Radiology lab HW
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
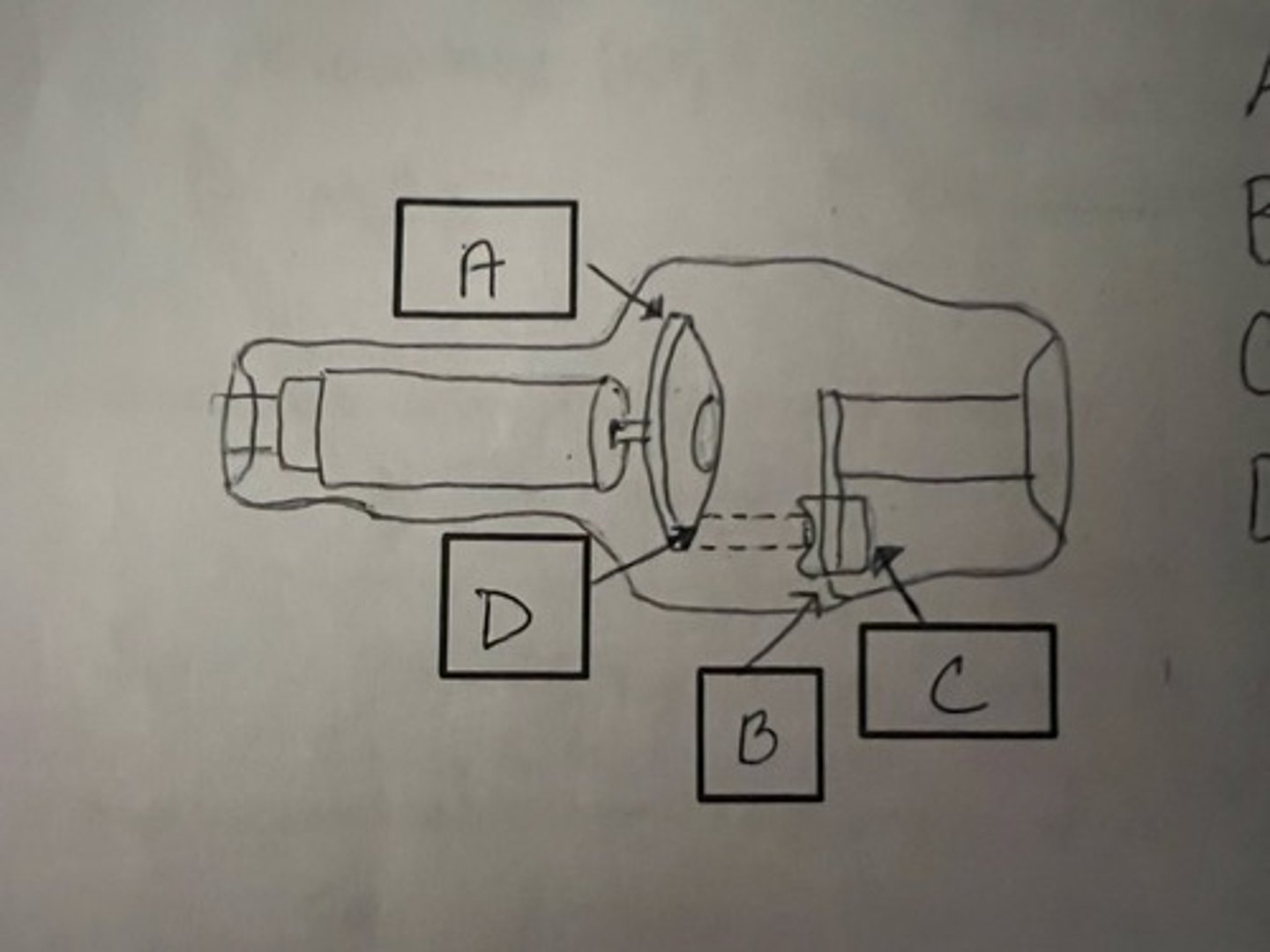
Identify parts of x-ray tube
A: rotating anode
B: cathode
C: filament (focusing cup)
D: focal spot
What is the "Heel effect" and how do you use it to your advantage
higher concentration of x-ray beam on cathode side. Put thicker end of animal on cathode side.
