Lecture 10: Ischemic Heart Disease
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Coronary circulation supplies the heart with __ (2) to maintain adequate function.
oxygen & nutrients
Coronary circulation must adapt to __ in the systemic metabolic needs.
rapid fluctuations
Imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply leads to: (3)
myocardial ischemia and contractile dysfunction
cardiac arrhythmia
myocardial infarction and possibly death
What are the 2 main coronary arteries?
right coronary artery & left coronary artery (which includes left anterior descending artery & circumflex artery)
Following a coronary artery occlusion, __ may occur beneath the __ surface & spread within the __.
necrosis; endothelial; myocardial tissue
What is ischemia?
myocardial oxygen demand in excess of supply (demand is larger than supply)
What is infarction?
continued ischemia leading to muscle damage
Myocardial O2 __ depends on heart rate, contractility, and wall tension.
consumption
Myocardial O2 consumption demand increases with factors that increase: (3)
rate
ionotropic stimuli (ca and catecholamines)
elevated aortic pressure
Myocardial O2 supply depends on: (2)
coronary arterial and capillary inflow
O2 transport and delivery
needs adequate inspired O2 (amount of oxygen in blood is normal) and normal hemoglobin (to allow for effective oxygen transport)
Coronary arterial and capillary inflow usually has [high/low] resistance unless __. The resistance is regulated by several factors, some dependent on __.
low; occluded; endothelial cells
Vascular endothelium has important __ functions that promote __.
homeostatic; vasodilation
How do vascular endothelium promote homeostasis? (2)
sense mechanical forces and regulating vascular tone
production of many other vasoactive substances (pro and anti-proliferative, pro and anti-thrombotic, and angiogenic factors)
How does vascular endothelium regulate vascular tone?
vasodilators: endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF), nitric oxide (NO), and prostacyclin
vasoconstrictors: endothelin 1 (ET-1), angiotensin II, thromboxane A2
__ inhibits recruitment and differentiation of inflammatory cells by inhibiting __. This is a __ effect in the setting of ischemia.
NO; inflammatory cytokines; protective (prevents excessive inflammatory response that can damage tissues during a time with limited blood supply)
What are the predisposing risk factors for ischemic heart disease? (3)
age: inc risk as inc age
sex: males > females, but more risk for females after menopause
family history
What are risk modulating behaviors for IHD? (behaviors that will increase risk) (5)
smoking
atherogenic diet
alcohol intake
lifestyle: physical activity
personality type: hard to measure but data appears real
What are some metabolic factors that increase risk of IHD? (7)
HTN
diabetes
obesity
metabolic syndrome
dyslipidemia
iron overload
homocysteine excess
Metabolic syndrome includes __ resistance and impaired __.
insulin; glucose tolerance
The best predictor of atherosclerotic heart disease is total __ ratio.
cholesterol to HDL (ideal is 3.5 or lower)
__ has antifibrinolytic properties. Elevation is strongly correlated with __.
lipoprotein (a); heart disease
__ is protective, while __ is damaging
HDL; LDL
__ occurs as a result of impaired plasma lipid control and is typically characterized by abnormal levels of lipoproteins.
Dyslipidemia
__ facilitates LDL oxidation.
iron overload
__ causes a direct toxic effect on endothelial cells, interference with clotting factors, and promotion of oxidation of LDL.
homocysteine excess
__ can correct homocysteine excess.
folic acid
Inflammation is emerging as an important __ for IHD.
risk factor
__ is a marker of systemic inflammation.
C-reactive protein (CRP)
CRP is produced by the __ and cells within the __.
liver; atheroma
CRP is strongly correlated with the risk of: (4)
MI
stroke
peripheral arterial disease
sudden cardiac death
__ can also be a risk factor for IHD, but the effect is weak.
plasma fibrinogen
Label each of the following with inc/dec to determine how each would be a risk factor for IHD.
