Bonding, Structure, and The Properties of Matter (exam qus) (copy)
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
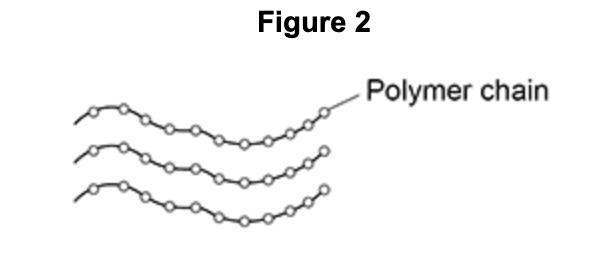
Compare the bonding within the chains with the forces between the chains in this polymer.
covalent bonds between atoms in the chain
intermolecular forces between the chains
covalent bonds are strong
intermolecular forces are weak
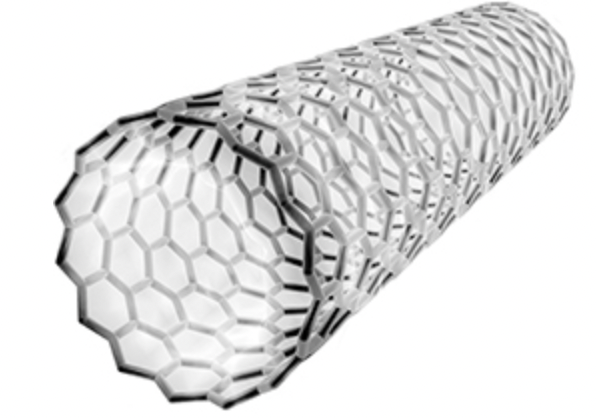
Suggest one property that makes the carbon molecule in Figure 1 useful in nanotechnology.
conducts heat
conducts electricity
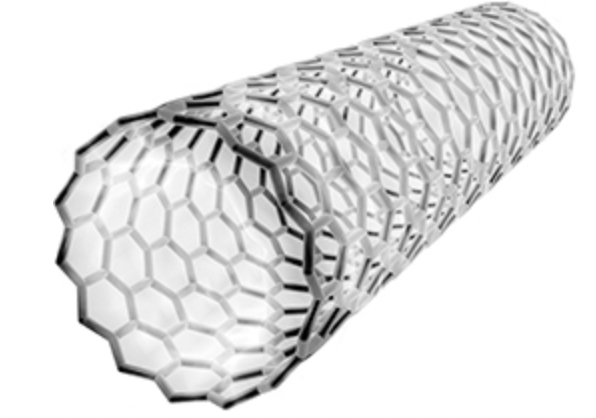
Name the type of carbon molecule in Figure 1.
fullerene
Suggest how anhydrous copper sulfate is used to test for water
Turns white to blue
Describe how copper sulfate solution is obtained from the plants used in phytomining
burned to produce ash
Copper compounds in ash dissolved in sulfuric acid
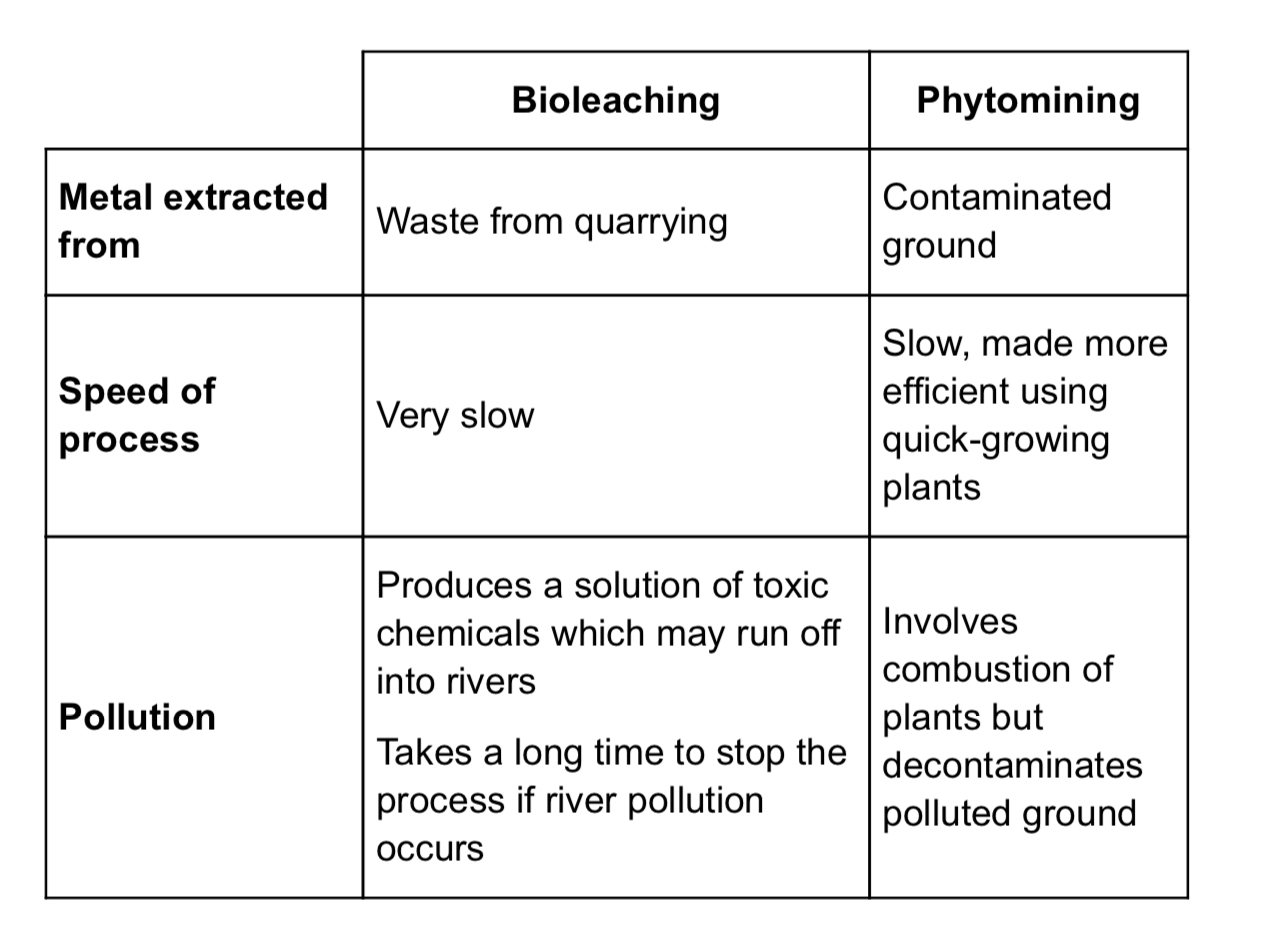
Compare phytomining and bioleaching
Bio leaching is very slow but although slow, phytomining can be made more efficient by growing quick growing plants
