Types and Properties of Dental Investment Materials and Casting Techniques
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Gypsum-bonded, Phosphate-bonded, and Ethyl silicate-bonded.
What are the three main types of dental investment materials?
Traditionally used for conventional gold alloy.
What is the primary use of gypsum-bonded investment materials?
Setting time, setting expansion, strength, temperature, and particle size.
What are the properties affected by the water/powder ratio in phosphate-bonded investment?
Alpha-hemihydrate (dental stone) and silica.
What is the composition of gypsum-bonded investment?
Acts as a binder and provides refractory during heating.
What is the purpose of silica in investment materials?
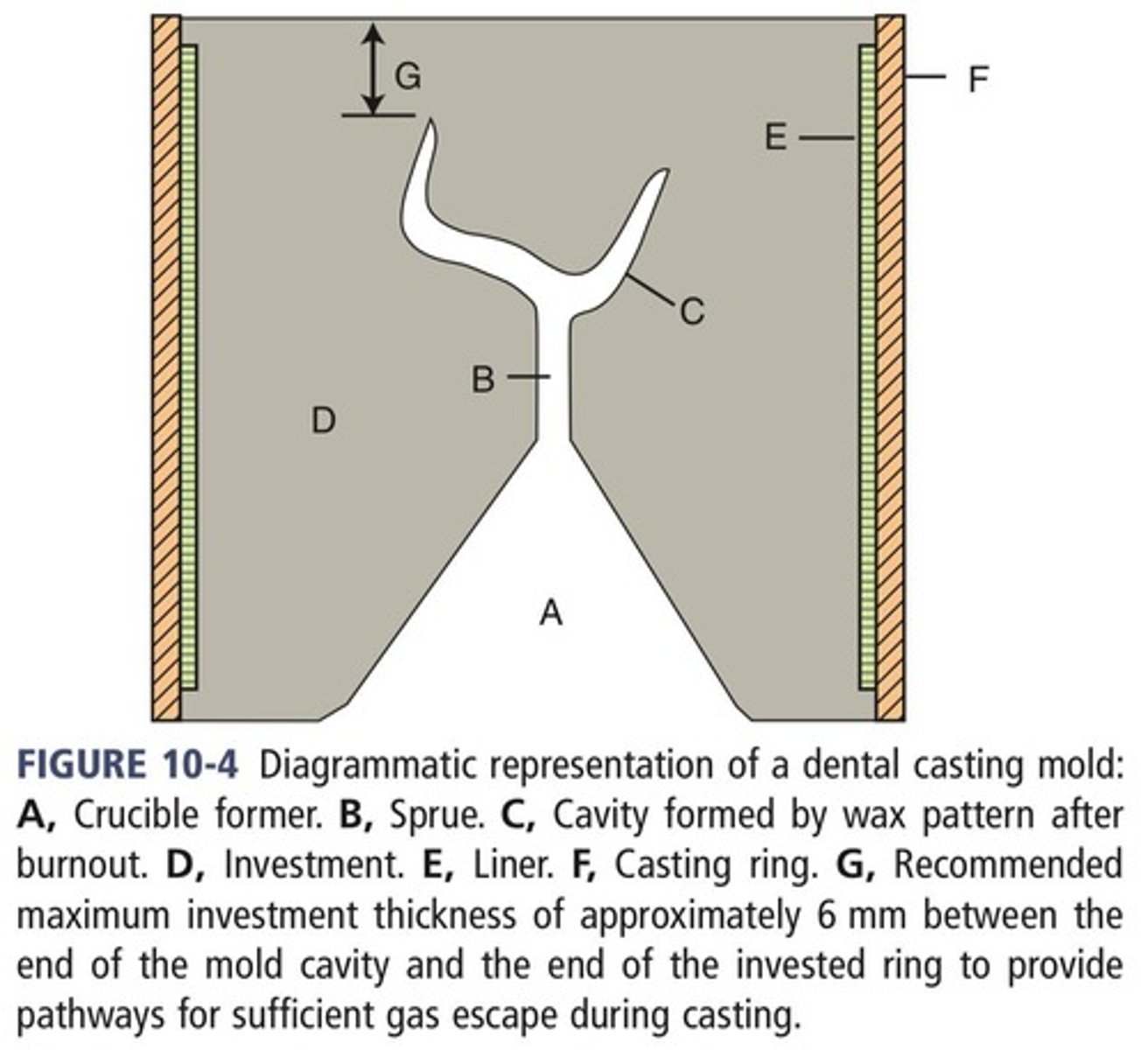
Acts as a channel for molten metal to reach the mold space.
What is the role of the sprue in the casting process?
Size of the wax pattern, dimension of the casting ring, type of casting machine, and length of the sprue.
What factors influence the size of the sprue?
Prevents localized shrinkage porosity and is needed for small patterns.
What is the purpose of the reservoir in casting?
The casting ring is dropped into water for rapid disintegration of the investment.
What happens during the quenching process?
Creating a wax pattern.
What is the initial step in the casting procedure?
It removes the wax pattern from the mold, allowing for the casting of metal.
What is the significance of the burn-out or wax elimination step?
Distortion, surface roughness, porosity, and incomplete or missing detail.
What are common causes of defective casting?
Porosity refers to air pockets within the casting and can be minimized by proper manipulation of the wax and handling of the pattern.
What is porosity in casting, and how can it be minimized?
Localized shrinkage porosity, microporosity, suck-back porosity, pinhole porosity, gas inclusions, subsurface porosity, and back pressure porosity.
What types of surface irregularities can occur in noble metal alloy castings?
They regulate setting time, control setting expansion, and prevent gypsum shrinkage.
What is the role of chemical modifiers in investment materials?
It cushions the dental investment to prevent crazing.
What is the purpose of the liner in the casting process?
Cleaning the cast metal with acids to remove surface contaminants.
What is the purpose of pickling in the casting process?
Must be accurately measured to avoid rough or thick castings.
What is the optimal liquid/powder ratio for investment materials?
It is the hottest part of the flame, essential for melting metal.
What is the significance of the blow pipe flame's blue zone?
They act as reducing agents to provide a non-oxidizing atmosphere in the mold.
What is the role of powdered copper and carbon in investment materials?
It produces a brittle black or gray layer on the surface of gold alloys.
What is the effect of sulfur contamination on castings?
It heats the casting ring and gold alloy, facilitating the pouring of molten metal.
What is the function of the casting machine in the casting process?
The sprue should be attached at a 45° angle to the wax pattern.
What should be done to ensure continuous metal flow during casting?
Approximately 1 hour.
What is the burn-out time for wax elimination in the casting process?