cold war all chapters
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
what was the grand alliance
1943 agreement between usa (roosevelt), britain (churchill) and soviet union (stalin) to stop germany in ww1
what river and when did britain and france meet soviets when attacking germany
1945, river elbe
which countries delayed the second front in 1944
france and britain
what were tensions like between grand alliance from 1917 to 1941 (backstroy)
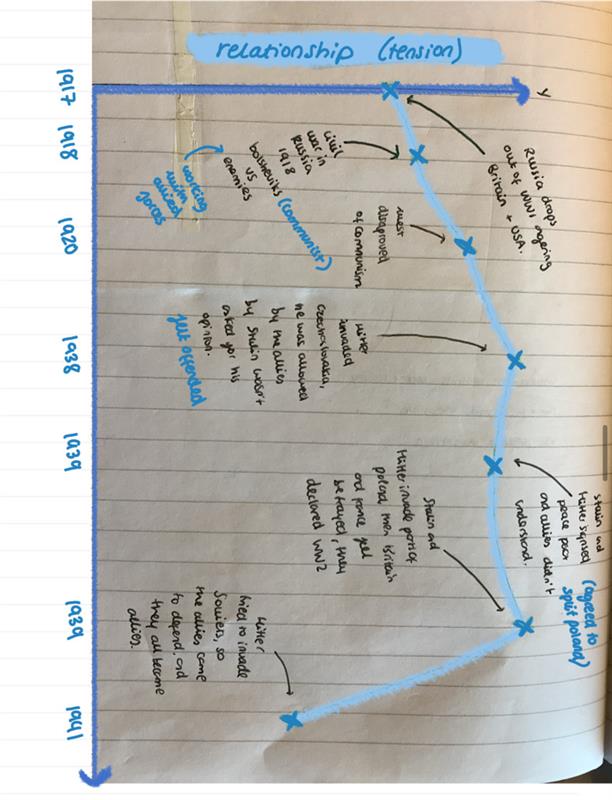
when were the atomic bombs in japan
august 1945, stalin was paranoid the usa would do it to him, because he was suspicious
what were the 3 main conferences in ww2 and when?
TEHRAN 1943
YALTA 1945
POTSDAM 1945
agreements in tehran
open a second front from france
keep germany weak, so polant could take land
ussr could keep polish seized land
usa viewed british colonialism as threat
agreements in yalta
germany into four zones : ussr, usa, brit, france
nazi banned
20B reparations to germany, ½ to ussr
future europe : free government elections
poland returned to 1921 position
united nations…..
when was the UN set up and how many members
june 1945, 51 members but not all 16 soviet republics given individual membership
potsdam agreements
new presidents = truman USA, Atlee Britain
worse relation between them and russia, no common enemy and atomic developing
germany economy run as a whole
berlin into 4 zones (soviet germany)
each country reparations from own zone
soviet zone was poor, so took ¼ industrial equpm. from other zones
what were the relationships between stalin and new presidents?
truman : more tough and harder line, imposing, waiting for discussions so atomic ready, wanted to see a less communist influence, so objected to poland agreements
Atlee : just wanted to go home and take charge
what things weren’t agreed on at the end? (conferences)
stalin wanted control of eastern europe to ensure security, but truman was suspicious because he thought stalin was trying to spread communism.
how many civilans were killed by both atomic bombs
over 120000
consequences of bombings from truman?
he could have won war without the bombs, but wanted to appear stronger in negotiations and confident. he wanted stalin to agree, but stalin was just more determined to be secure and build buffer zone.
when did soviets start to develop bomb, starting the arms race?
29 august 1949, then other countries, increasing cold war tensions.
what countries did stalin want to keep that he liberated
estonia, latvia and estonia, conquered in 1940
in what year did soviets overthrow czech government
1948, under klemend gottwald
in what year did hungary become a one party state after being threatened in 1947
1949
in 1945, soviets took control of these two countries
bulgaria and romania
what was the telegram in 1946 about soviet attitudes about
by george kennan, long telegram, stalin wanted destruction of capitalism, so america decided on containment: limiting spread of communism
how about usa attitudes in telegram?
by nikolai novikov, in washington embassy, usa didnt want to cooperate and that usa wanted to use military to take over
when was the iron curtain speech by winston churchill?