total cholesterol
LDL
lipoprotein a
homocysteine
CRP
fibrinogen
HDL
all inc except dec for HDL will put a person at higher risk for IHD
__ are used to determine and diagnose a patient’s risk of coronary heart disease.
risk charts
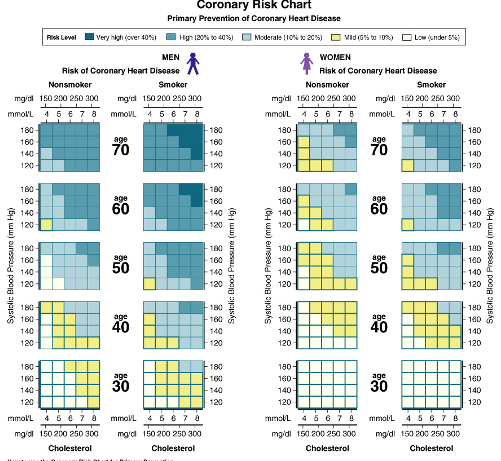
What does this risk chart study show?
color- where risk is
highest risk = man who is smoker over the age of 70, high systolic pressure & high blood cholesterol
lowest risk = young man <30 y/o, nonsmoker, good BP, even with high BP if cholesterol is managed —> risk is same
if cholesterol high, but BP is good —> risk stays low
when women age, risk becomes similar to men
__ consists of an atheroma plaque and thrombosis. It is involved in most cases of infarction.
Atherosclerosis
Plaque rupture and hemorrhage into vessel wall precipitates many cases of __, even with coronary artery lumen __ of less than 70%.
infarction; narrowing
meaning can occur even if coronary artery is not significantly narrowed by the build-up plaque (which causes stiffness and narrowing of the vessel)
__ is a significant cause of ischemia characterized by normal coronary arteries. Usually it doesn’t lead to infarction unless:
spasm; significant atherosclerotic lesion
What is an example of spasm?
prinzmetal’s angina
spasms in (normal) coronary arteries that temporarily restrict blood flow to heart muscle —> reduced oxygen —> pain/angina
__ caused by leutic, collagen, or immune-mediated diseases can lead to cardiac ischemia.
arteritis
__ to coronary arteries can cause cardiac ischemia.
emboli
Infective endocarditis can cause __
emboli to coronary arteries
What occurs when atheroma is initiated?
extracellular lipid accumulation and oxidation: usually occurs when diet is high in cholesterol or saturated fat
leukocyte recruitment via expression of adhesion molecules
foam cell formation: via endothelial and smooth muscle cell chemokine release —> recruit monocytes that differentiate into foam cells
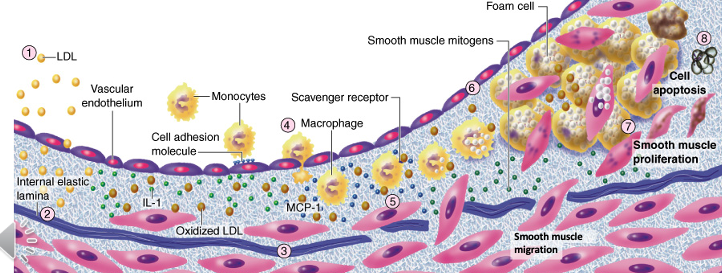
During innate and adaptive inflammation in atherogenesis, there is release of __ by foam cells and __ activation.
proinflammatory cytokines; T cell
proinflammatory cytokine release is not Ag (antigen) dependent, but T cell activation needs Ags as infectious agents
How do smooth muscle cells respond during atheroma evolution?
