BMS 213 final (work in progress)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
aseptic technique
method used to keep surfaces and objects free of unwanted bacteria
inoculation
purposefully transferring bacteria with the intention for it to grow
eye piece/ocular lens of microscope
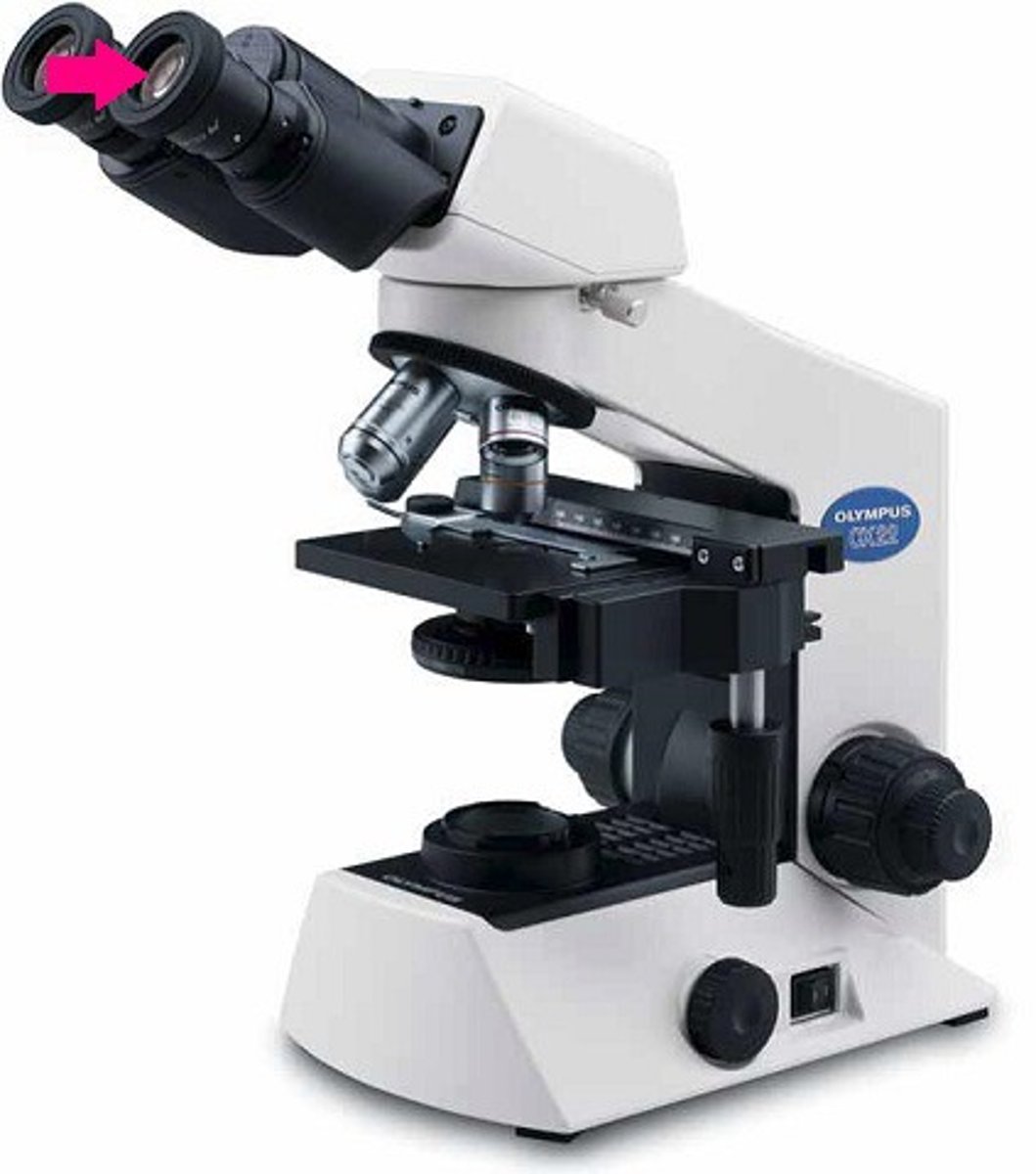

diopter of microscope

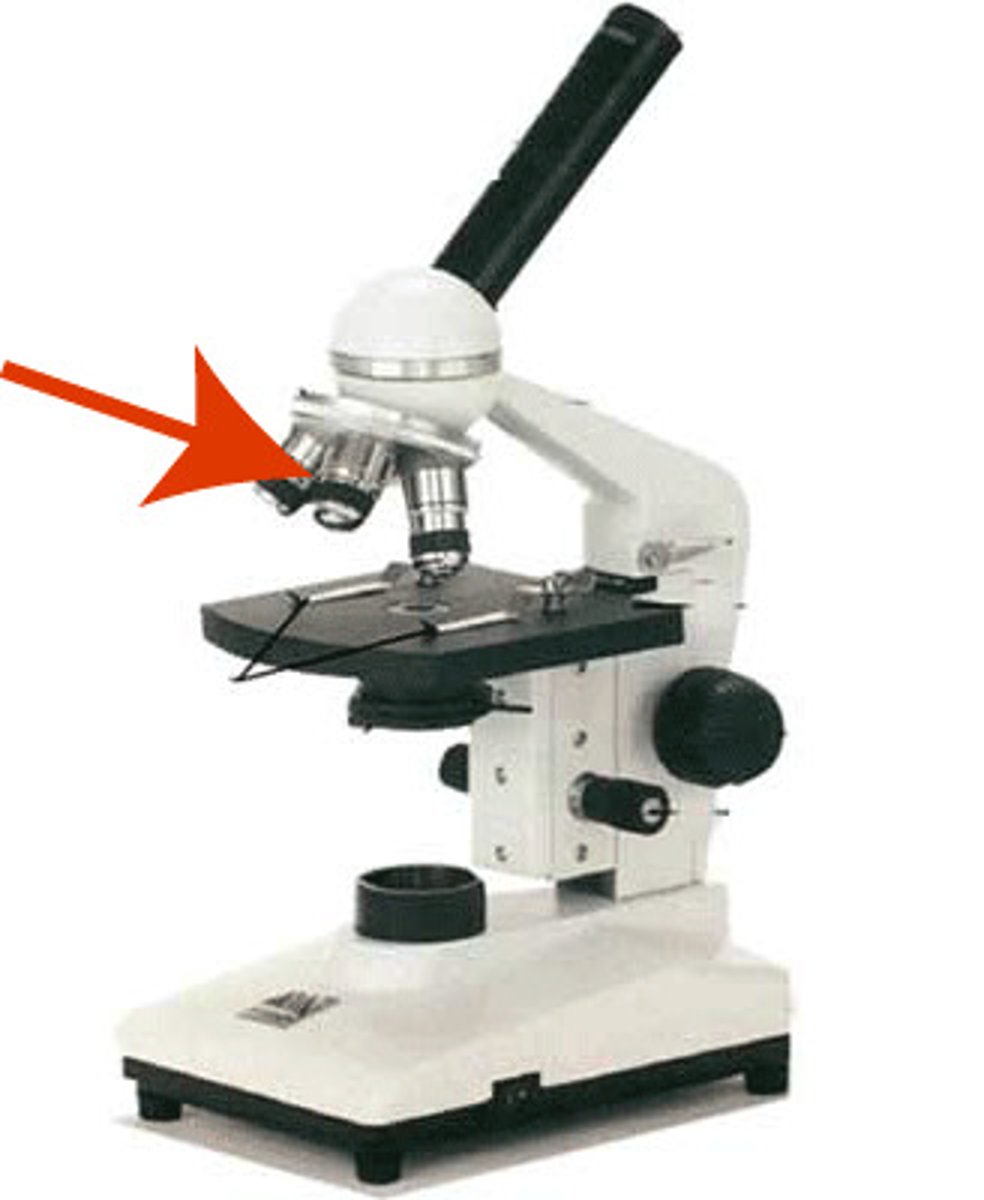
objective lens of microscope

stage of microscope
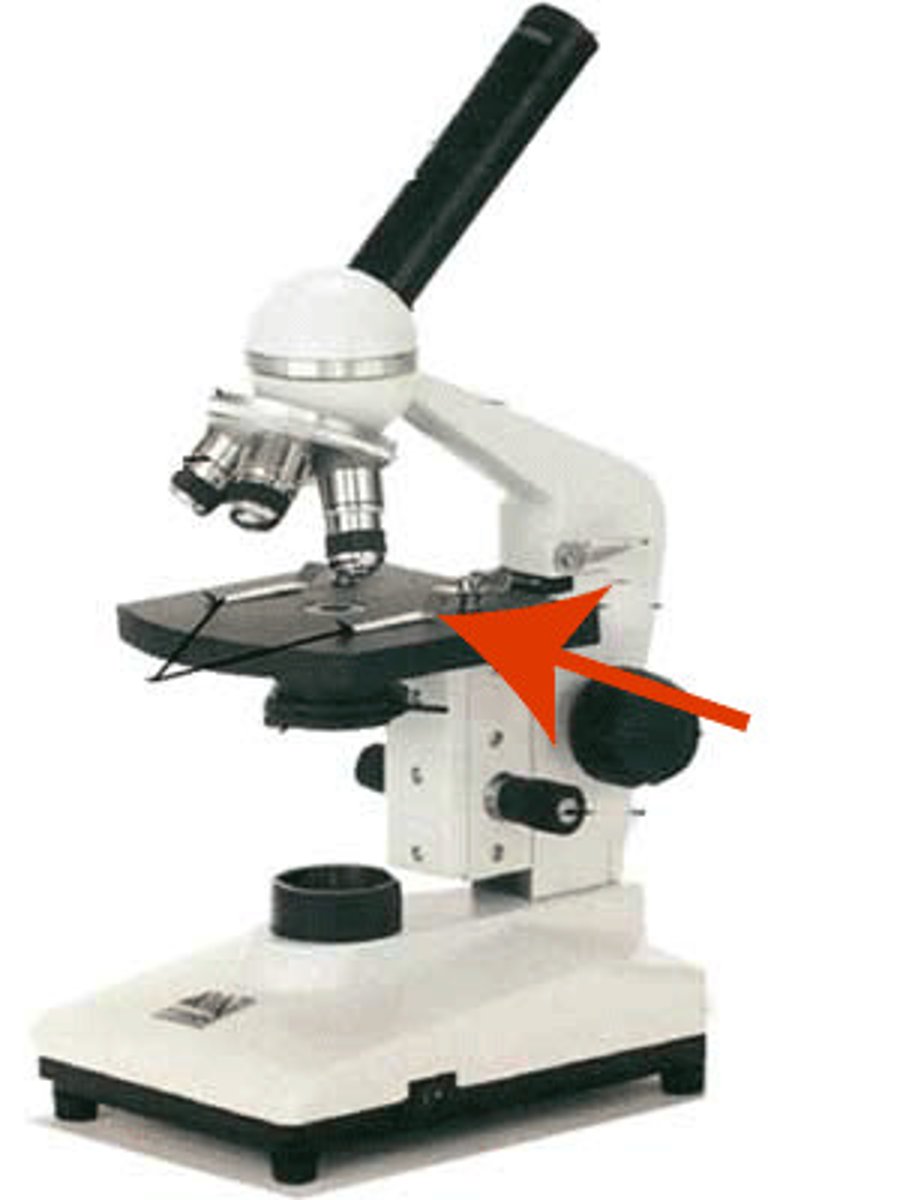
condenser lens of microscope
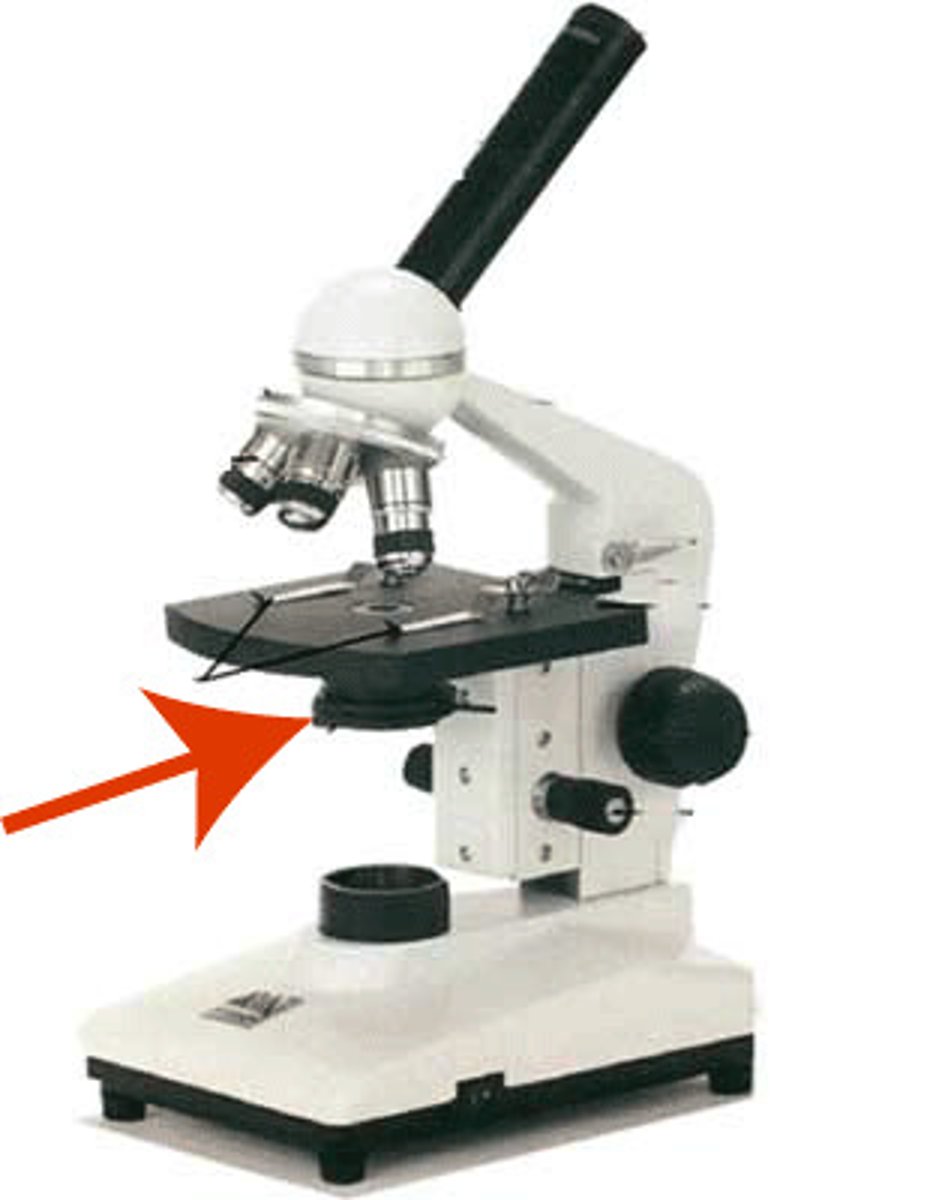