1946, cleared that soviets were a threat to peace, and since it was from missouri soviets thught it reflected american beliefs.
who was communism attracted to?
poor soviet people after war destruction, so stalin wouldnt need to fight a war
what was the truman doctrine and when did it happen
1947, truman gave aid to greek guerrillas, and sending troops to reist communism, stating they were evil. aid package to turkey and greece of 400 M dollars
what was the marshall plan and when did it happen
by george marshall, to provide europe with aid so the poor wouldnt turn to communism. from 1948-1952 13.7 B aid. it gave hope when there was none, many aid to britain. eastern europe countries not included due to stalin’s orders.
what was dollar imperialism
soviets tthought marshall plan was to spread influence from usa and establish economic empire
what where the usa plans impacted on relations
no more grand alliance, more suspicion and tension, rivalry and economic division.
association of commmunist parties giving stalin control, created loyalty?
cominform 1947
to keep independence from capitalist governments, refuse economic aid, gave aid package.
comecon 1949
what disagreements did usa and soviets have on germany
soviets wanted to take materials to repair ussr, usa wanted to build up germany economy, for trading.
when did trizonia unite?
1948
what was the deutchmark
trizonia currency, separating west and east economy. stalin saw this as usa deliberately forcing ussr into poverty.
june 1948 berlin blockade
stalin blocked routes in west berlin because west berlin was in ussr germany
huge propaganda and direct challange to truman
operation vittles what was it.
to counter berlin blockade, berlin airlift, flew coal food to allied zones, airport in tegel created. american victory and stalin looked foolish, turned down blockade in may 1949
how many tonnes of food was flown by jan 1949
170000 tonnes
new name of trizonia
1949 federal republic of germany, with own parliament bundestag, chancellor adenauer.
new name of east germany
1949, german democratic republic, but only they recognised it as a nation.
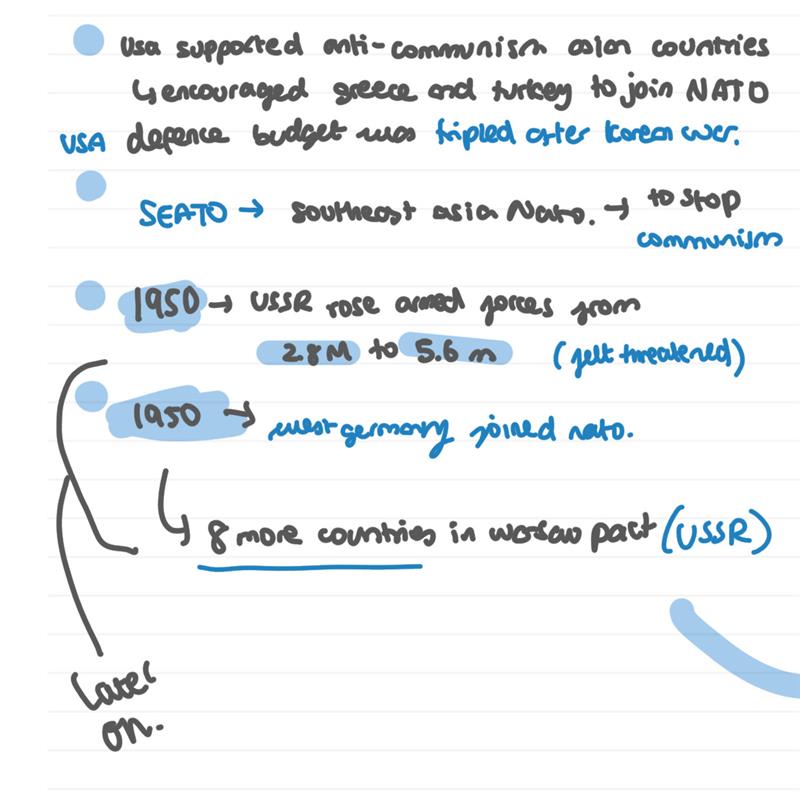
when was nato created
1949 april, military alliance, west europe, collective security
how did the korean war start
june 1950, the north invaded south, by kim II sung, who promised communism
who helped south korea?
american troops and 16 UN countries, general douglas McArthur
continue of korean war..
