Pop Health Final Exam 1
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Describe what information is used to derive the wealth index from the Demographic and Health Survey questionnaire data. Name 3 items included.
Wealth index is derived from asset indicators such as having a refrigerator, TV, car/motorcycle
Name two essential features of a census.
1. Individual enumeration (every person counted), 2. Universality (everyone included), 3. Simultaneity (certain reference date), 4. Periodicity (taken every X years)
Give one reason why surveys can generally yield more accurate information than censuses.
You can better train the interviewers. There is better supervision and qualification.
What are the three main types of sources of demographic data?
Vital registration, censuses and surveys
Why was 1790 census of USA not a census by definition?
Didn’t have individual enumeration
What does GDP stand for?
Gross domestic product. The total market value of all final goods and services produced within the country in a given period of time.
Why might study of cemetery records give a biased picture of mortality in the past?
Not everyone could afford to buy a plot to be buried in
When did the world reach 1 billion people, 2 billion, 7 billion?
1800, 1930, 2011
Name 1 country in the top 10 with highest natural increase rate
Niger, Uganda
Why do scientists talk of a demographically divided world?
Some regions have below replacement fertility while others have high growth rates. Countries have differing growth rates.
Define the crude birth rate, crude death rate, and crude rate of natural increase
Crude birth rate: number of births in a given year per 1000 mid-year population
Crude death rate: number of deaths in a given year per 1000 mid-year population
Crude rate of natural increase: crude birth rate - crude death rate, it does not take into account immigration.
In what decade was the peak of the world population growth rate?
60s
What is the bookkeeping equation of population growth?
Pt = Po +B -D +I -O
Where B=births, D=deaths, I= In-migrants, 0=out-migrants
Approximately what percent of world population growth is occurring in developed countries?
5%
How can the absolute number of births increase if the birth rate is declining?
The denominator of the birth rate is increasing (population size). So even though the number of births is increasing, the portion of people eligible to give birth is also increasing, resulting in a decreasing birth rate overall.
Which subregion has quite a few countries with negative natural increase?
Eastern Europe
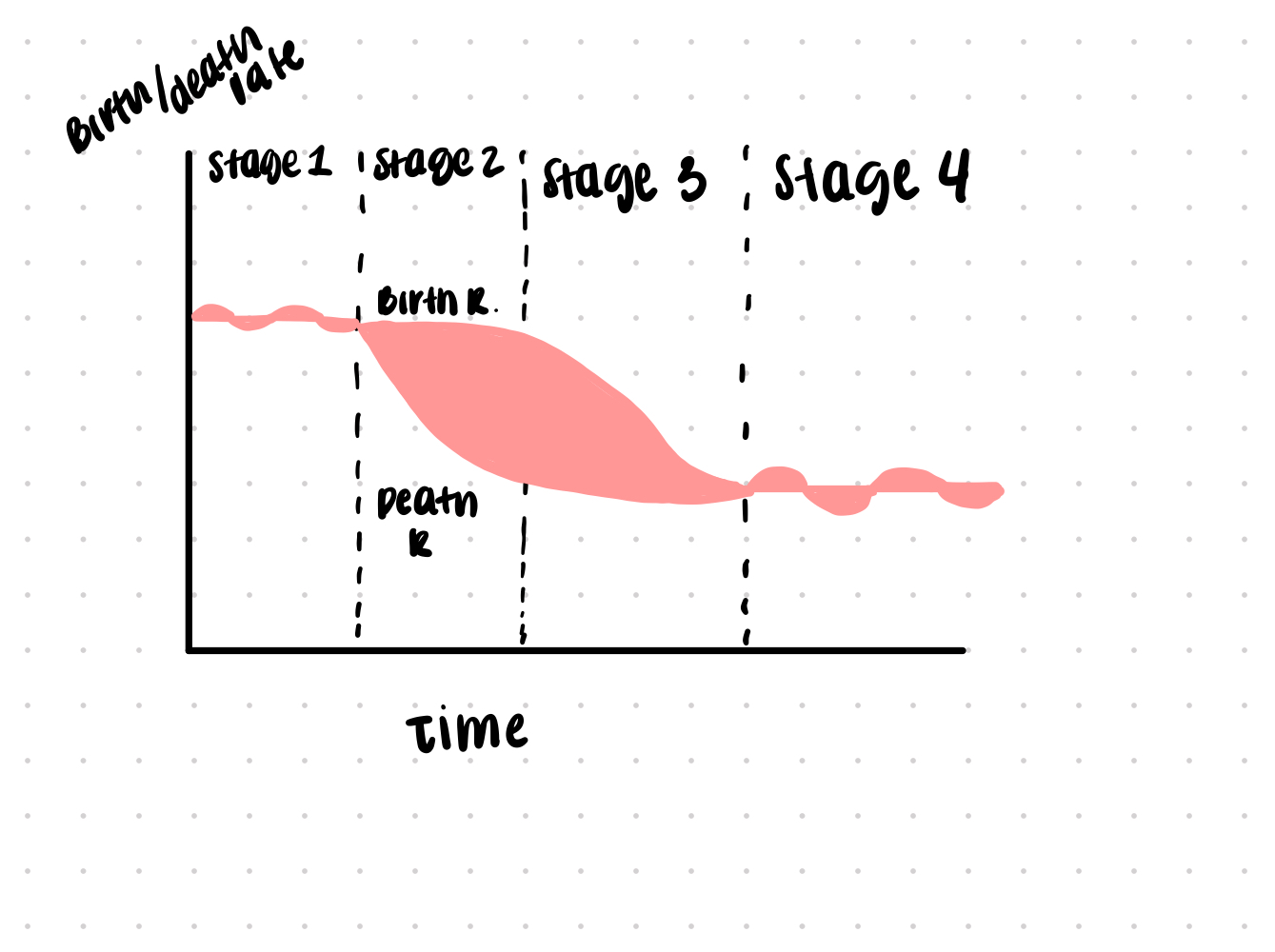
Describe the stages of the demographic transition and draw a graph of same.
