oxidation curve
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
describe haemoglobin
Haemoglobin is made up of 2 different types of subunits A and B there are 2 of each of these types so in total 4. Each subunit has the prosthetic group haem attached. Within the haem group there is the Fe2+ ion which oxygen can bind to
what is the equation for oxygen binding (loading) and unbinding (unloading)
Hb+4O2=Hb(O2)4 this is a reversible reaction
what does affinity mean
How strongly the oxygen is bound the haemoglobin
what is this called
What is the partial pressure
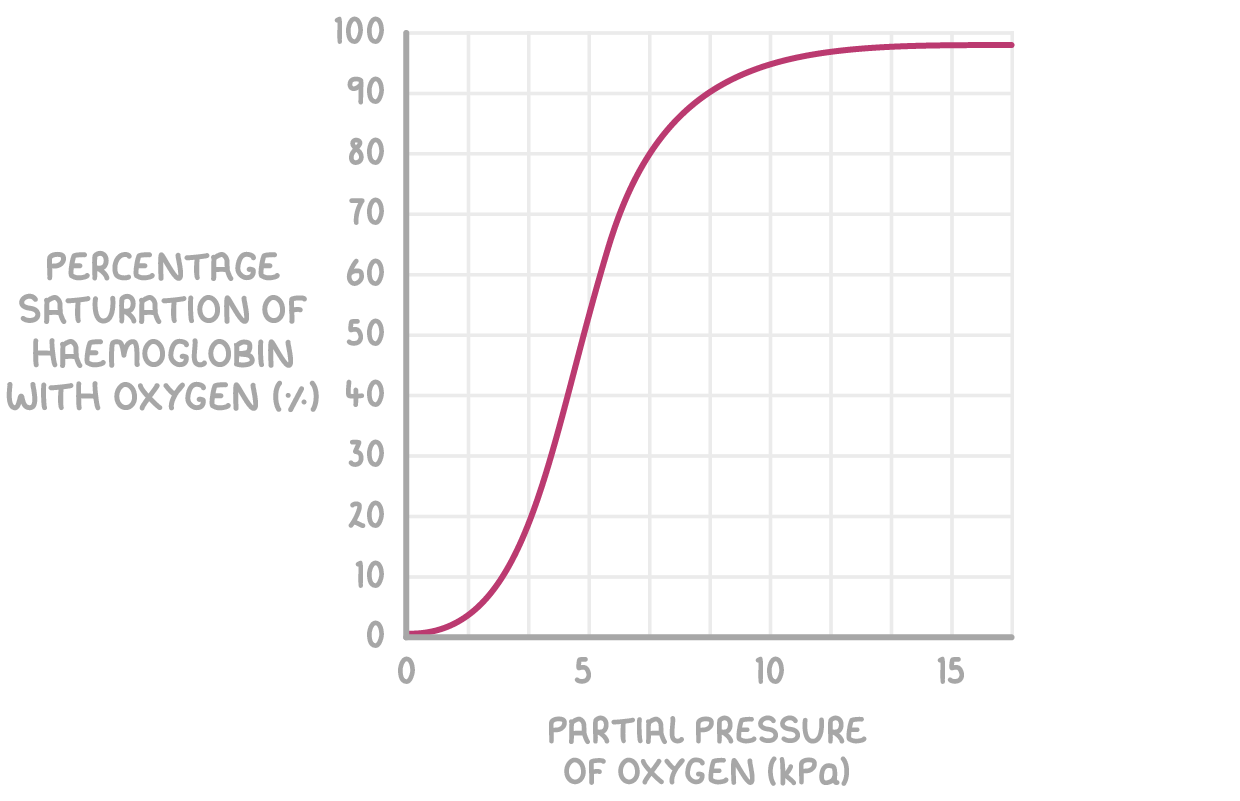
what is this type of curve called
oxygen dissociation curve
basically the concentration of oxygen
sigmodal
At low partcial pressure the percentage of oxygen bound is low to heamoglobin is low what does this tell us
That at low partcial pressure there is low affinity for O2
Once we reach 25 % where one O2 has joined onto the haemoglobin what happens to the gradient and what does this tell us about the structure of haemoglobin
The gradient gets steeper
takes a relatively large partial pressure to get the first one to join. But once one oxygen has joined it changes the structure making it easier for the other oxygen to join.
why is it hard for the first one to join on
Its hard for the first oxygen molecules to bind to one of the four sites on haemoglobin because the polypeptide subunits are closely held together so its hard for the oxygen molecule to access the Fe2+ ion. Therefore at a low practical pressure little oxygen binds to haemoglobin so the curve is shallow.
why is it easier for the other 2 to join on
Once an oxygen binds to the haemoglobin it changes the quaternary structure of the haemoglobin. the globin chains open up so that the second and third oxygen molecules can bind easier to Fe2+ ions. Only a small increase in partial pressure causes lots more oxygen to bind
where does the steep gradient go up to
75% when 3 have joined
After 75 % the relatively partial pressure to get another ( the final) oxygen to join increases why.
