Autonomic Nervous System Basics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
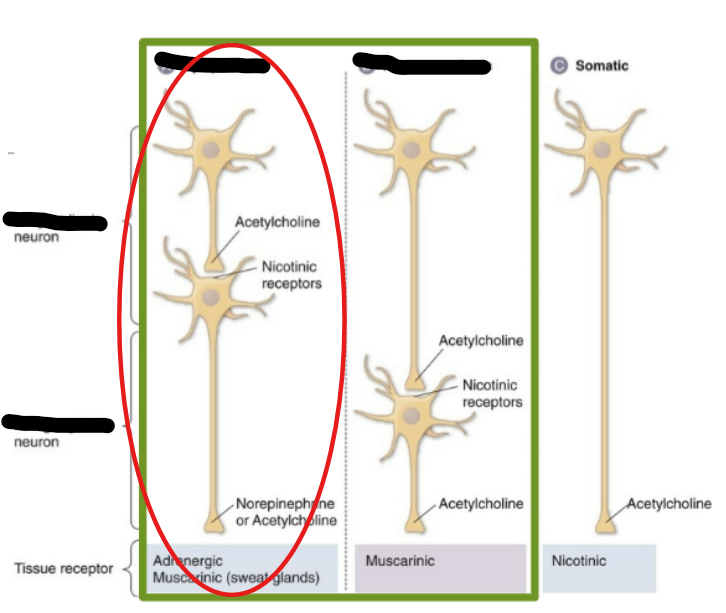
Sympathetic Neurons
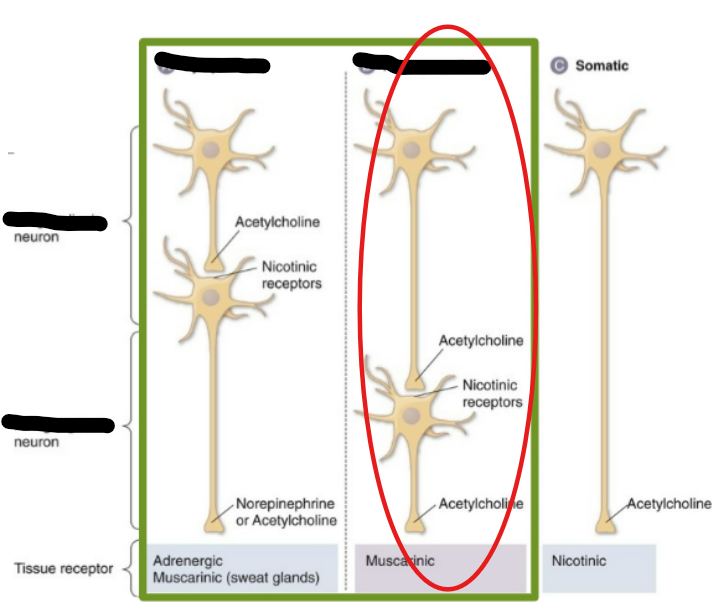
Parasympathetic Neurons
Preganglionic, postganglionic
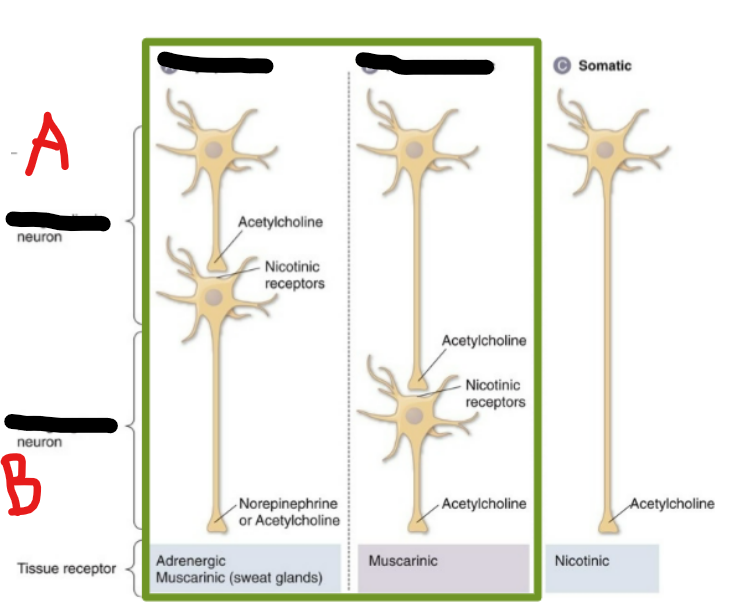
A = ? neuron
B = ? neuron
Autonomic, peripheral, unconscious
The __ NS is a division of the __ (central/peripheral) nervous system: mediating __ actions
cardiac output, blood flow, digestion, etc
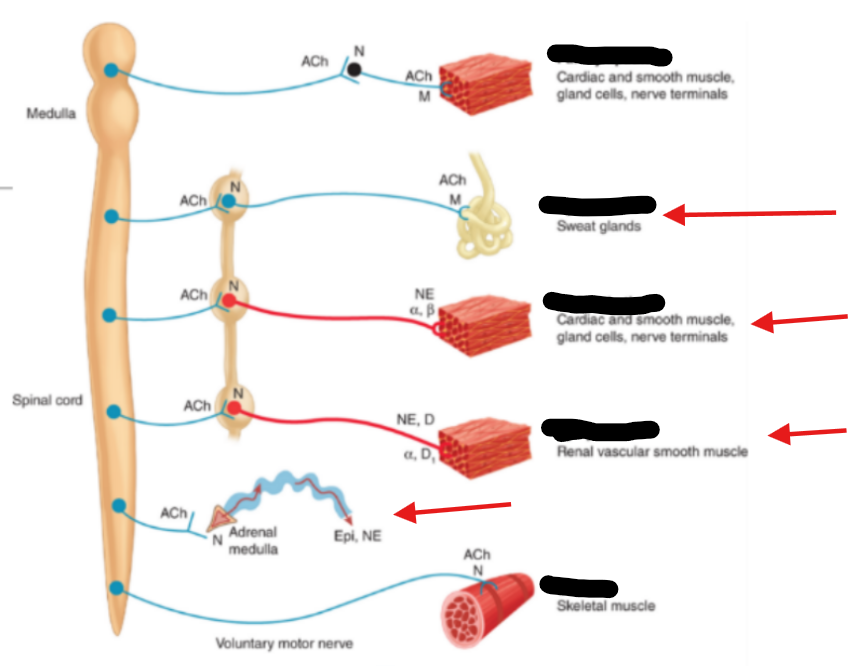
Thoracolumbar, short, long, craniosacral, long, short
The sympathetic ANS is associated with the __ division of the spine
Preganglionic neurons are __ post-ganglionic neurons are __ (short vs long)
The parasympathetic ANS is associated with the __ division of the spine
Preganglionic neurons are __, post-ganglionic neurons are __ (short vs long)
ACh, Norepinephrine (NE)
Neurotransmitters related to the Paras ANS are __
Neurotransmitters related to the Symp ANS are mainly __, also epinephrine, ACh, and DA
Nicotinic, iono, muscarinic, metabo
Receptors linked to the Parasympathetic ANS are __ that are __tropic and __ that are __tropic
(2)
Alpha, metabo, beta, metabo, nicotinic (nACh), iono, muscarinic (M), metabo
Receptors linked to the Sympathetic ANS are __ that are __tropic, __ that are __tropic, __ that are __tropic, and __ that are __tropic
(4)
Parasympathetic
Para vs symp
Sympathetic
Para vs sym
