3 - Radioactivity
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To be accompanied with exam questions as there are calculations etc to practice
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Radioactivity
The spontaneous disintegration of certain unstable nuclei, accompanied by the emission of radiation
Half-life
The time taken for half of the radioactive atoms present to decay
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number but different mass number
Radioisotope
Unstable radioactive isotopes
Nuclear reaction
Process that alters the composition, structure, or energy of a nucleus
Alpha particles
Helium nuclei (2 protons + 2 neutrons)

When an iodine-131 nucleus decays to form a xenon-131 nucleus, a beta particle is released. Complete the nuclear equation for this decay reaction.
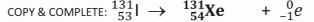
Explain the origin of the electron released as a beta particle in this reaction
Neutron //
changes into proton and electron
Alpha particles can be stopped by a sheet of paper.
Are beta particles more or less penetrating than alpha particles?
More

Complete the following equation for the alpha decay of polonium-208.
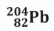

Complete the following nuclear equation for the alpha decay of the radon-222 isotope.
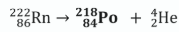
Suggest a reason why it is not possible to change lead (Pb) atoms into gold (Au) atoms by a chemical reaction or a series of chemical reactions
Lead into gold involves nuclear reaction (change to nucleus, change of atomic number) /
chemical reactions involve electrons only /
transmutation is not a chemical reaction
What name is given to the type of nuclear reaction involving the release of electrons?
Beta radiation
Compare the penetrating power of this type of radiation with the penetrating powers of the other forms of radiation emitted by radioactive substances
Gamma is more penetrating than beta //
Alpha is less penetrating than beta
[alpha < beta < gamma]
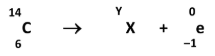
Identify the element represented by X and state the value of Y, the mass number of the daughter nucleus
X: Nitrogen (N) //
Y: 14
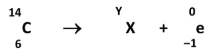
Explain clearly where the electron lost by the carbon atom in this process comes from
A neutron changes into a proton and this electron
What happens in a radioactive nucleus during beta decay?
Neutron changes into a proton //
and an electron which is emitted

Bananas contain small quantities of potassium-40, a radioactive isotope.
What is the daughter nucleus when K-40 emits an electron in beta decay?
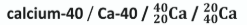

Explain why the fragment of yew must have contained 3.0 × 1012 carbon-14 atoms 5730 years before the analysis
5730 is the half life of carbon-14 / number of C-14 atoms halved in 5730 years / half the C-14 atoms have decayed
[C-14’s half life is in the log tables!!!]

What mass of carbon-14 did the fragment contain 5730 years before the analysis?
7.0 × 10-11g of carbon-14 originally
{2018 - Q5 (d)}

Complete the nuclear equation to show the alpha decay of radium-226
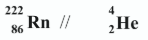
Give two differences between chemical reactions and nuclear reactions
Chemical: involves electrons // no change to nucleus // bonds broken (or formed) // elements unchanged // mass conserved // energy comes from bonds
Nuclear: electron cloud not involved // nuclear change // no bond breaking (or forming) // new elements (transmutation) // mass not conserved // energy comes from mass
Give two properties of beta-particles
Negative charge // negligible mass (mass of electron) // high speed // moderately penetrating // damage body cells (cause cancer, mutations)

A certain mass of caesium-137 leaked on a particular day. What fraction of this mass remained as caesium-137 after 90 days?
one-eighth / 12.5%
Explain how the carbon-14 isotope allows certain archaeological discoveries to be dated
In living things, the ratio of carbon-12 to carbon-14 is constant