Soil Colloids and Cation Exchange: Types, Properties, and Soil Fertility
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What are soil colloids?
The smallest particles in soil, which are electrically charged and chemically reactive.
What is the soil colloidal fraction?
A collective term for clay and other tiny particles in soil, less than 1 µm in diameter, that behave as colloids.
What are the four main types of soil colloids?
1. Crystalline Silicate Clays, 2. Noncrystalline Silicate Clays, 3. Iron/Aluminum Oxides, 4. Organic particles (Humus).
What characterizes crystalline silicate clays?
They are made of O, Si, Al and have a layered sheet structure.
How do noncrystalline silicate clays differ from crystalline silicate clays?
They are also made of O, Si, Al but are amorphous and poorly structured.
What are iron/aluminum oxides in soil colloids?
They are made of Fe or Al with O (usually -OH) and can be crystalline or amorphous.
What is humus in the context of soil colloids?
Organic particles that are not minerals, lack crystalline structure, and are the most chemically active fraction of organic matter.
What processes lead to the development of silicate clays?
1. Alteration—slight changes in structure or charge, 2. Recrystallization—complete degradation of structure followed by new formation.
What is the order of colloid types based on weathering stages?
1. Early: Micas/Chlorites, 2. Intermediate: Smectites/Vermiculites, 3. Advanced: Kaolinites, 4. Extreme: Fe/Al Oxides.
What are tetrahedral sheets made of?
They consist of silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) arranged in a tetrahedral structure.
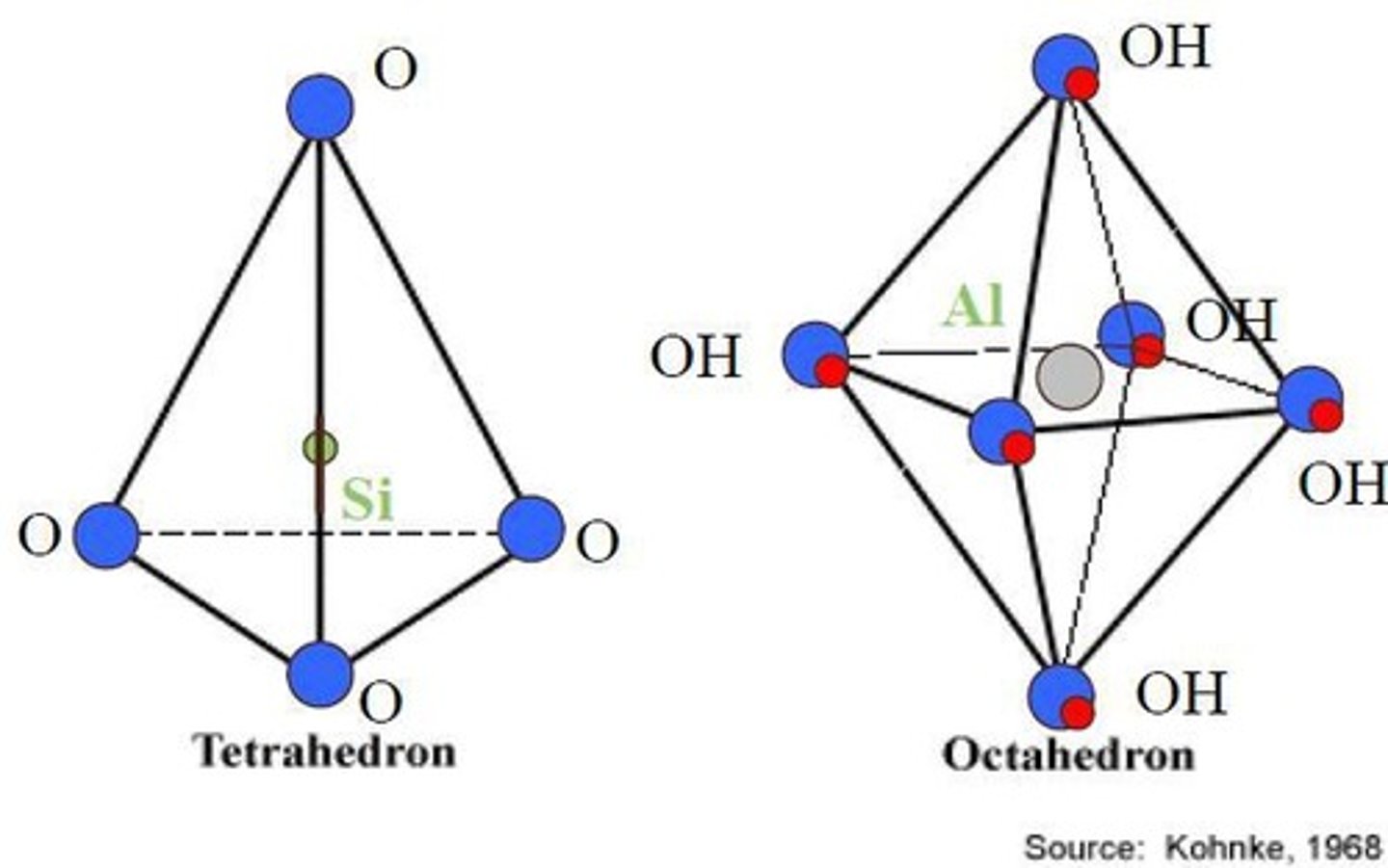
What are octahedral sheets made of?