migrate to intima layer in response to signals from inflammatory cells and growth factors —> contribute to plaque formation
proliferate in the intima & form ECM —> fibrous cap that stabilizes the plaque
can undergo apoptosis/cell death —> increases risk of plaque rupture and triggers thrombosis
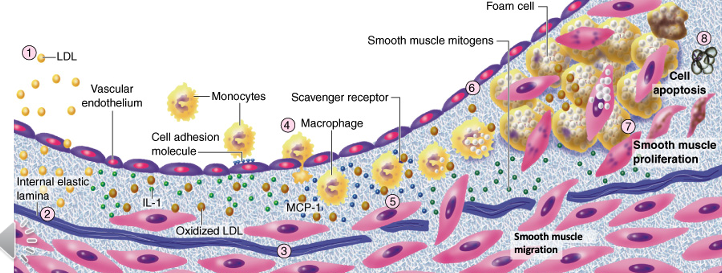
In a developing atheroma, there is deposition of __ in the arterial extracellular matrix, which contributes to the outward growth of the __.
fibrillar collagen; intima
**this makes atheroma irreversible in size
During atheroma evolution, plaque __ contribute to plaque __.
neovessels; growth
bc more fibrillar collagen deposition means needs more blood supply
demonstrates that this is a continuously growing living tissue
Atheroma can become __ to become a fixed, dense plaque on the blood vessel.
mineralized
In arterial stenosis, gradual occlusion and flow limitation occurs, characterizing __ ischemic disease or __.
chronic; angina
can be stable bc occurs very gradually, severity increases as plaque formation increases
A disruption of the plaque or rupture and thrombosis characterizes an __ ischemic disease or __.
acute; acute coronary syndrome (MI/heart attack)
What types of chest pain are consistent with chronic or acute ischemia?
pressure, squeezing, burning (elephant sitting on chest)
less common = sharp and stabbing
Label what type of angina/ischemia might be indicated for the following presentations of chest pain:
chest pain present with exercise, emotional stress, large meals relieved with rest
chest pain prolonged at rest
chest pain frequent at early AM
new and acute chest pain (no chest pain before)
stable angina
unstable angina
atypical/prinzmetal’s angina
myocardial infarction/MI/heart attack
Pain radiating to left shoulder, jaw, and left arm are consistent for
ischemia
Chest pain is presented for the following durations. Label each as stable angina, unstable angina, or MI.
brief (2-10 min)
long pain but <20 min
prolonged pain of 30+ min
stable angina
unstable angina
MI
What are some symptoms associated with acute ischemia? (4)
nausea
vomiting
cold sweat
SOB
Coronary vasodilators relieve __.
angina
In __ ischemia, no symptoms are present. This occurs commonly and mortality is as high as __.
silent; when patients present with pain
How does the heart sound in ischemic patients?
usually very distant, gallop rhythms, occasional murmurs
How do the lungs present in ischemic disease?
may be signs of rales/congestive heart failure (congestion in lungs)
How does the patient appear when they have ischemic disease?
pale and in distress
Taking patient’s __ is the most important element of diagnostic work up of acute vs chronic ischemia.
history
When diagnosing IHD with an ECG, it must be taken both __ and __.
at rest; during exercise
How are early/late (serious) ischemias reflected in an ECG reading?
evidence of myocardial/early ischemia —> ST and T wave abnormalities
evidence of loss of electrically functional cardiac tissue = serious ischemia —> Q wave abnormality
What are limitations of using ECG to diagnose IHD?
when combined with exercise for ischemia work up, sensitivity (identifies disease correctly) of ECG is only about 65% while specificity (identifies who does not have correctly) about 90% → better for ruling out ischemia
when diagnosing an infarction, changes in infarction may take days to develop following the event
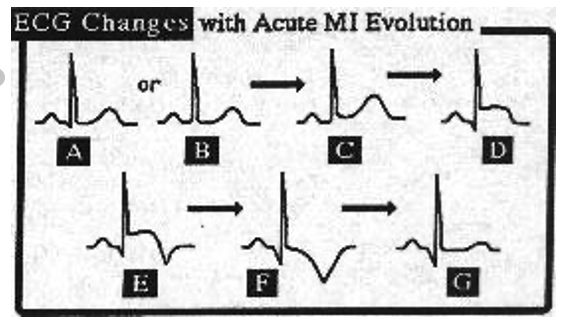
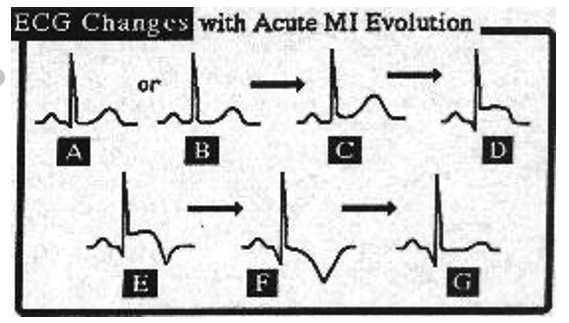
How do ECG readings change with acute MI evolution?
