Geo C.O.4
1/391
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
392 Terms
Mass Wasting
downward movement of rock and soil on a slope, primarily driven by the force of gravity.
Mass Wasting
with proper planning, the most easily avoidable of all major geologic hazards
Mass Wasting
Various forms of mass wasting: rock falls, slumps, debris flows
Gravity
Driving force for mass wasting
○ Normal force
○ Shear force
○ Shear resistance
Slope Angle
Steeper slope = higher shear force (less stable)
Rock Type
Loose debris = less stable than solid rock
Vegetation
Roots hold debris together
Climate
freeze/thaw = expansion/contraction lifts materials
As water content increases
shear strength decreases
Stress
is transferred from clay to fibers, which have excellent tensile strength
Stronger bond between clay and fibers
= higher reinforcing effect
Shear Strength
resistance to movement or deformation
Shear Strength
Saturated soil has reduced shear strength due to increased pore pressure
Shear Strength
Small amount of weather can prevent downslop movement (building a sandcastle)
Mass Wasting Triggers
Increased water content within the slope is the mose common
Mass Wasting Triggers
Seismic (earthquake) activity
Heavy rainfall
Construction
Lack of vegetation (no roots to hold rock/soil in place)
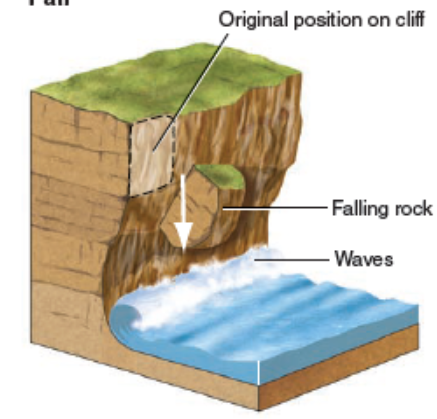
Fall
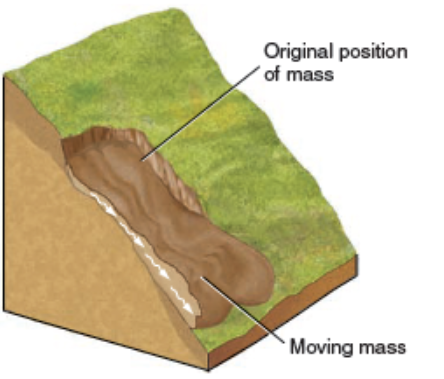
Flow
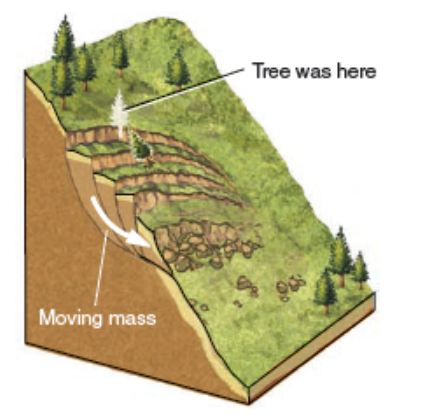
Trans
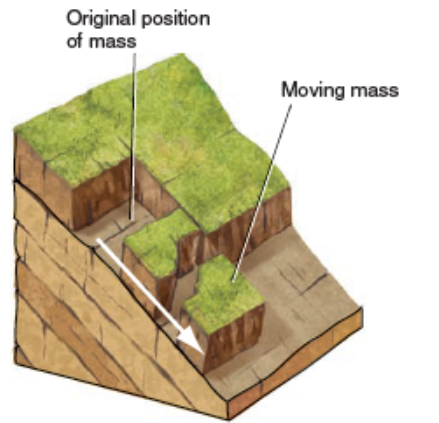
Rotational Slide(Slump)(pic)
Rate of movement
1cm/year -> 100km/hour
Solid bedrock or debris (unconsolidated material at Earth’s surface)
Type of material
Creep
very slow downslope movement of soil
Creep
Major contributing factors include water in soil and daily freeze-thaw cycles
Creep
Can be costly to maintain homes on creeping ground as foundations, walls, pipes and driveways crack and shit downslope over time
Flow
descending mass moves downhill as a viscous fluid
Earthflow
debris moves downslope, slowly or rapidly, as a viscous fluid
Debris Flow
flowing mixture of debris and water, usually down down a channe
Mudflow
only soil and water
Debris Avalanches
very rapid and turbulent
Solifluction
Flow of water-saturated debris over impermeable material
Solifluction Permafrost
common in colder climates
Slide
downward movements of soil or rock along a surface and can vary in depth, being either deep-seated or shallow
Translational slide
movement along plane parallel to motion
Rotational slide (slump)
movement along a curved surface
Rockslide and rock avalanche
the rapid sliding of a mass of bedrock along an inclined surface of weakness
Underwater landslides
turbidity currents
Underwater landslides
Can create a tsunami
Fall
sudden rock movements that detach from steep slopes or cliffs
Rockfall