They consist of oxygen (O) or hydroxyl (OH) bonded to aluminum (Al), magnesium (Mg), or iron (Fe).
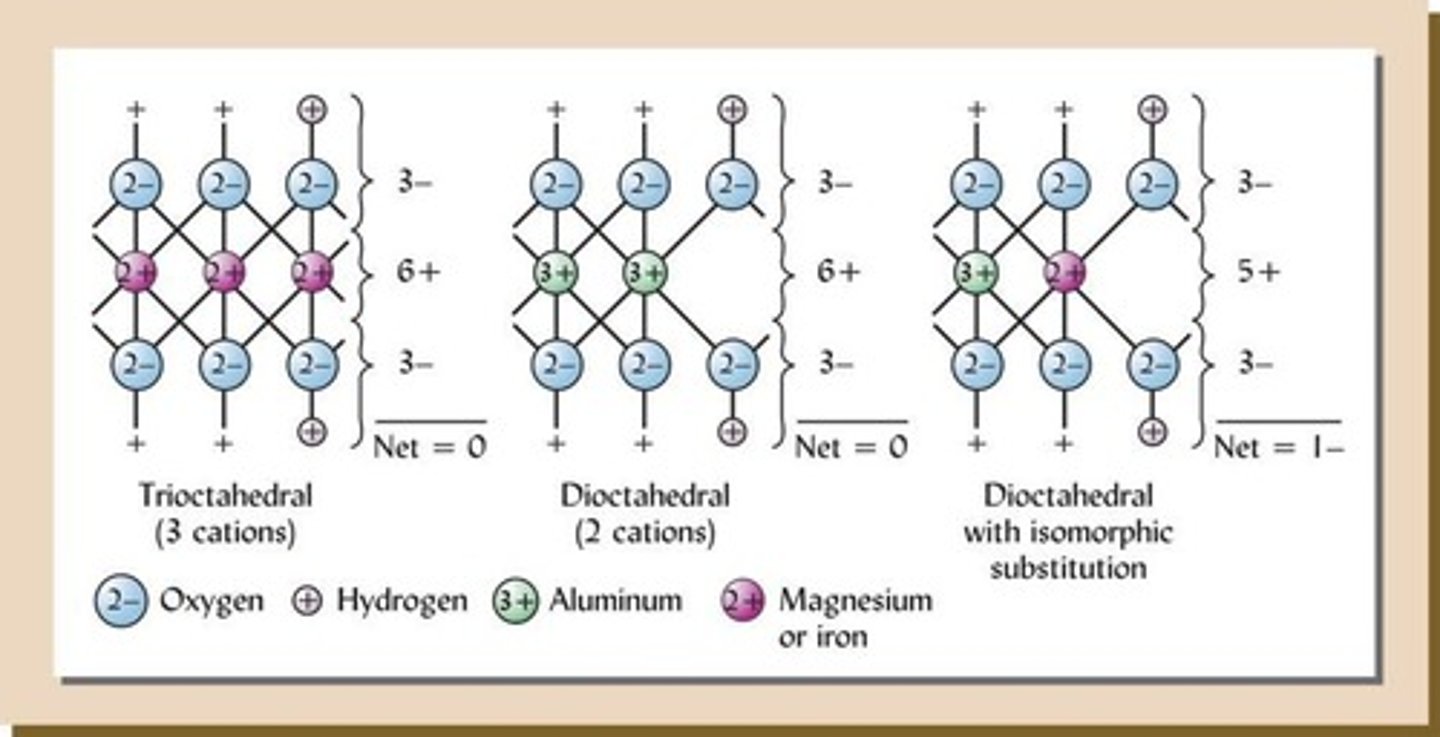
What is isomorphous substitution?