fine focus of microscope
make fine, final focus adjustments
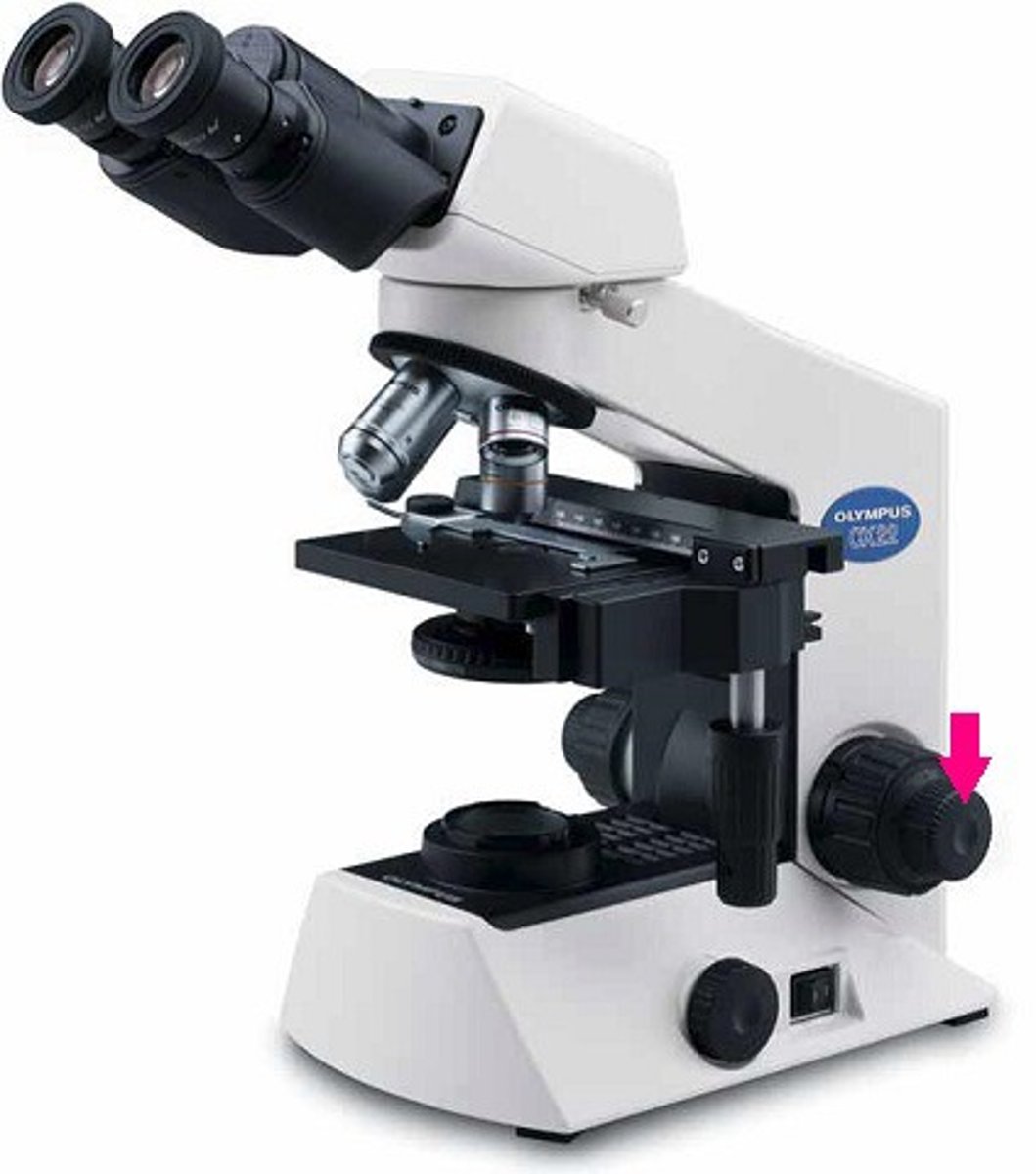

course focus of microscope
large movements of stage
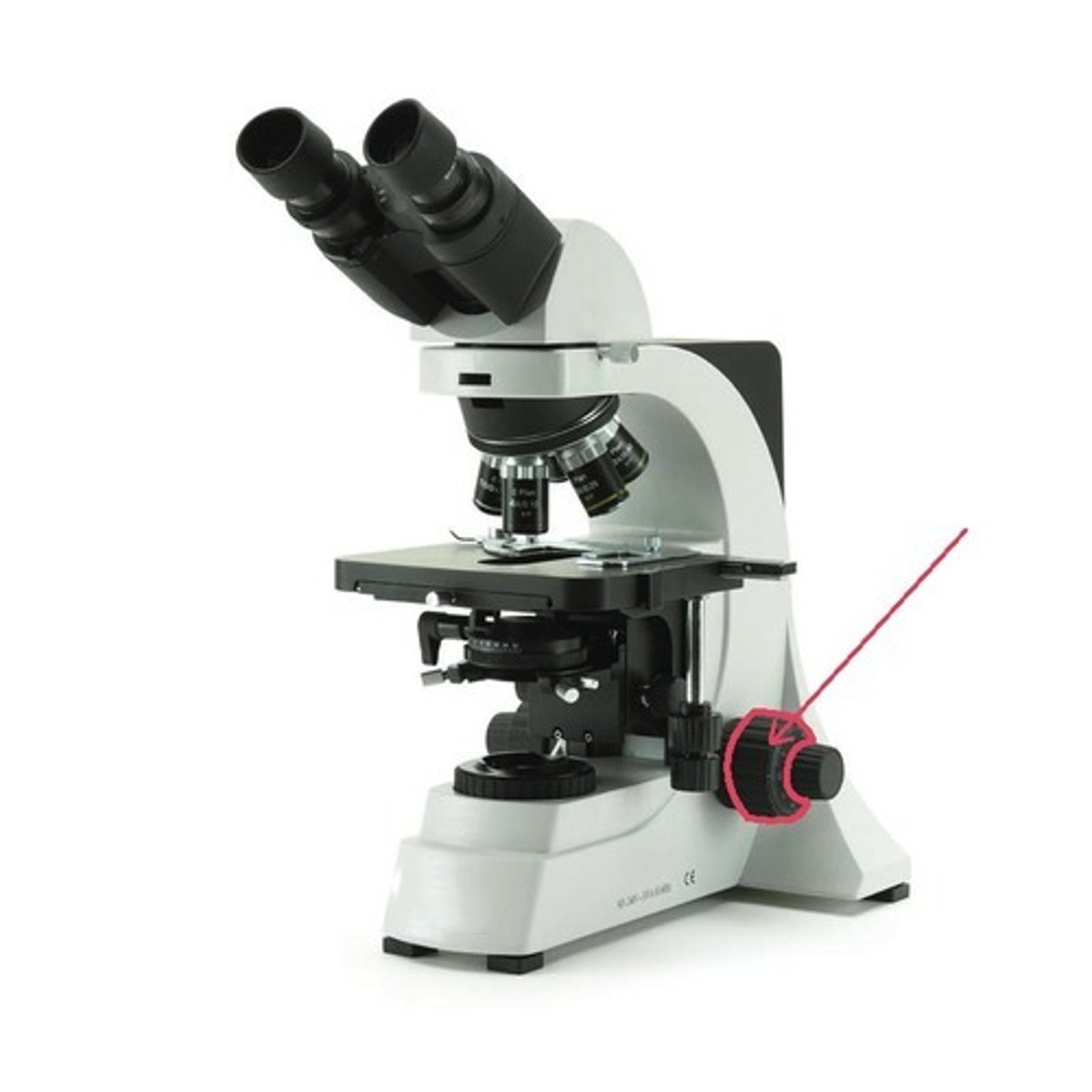

light source of microscope
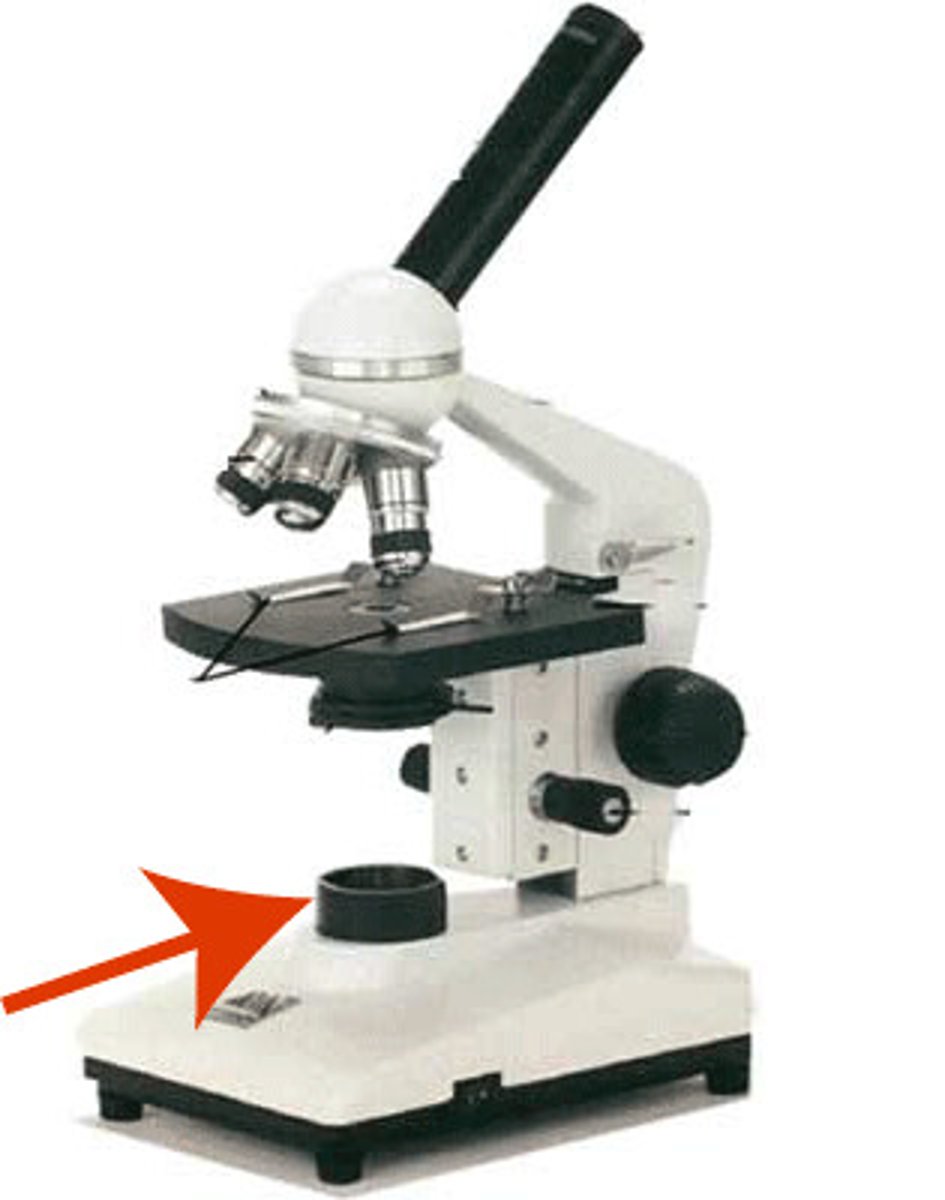

base of microscope
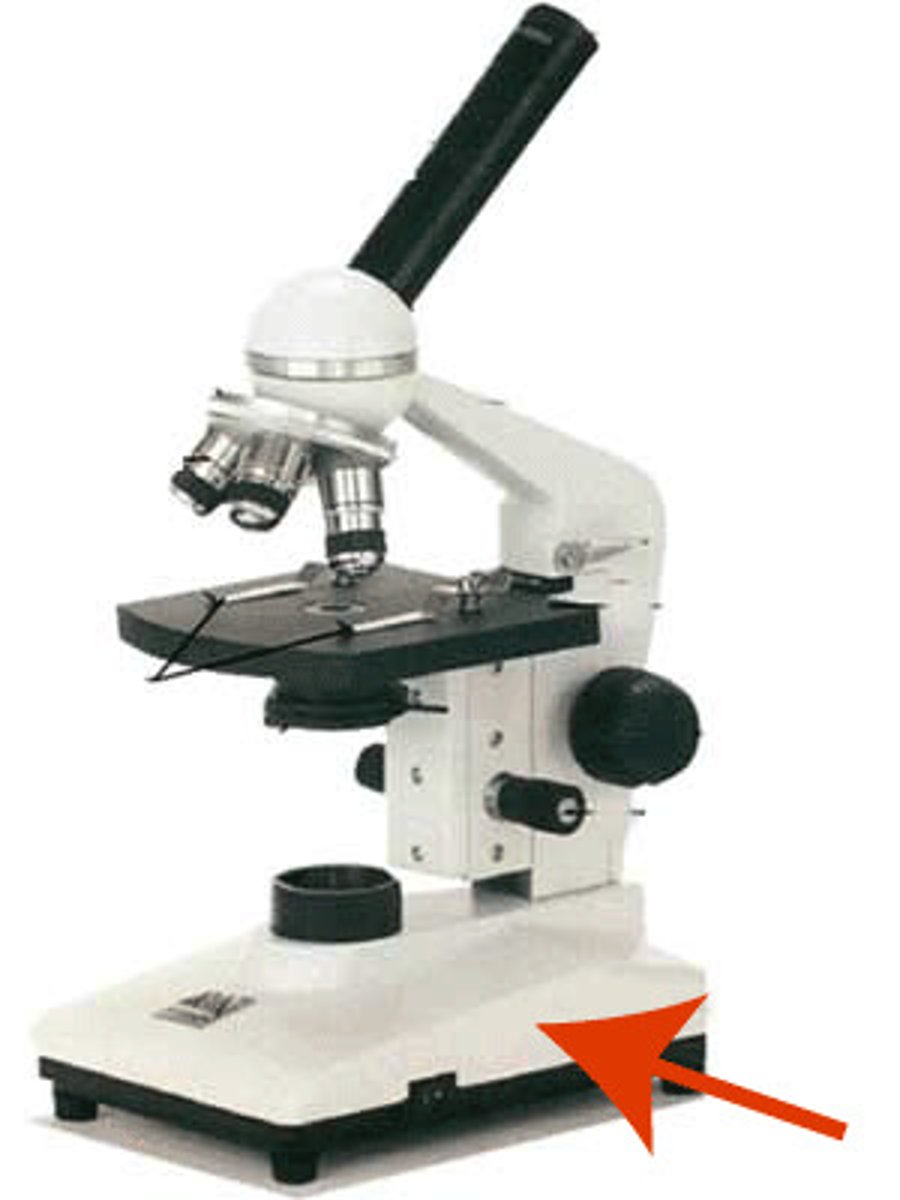

move stage of microscope
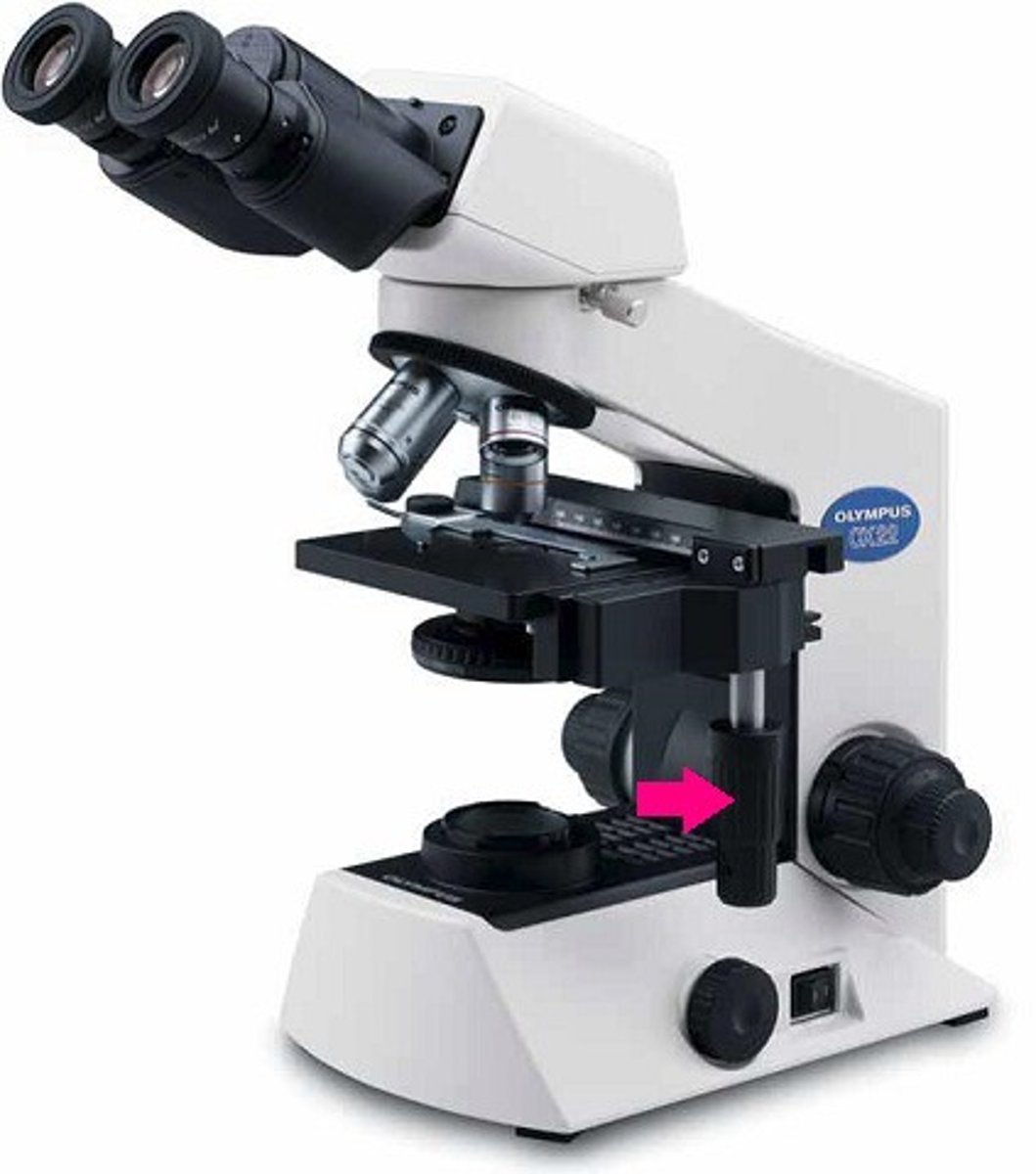

brightness of microscope
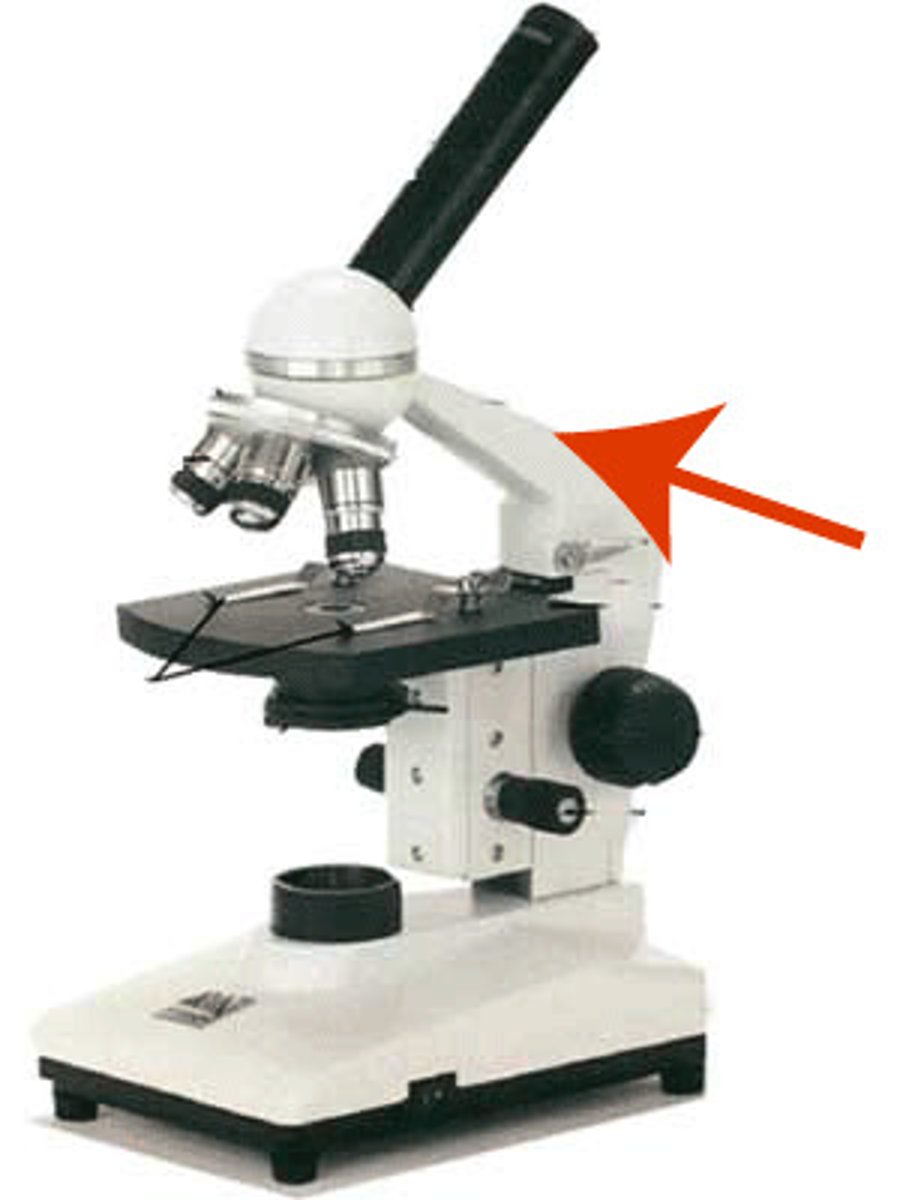
neck of microscope
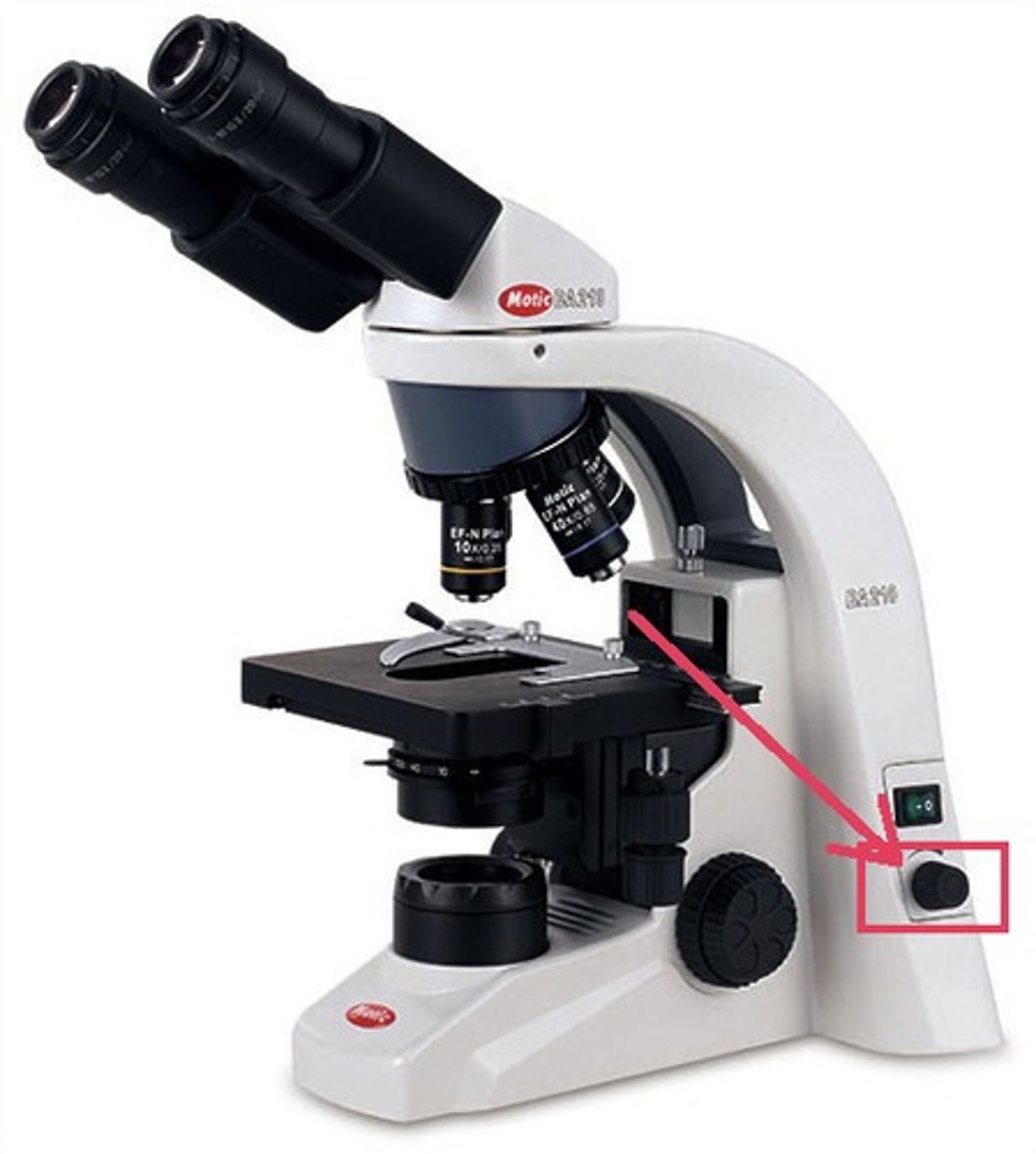