List components of x-ray machine
foot pedal
Bucky or film tray
control panel
generator
tube head
collimator
What is collimator and why is it important
Beam restricter controls size of primary beam and decreases scatter to patient and personel
what are the common loss of detail on a radiograph
patient movement and penumbra (using large focal spot, too long an object film distance)
Define milliamperage (mA)
quantity of electrons produced by the filament
define Kilovoltage (kVp)
voltage applied between the cathode and the anode. Increases the speed of thex-ray beam and gives it more penetrating power
define mAs
product of exposure time (s) and x-ray tube current (mA)
define exposure time (ms)
duration of the exposure, Longer exposure times will produce more x-rays
what is scatter radiation and what are ways to reduce it
lower energy radiation that is produced by interaction with objects in path of primary beam redirected and scatter all direction up to 6 ft. collimation and grid reduce scatter
what is source image distance
distance from the tube to the film tray or cassette
how do you choose what mA and time setting to use for exposure
choose the fastest time setting and highest mA station
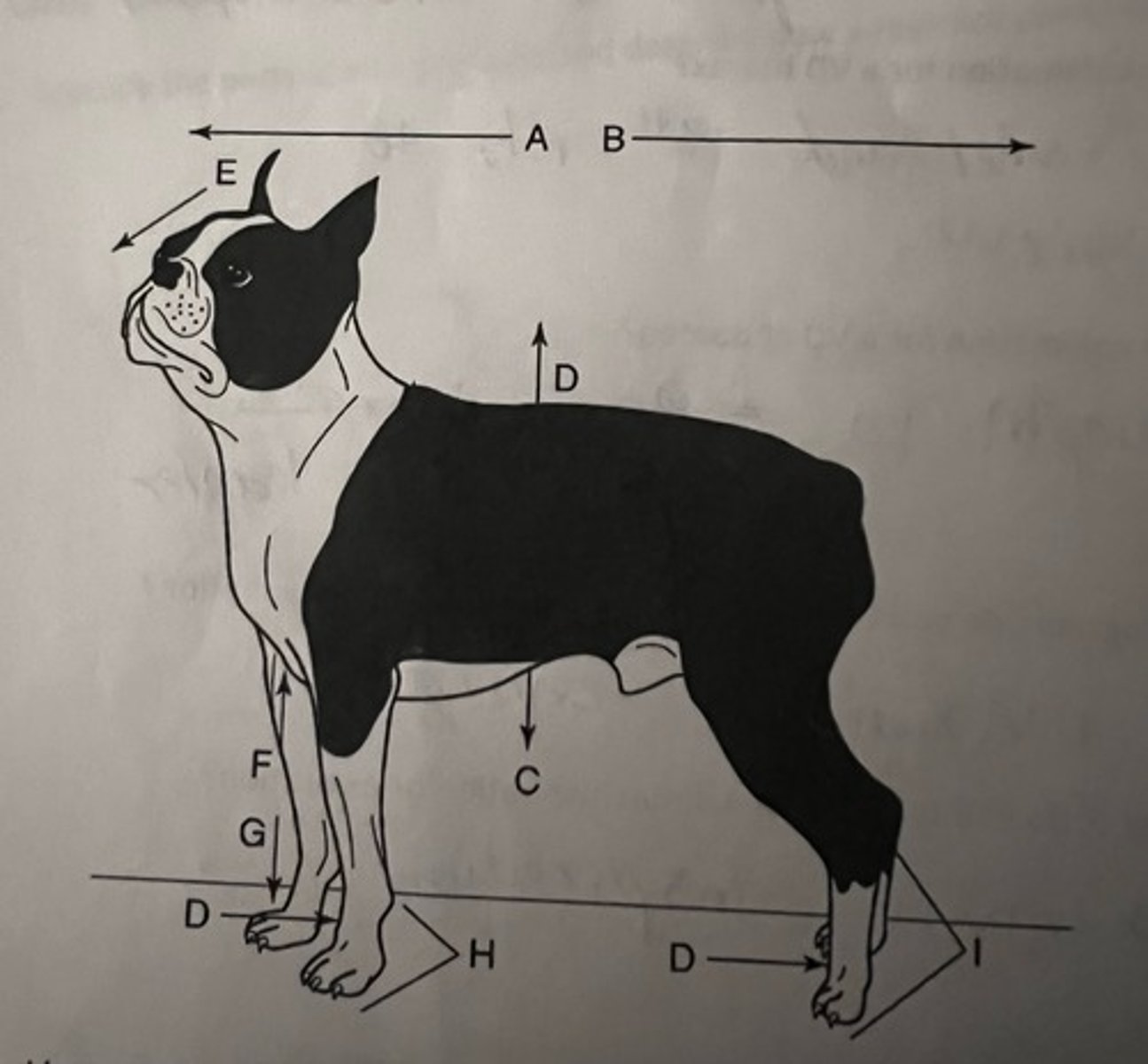
List anatomical position terminology
A: cranial
B: caudal
C: ventral
D: dorsal
E: rostral
F: proximal
G: distal
H: palmar
I: plantar
describe how to check if an animal is in true straight lateral recumbancy
palpate spine and sternum should be parallel. can correct rotation with sponge
landmarks of collimation for a lateral thorax view
thoracic inlet and 13th rib (L1)
landmark of collimation for lateral abdominal view
diaphram to greater trochanter
landmarks of collimation for VD thorax
thoracic inlet and 13th rib (L1)
landmarks of collimation for VD abdomen
diaphram to greater trochanter
abdominal radiograph is taken at maximum __________
expiration
thoracic radiograph is taken at maximum __________
inspiration
proper storage and handling of x-ray film
unopened- film upright in cool dry area
opened film-light proof box and handled with dry hands
describe proper layout for a darkroom
There must be a dry work area for loading and unloading cassettes. A light proof film bin for openfilm boxe storage. There must be separate wet work area for processing films. It must haveadequate ventilation to keep the chemical fumes from accumulating. It must have a red filtersafety light that is at least 4 feet away from the film working area
List methods of identifying x-ray film
Graphite Tape, Light film flasher, lead letters
what information is needed to be included on film label
clinic name and address
medical reccord number
date film is taken
patient and clients name
what is safe light color for different film types
dark red filter
what is ALARA
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
list the basic steps of film processing
Developing
Rinsing or stop bath
Fixing
Washing
Drying
list organ systems most sensitive to radiation exposure
thyroid, lens of eye, gonads, bone marrow, lymphatics
List the five radiographic densities as discussed in lecture.
