ILU- Describing Matter
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
*note this is most likely not everything* Elements (including diatomics), Compounds and Mixtures, Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous, Solutions vs. Colloids vs. Suspensions, Tyndall Effect,Intensive Properties vs. Extensive Properties Qualitative Data vs. Quantitative Data, solid, liquid, gas (and vapor), plasma, Physical and Chemical Changes, Physical and Chemical Separations, Law of Conservation, LABS INFO: Paper Chromatography, chemical reactions/equations NOT ADDED YET: Analyzing particle level diagrams, images of samples/ laboratory steps/results
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Pure substances
Uniform, fixed composition & properties, CANNOT be broken down by physical separations
Particle size from smallest to largest for colloid, solution, and suspension
Solution
Colloid
Suspension
Physical separations
Separation of a mixture into pure substances that DOES NOT change the chemical composition —> all materials that make up the mixture are available after separation
Chemical separations
Separations of substances that ALTERS CHEMICAL COMPOSITION (bonds formed or broken)
Monatomic
A molecule with only one atom (and remains stable)
Diatomic
A molecule with two atoms (contains a chemical bond)
He, Ne, Ar
Examples of monatomic molecules
O2, N2
Examples of diatomic molecules
Compounds (aka formula units or molecules depending on how they chemically combine)
Substance containing more than one atom, contains a chemical bond, CHONPS are 6 main atoms that things are made of
Homogenous mixture
A mixture that is evenly distributed (ie. coffee, wine, blood)
Heterogenous mixture
A mixture that is NOT evenly distributed (ie. water and oil, sandwich)
Electrolysis
use electricity to decompose a substance
Tyndall effect
The phenomenon happens when light passes through a small particle or liquid
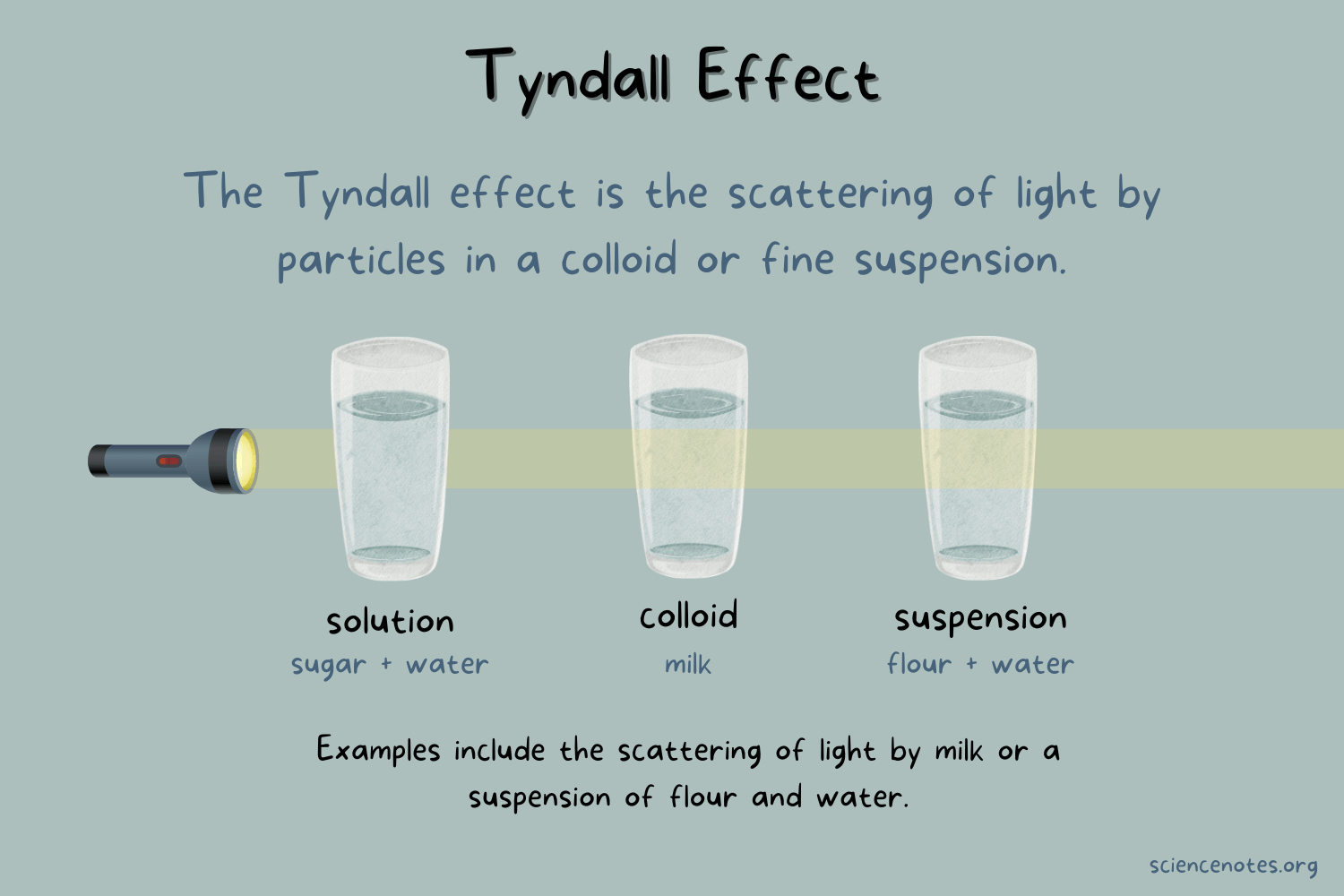
Solutions
Homogenous
Smallest particles
Transparent —> completely allows light to pass through
Colloids
Homogenous
Exhibits Tyndall effect (light passes through un the form of a beam due to light colliding with larger sized particles)
Particles will NOT “settle out”
ie. Jello, fog, milk
Suspensions
Heterogeneous
Biggest particles
Particles can be filtered or “settle out”
ie. Muddy water
Extensive properties
Properties that DEPEND on the sample size
mass, volume
Intensive properties
Properties that ARE NOT dependent on sample size —> considered “constant” within the range of standard chemisty practices
density, melting point, etc.
Physical properties
Quality or condition of a substance that can be observed or measured WITHOUT changing the substances composition
Chemical properties
Quality or condition of a substance that CANNOT be observed or measured without changing the substances composition (undergoing a chemical reaction)
Color, state of matter, boiling point, melting point, conductivity, magnetic
Examples of physical properties
Rust, corrosive, flammability, toxicity, combustion, reaction with water
Examples of chemical properties
Physical changes
Changes that DO NOT alter chemical composition of the substance
CAN be irreversible
Chemical changes
Changes that chemically alter the composition of the substance
Completely new substances with new properties are formed
Synonymous w/ chemical reactions
Changes of state/phase, dissolving, cutting, tearing, grinding, reshaping, etc.
Examples of physical changes
Burning, scorching, cooking, fermenting, decomposing
Examples of chemical changes