a block of bedrock breaks free and falls or bounces down a cliff (commonly an apron of fallen rock fragments (talus) accumulates at cliff base)
Preventing Landslides
1. Modifying slope geometry to create more stable conditions
2. Using chemical agents to strengthen and reinforce the slope material
3. Installing structures like piles and retaining walls to provide stability and support
4. Grouting rock joints and fissures to improve rock mass cohesion
5. Diverting debris pathways to prevent material from accumulating on hazardous slopes
6. Rerouting surface and underwater drainage to minimize water-induced instability
Seasonal Flooding
Often arises from spring rains or melting of snow
Seasonal Flooding
Leads to increase in flow of rivers
During a flood event
river /stream’s channel becomes inundated -> water spills to adjacent floodplain -> speed decreases -> capacity to carry sediment/materials diminishes
Hydrologic Cycle
Encompasses processes which water moves from land to ocean surfaces to the atmosphere & returns in form of precipitation
atmosphere & precipitation
Encompasses processes which water moves from land to ocean surfaces to the _____ & returns in form of _____
land to ocean
Encompasses processes which water moves from _____ to _____ surfaces to the atmosphere & returns in form of precipitation
Hydrologic Cycle
Relies on various factors and is influenced by both oceans and land surfaces
Hydrologic Cycle
Represents continuous circulation of water on the plant
Hydrologic Cycle
Playing a vital role in regulating distribution and availability of water resources
Hydrologic Cycle
Distribution of water in the atmosphere
96.5%
Oceans
1.76%
Glacial ice
1.70%
Groundwater
0.014%
Lakes & Streams
0.001%
Soil moisture
98.8%
Glacial ice & groundwater contains _____ of the freshwater on Earth
Evaporation
Water vaporizes from the surfaces of water bodies & from moist soil and vegetation into the atmosphere
Precipitation
Water is released from the atmosphere in form of rain, snow, sleet/hail & falls back to the Earth’s surface
Runoff
Portion of precipitation that does not infiltrate the ground & flows over the land surface, eventually reaching water bodies
Infiltration
Water that penetrates into the soil & moves into underground aquifers
Transpiration
Water taken up by plants from soil released into the atmosphere as water through stomat
Running water
Stream
Headwaters
Mouth
Channel
Stream banks
Streambed
Floodplain
Stream
Body of running water confined to a channel that runs downhill under the influence of gravity
Headwaters
Upper part of stream near its source in the mountains
Mouth
Where a stream enters sea, lake, or larger stream
Channel
A long, narrow depression eroded by a stream into rock or sediment
Stream banks
Slides of channel
Streambed