Bioleaching extracts copper from quarrying waste but phytomining extracts copper from contaminated ground
Phytomining decontaminates polluted ground but bioleaching can produce toxic run off which may go into rivers
Phytomining takes a long time to stop
Bioleaching is a very slow process
Plants are burned in phytomining
Emissions from car contain co2.
Explain why co2 emissions during the use and operation are not the total carbon footprint for a car.
Refer to LCA
extracting raw materials
Disposal at the end of life
Manufacturing
Compare the bonding within the chains with the forces between the chains in this polymer
bonding within the chains are covalent and are strong
Forces between the chains are intermolecular and weak
Suggest one property that makes the carbon molecule in figure 1 useful in nanotechnology
conducts heat
Conducts electricity
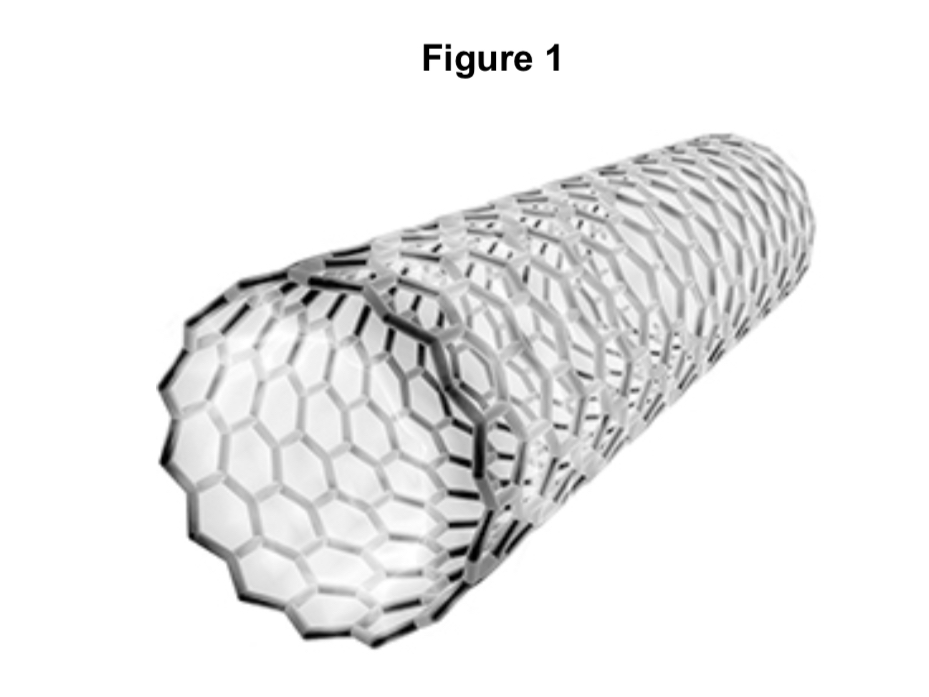
Name the type of carbon molecule in figure 1
Fullerene
Explain why graphite is:
a good electrical conductor
soft and slippery
You should answer in terms of structure and bonding.