Dilation, constriction, secretions
Sympathetic component to trachea and bronchioles is __
Parasympathetic component to trachea and bronchioles is __ with increased __
Nicotinic AChRs
A common similarity of the PANS and SANS is ALL ganglia in both have __ __ (receptors)
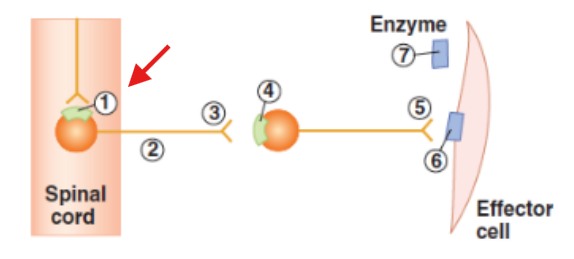
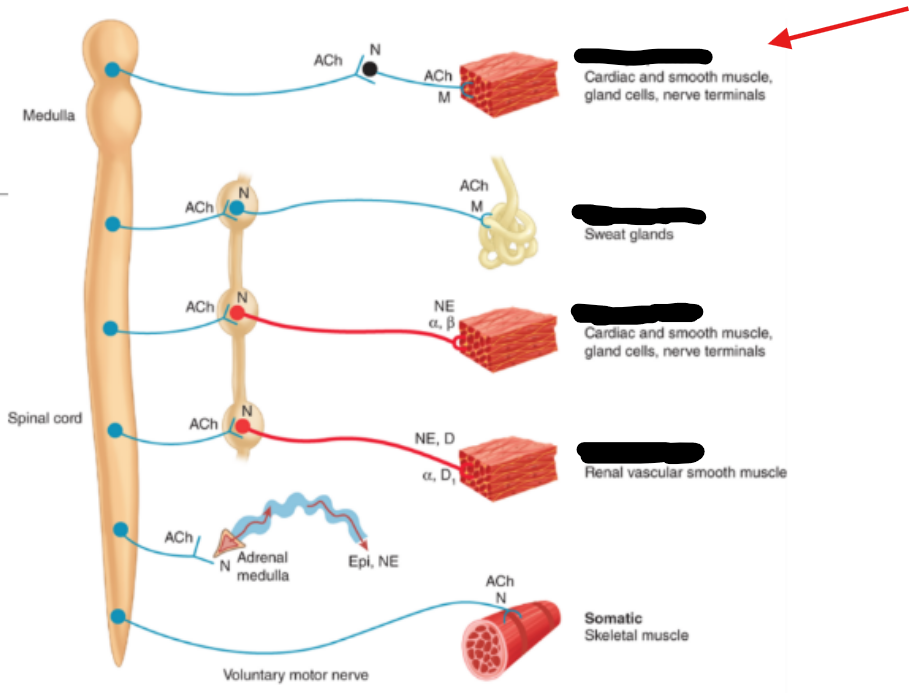
Cell body of pre-ganglionic neuron in the spinal cord
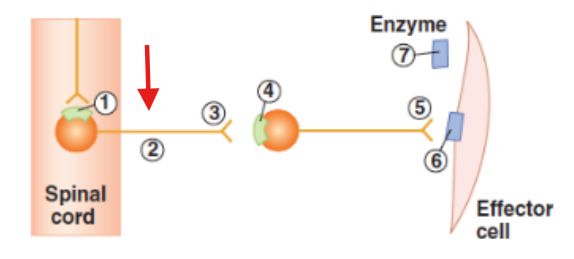
Axon of the pre-ganglionic neuron
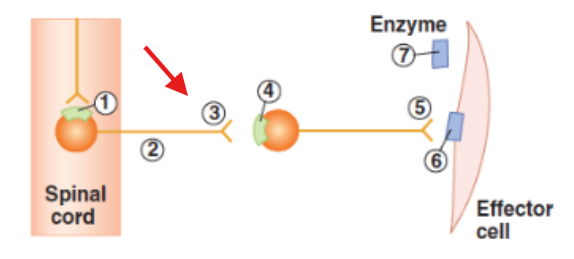
Synaptic terminal of pre-ganglionic neuron
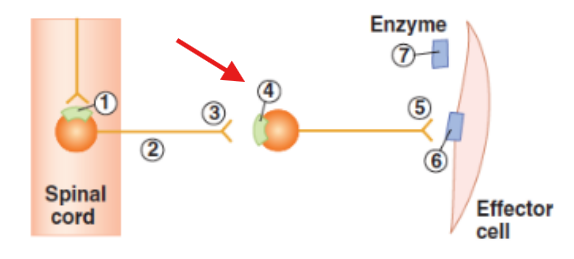
Cell body of post-ganglionic neuron in ganglia
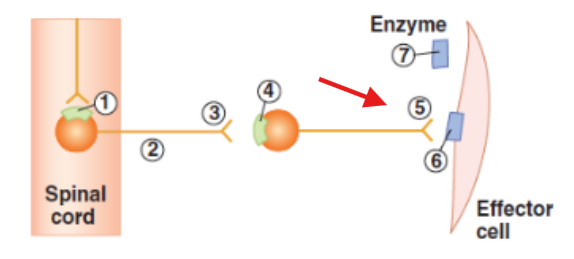
Synaptic terminal of post-ganglionic neuron
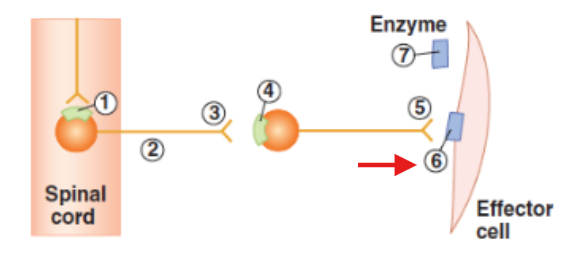
Effector cell with receptors or neurotransmitter released from post-ganglionic neuron
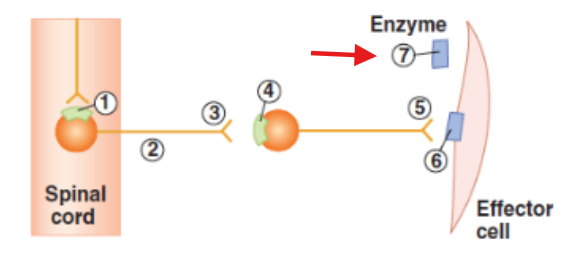
Enzyme in the neuroeffector junction
Ionotropic, metabotropic
Voltage-gated and ligand-gated ion channels are __, (fast)
G-protein coupled receptors are __, (slower)
Muscarinic Rs
Contract smooth muscle, M2 regulates cardiac function (receptor type- muscarinic or nicotinic or B/A)
Nicotinic Rs
Mediate neurotransmission in ALL ganglia, including adrenal medulla (receptor type- muscarinic or nicotinic or B/A)
Alpha1 Rs
Stimulate contraction of all smooth muscle, constrict sphincters, vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle (norepinephrine receptor type)
