Materials - Hooke’s Law, Energy Stored
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
forces that produce extension
tensile forces
forces that produce compression
compressive forces
tensile force
equal and opposite forces acting on a material to stretch it
compressive force
two or more forces together that reduce the length or volume of an object
tensile deformation
a change in the shape of an object due to tensile forces
compressive deformation
a change in the shape of an object due to compressive forces
elastic deformation
a reversible change in the shape of an object due to a compressive or tensile force - removal of stress or force will return the object to its original shape and size (no permanent strain)
plastic deformation
an irreversible change in the shape of an object due to a tensile or compressive force - removal of the stress or force produces permanent deformation
Hooke’s Law
the force applied is directly proportional to the extension of the spring unless the limit of proportionality is exceeded
F = kx
force constant
a quantity determined by divided force by extension (or compression) for an object obeying Hooke’s Law - called constant of proportionality “k” in Hooke’s Law, measured in Nm⁻¹
stiffness
the ability of an object to resist deformation
elastic limit
the value of stress or force beyond which elastic deformation becomes plastic deformation and the material or object will no longer return to its original shape and size when the stress or force is removed
limit of proportionality
the value of stress or force beyond which stress is no longer directly proportional to extension
Improving Hooke’s Law experiment (4)
Length:
use a set square
take reading at eye level to reduce parallax errors
Mass:
use a digital balance
Take 6 different reading and repeat each one
How to find work done from a graph
Area under a force-extension graph
elastic potential energy
the energy stored in an object because of its deformation
steps to relate work done and Hooke’s Law (4)
W = area under graph - W = ½ Fx
F = kx - W = ½ (kx)x
∴ W = ½ kx²
where W is directly proportional to x²
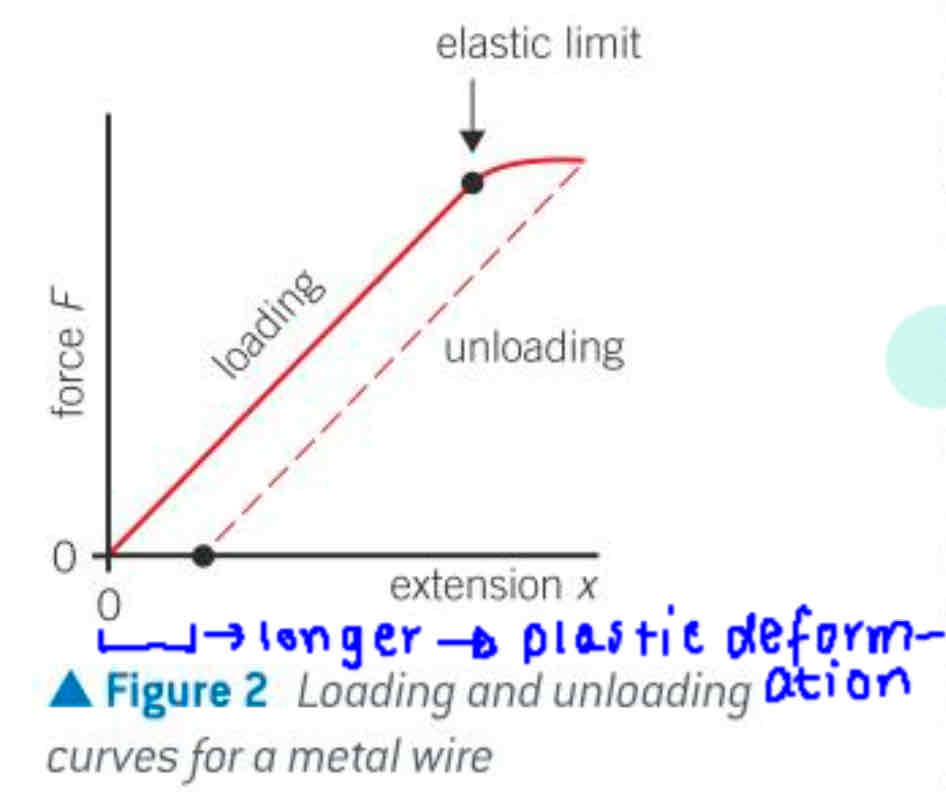
F-x graph of a metal wire
unloading curve is identical to loading curve if forces are under elastic limit, otherwise unloading is parallel but not equal
F-x graph of rubber
gap in between shows thermal energy produced
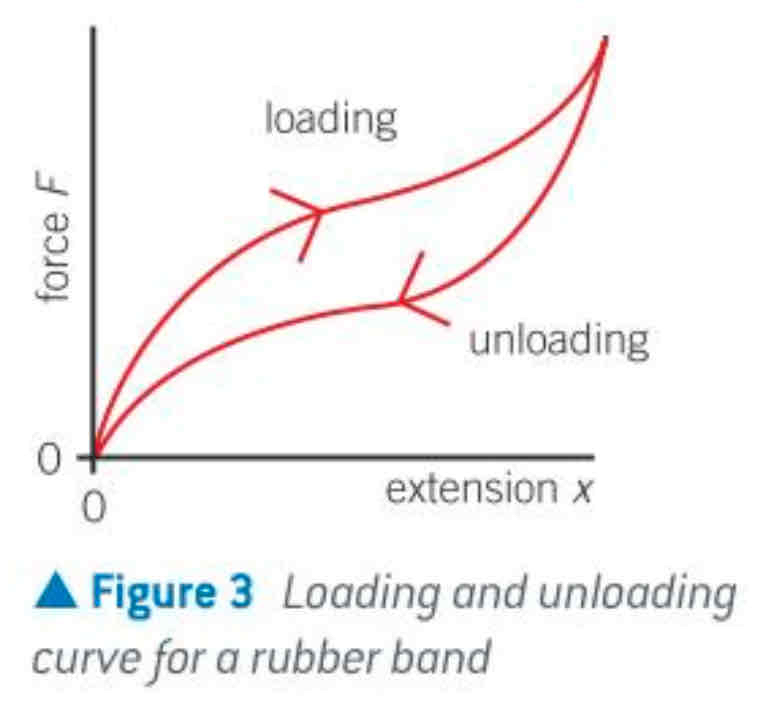
hysteresis loop
a loop-shaped plot obtained when loading and unloading a material produce different deformations - more work is done in stretching a band than releasing it
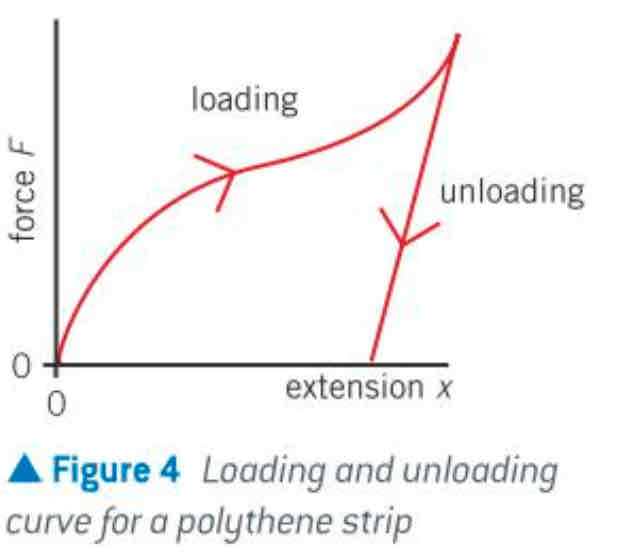
F-x graph of polythene
suffer plastic deformation under relatively little force