The substitution of one element for another in a mineral without significant change in crystal structure, often causing a change in charge.
What charge results from isomorphic substitution with a lower charge ion?
It results in a net negative charge on the soil colloid.
What charge results from isomorphic substitution with a higher charge ion?
It results in a net positive charge on the soil colloid.
What is the difference between 1:1 and 2:1 silicate clays?
1:1 silicate clays have one tetrahedral and one octahedral sheet, while 2:1 silicate clays have two tetrahedral sheets surrounding one octahedral sheet.
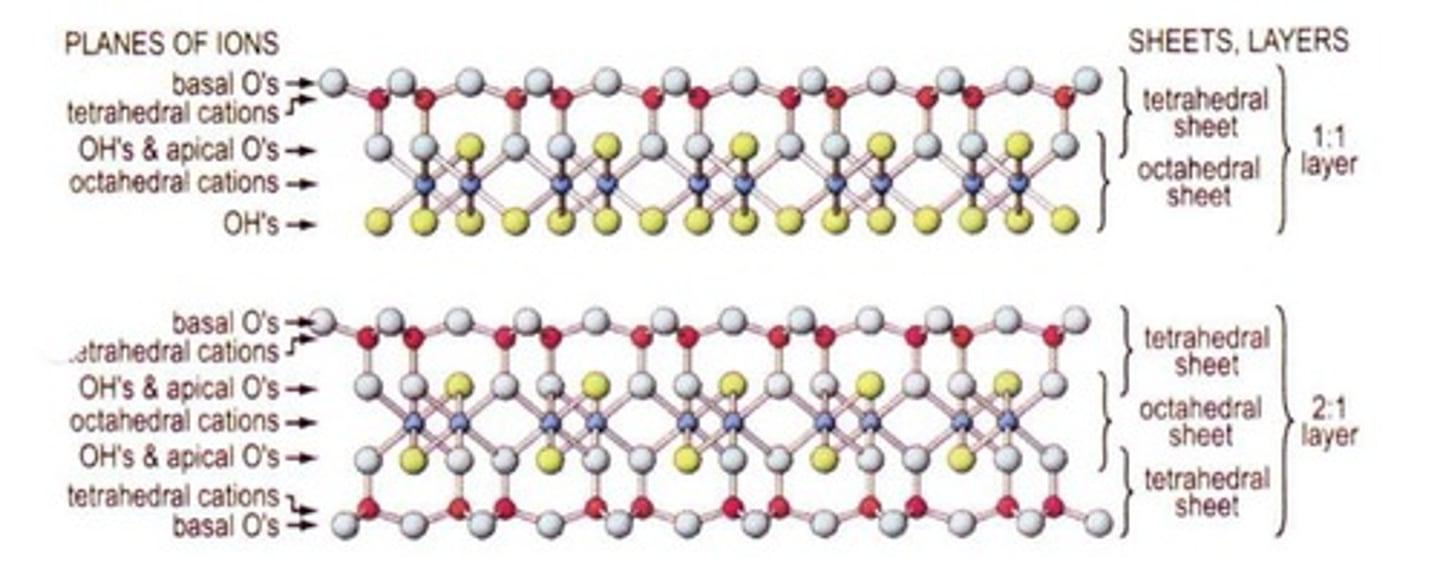
What is kaolinite?
A 1:1 silicate clay that is less sticky or reactive, good for ceramics and cultivation, and has little to no isomorphous substitution.
What is the significance of surface area in soil colloids?
The large surface area makes colloids the most chemically active soil fraction, allowing them to adsorb cations, anions, and water.
What is the effect of weathering on soil colloids?
Weathering leads to the loss of silicon over time, resulting in a low Si:Al ratio in highly weathered soils.
What is the role of cation exchange capacity (CEC) in soil colloids?
CEC refers to the ability of soil colloids to hold and exchange cations, affecting soil fertility and nutrient availability.
How does the structure of 1:1 silicate clays affect their properties?
They have tightly-fitted layers with no interlayer space, cannot expand when wet, and are stable due to hydrogen bonding.
What type of soil colloid is most common in soils of the southeastern USA?
Kaolinite, which is a product of acid weathering and has low nutrient availability.
What is the structure of 2:1 silicate clays?
They consist of 2 tetrahedral sheets and 1 octahedral sheet (TOT).