Air, fat, water( or muscle), bone, metal( or barium)
Compare and contrast OFA vs Penn Hip views
OFA one view pen 3 view
Describe proper positioning for lateral stifle
Affected limb on table
Describe positioning for OFA pelvis view. How many views submitted
One view submitted
Explain the difference in positioning for a joint and long bone view
1/3 of surrounding anatomy
What are different views for an elbow radiograph
Straight lateral, flexed lateral, and craniocaudal
What is proper view for OFA certification elbows
flexed lateral
Describe the positioning of lateral pelvis
Place the animal in lateral recumbency with the affected leg down. Place a foam wedge between the hind limbs so that the pelvis is superimposed. Scissor the limbs so that the limb closest to the cassette is cranial and the contralateral limb is pulled caudally to differentiate the femurs.
In lateral pelvis view, which limb is magnified and why
Upper limb Closer to tube head
What are the routine views of shoulder
Lateral and caudocranial
What recumbency is the animal in for shoulder views
dorsal
What are the routine views for the humerus
lateral and caudocranial
What recumbency is the animal in for the humerus
Dorsal
What are the routine views for the elbow, radius and/or ulna
Lateral and craniocaudal
What recumbency is the animal in for the elbow, radius and/or ulna
Sternal
What are routine views for the carpus, metacarpus and/or digits
Lateral and dorsopalmar
What recumbency is the animal in for views of the carpus, metacarpus and/or digits
Sternal
Ideally, where should the label be placed on the radiograph in both sets of views
Cranial for lateral
laterally for perpendicular
What do you include when collimating for a view of a joint
1/3 of proximal and distal bones
What do you include when collimating for a view of the long bones
Joints proximal and distal on collimation
Explain the difference between positive and negative contrast
Positive- Radiopaque - appears white in radiograph
Negative- Radiolucent - appears black on radiograph
1 multiple choice option
Describe patient preparation before a contrast study
animal should be fasted 12-24 hours. Enema 4 hours prior to genitourinary contrast study
List 6 common contrast procedures and the correct contrast to use each study
Cytourethrogram- iodinated contrast
Myelograms- non-iodinated contrast
Esophogram- barium paste
Excretory urogram- iodinated contrast
Gastrogram, GI series- barium
Pneumocolon- air
Fistulogram- iodinated contrast
Pneumocystogram- iodinated contrast and air
Describe the steps to perform an upper gastrointestinal study
animal is fasted, scout views prior to contrast admin, use gastric tube. Give 50% diluted barium water mix. use 5-8ml/lb as bolus to give directly in stomach. Use timer take r and l lat and VD immediately, 15 min, 30 min, 60 min, 90 min then hourly until barium enters colon
List common contrasts agents and the preferred route of admin
Barium sulfate- orally or rectally
Ionic contrast- IV, orally, urinary studies, fistulous tracts
Non-ionic contrasts- same as ionic but can also used for myelograms