Delta
Represents change
Evidence of chemical change
*not always a sign of chemical change
Change in temp*
Change in color*
Evolution/formation of gas (effervescence)
Production of light
Production of precipitate
Law of conservation
mass/energy/matter cannot be created or destroyed during a normal chemical reaction
Qualitative
description, quality > quantity
Quantitative
Measurements, quantity
How do substances change state of matter


What type of mixture is this
Solution


What type of mixture is this
Colloid


What type of mixture is this
Suspension

E or I: Density
Intensive
E or I: Mass
Extensive
E or I: Melting point
Intensive
E or I: Volume
Extensive
Pc or Cc: cutting
Physical change
Pc or Cc: burning
Chemical change
Pc or Cc: cooking
Chemical change
Pc or Cc: dissolving
Physical change
Solid
Fixed shape & fixed volume
Liquid
Variable shape & fixed volume
Gas
Variable shape & variable volume
Vapor (related to gas)
When the substance is typically liquid or solid @ room temp
Plasma
Variable shape & volume
HIGH energy excited and ejects electrons
How to analyze paper chromatography
The results of paper chromatography can be analyzed and interpreted by visualizing the separated components on the paper and measuring the distance traveled by each component. The distance traveled can be compared to a known standard to identify the components.
Balance this equation:
C2H6O + _O2 —> _CO2 + _H2O
C2H6O + 3O2 —> 2CO2 + 3H2O