at 75 % its almost fully saturated (there are less spaces for O2 to collide with and bind) Its harder for it to bind to an Fe2+ ion. This cause the gradient of the curve to decrease and plateaus. so increasing the “conc” doesn’t have as great of an effect as its harder for it to bind as less spaces.
why does haemoglobin become 100% saturated at bellow a partial pressure of 21 which is the level of oxygen in the atmosphere
Although atmospheric oxygen partial pressure is 21 kPa, the partial pressure in the alveoli is lower due to humidification and diffusion into the blood. However, haemoglobin becomes fully saturated at these lower partial pressures because it has a high affinity for oxygen and shows cooperative binding, reaching the plateau of the oxygen dissociation curve.
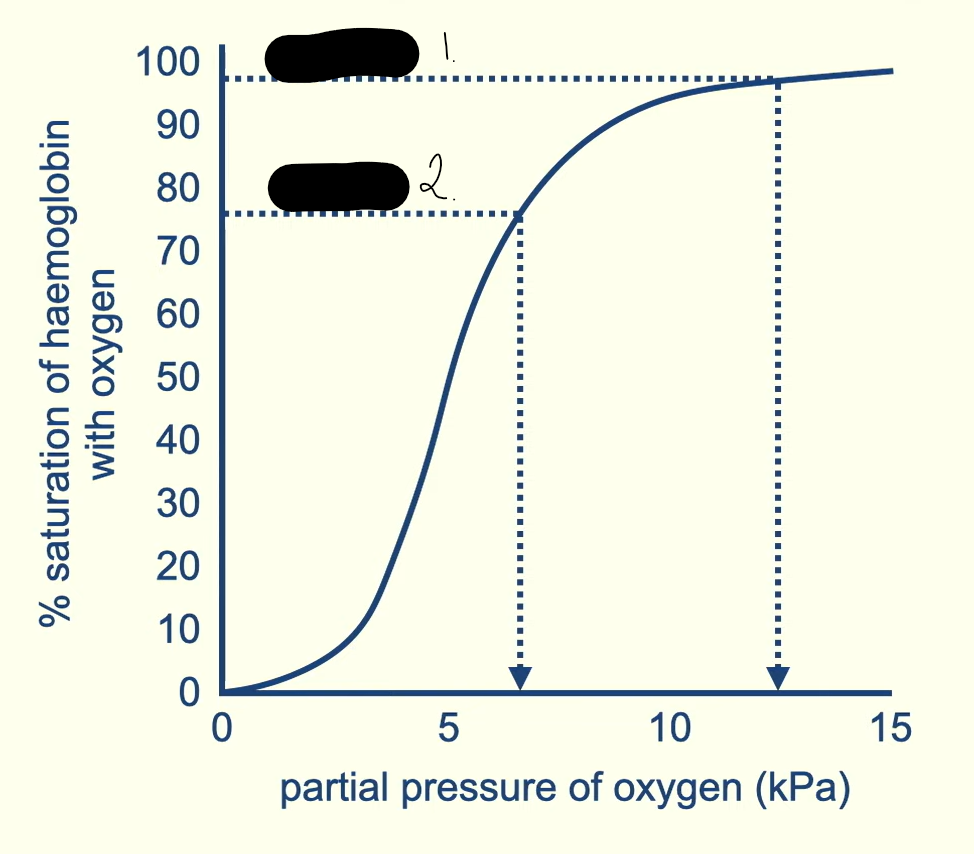
1 and 2 are tissues one has a higher partial pressure identify the tissues and explain why
alveoli are in the lungs there oxygen is breathed in so its at its highest conc
tissue respires using oxygen meaning that it diffuses in and unloads. As some of the oxygen is used up there is a lower conc
when one oxygen unloads from saturated haemoglobin what effect does this have
it changes the quaternary structure of the haemoglobin. This reduces the affinity for oxygen making it easier for more molecules to unload
what is a factor that effects the graph
carbon dioxide
Describe how high levels of CO2 impact the oxidation curve
high levels of CO2 cause the oxygen dissociation curve to shift the right. Meaning that at the same partial pressure of oxygen less will bind in high CO2 conditions vs low CO2 conditions. CO2 causes the oxygen affinity of haemoglobin to decrease. So its easier to unload the oxygen
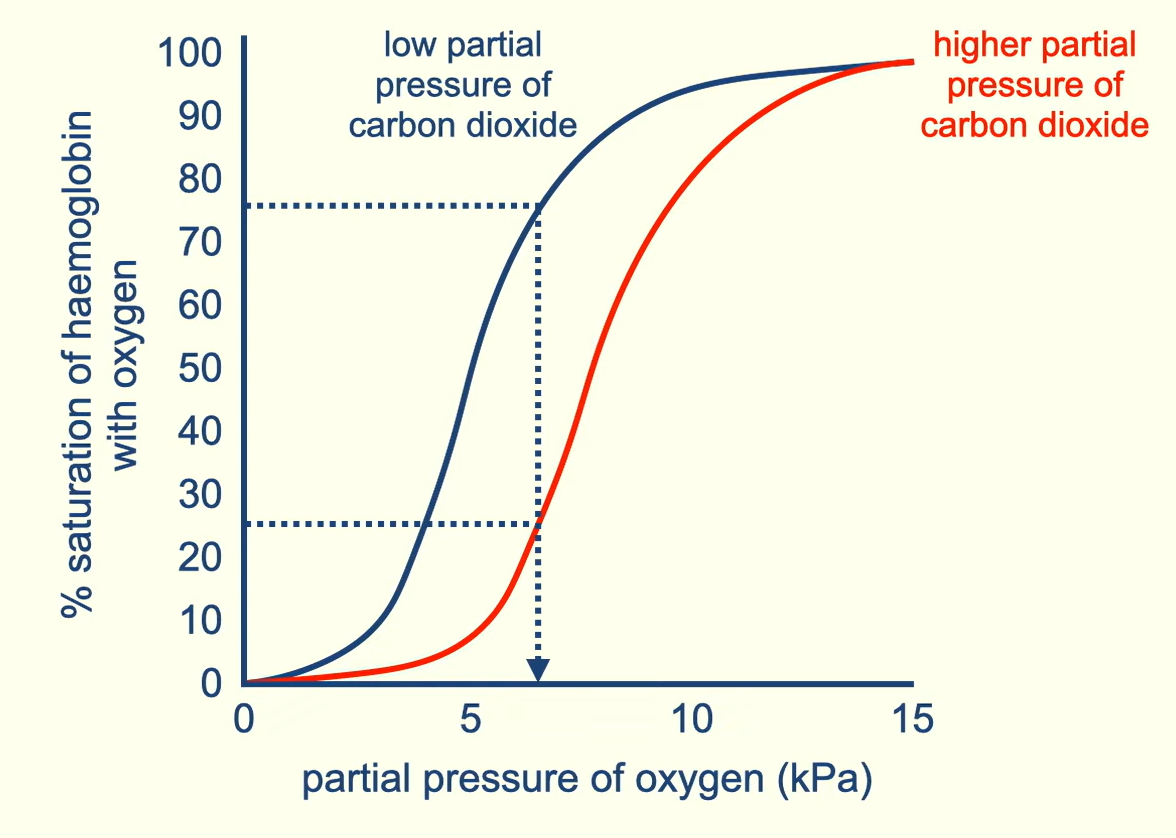
what is the shift right called
Bohr effect
does does the bohr effect positively impact the transport of oxygen
The lungs have a low CO2 conc so there will be high oxygen affinity and tissue which is respiring will produce lots of CO2. This high conc of CO2 will mean that oxygen is more easily unloaded where its most needed.
How does CO2 cause the structure of the haemoglobin to change