usa troops pushed north korea down 38th parallel
communist china was disturbed and was communist, so pushed them back down
war was for 2 years, and invasion was stopped because it ended on 38th parallel
impacts of korean war
development of atomic bomb
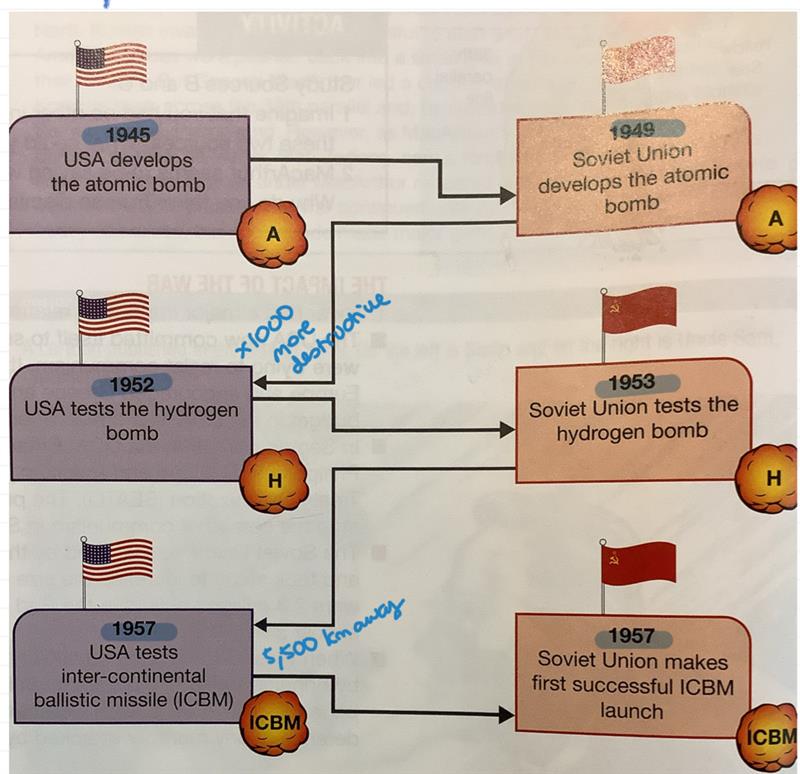
what was MAD and deterrent?
weapons were now designed to ensure no war, and show superiority, otherwise there would be mutually assured destruction, the risks were too many.
who were the new leaders in 1950
Eisenhower (strong anti communist but wanted improved relations) and Kruschev (critisized stalin and wanted peacful co-existance)
what was peacful co-existance for Kruschev
he thought that capitalism would eventually collapse, so not useful to start war, wanted less weapons made to improve economy.
when was geneva summit meeting
july 1955, atmosphere of cooperation
1955 may west germany joins nato
short lived good vibes. western block strengthened, soviet union felt threatened, restoration of west germany, gained security.
warsaw pact 1955
eastern bloc, divided europe, done because kruschev was worried of allied germany so close.
after the red army liberated hungary in 1945, what happened and who was leader
communism was implanted, strict soviet control under matyos rakosi.
when did the hungarian invasion take place
1956
what was rakosi like as a leader?
stalin supporter, strict, from 1949 300000 imprisoned and 2000 executed
effects of kruschev speech in 1956, critizising stalin
gomulka reforms, encouraging hungarians to protest for freedom, kruschev bought red army to restore order
who was rakosi replaced with
Nagy, communist
what were the nagy reforms
wanted to leave warsaw pact, become neutral, but krush could not allow threat to soviet security
consequences of nagy reforms
krush launches soviet invasion in 1958, no one leave pact, 3000 killed, kadar new leader, lesson to socialist countries.
consequences of the hungarian invasion

when did the berlin crisis start? + follow up
1958, refugee problem, usa and ussr disagree on berlin, since quality of life in east germany was so bad, 2.7 million escaped, economic decline, good jobs left, bad for soviet propaganda.
kruschevs berlin ultimatum
27 november, demanded western troops withdrawn and berlin be a free city controlled by soviets and to recognise east germany as an independent country, west saw this as extended communism.