bonds are covalent
giant structure
a good electrical conductor
only 3 electrons per carbon atom used in bonds so one is delocalised
these delocalised electrons can move through the structure carrying electrical charge
so graphite conducts electricity
soft and slippery
layered structure of hexagonal rings with weak intermolecular forces between layers
there are no bonds between the layers so the layers can slide over each other
so graphite is soft and slippery
Give two observations you could make when a small piece of potassium is added to water.
effervescent and lilac flame
Explain why the reactivity of elements changes going down Group 1.
reactivity increases going down the group
outer shell is further from the nucleus
there is less attraction between the nucleus and the outer shell
the atom is able to lose an electron more easily
Explain why sodium oxide has a high melting point.
giant structure
with strong electrostatic forces of attraction between ions
therefore large amounts of energy are needed to break the bonds
Compare the structure and bonding of the three compounds:
carbon dioxide
magnesium oxide
silicon dioxide.
silicon dioxide and magnesium oxide are giant structures
carbon dioxide is small molecules with weak intermolecular forces
all 3 compounds have strong bonds
co2 and sio2 are formed from 2 non metals and therefore are covalent
so electrons are shared
mgo is formed with a metal and a nonmetal so bonds in mgo are ionic
so electrons are transferred from mg to o (2 electrons transferred)
bonds in sio2 are single bonds where each silicon forms 4 bonds and each oxygen form 2 bonds
in co2 the bonds are double bonds where carbon forms 2 double bonds and oxygen forms one double bond
Explain why nitrogen is a gas at room temperature.
Answer in terms of nitrogen’s structure.
there are weak intermolecular forces which need little energy to overcome
Silver nanoparticles are sometimes used in socks to prevent foot odour.
Suggest why it is cheaper to use nanoparticles of silver rather than coarse particles of silver.
nanoparticles have a larger sa to v ratio so less can be used for the same effect
Explain why iodine has a low melting point.
simple molecules with weak intermolecular forces which require little energy to overcome
Silicon dioxide has a very high melting point.
Other substances are added to silicon dioxide to make glass. Glass melts at a lower temperature than silicon dioxide.
Suggest why.
weaker bonds
Describe the structure of a metal.
layers of positive ions with delocalised electrons
Describe, in terms of electrons, what happens when magnesium reacts with iodine.
magnesium loses 2 electrons
iodine gains 1 electron
Explain why a high temperature is needed to melt potassium iodide.
forces of attraction are strong because oppositely charged ions attract in giant structure
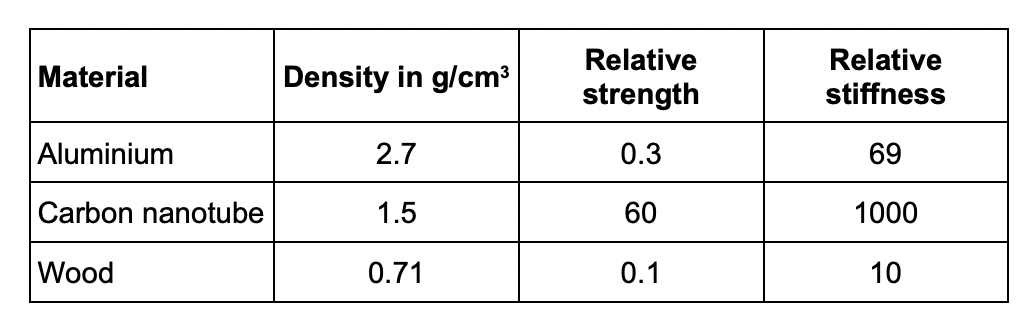
Evaluate the use of the materials to make badminton racket frames.