In the blood carbon dioxide can firm the acidic molecule carbonic acid. This releases the hydrogen ion H+. This H+ combines with the haemoglobin and causes it to change its quaternary structure. This results in haemoglobin having a lower affinity for oxygen.
what is a myoglobin
Myoglobin is a protein found only in muscle cells. It is like a single haemoglobin chain, with a single haem group, and it also binds oxygen. It is myoglobin that gives red meat its colour. As the dissociation curve shows, myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen, especially at low partial pressures. So in muscle cells oxygen will unload from haemoglobin and bind to myoglobin. Oxygen will only be unloaded from myoglobin at very low partial pressures, when muscle cells are respiring rapidly. So myoglobin acts as an oxygen store, making oxygen available when needed
how does oxygen from the mother blood get into that of the foetus
if diffuses from the mothers into the foetuses as there close it goes down a concentration gradient
What is the affinity of haemoglobin in a foetus like
The foetus obtains its oxygen from the mothers blood. The foetal haemoglobin has a slightly higher oxygen affinity at the same partial pressure This means it can become fully saturated at a low partial pressure so its oxygen dissociation curve is shifted to the left.
( even if Q not about a foetus if its shifted to the left state what is in red you need the comparison about the more O2 affinity at same partial pressure)
why is it important that the foetal haemoglobin is only slightly higher than that of the mothers
As then it wouldn’t be unable to load at tissue
how does CO2 play a role in causing O2 to diffuse into the foetus
As it diffuse out from the foetal blood into the mothers it lows the oxygen affinity of the haemoglobin in the mother blood making it easier to unload
explain why oxygen dissociation curves are s shaped.
co operative binding of oxygen to the 4 polypeptide chains
binding of the first oxygen molecule changes the shape of haemoglobin molecules
therefore facilities binding of other oxygen molecules.
If an animals oxygen dissociation curve is more to the left then what does this mean in terms of movement.
the one to the left is more saturated at a lower pressure than the other animal
so more oxygen up take
more available to muscles.
so can move more