Pargas Exam 2: Motivation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Motivation
Set of forces that initiates, directs, and makes people persist in their efforts to accomplish a goal
Employee Engagement
Job Performance = Motivation X ability X Situational Constraints
What we need to hear
Telling someone the brutal facts
- telling someone what they "need" to hear
Needs
The physical or psychological requirements that must be met to ensure survival and well-being
- Unmet needs create an uncomfortable, internal state of tension that must be resolved
- People are motivated by unmet needs
- managers must learn what those unmet needs are, and address them
- Once a met is need, it no longer motivates
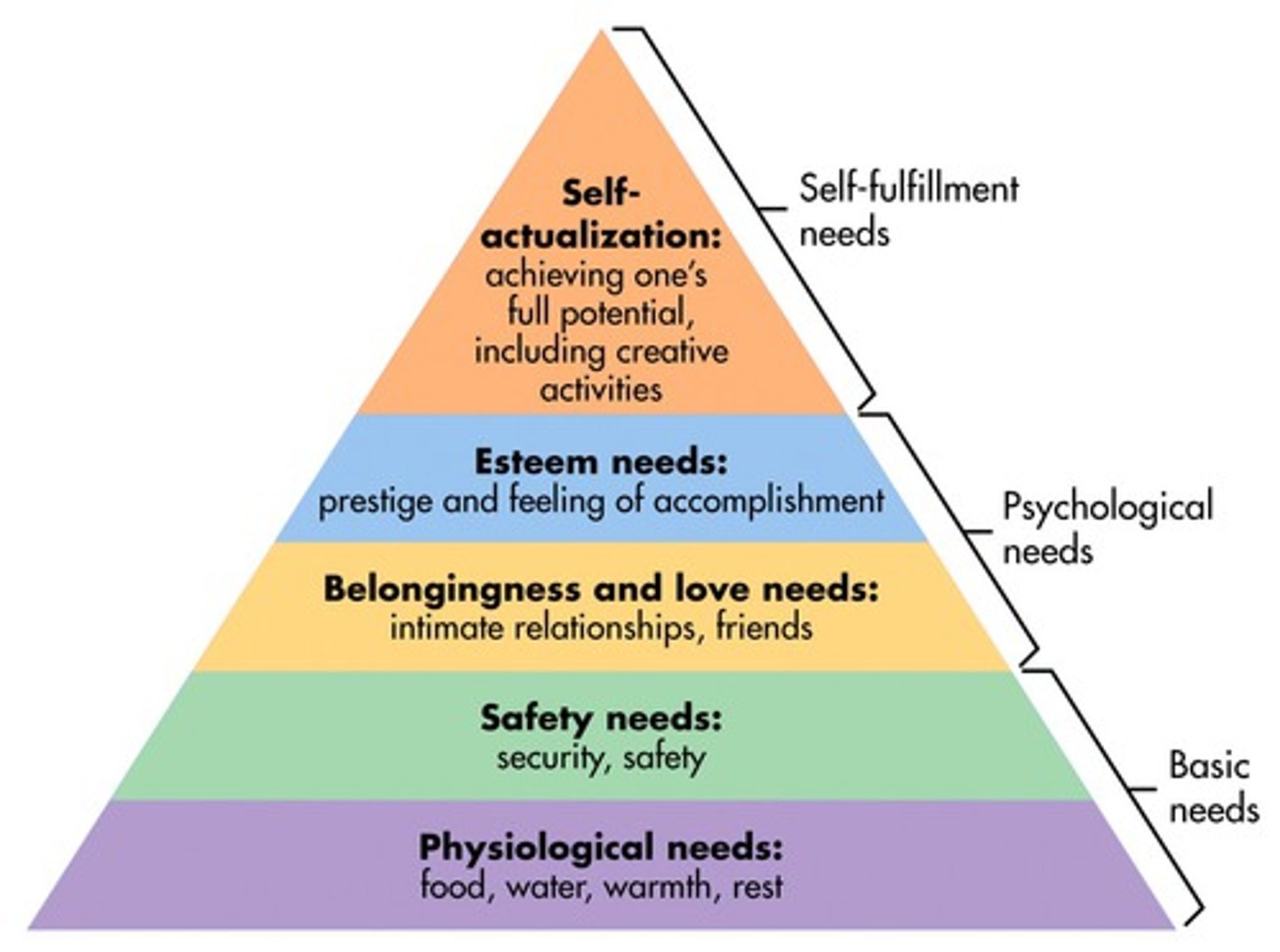
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Needs are arranged in a hierarchy from low to high and people are motivated by their lowest unsatisfied need first
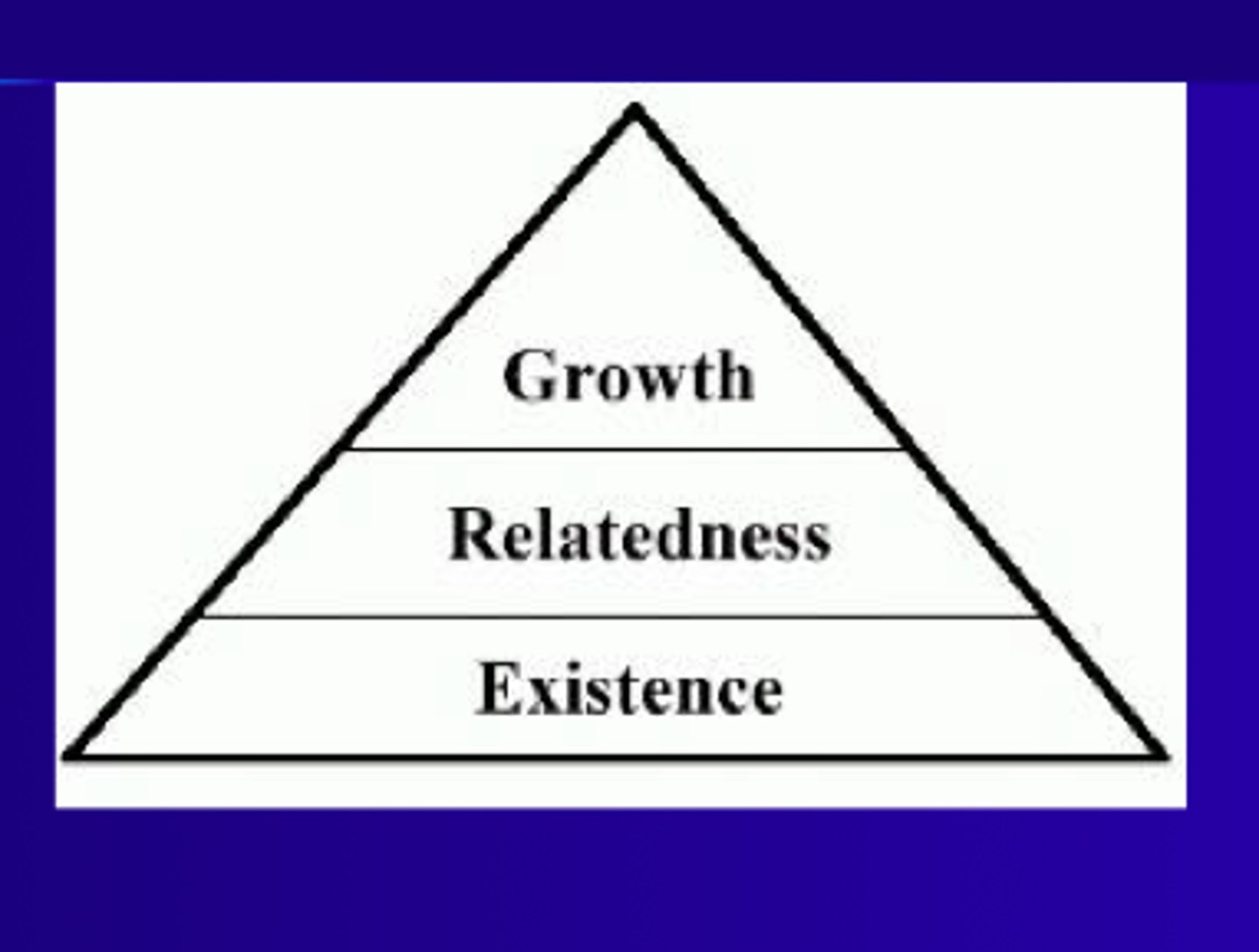
Alderfer's ERG Theory
People are motivated by different needs at different times in their lives and can be motivated by more than one need at a time
- Assumes three basic needs influence behavior: existence, relatedness, and growth
- cultural differences influence our need states
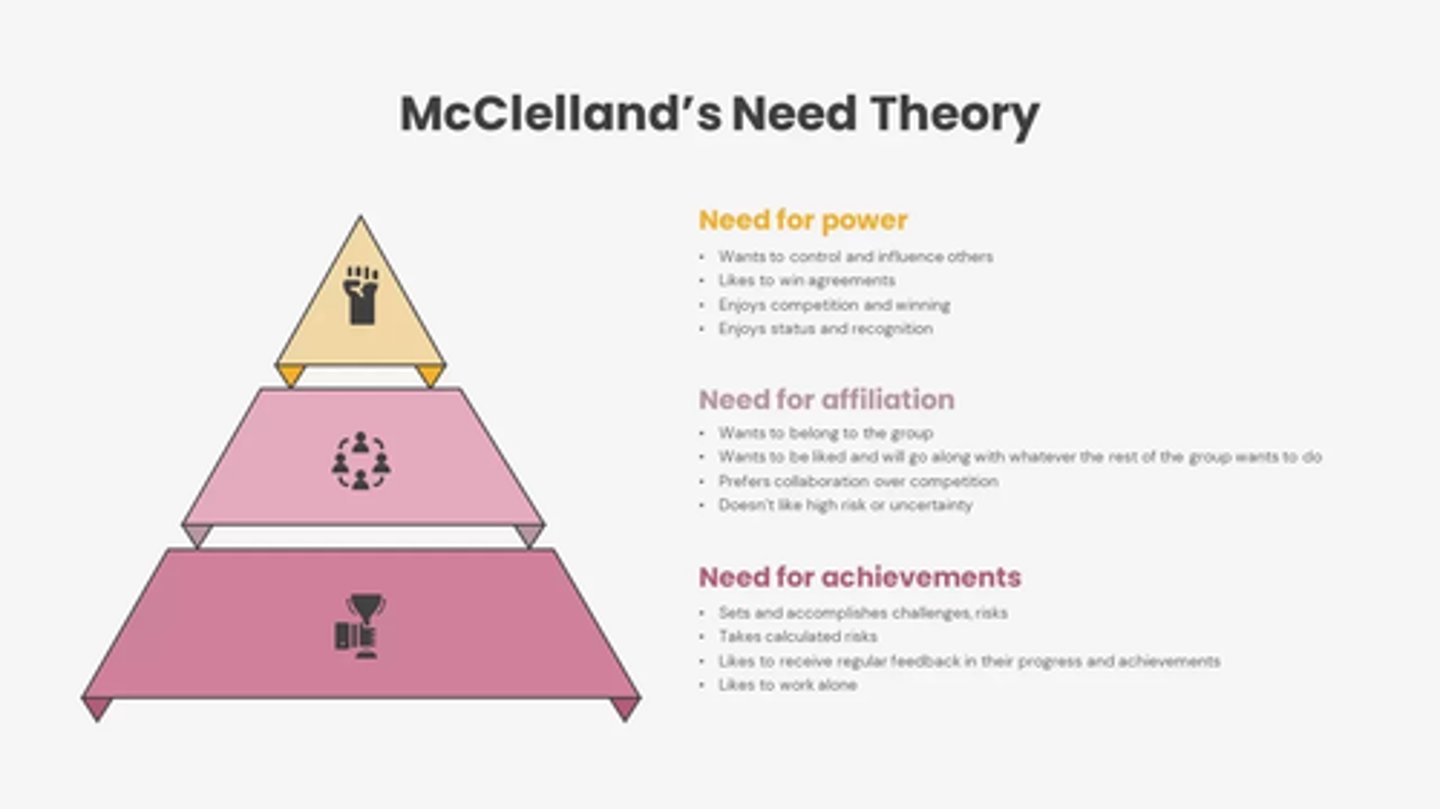
Mclleland's Acquired Needs Theory
Suggests people are motivated by the need for affiliation, the need for achievement, or the need for power
"Power" Paradox
Although people often gain power through traits and actions that advance the interests of others, once power is gained and people feel powerful, those admirable behaviors tend to be replaced with selfish (and sometimes unethical) behavior
