Driver's Ed Flashcards
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
What is one of the leading causes of death for teens?
Car crashes.
What is a vulnerable roadway user?
Bikers, pedestrians, etc.
What is the single most effective thing you can do to protect yourself in a crash?
Wear your seatbelt!
What are the advantages of properly adjusted mirrors?
You can see your blind spots better.
What are the five steps listed to secure your vehicle?
Keep foot on the brake, Activate parking brake, Shift to park, Turn off accessories (ex: radio, A/C), Turn off vehicle.
What are the three types of vision and what does each allow you to see?
Peripheral, fringe, central: Peripheral is where your blind spots usually are, Fringe is near the edges, Central is in the center.
What are the three requirements of a target?
Target range, secondary range, immediate range.
What is trail braking and what can this technique do?
Trail braking is gradually putting your foot on the brake and slowly coming to a stop.
How should you hold your hands on the steering wheel?
9 to 3 or 8 to 4.
When is a hand-over-hand steering technique used?
Whenever you are making sharp turns, or parking.
What is the transition point for a left turn? What does it help you know?
The point that helps you to change speed, direction, etc. For a left turn, it is a corner post.
What do reference points allow you to do?
Allow you to have a reference before turning; it helps align your steering.
What does SIM stand for?
S: Search, I: Identify, M: Manage.
Vision Restrictions
Examples include heavy greenery (trees, bushes), cars in front, and nature-related issues (fog, heavy rain, snow).
Path-of-Travel Restrictions
Examples include pedestrians, animals, and construction.
What is the purpose of effective communication?
Allows people to know your intentions and what is happening.
What is the definition of a precision turn?
Placing your vehicle precisely and accurately, before, during, and after the turn.
What are the steps to perform a precision stopped right turn?
Check rear, smoothly stop, look through and around the intersection, find the target, turn the wheel to the front, move from brake to accelerator, begin to straighten the wheel, apply smooth steady acceleration.
What are the steps to perform a precision moving left turn?
Look around the intersection, check rear, apply brakes, keep wheels straight until ready to turn, look to target and turn wheel, trailbrake, move from brake to gas at transition point, straighten wheel, apply steady acceleration, check speed limits.
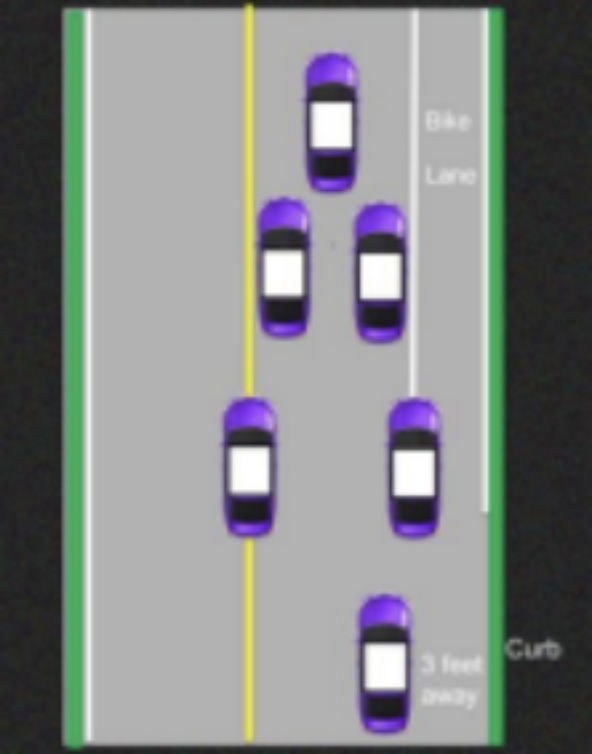
Write the correct lane position or side position on each car in the diagram below.
From top to bottom: LP1, LP2, LP3, LP4, LP5, SP3

You are the driver in the photo on the right. You are about to turn right. Explain which areas you should see using your central vision and which you should see with your fringe vision while turning.
Central: B
Fringe: Everything else
What are the three purposes of signs?
Regulation, Warn, and Guide.
What is the speed limit in a school zone?