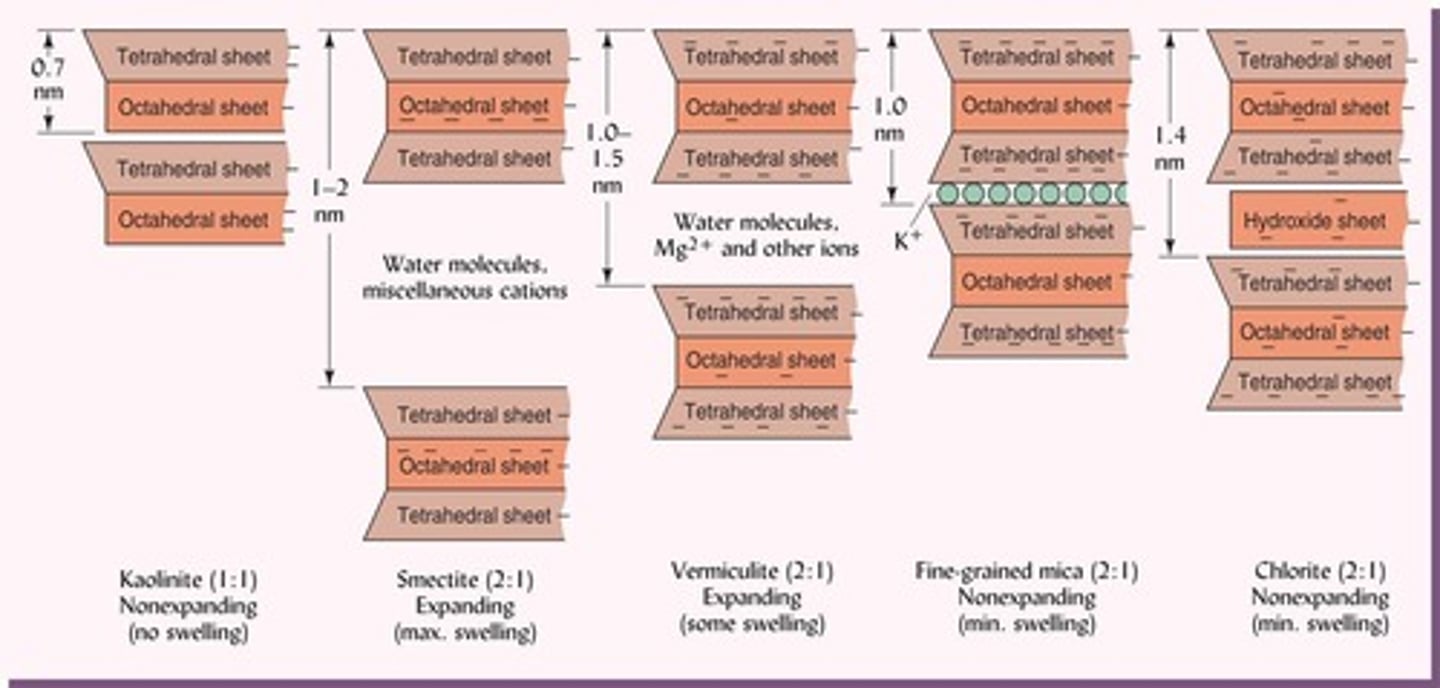
What is a common sub-group of 2:1 silicate clay?
Montmorillonite, which is a type of smectite.
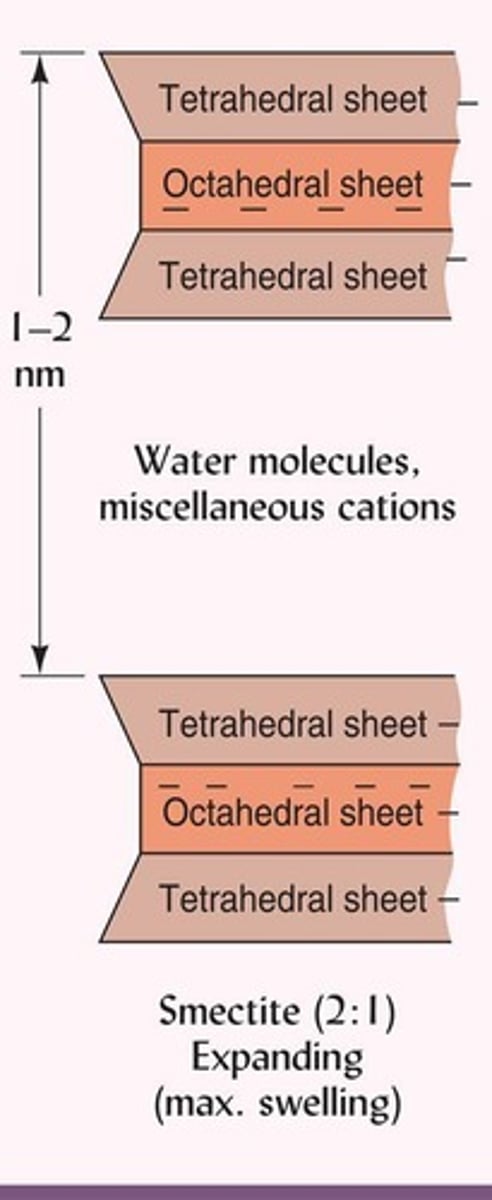
What characterizes the internal surface area of smectite?