Motivating with the Basics
- Higher order needs will not motivate as long as lower order needs remain unfilled
- Start by asking what their needs are
- Satisfy lower-order needs first
- Expect people's needs to change
Extrinsic Rewards
Tangible and can be seen to others and are given to employees contingent on the performance of specific tasks or behaviors
Intrinsic Rewards
Natural rewards associated with performing a task or activity for its own sake
Equity Theory
People will be motivated at work, when they perceive that they are being treated fairly
- stresses the importance of perceptions
Equity Theory Components
Inputs, outputs, and referents
- Inputs: Contributions employees make to the organization
- Outputs: What employees receive for their contributions
- Referents: others people compare themselves to
Underreward
- Form of Inequity
- When you're getting fewer outcomes compared to your inputs than the referent
Overreward
- Form of inequity
- When you're getting more outcomes compared to your input than the referent
Motivating with Equity Theory for Managers
- Start by looking for and correcting major inequities
- Reduce emloyees' inputs
- Increase employees' outcomes
- Make sure decision making process is fair
Distributive Justice
Outcomes and rewards are fairly distributed
- equity theory focuses on this
Procedural Justice
Fairness of the procedures used to make reward allocation decisions
Expectancy Theory of Motivation
People will be motivated to the extent to which they believe their efforts will lead to good performance, good performance will be rewarded, and that they will be offered attractive rewards