Bottom of the channel
Floodplain
Flat valley floor composed of sediment deposited by the stream
Drainage Basins
Also known as a watershed or catchment area
Drainage Basins
Where water from precipitation gathers and flows downhill into a common outlet (river, lake, wetland, ocean)
Drainage Basins
Includes network of streams and rivers that carry water & land surface from which water is collected and directed into those channels
Tributary
Small stream flowing into a larger one
acute angle
Most tributaries join the mainstream at an ______ forming a V or Y pointing downstream
Divide
Ridge or high ground that divides one drainage basin from another
Continental Divide
Separates streams that flow into the Pacific from those that flow into Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico
Dendritic
Drainage pattern resembling the branches of a tree

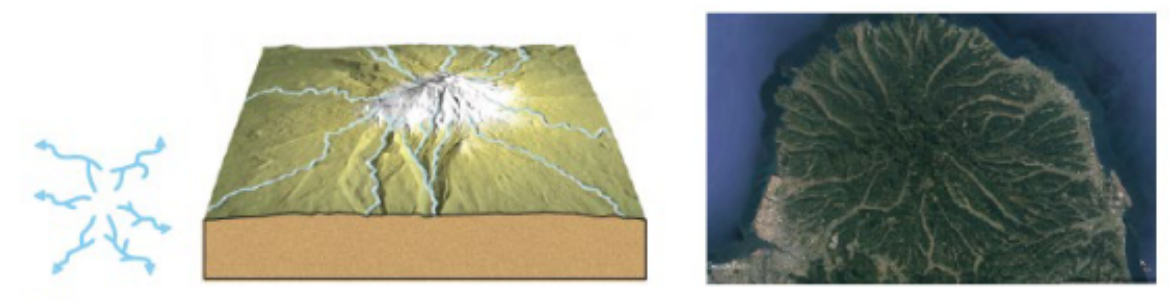
Radial Pattern
Streams diverge outward like the spokes of a wheel (conical mountains)
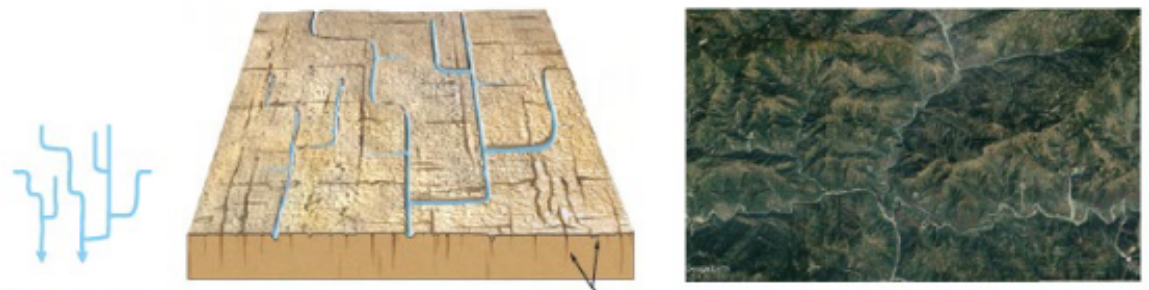
Rectangular pattern
Tributaries have frequent 90-degree bends and join other streams at right angles
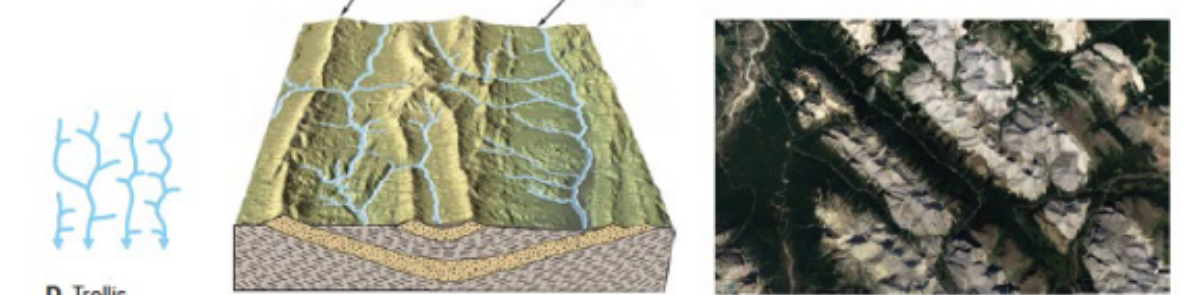
Trellis pattern
Parallel streams with short tributaries meeting at right angles
Drainage Patterns
Arrangement of streams, rivers, and lakes within a specific drainage basin
Drainage Patterns
Influenced by topography of the land, type of rocks present, and gradient of the terrai
Factors affecting stream erosion and deposition
Natural Factors
Human-caused factors
Natural Factors
Gradient (Steepness) of the streambed
Precipitation
Stream discharge
Gradient (Steepness) of the streambed
Slope of streambed affects water flow speed
Steeper gradients
= faster flow = increasing erosive power
Precipitation
Rainfall & snowmelt contribute to water volume in a stream
Higher precipitation rates
= increased water flow & erosive potential
Stream discharge
amount of water flowing through a stream
Stream discharge
is influenced by rainfall, snowmelt, and groundwater contributions, impacting erosive capacity of the stream
Human-caused factors
Deforestation
Urbanization
Damming and channelization
Deforestation
leads to increased erosion due to loss of root systems that stabilise the soil
Urbanization
Construction in urban areas can alter natural drainage patterns, leading to higher runoff rates and increased erosion
Damming and channelization
for flood control or navigation purposes can change flow patterns and sediment transport, impacting erosion downstream
Factors essential for managing and mitigating erosion in streams
Velocity
Gradient (slope)
Channel shape and roughness
Discharge
Velocity
Maximum ____ near center of channel
Velocity
Higher stream _____ promote erosion and transport of coarser sediments