Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2.4-2.5 on OCRA book
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What type of cell wall do plant cells have?
Cellulose cell wall
What is the function of the cellulose cell wall?
Provides strength, support and prevents bursting under osmotic pressure
Do plant cell walls provide a barrier to substances?
No, they are fully permeable
What pigment do chloroplasts contain?
Chlorophyll
What is the function of chlorophyll?
Absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
What is the name of the flattened membrane sacs in chloroplasts?
Thylakoids
What is a granum?
Stack of thylakoids
What is the stroma in a chloroplast?
Fluid-filled space containing enzymes for the light-independent reactions
What is the function of the starch grains found in chloroplasts?
Energy storage (product of photosynthesis stored as starch)
What organelle maintains cell turgor in plant cells?
Central vacuole
What is the membrane surrounding the central vacuole called?
Tonoplast
What does the vacuole contain?
Cell sap (water, ions, sugars, pigments, waste products)
What is the role of the vacuole in plants?
Maintains turgor pressure, stores substances, pigments contribute to colour of petals/fruits
Name two organelles present in plant cells but not in animal cells.
Chloroplasts and permanent vacuole
What is the diameter of a typical plant cell?
~10–100 μm
What is the function of plasmodesmata?
Channels through cell walls for transport and communication between plant cells
What is the difference between amyloplasts and chloroplasts?
Amyloplasts store starch; chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis
Why don’t plant cells burst in hypotonic solutions?
The cellulose cell wall prevents lysis, leading to turgid cells instead
What happens to a plant cell in a hypertonic solution?
The cell becomes plasmolysed (cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall)
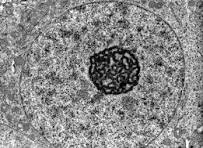
What is the function of the nucleus and nuclear envelope in a eukaryotic cell?
Contains genetic material (DNA);
nucleolus makes rRNA and ribosomes;
What is the role of the nucleolus?
Site of ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosome assembly
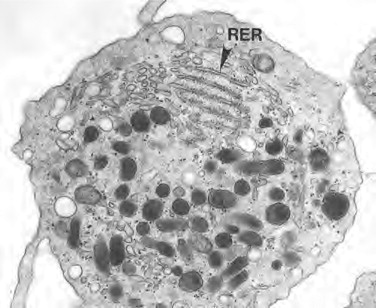
What is the structure of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
Flattened membrane sacs with ribosomes
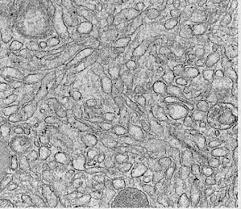
What is the structure of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)?
Membrane network without ribosome
What is the role of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells?
site of protein synthesis
(translation of mRNA)
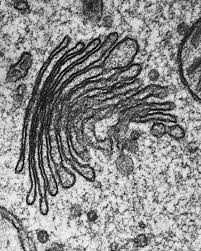
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
modifies and packages proteins/lipids
into vesicles for transport or secretion;
makes lysosomes
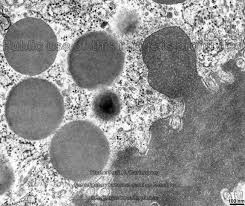
What is the function of vesicles?
Membrane-bound sacs that transport substances within cells or to the cell surface
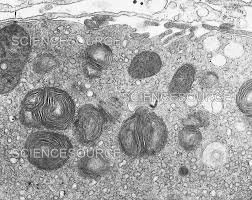
What is the function of lysosomes?
Contain hydrolytic enzymes in order to
digest waste, pathogens, and old organelles
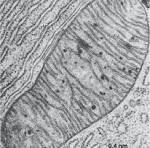
What is the structure of mitochondria?
Double membrane
inner membrane folded into cristae
matrix contains enzymes
What is the structure of the cell surface (plasma) membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol (fluid mosaic)
What is the structure of centrioles in animal cells?
Pair of cylindrical microtubules in 9 + 2 structure
What is the function of centrioles in animal cells?
organise spindle fibres during cell division
What is the structure of cilia and flagella and what are their differences?
Microtubule-based structures; cilia move substances across cell surfaces; flagella move whole cells
What is the structure of the cytoskeleton?
Network of microtubules and microfilaments;
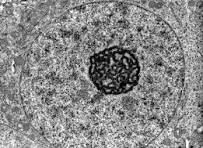
What is the structure of the nucleus and nuclear envelope in a eukaryotic cell?
double membrane with pores which help control exchange with cytoplasm
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
folds, processes, and transports proteins
What is the function of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum?
synthesises and processes lipids, steroids and carbohydrates
Where are the ribosomes in eukaryotic cells?
80S ribosomes free in cytoplasm or attached to RER
What is the importance of the cytoskeleton?
To provide mechanical strength to cells,
aiding transport within cells
and enabling cell movement.
Explain the role of the membrane in the RER
compartmentalisation
seperating proteins from cell cytoplasm
holds ribosomes/ enzymes in place