A&B) show normal QRS
T wave becomes broader and peaks (C)
ST elevation (D)
waves become bigger, ST elevation is maximal, and eventually T wave inversion begins (E&F)
T waves evolve as ST returns to baseline (F)
becomes normal, except Q wave dips a lot —> persistance of Q wave abnormality (G)
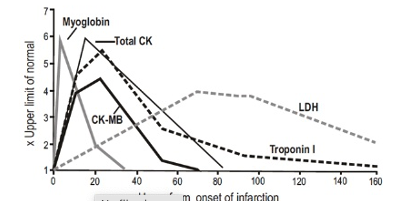
What markers/enzymes in plasma indicate ischemia?
troponin I (TpI) and troponin T (TnT)
creatine kinase (CK) MB isoenzyme
lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
these enzymes are released from damaged cells when infarction occurs
troponin & CK are present in a lot of cells: have higher concentration at onset
LDH increases slowly after onset and then decreases
How does nuclear cardiology diagnose ischemia?
myocardial perfusion diminishes with ischemia
How do echocardiograms diagnose ischemia?
abnormal wall motion from ischemia or infarction
How do coronary angiographies diagnose ischemia?
demonstrates vessel obstruction
What is the most commonly used nuclear cardiology test?
SPECT scan
How does a SPECT Scan work?
radioactive tracers/radioisotopes injected via IV and images are obtained with heart at rest or after exercise. because radioisotope concentration in myocardium depends on perfusion rate, the test shows ischemia
What 2 radioisotopes are used in SPECT scans? What are the differences between them? How do they help with diagnosis?
technetium-99m: emits high photon energy and has short half life
thallium-201: emits lower photon energy and has longer half life
can provide more detailed images to show severity of ischemia
What three views can be viewed in a SPECT scan? What do the colors mean?
short axis: anterior, inferior, lateral, septal walls
vertical long-axis: anterior and inferior walls and apex
horizontal long axis: septum, apex, and lateral walls
colors: yellow = more perfused, blue/purple = less perfused
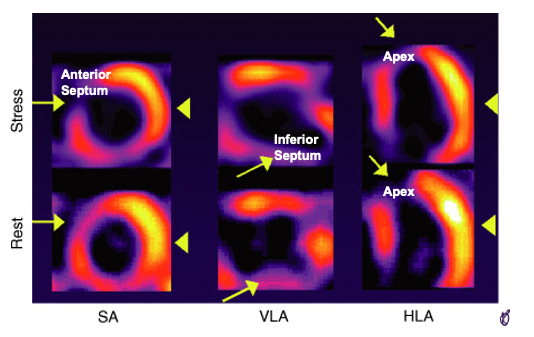
How does this SPECT Scan show abnormalities?
theres areas of less perfusion, seen by cooler colors, that are in the middle of continuous yellow/more perfused areas
How does a PET scan work?
isotope tracers are tagged to a glucose analog with a positron-emitting Fluorine-18 molecule. glucose is taken up for metabolic function, so can track metabolic function and tissue viability.
How do SPECT and PET scans compare?