20 mph.
What are the three stopping locations?
Legal, Safety, Staggered.
What does ‘yielding’ mean?
Stopping or slowing to allow another roadway user to go before you.
What are the yielding requirements when turning left?
Yield to oncoming traffic and wait for a gap, then turn left.
What are the yielding requirements at a four-way or all-way stop?
The first to arrive has the first right of way.
What are the steps to enter traffic?
Use MSMOG--mirror, signal, mirror, over the shoulder, go.
What is the difference between a controlled intersection and an uncontrolled intersection?
Controlled intersections have signs or signals, uncontrolled do not.
How do you search intersections while stopped?
While stopped, search 90 degrees to left, front, and right; when no stop is required, use 45 degrees.
Why do you need to turn the wheels when parking on a hill?
To make sure that your vehicle doesn’t roll out into traffic.
How should you use your central and fringe vision while driving through curves?
Use central vision to look at the target area before and while turning; use fringe vision to monitor your position and vehicle path.
What is needed for a space to be open?
No path restrictions, visibility for at least 15 seconds, and at least 4 seconds of following distance.
What is the difference between seeing the driving environment and perceiving that same environment?
Seeing involves looking at the target area without awareness of surroundings; perceiving means being aware of the entire environment, including obstacles.
What is the point of no return and where is it located?
The point where you can no longer stop safely if something changes, located two seconds away from any situation or object.
What are the advantages of maintaining an adequate following distance?
Keeping an adequate following distance decreases your risk.
Where should you place your hands when backing straight?
One hand at the top of the steering wheel and the other behind the passenger seat for improved visibility.
What is the pivot point used for?
Used when backing to align with the curb or line and adjust steering direction.
What are the ways to turn around after missing a turn?
Right alley turnaround, left alley turnaround, 3-point turnaround, U-turn.
What is an example of a fixed side space and a moving side space?
A fixed side space could be a curb because it is unmoving and still. A moving side space could be a cyclist because they are in motion.
What three solutions should you apply as you approach an intersection?
Lane position, speed, communication.
What are four disadvantages of charging a closed space?
Increases chances of collision, sends late communication, compromises vehicle balance, causes wear and tear on vehicle.
When should you check your rear-view mirrors?
Before and after turning, speed change, lateral maneuver, changing to the front space, and stopping.
How might you respond when your rear space is closed?
Provide more space to the front by increasing the following distance or pull over.
What should you be able to see when stopped behind a vehicle in a line of traffic?
The rear tires of the car in front of you, touching the pavement.
What are some advantages of delaying your start by two seconds when stopped in traffic?
Gives you extra space to proceed.
How does knowing the point of no return help you control intersections that have traffic lights?
You will be able to better time and judge the traffic signals and when it's safe to stop or go.
What three behaviors should you perform before you turn the wheel to change lanes?
Check front and rear for open and stable gap, communicate with turn signal and lane position, check mirrors and blind spots.
When changing lanes, where should your central vision be focused and how should you move?
Your central vision should be focused on your target area, and you should keep a shallow angle as you move.
What are three examples of vulnerable roadway users?
Pedestrians, cyclists, and motorcyclists.
In most situations, what lanes must a pedestrian clear before you can proceed?
Pedestrians must clear your lane and the next lane before you can proceed.
How much room should you leave when passing a cyclist?
You should leave enough room so that if the cyclist falls they won't come into contact with your car.
How much following distance should you keep between your car and a motorcycle? Between your car and a semi-truck?
You should keep 4 to 6 seconds of following distance between your car and a motorcycle. Same with a semi-truck.
What is a truck’s “No-Zones” and how can you lower the risk of those zones?
No zones are a truck's blind spots which are very large. Maintain a good distance between your car and the truck.
How do we respond when a school bus has amber (yellow) lights flashing? When the red lights are flashing?
If a school bus has amber lights flashing, it is preparing to stop and we should too. Red lights flash when the bus comes to a stop, we are required to stop and cannot pass the bus.
How do we respond when an emergency vehicle (police, fire, ambulance, etc.) is approaching us while driving? When we approach an emergency vehicle that is parked with lights flashing?