3 summit meetings in that

how did krushev see newly president kennedy + kennedy army fact
1960, unexperienced so renewed ultimatum, but they had a strained relation ship and no agreements.
increased armed forces by 2 million dollars seemed prepared.
tensions between east and west in berlin crisis
very tense, east germans left 40000 in 1961, then ulbritch in 1961, closed border with barbed wire
when was berlin wall built
13th august 1961, they would cross at check point charlie
impact of berlin wall on germany

impact of berlin wall on east-west relation

when did “I am citizen of berlin” by kennedy happen
1963, west berlin visit
when did the cuban missile crisis happen + lead up
january 1959-
revolution - led by castro and guevara, overthrew dictator batista
eisnhower worried - americans had loads of investments, oil, land, sugar, electricity
castro regime - nationalist, rebelled of american control
what america said to castro
accepted government reluctantly, but didnt give econ aid unless they followed guidelines
castro thingssss 1959
1959- took land from foreigners paid previous owners
1960- appointed communists + soviet union pacts → sugar for soviet union then aid for cuba
eisenhower was worried with castro…
very close communism next to him (145km), so banned trade
1961- broke diplomatic relations
bay of pigs incident :
1961, kennedy gave support to CIA plan to launch invasion
sending cuban exiles would look like counter revolution (no usa)
april, 1400 exiles, bay of pigs, brigade 2506, but complete failure
no military experience, no air strikes from usa cus had to seem cuban, cuba=20000 men, and had no support from ordinary cubans
humiliated americans, failed pics published, 1202 captured, requested 28M and 53M, tractor and food
bay of pigs effects :
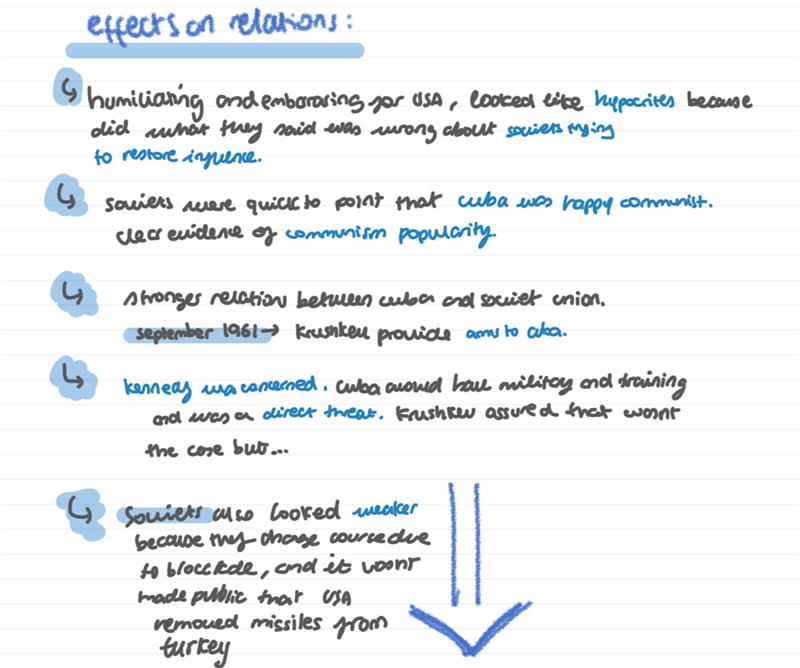
when did the actual missile crisis start + lead up
october 1962, american u-2 plane spotted missile sites in cuba,with soviets bringing more ships and missiles avaiable to hit any american land.
why were the missiles in cuba provocative
usa could now feel threat because they also had missiles in turkey
restored reputation after berlin wall fail
he feared american attack
increase tension and unease feeling
kennedy thoughts on situation
stand up to kruschev, or this huge blow will affect democratic party.
things would be harder in germany if he can just push kennedy around
how did kennedy want to take action (options)
invade cuba
bomb missile sites in cuba
sink soviet ships
the 13 days - what were they
1962, 16 october, kennedy called excomm to discuss nuclear threat, and set a naval blockade around cuba, with 54 and 4 bombers and warheads in case
the world held its breath…
soviets sent ships away, but usa was not aware, so was prepared to launch attack.