SPECT: shows reduced perfusion areas and highly perfused areas
PET: shows quantative measurement of myocardial perfusion and metabolism (bc tracks through glucose = which is taken up for metabolic fxn)
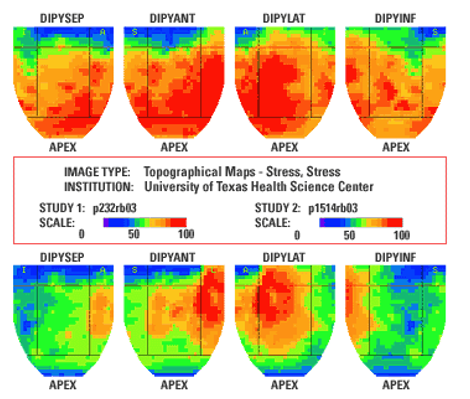
What does this PET scan show?
5 years later, decrease of color bc of less metabolic activity, especially at apical area and inferior segment of myocardium
How does coronary angiography work?
maps blood vessels in coronary system
receives dye that goes through systemic vessel —> shows interruptions
Ambulatory EKG / Holter can be useful for screening __ ischemia.
silent ischemia
What diagnostic tests are useful to evaluate risk of ischemia?
measurement of lipids and CRP (c-reactive protein)
What are some preventive approaches to IHD? (6)
control BP
stop smoking
dietary changes
exercise
aspirin —> prevents clotting
lipid lowering agents
What would medications prescribed for IHD target?
decrease oxygen demand of myocardium or workforce of myocardium
increase oxygen delivery to heart muscle or increase blood flow to heart = vasodilators
If a patient has already had a thrombotic event already, what can be done immediately?
chew on aspirin to reduce progression to heart attack and symptoms
What are 4 invasive procedures that can treat IHD?
coronary angioplasty- percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA): uses balloon catheter & intravascular stents
coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG): can be done off pump
laser angioplasty: for definitive large clots that are already identified
mechanical atherectomy: device that scrapes areas with plaque
done after initial preventative measures and medications fail to reduce symptoms
How does an angioplasty with stent work?
inserts catheter with balloon into heart to access coronary arteries. balloon dilates and crushes cholesterol plaque against artery wall. once catheter and balloon are removed, stent remains in place to prevent reobstruction
Angiography and angioplasty are usually done __
at the same time
angiography = imaging procedure that uses dye to visualize inside blood vessels
during angioplasty, when inserting catheter, they also insert dye to map and visualize blockages in vessels
How does CABG (coronary artery bypass graft surgery) work?
establish new pathway to avoid blocked area = bypass
heart can’t be beating during this surgery, so use heart-lung machine that takes blood, filters, and repumps back into circulation
shocks heart to start beating again
If a patient presents with a high risk of IHD (unstable coronary syndromes, unstable angina, or recent MI) in a dental setting, how should you proceed?
avoid any elective care in the 1st six months after an MI
emergency care can be done to target management of pain and infection
support patient with vasodilators avail, need IV line, EKG, and pulse oxymeter connected
If a patient has an intermediate risk (mild angina, previous MI >6 mo ago) in a dental setting, how should you proceed?
reduce stress, pre-treatment vital signs, sedation maybe, limit epi, no epi cords
__ is not recommended for patients with a history of previous bypass graft surgery, with or without intravascular stents performed > 6 mo ago
antibiotic prophylaxis
they may be considered immediately after surgery and up to first 6 months
If a patient with IHD is in the dental setting, what medications should you be cautious of?
anticoagulants
When does ischemia occur?
when myocardial oxygen demand is not met adequately
__ plays a large role in IHD.
atherosclerosis
Ischemia can lead to: (3)
contractile dysfunction
arrhythmia
infarction
What are some common diagnostic tests for IHD? (3)
cardiac perfusion tests
electrical conduction
cardiac enzymes
What common modalities are available for treatment of IHD? (3)
drugs that improve coronary circulation
angioplasty
bypass graft surgery