powers of microscope
4x, 10x, 40x, 100x
count plate procedure
process of getting 5 tubes and plates and diluting the original bacteria until it is not too numerous to count and calculating results
count plate equation
(# of colonies/mL plated) X (1/dilution factor) - cfu/mL
gram staining procedure
Heat Fix
1. Primary stain- Crystal violet (1 minute)
Wash off stain with di-water
2. Mordant- Gram's Iodine (1 minute)
Wash off the iodine
3. Decolorization- Acetone-alcohol (hold slide at 45 degree angle and apply decolorizer, do this for a few seconds)
Stop decolorization by washing slide with gentle stream of di-water
4.Counterstain- Safranin (1 minute)
Wash off gently for only a few seconds
5. Blot dry with bibulous paper & air dry
6.Examine slide under oil immersion
gram stain: gram positive
purple and no outer membrane
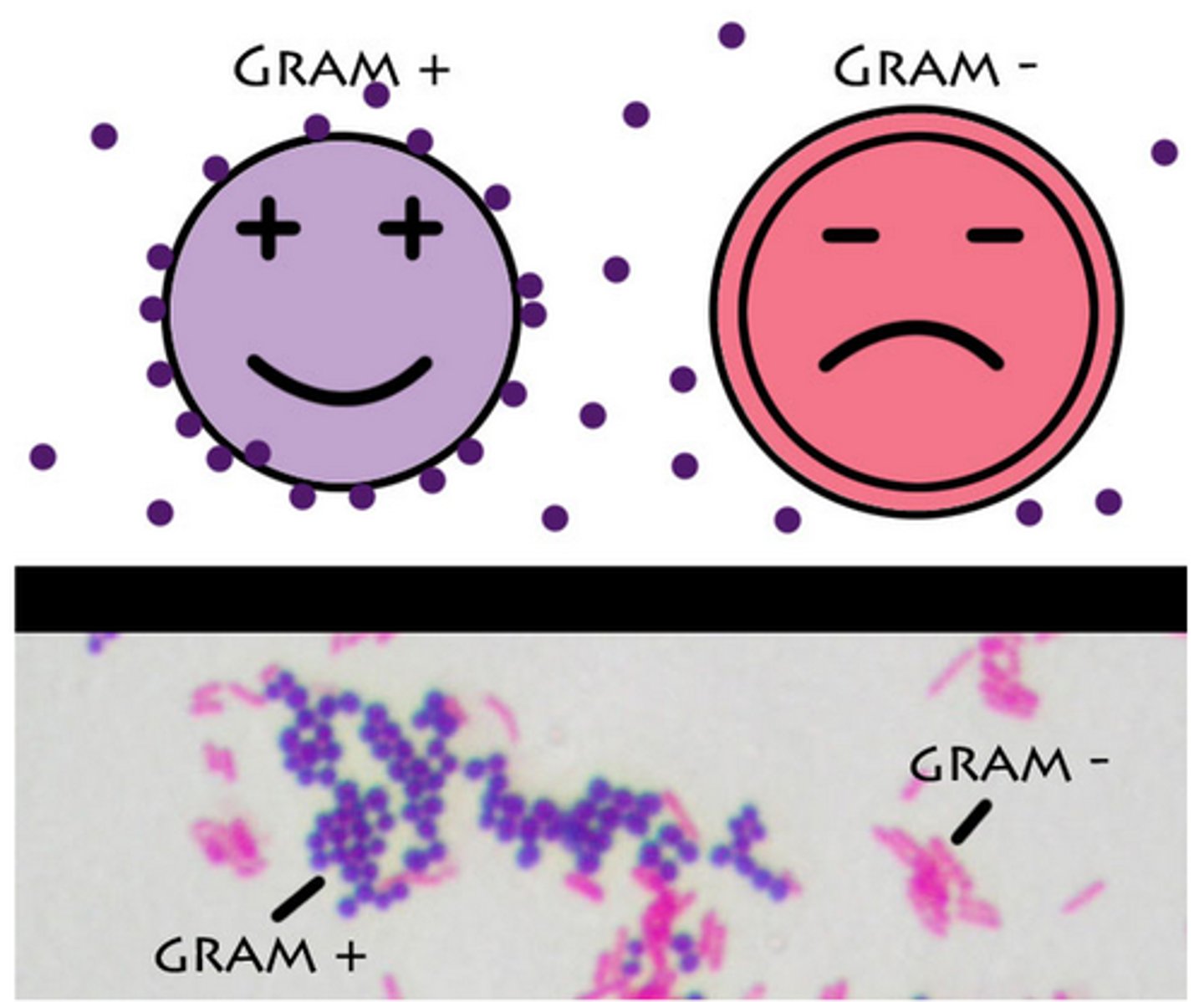
gram stain: gram negative
pink with an outer membrane and thinner
capsule stain procedure
1. Begin w/ drop of serum & add Congo red stain
2. Add organisms & emulsify
3. Use 2nd clean slide to draw drop across to other end