Factors of Expectancy Theory
- Valence: attractiveness of various rewards/outcomes
- Expectancy: belief that a certain level of effort will lead to a certain level of performance
- Instrumentality: expectation that successful performance of the task will lead to the desired outcome
Reinforcement Theory
The theory that behavior is a function of its consequences
- behaviors followed by positive consequences will occur more frequently
- behaviors followed by negative consequences, or not followed by positive consequences, will occur less frequently
What is Reinforcement?
Process of changing behavior by changing the consequences that follow behavior
- Components:
- Reinforcement Contingencies
- Schedules of Reinforcement
Reinforcement Contingencies
Cause-effect relationships between the performance of specific behaviors and specific consequences
Schedules of Reinforcement
Set of rules regarding reinforcement contingencies that specifies which behaviors will be reinforced, which consequences will follow those behaviors, and the schedule by which those consequences will be delivered
Positive Reinforcement
Strengthens behaviors by following behaviors with desirable consequences
Negative Reinforcement
Strengthens behavior by withholding an unpleasant consequence when employees perform a specific behavior
Punishment
Weakens behavior by following behaviors with undesirable consequences
Extinction
Positive consequences are no longer allowed to follow a previously reinforced behavior
- removing positive consequence, extinction weakens behavior, making it less likely to occur
Reinforcement Theory Steps