We should pull over to the right and stop. We can only proceed once the emergency vehicle has passed. If the emergency vehicle is parked with its lights flashing, it indicates that there is an emergency. We should either move away to another lane or slow down.
What are the two possible ways we can follow the move-over law, and respond to any vehicle parked with lights flashing?
Move over to a non-adjacent lane or slow down.
Who is most likely to be injured or killed in a work-zone crash? What type of collision is most common?
Drivers and their passengers are most likely to be injured; the most common type of collision is rear-end collisions.
List at least three ways you can lower your risk when interacting with railroads and streetcars.
Search and listen carefully for a train before crossing the railroad, never stop on the tracks, or turn in front of a streetcar.
What are some of the factors that affect the way your vehicle handles in a curve?
Type of vehicle, load, tires, road type, environmental conditions, type of curve.
Which areas in front of your car are considered closed as you approach a hillcrest? What is the best lane position to use as you approach?
All areas in front of your car are closed because your visibility is limited. The best lane position to use is LP1 unless a change is needed.
How much clear distance do you need between you and an oncoming vehicle to safely cross into the oncoming traffic lane to pass a semi-truck?
4320 feet, almost a full mile.
What is the best lane position, following distance, and speed choice to initiate a passing maneuver?
For passing, the best lane position is LP2, following distance should be 3 seconds, speed should be at or below the speed limit.
What are three differences between city driving and freeway driving?
Freeways have higher speed, controlled lanes and ramps, and no cyclists or pedestrians.
At what point should you slow down when exiting the freeway?
When you get on the off-ramp.
When must you dim your high beams for an oncoming car and for a car you are following?
You must dim your high beams when you are within 500 feet of an oncoming vehicle and 300-350 feet of a car you are behind.
What action should you take to avoid the glare of oncoming headlights at night?
Look to the right and watch the road edge or fog line.
How can you prepare your vehicle for driving at night and in bad weather conditions?
Make sure all your lights work, dim your dash and accessory lights, and adjust the day/night switch on the mirror.
What are some actions that will reduce risk in inclement weather conditions?
Check road conditions beforehand, reduce speed, brake and accelerate gradually, and keep a minimum of 6 seconds of following distance.
What are at least three signs that you are dangerously drowsy?
Difficulty focusing, frequent blinking, yawning repeatedly.
What are at least three ways to respond when you notice you are driving and feeling sleepy?
Drink a caffeinated beverage, take a power nap, take a quick walk.
What is the implied consent law?
Anyone who receives a driver's license automatically consents to be tested for blood-alcohol content and other drugs if they are stopped for suspicion of alcohol or drug use while driving.
What are at least three ways alcohol impairs your driving?
Affects judgment and reasoning, slows reaction time, blurred vision.
What are at least three ways cannabis impairs your driving?
Delayed reactions to sights and sounds, judging distances, multi-tasking.
What is your personal plan to make sure you are not distracted by your phone while driving?
Put phone away, don’t look at it while driving!
Besides their phone, what are three other common ways that teens get distracted while driving?
Radio, eating/drinking, putting makeup on.
How should we respond to aggressive driving?
Do not engage, if escalates, call 911!
What are some ways to prevent road rage?
Control your emotions, take a deep breath, think calm thoughts!
What are some basic maintenance tasks you should have a basic working knowledge of?
How to change a flat tire, check air in tires, replace windshield wipers, check engine fluids.
Where is the best place to find information specific to your vehicle?
Owner’s manual
What three common practices can be applied during any emergency?
Remain calm, firmly grip the steering wheel, look to your target.
List some things you want to have in an emergency kit in your vehicle.
First aid kit, cell phone charger, water, toilet paper, etc.
What three things are you required by law to produce upon request during a traffic stop?
License, registration, proof of insurance
What are some ways you can show cooperation and respect to an officer during a traffic stop?
Use polite tone of voice, don’t argue, hands on wheel when officer approaches.
Besides signing up at the DMV or online, who should you talk with about your decision to be an organ donor?
Talk to your family!