Alpha2 Rs
Feedback inhibition of norepinephrine release, inhibit secretion (norepinephrine receptor type)
Beta1 Rs
Regulate cardiac function and renin release (norepinephrine receptor type)
Beta2 Rs
Relax all smooth muscle (vasodilation, bronchodilation), increase contractility in heart, and regulate metabolic functions (norepinephrine receptor type)
Agonist, Antagonist
An __ is a drug that binds to and alters activity of receptor, mimics endogenous ligand
An __ is a drug that binds to receptor and prevents activation of receptor, inhibitors/blockers
Detrusor, relaxed, contracted
The __ muscle of the bladder is
__ (contracted/relaxed) by sympathetic with filling bladder - via Beta-2 R
__ (contracted/relaxed) by parasympathetic when emptying bladder - via M R
Internal, contracted, relaxed
The __ sphincter of the bladder is
__ (contracted/relaxed) by sympathetic with filling bladder - via Alpha-1 R
__ (contracted/relaxed) by parasympathetic when emptying bladder - via M R
External sphincter
Contracted voluntarily with filling bladder, relaxed voluntarily when emptying bladder
Baroreceptor reflex, tachycardia
Reciprocal functions of ANS on heart rate work synergistically via __ __
Drop in BP —> Increase SANS activity, decrease PANS
results in vasoconstriction + reflex __ (vital sign)
M2, Beta1, NE, ACh
Baroreceptor changes in ANS receptors If BP drops