wood is the least dense so lightest to use
aluminium is the most dense so it will make the racket heavy
carbon nanotube is the strongest so less likely to break
wood and aluminium are too weak so they will break more easily
carbon nanotube is the stiffest so least likely to bend out of shape
wood and aluminium are not very stiff so could bend out of shape
conclusion
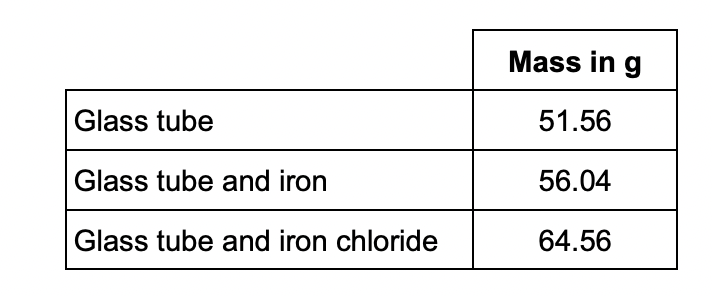
Calculate the simplest whole number ratio of:
moles of iron atoms : moles of chlorine atoms
Determine the balanced equation for the reaction.
Relative atomic masses (Ar): Cl = 35.5 Fe = 56
4.4g of iron and 8.52g of chlorine
iron moles = 4.48/56 = 0.08
chlorine moles = 8.52/35.5 = 0.24
0.08:0.24 = 1:3
2Fe + 3Cl2 → 2FeCl3
A student wants to compare the reactivity of an unknown metal, Q, with that of zinc.
Both metals are more reactive than silver.
The student is provided with:
• silver nitrate solution
• metal Q powder
• zinc powder
• a thermometer
• normal laboratory equipment.
No other chemicals are available.
Describe a method the student could use to compare the reactivity of metal Q with that of zinc.
Your method should give valid results.
measure temperature change when each metal is added to silver nitrate solution
make sure there is the same concentration of solution and mass of the metal
the greater the temperature change, the more reactive the metal is
Describe a method for making pure crystals of magnesium chloride from magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid.
In your method you should name the apparatus you will use.
You do not need to mention safety.
HCl in a beaker and add small pieces of mg ribbon until magnesium is in excess
filter excess mg using filter paper and funnel
pour solution into evaporating basin
heat using bunsen burner
leave to crystallise and pat dry afterwards
Describe a safe method for making pure crystals of copper sulfate from copper carbonate and dilute sulfuric acid.
Use the information in the figure above to help you.
In your method you should name all of the apparatus you will use.
sulfuric acid in beaker and add copper carbonate one spatula at a time
add until copper carbonate is in excess
filter the excess carbon carbonate using filter paper and funnel
pour solution into evaporating dish
heat using bunsen burner
leave to crystallise and pat dry
wear safety goggles
“The more energy levels (shells) of electrons an atom has, the weaker the covalent bonds that it forms.”
Use the above statement to predict and explain how the overall energy change for the reaction of ethene with chlorine will differ from the overall energy change for the reaction of ethene with bromine.
chlorine atoms have fewer electron shells
Cl-Cl and C-Cl bonds are stronger then C-Br bonds and Br-Br bonds
more energy is required to break bonds with chlorine
more energy is given out when making bonds with chlorine
if Cl-Cl bond changes more, then less exothermic
if C-Cl bond changes more then more exothermic
can’t tell how overall energy change will differ as we do not know which changes more
Why does manganese oxide conduct electricity as a liquid?
Ions move around in the liquid
Describe what happens when a lithium atom reacts with a chlorine atom. Answer in terms of electrons.
lithium loses one electron
chlorine gains one electron
transfer of one electron to form positive and negative ions
The relative formula mass (Mr), in grams, of sodium fluoride is one _______________ of the substance.
mole
one advantage of using nanoparticles in sun creams
better coverage
disadvantage of using nanoparticles in sun creams
potential cell damage