It has a large internal surface area.
What causes the layer charge in smectite?
The substitution of Mg2+ for Al3+ in the dioctahedral sheet.
Under what conditions does smectite become unstable?
It weathers to something else under low pH and high moisture.
What is the swelling behavior of smectite?
It exhibits the most swelling and shrinking of all clays.
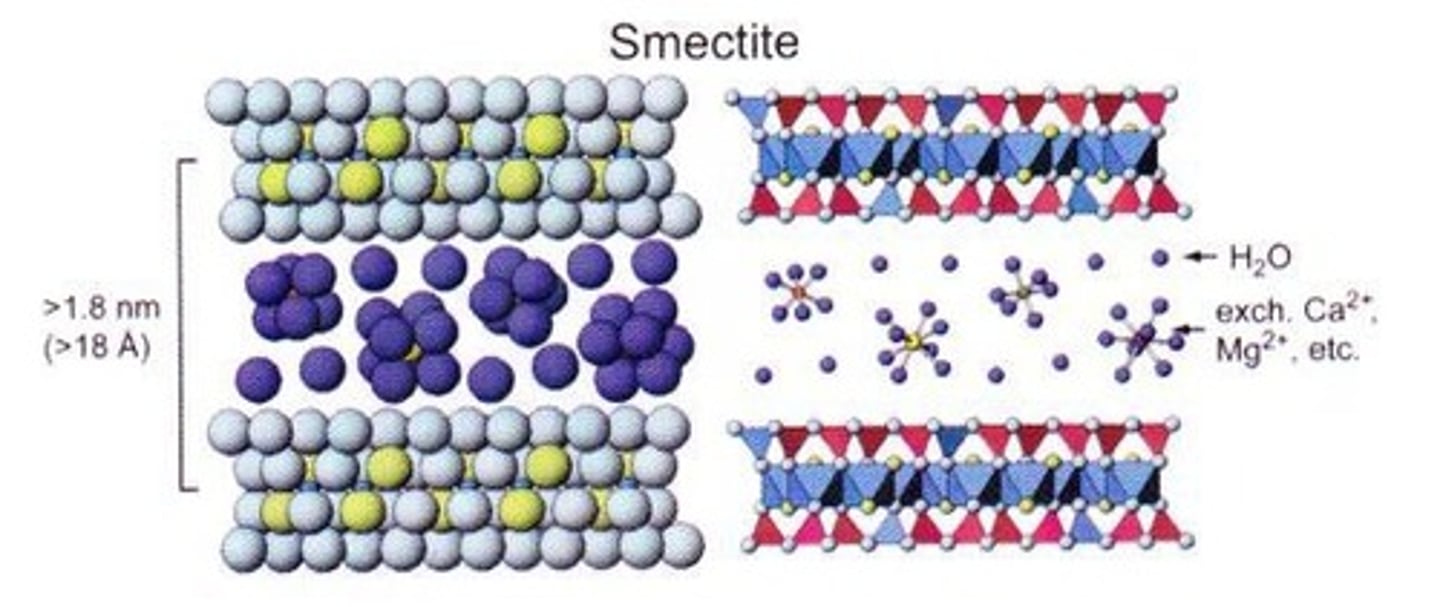
What is the cation exchange capacity (CEC) of smectite?
It has a high CEC, indicating a high degree of plasticity, stickiness, and cohesion.
What is the origin of vermiculite?
It is an alteration product of micas formed from the loss of K+.
How does the tetrahedral sheet of vermiculite differ from that of smectite?
Vermiculite has a little isomorphic substitution in the Al3+ dominated dioctahedral sheet.
What is the water behavior in vermiculite?
It contains strongly adsorbed water molecules that act as a bridge to hold the units together.
What is the swelling behavior of vermiculite?
