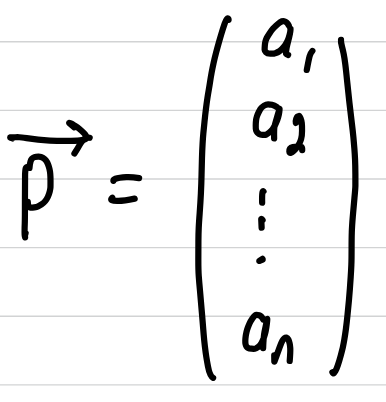
zero vector facts
for all A m x n, A0→ = 0v1 + 0v2 + … + 0vn = 0→
for all v ∈ Rn, v + 0→ = v
dot product
Let v and u be column vectors
their dot product is the scalar v·u = a1b1 + a2b2 + … + anbn
properties of matrix vector multiplication
A(x + y) = Ax + Ay
A(cx) = c(Ax) = (cA)x
(A + B)x = Ax + Bx
standard basis vectors e1, e2, en
e1 = column of 1, 0, 0…, 0
e2 = column of 0, 1, 0, …, 0
en = column of 0, 0, 0…, 1
Aei =
vi (only picks up one column)
identity matrix
the matrix with columns e1, e2, …, en
for every v ∈ Rn, Inv =
v
any linear combination of solutions to _ system is also a _
homogeneous, solution
associated homogenous system
for system Ax→ = b→, the system Ax→ = 0→ is called the associated homogeneous system