electromagnetics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
diathermy
application of electromagnetic waves (radio frequency range)
most common diathermy
short wave diathermy (SWD)
types of diathermy
PSWD, CSWD, MWD
physical properties of diathermy
absorption of energy by tissues causes heating (deep tissues)
shortwave: 1.8-30 MHz
microwave: 300 Mhz-300 GHz
diathermy parameters: shortwave frequency bands
13.56, 27.12, and 40.68 MHz
diathermy parameters: microwave frequency
2450 MHz
diathermy parameters: mode
continuous or pulsed
types of diathermy devices
capacitive, inductive, microwave, pulsed shortwave, pulsed electromagnetic
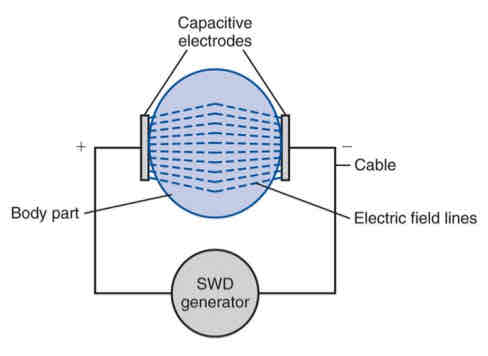
capacitive method
aka electric field method
tissues are part of the dielectric of a capacitor
subcutaneous fatty tissue heated greater than muscle
electrodes placed 1-3 in away from skin
contraplanar or coplanar set-up
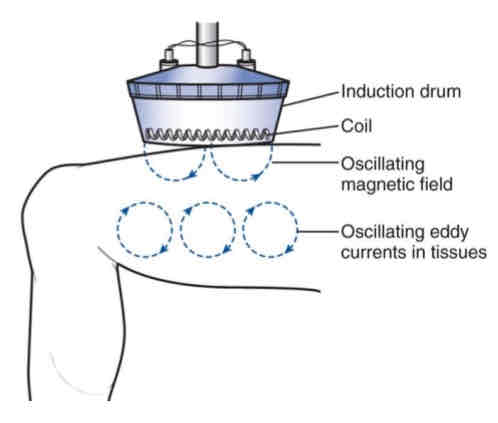
inductive method
aka magnetic field method
eddy currents produce in tissues w/ lowest impedance
drum or sleeve applicators
monode or diplode drums
pulsed electromagnetic fields/PEMF
deliver very low intensity electromagnetic waves that do not heat tissues
selection of proper dosage
pt’s subjectivity important for dosing
dose I
<38 W mean power, acute injury stage
dose II
38-80 W mean power, subacute injury stage
dose III
80-300 W mean power, late subacute injury stage
dose IV
>300 W mean power, chronic injury stage
types of applicators
inductive coils—SWD
capacitive plates—SWD
magnetron—MWD “MASER”
capacitive diathermy advantages over inductive SWD
ease of depolarization of polarizable material—dielectric constant
high dielectric constant—muscle and skin
low dielectric constant—fat and bone
heating of fat greater
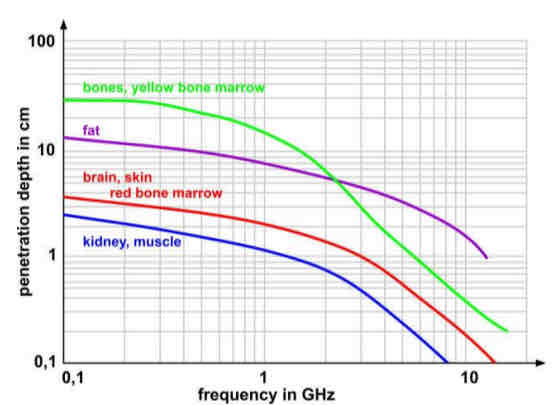
microwave diathermy (MWD)
use magnetron device similar to those used in microwave ovens
applicator positioned perpendicular to skin’s surface
less penetration depth than SWD
uncommon in USA
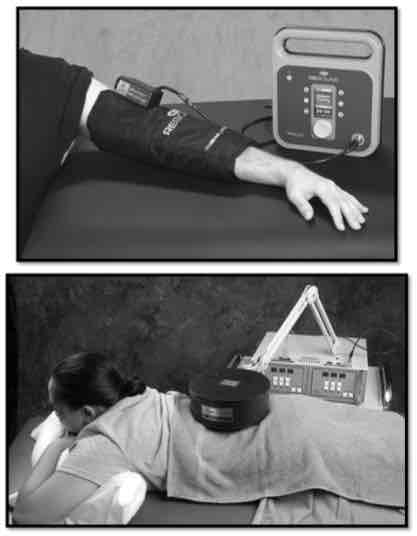
pulsed shortwave diathermy (PWSD)
most modern devices are this or a combo w/ CSWD
easier set-up
portable
inductive sleeves
PSWD parameters
high pulse rate (~800 pps), short pulse duration (~400 microseconds)
duty cycle=(pulse duration/(pulse duration+interpulse interval))
example parameters for PSWD
pulse duration 0.4 msec
pulse freq 200 pps
peak pulse power 800 W
physiological effects of diathermy
deeper heating than superficial modalities
larger area treated compared to US
does not require constant attention
cannot depolarize motor nn.
thermal effects
deeper heating than superficial modalities
affect tissue extensibility, muscle strength, pain, healing
factors to consider of diathermy thermal effects
continuous or pulsed
distance btwn applicator and skin
duration of treatment
intensity
effects on tissue extensibility
combo of prolonged low load stretch and heat shown to effectively increase tissue flexibility
effects on pain
analgesic effects—SWD may be more effective than moist heat for deeper tissues
possible non thermal mechanisms of relief
effects on tissue healing
promotes soft tissue and bone healing
what is temperature determined by?
field intensity
tissue type
duty cycle
distance from pt
nonthermal effects of diathermy
increased microvascular perfusion
altered cell membrane function and cellular activity
clinical applications
thermal: pain control, tissue healing, decreased stiffness, increase ROM
nonthermal: pain & edema control; soft tissue, nerve, bone healing; improvement of osteoarthritis symptoms
indications
mostly the same as regular thermotherapy
greater depth of heating than superficial modalities and larger area than US
muscle spasms, joint stiffness
mild heating for inflammation
PEMF: superficial wound and bone healing
general contraindications for all diathermy
implanted or transcutaneous stimulators, including pacemakers; pregnancy
thermal diathermy contraindications
metal, malignancy, eyes, testes, growing epiphyses
nonthermal diathermy contraindications
deep tissue/internal organs
substitute for conventional therapy for edema and pain
pacemakers, electronic devices, metal implants
precautions for all types of diathermy
near electronic or magnetic equipment
obesity
copper bearing IUD
burns—particularly fat layers, keep skin dry
precautions for nonthermal diathermy
pregnancy, skeletal immaturity
application technique (after preparation etc)
tune device
select parameters
turn on machine
assess at 5 min for adverse effects
document
when do you use US over diathermy?
smaller areas of dense collagen tissue—ligaments, tendons, joint capsules
when to use diathermy instead of US
tissues with high fluid content, large areas (muscles)
why is diathermy more common in other countries?
practitioner bias, high cost, reimbursement issues