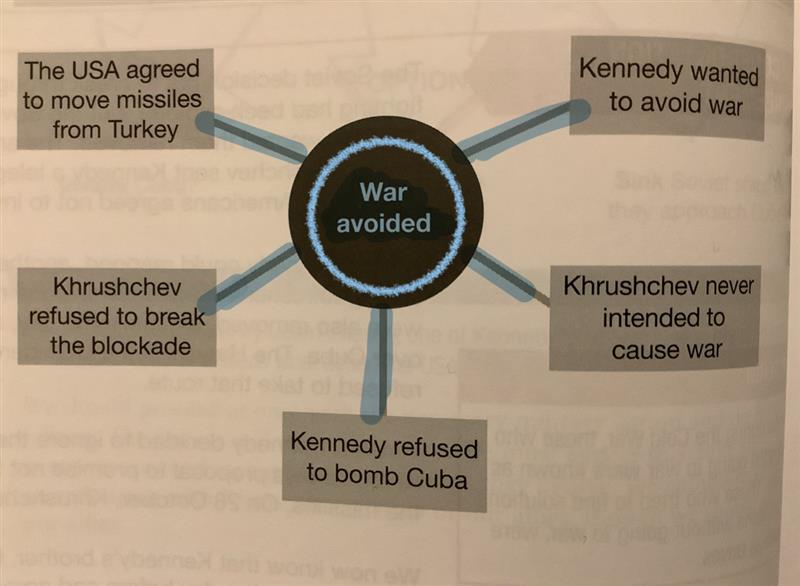
what deal did kruschev and kennedy agree?
soviets removed missiles, and usa agreed not to invade - usa looked good, but then it was also kept secret that usa removed missiles from turkey. gave kennedy confidence for standing up and this secret.
consequences of cuban missile crisis
tension and brinkmanship - they were under pressure
1963- washington moscow communication hotline
1968- nuclear non-proliferation treaty - stop the spread
eventually, the world became safer
when did kruschev get dismissed
1964
war avoided (bubble ideas)
in what years did the czechs really protest from no freedom under gottwald communism
1949-1954 - purges continued, jews and catholics and democrats as victims
1966- student demonstartions
when was the prague spring, and what was it
1968 - alexander dubdek, made a more effective government, still mantaining loyalty to communism and warsaw pact, but one step down- socialism. people had own control.
good things about prague spring
people enjoyed life and expressed views
no constant fear
czechs were enthusiastic
bad reactions to prague springs
1968- brenhzev, new leader dissaproved, he thought others would follow in reforms
romania started to refuse meetings and yugoslavia not accepting moscow control
breznev decided to act when dubdek invited countries to talk!
when did prague spring end and why
august 1968, 500000 soviet troops invaded czechoslovakia, invasors were shocked by hostility (negative) because they were only told to restore order. civilians tried a bit, like blocked roads and tanks
reforms revered and dubdek arrested
in 1969, who replaced dubdek
gustav husak, who was extreme loyal communist, introduced opression and 1000 arrested
justified invasion by breznev?
knew west wouldnt help czechs
soviet satellites would want same rights, refors offered dangerous freedoms
endangered warsaw pact
buffer zone under threat
soviet union wanted to seem powerful not weak
what was breznev doctrine
if one single country actions affected safety and control of soviet countries, action had to be taken, to protect the unity of communist movement
impact of prague spring and soviet invasion

when did breznev and nixon become presidents
1964 and 1969
when was the communication hotline set up? (thaw and detente)
1963, led to more communication in 1971
1963, limited test ban treaty (thaw and detente)
for the radioactive tests, and stop the dangerous radioactive fallout. no nuclear carrying out in atmosphere, water or space. 113 countries agreed
nuclear non-proliferation treaty 1968 (thaw and detente)
further step to prevent nuclear weapons, promote peace, non weapons states couldnt manufacture.
outer space treaty 1967 (thaw and detente)
no arms race in space and no one owned moon, open for exploration, but no destruction of celestial bodies,avoid space contamination, 15 countries.
what was the détente?
since they had been so close to starting a war, and it was better for both countries to be at peace.
why did the usa and ussr want detente? (long exp.)

good relations, china and ussr
both communist
1950, sino soviet treaty of friendship, military assistance in case
1950, worked together in korean war
bad relations between china and ussr
both wanted to be most powerful, chinese delegated treated bad in moscow
kruschev replaced stalin and they didnt get along in 1958 visit
critizised each other, mao criticised brehnev invasion and brehnev critisiced mao policies.
calling kruschev a coward because because of cuban missile crisis.
in 1969 - fights broke out