4. Air-dry (do NOT heat-fix)
5. Flood w/ Maneval's stain for 1 min. then rinse
6. Blot dry
capsule stain: gram positive
clear visible halo
capsule stain: gram negative
no visible halo
Spore stain procedure
1. heat fixed smear
2. malachite green (forces into endospore) then wait 10 min
3. rinse with water
4. add safranin (vegetative cells)
5. rinse with water, blow dry
spore stain: positive
green cells
spore stain: negative
red/pink cells
requirements for bacterial growth
temperature, pH, osmotic pressure/salt concentration, oxygen
Psychrophiles
cold-loving microbes (-5 to 15 C)
thermophiles
heat loving microbes (45 to 70 C)
mesophiles
moderate temperature loving microbes (25 to 40 C)
acidophiles
grow in acidic environments
Alkalophiles
grow in basic environments
halophile
salt loving microbe
halotolerant
microbe that can tolerate some salt
halosensitive
microbe that cannot tolerate salt
aerobes
microbes that grow in the presence of oxygen
anaerobes
microbes that grow without oxygen
facultative anaerobes
microbes that can grow in the presence and absence of oxygen
CNA blood agar
used to grow gram positive bacteria, 5% sheeps RBC, nutrients, hemolysis
catalase test procedure
put bacteria on slide and then apply 3% hydrogen peroxide to sample, positive result will show bubbles
coagulase test procedure
transfer bacteria to tube with rabbit plasma and then incubate at 35 C, positive result will show a clot
Novobiocin (NB5) procedure
make a lawn plate with bacteria, place novobiocin disc in middle, incubate for 24 hours, zone of inhibition >16 is sensitive, <16 is resistant
Enterococcus faecalic
microbiota in gut
Streptococcus alagactiae
group B strep, in women, can infect infants during birth
Streptococcus mitus
mouth, major cause of cavities
Streptococcus pneumoniae
kids: ear infections elderly: meningitis
sensitive to A disc
Streptococcus pyogenes
group A strep, cause of strep throat
sensitive to P disc
A disc
includes bacitracin which targets cell wall
P disc
includes optochin which inhibits protein pumps
MAC plate
used to grow gram negative bacteria
selective: crystal violet and bile salts
differential: lactose and neutral red