Downregulate __ _ receptors of heart of PANS
Upregulate __ _ receptors of heart of SANS
Net increase of __ over __ (neurotransmitters)
Choline, acetate
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an enzyme that catalyzes ACh hydrolysis into __ and __
Axonal, synaptic, ACh, end organ
Cholinergic neurotransmission
(1) __ conduction
(2) __ transmission - Synthesis of ACh, storage, release, destruction
(3) __ signaling
(4) __ __ effects
Reuptake of NE, catecholamines
Major mechanism of signal termination for adrenergic is the __ (action) of __ (neurot) into the nerve terminal
After this step, __ (neurot class) are stored in vesicles by vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT)
Cocaine, reserpine
__ inhibits NE transporter and __ inhibits VMAT in adrenergic signal termination (drugs)
Axonal, synaptic, post, end organ
Adrenergic neurotransmission
(1) __ conduction
(2) __ transmission - Synthesis of catecholamines, storage, release, reuptake
(3) __synaptic signaling
(4) __ __ effects
Cholinergic agonists
Drugs mimicking ACh (aka parasympathomimetic agents)
AChR agonists, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Cholinergic antagonists
On AChr (aka parasympatholytic agents)
Sympathomimetics (Adrenergic agonists)
Drugs that mimic or enhance alpha/beta R stimulation
Agonists, enhance catecholamine release, block reuptake
Adrenergic antagonists
Alpha/beta R blocking drugs (aka sympatholytic agents)