bio 20 - photosynthesis & cellular respiration
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
metabolic pathways
biological processes that involve matter & energy
formula for photosynthesis
6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
formula for cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
site of photosynthesis
chloroplasts
site of cellular respiration
mitochondria
stroma
fluid that contains proteins & chemicals needed for photosynthesis
granum
a stack of thylakoids
matrix
the fluid-filled space within the inner membrane of the mitochondria
anabolic
creation of large molecules from smaller ones
catabolic
breaking down of large molecules into smaller ones
enzymes
protein catalysts within cells; reduce the amount of activation energy required
oxidation
loss of electrons and energy
reduction
gain of electrons and energy
heterotrophs
ingests their food source
autotrophs
produces their food source; self feeder
what wavelengths do pigments in plants absorb?
wavelengths in the the visible light spectrum; some colors are not absorbed though and are reflected instead
why are plants usually green?
pigments in plants reflect green light wavelengths
white light
when all wavelengths in the visible light spectrum are present simultaneously
chlorophyll A
obtains the best type of wavelengths for photosynthesis; most important pigment
chlorophyll B
absorbs a similar spectrum of wavelengths as chlorophyll A but in lower amounts
carotenoids
absorbs other wavelengths then passes the energy to chlorophyll A; one of the main accessory pigments
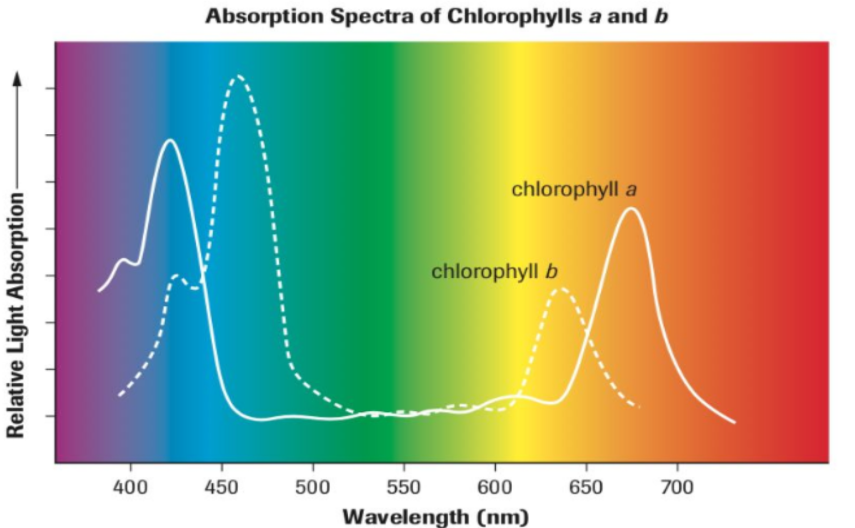
absorption spectrum
amount of each wavelength absorbed
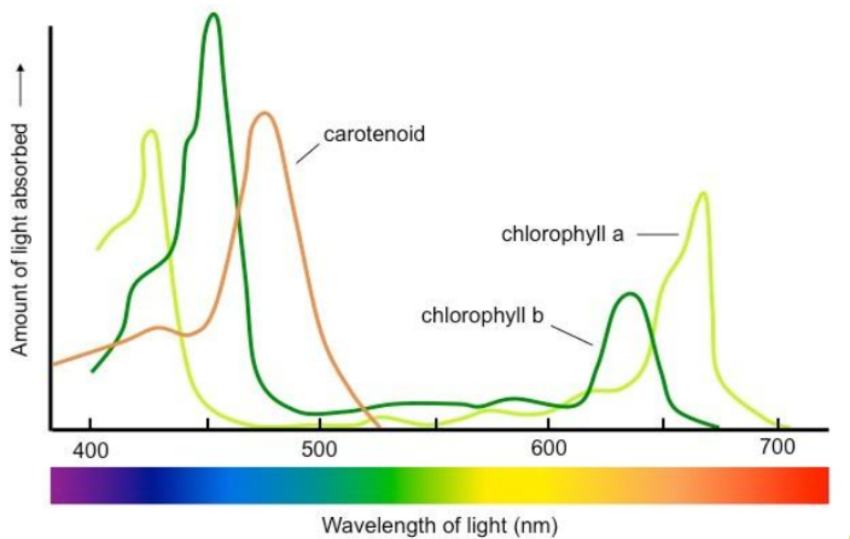
action spectrum
effectiveness of a wavelength in the action of photosynthesis
light dependent reaction
light is absorbed which causes electrons to “jump and that energy is used to create ATP & NADPH; happens during the day and in the thylakoids
light independent reaction
carbon is fixed to a molecule and glucose is eventually formed; happens all the time and in the stroma
photosystem
acts like a light-gathering “antenna complex” consisting of pigments; a collection of chlorophyll molecules in the thylakoid
reaction center
a specialized chlorophyll A molecule in the middle of a photosystem
reactants of light independent reaction
CO₂, NADPH & ATP (from LDR), and raw organic compounds
products of light independent reaction
glucose and water
carbon fixation
the process by which plants inorganic carbon into organic compounds; also known as carboxylation
aerobic
when a system needs oxygen to carry out its functions
anaerobic
when a system does not need oxygen to carry out it functions
fermentation
modified form of anaerobic respiration
aerobic reactions
glycolysis, link reaction/krebs pre, krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation
anaerobic reactions
glycolysis and fermentation
glycolysis
conversion of glucose into pyruvic acid/pyruvate with ATP & NADH are also produced; oxygen is not needed
where does glycolysis happen?
in the cytosol
link reaction / krebs prep
when pyruvate loses a carbon and attaches with coenzyme A to turn into acetyl-CoA which goes to the krebs cycle
role of the krebs cycle
to create NADH and FADH₂
which reaction produces the most ATP?
oxidative phosphorylation / aerobic cellular respiration
how much ATP does aerobic cellular respiration make?
36 - 38
what’s more effective: aerobic or anerobic?
aerobic cellular respiration
lactate fermentation
when cells that are temporarily without oxygen turn the pyruvate into lactate/lactic acid
where is lactic acid produced?
in the muscle cells of bacteria and animals
what happens to the lactic acid when cells have enough oxygen again?
it gets converted to pyruvate and continues aerobic cellular respiration
ethanol fermentation
when an organism functions anaerobically and turns the pyruvate into ethanol along with releasing CO₂
ATP
the energy used and stored at the cellular level
what is the final electron acceptor?
oxygen
what would happen if oxygen wasn’t present?
the whole process of aerobic respiration would stop and anaerobic respiration/fermentation would start happening instead
phosphorylation
gain of phosphate
photolysis
splitting of a molecule with light
chemiomosis
when hydrogen passes through the ATP synthase to combine with ADP + P to create ATP
3 ways to measure the rate of photosynthesis
oxygen created, carbon dioxide taken in, and carbohydrates formed
3 biggest factors of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide, temperature, and light