It has limited shrink-swell capacity.
What characterizes fine-grained mica?
It has Al3+ substitution for Si4+ in the tetrahedral sheet and is non-swelling.
What is the stability of fine-grained mica under pH conditions?
It is stable under moderate to low pH.
What is the nutrient status of fine-grained mica?
It is fairly nutrient poor due to tightly bound potassium in the interlayer.
What distinguishes chlorite from other 2:1 silicate clays?
Chlorite has Fe or Mg occupying many octahedral sheets and includes a hydroxy sheet.
What is the swelling behavior of chlorite?
It has restricted swelling and is nutrient poor.
What is the structure of noncrystalline silicate clays?
They have an amorphous structure, not arranged in neatly-stacked sheets.
What are examples of noncrystalline silicate clays?
Allophane and imogolite, which form from volcanic ash.
What characterizes Fe/Al oxides?
They have modified octahedral sheets with Fe3+ or Al3+ and do not expand.
What is the role of organic molecules (humus) in soil?
They are an amorphous mix of organic compounds that can adsorb nutrients and water.
What are the two sources of charge on soil colloids?
Constant/persistent charge from isomorphic substitution and pH-dependent charge from H+ ion exchange.
What happens to soil colloid charge at increased pH?
Increased pH pulls H+ off surface OH groups, resulting in a negative charge.
What is cation exchange in soils?
It is the process where cations adsorbed to soil colloids can be replaced by different cations from the soil solution.
What does CEC stand for?
Cation Exchange Capacity, which is the sum of exchangeable cations that a soil can adsorb.
What is the significance of cation selectivity in soils?
It helps predict which cations will be exchanged based on their relative affinities.
What is the difference between buffered CEC and effective CEC?
Buffered CEC is measured under specific conditions, while effective CEC reflects the actual cation exchange occurring in the soil.
What is Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)?
The ability of soil to hold and exchange cations, expressed in cmolc/kg or meq/100 g.
What does 15 cmolc/kg indicate about soil?
It means 1 kg of soil can hold/exchange 15 H+ ions' worth of charge.
How is CEC affected by soil texture?
CEC is higher in soils with greater clay content compared to sandy soils.
What is the relationship between pH and CEC?
CEC generally increases with higher pH levels.
How does organic matter influence CEC?
Soils with more organic matter have higher CEC, especially at higher pH.
What is the charge behavior of smectite clay at different pH levels?
Smectite has a constant charge below pH 6.0 and increases slightly above pH 6.0 due to ionization.
What happens to the charge of kaolinite and humus as pH increases?
The charges on kaolinite and humus are variable and increase with rising pH.
What are the principles of cation exchange reactions?
They include reversibility, charge equivalence, ratio law, anion effects on mass action, cation selectivity, and complementary cations.
What does charge equivalence in cation exchange mean?
Exchange occurs on a charge-for-charge basis, requiring charge balance.
How does the ratio law apply to cation exchange?
At equilibrium, the ratio of cations on the colloid matches the overall system ratio.
What is the significance of anion effects on mass action?
An exchange reaction is more likely to proceed if the released ion is prevented from reacting in reverse.
What is cation selectivity?
Cation selectivity is influenced by positive charge and hydrated radius, affecting ion exchange preferences.
What is base saturation in soil?
Base saturation is the percentage of CEC satisfied by base cations that reduce acidity and increase soil pH.
What are base cations and acid cations?
Base cations include Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+; acid cations include Al3+ and H+.
How is total CEC calculated?
Total CEC is the sum of individual exchangeable ions associated with soil colloids.
What does a high CEC indicate about soil fertility?
Higher CEC typically indicates greater nutrient mobility and availability for plants.
What is the significance of complementary cations?
Ions that occur together on exchange sites can impact each other's activity and nutrient availability.
What is the effect of organic matter on nutrient availability?
Increased organic matter enhances CEC, improving nutrient retention and availability for plants.
What is the impact of weathered soils on CEC?
Weathered soils like Oxisols and Ultisols typically have low CEC due to their composition.
How do you estimate CEC based on soil properties?
CEC can be estimated using standard cmolc/kg values for different colloids and soil properties.
What is the role of hydrogen ions in cation exchange?
Hydrogen ions can displace other cations from colloidal surfaces, affecting nutrient availability.
What is the significance of calculating base saturation percentage?
Base saturation percentage indicates the proportion of base cations relative to total CEC, affecting soil health.
How does soil texture influence CEC?
Soils with higher clay content generally have higher CEC compared to sandy soils.