- Identify: singling out critical, observable, performance-related behavior
- Measure: determining the baseline frequencies of these behaviors
- Analyze: studying the causes and consequences of these behaviors
- Intervene: changing the organization by using positive and negative reinforcement to increase frequency of these critical behavior
- Evaluate: assessing the extent to which the intervention actually changed workers' behavior
Goal-Setting Theory
People will be motivated to the extent that they accept specific, challenging goals and receive feedback that indicates their progress toward goal achievement
Components of Goal-Setting Theory
- Goal specificity
- Goal difficulty
- Goal acceptance
- Performance feedback
Goal Specificity
The extent to which goals are detailed, exact, and unambiguous
Goal Difficulty
The extent to which a goal is hard or challenging to accomplish
Goal Acceptance
The extent to which people consciously understand and agree to goals
Performance Feedback
Is information about the quality or quantity of past performance and indicates whether progress is being made toward the accomplishment of a goal
Popular Incentive Compensation Plans
•Piece rate
•Sales commission
•Bonuses
•Profit-sharing
•Gainsharing
•Stock options
Pay for knowledge
Cost of Demotivation and Layoffs
•Loss of unintended and most talented employees
•Decrease in productivity due to fear and low morale
•Severance packages
•Counseling
•Workplace violence
•Fear of taking risks
•Books written about you
•Customer defections and boycotts
•Lawsuits
•Loss of trust in Management
•Laid off employees often band together and open a competitor company