High birth and death rates (zero to low growth)
High birth rate, declining death rate (high growth)
Death and birth rates declining
Both death and birth rates low (zero to low growth)
By approximately how many persons is the world population growing each year?
76 million
Name 2 of the five largest urban agglomerations in 1950.
Tokyo, Moscow, Paris, New York
In what region do most of the people of the world live?
Asia
Which region has the highest population growth rate?
Sub-Saharan Africa
What is the estimated world population size in (mid-)2022?
7.9 Billion
What is the estimated world population size in (mid-)2023?
8.0 billion
What is the simple rule to find doubling time given the rate of growth?
Rule of 70. # years to double = 70/growth rate (ex 2% takes 35 years to double)
Why is population momentum an important concept for countries concerned about population growth in the future?
Higher population growth is associated with a lower rate of economic growth. We live on a finite planet, with limited resources.
population increase that continues even after a fall in birthrates because of a large youthful population that widens the population's parent base
About what percentage of world population lives in urban areas now?
50-57%
Name 3 countries among the top 10 contributors to world population growth (numbers of persons added per year)
India, China, Nigeria, USA, Ethiopia
About how many years did it take to add the last billion persons to the planet?
11 years
What is the only sustainable population growth rate in the long term?
0, because we live on a finite planet
What can be done to decrease high wanted fertility in Sub-Saharan Africa?
Invest in human capital (educate girls)
If unwanted you would strength family planning
Why is the 1-child family norm important for stabilizing human population size in the not-to-distant future?
To counteract the effect of momentum, the one child family norm is below replacement fertility
What is the shape of the age specific death rate?
J-shaped curve
Define in words the expectation of life at birth
expected years a newborn will live according to survival rates in the population
Name one public health intervention that led to declines in mortality in 19th century Europe.
Sewage management, clean drinking water
Describe the epidemiological transition
Change in patterns of mortality and morbidity by cause of death; from infectious diseases to non-communicable diseases. Shift in age structure from younger age groups to older.
Is malaria transmitted by female mosquitos, male mosquitos or both?
Female mosquitos only
What has been the main intervention to eliminate polio from most of the world?
Vaccines
Name 2 of the major causes of death of children under 5 in the world
Pneumonia, preterm, birth complications, diarrhea
Define the infant, neonatal and post-neonatal mortality rates
Neonatal mortality rate: number of deaths of newborns in the first month (28 days) of life per 1000 births = D0-3weeksB*1000 or D<1 monthB*1000
Postneonatal mortality: # deaths of children 1-11 months / # births for a given time period (usually one calendar year
Infant mortality: number of infant deaths in a year *1000number of life births in a year neonatal mortality + postneonatal mortality
What is a simple low-cost treatment for diarrhea?
Oral rehydration treatment. ORT includes ORS (oral rehydration solution/salts) (salt, sugar, water.. have to get portions right).
Why is malnutrition very important even though it is rarely a cause of death in children?
Malnutrition refers to the imbalance between the amount of food and other nutrients that the body needs vs the amount that is receiving. Could result in under or over nutrition. It can cause increased risk of infection and disease associated with development and death.
Why is CDR a poor measure to compare the health of populations?
CDR is affected by the population age structure. Very young populations will have lower CDRs. Needs to be adjusted for differences in age compositions.
Name one way to prevent malaria
Mosquito net, vaccine
What is the intervention that prevents polio and measles?
Vaccine early
The sum of cause-specific death rates in a population gives what rate?
Crude death rate
Why did the expectation of life at birth decline in Southern African countries in the 1990s?
HIV/AIDS
What is the definition of low birth weight?
Babies who were born less 2500 grams
Why is it nearly impossible to isolate persons infected with polio as a public health strategy?
90% of polio infections cause no symptoms. You don’t know who the cases are
What is the definition of fecundability?
probability that a women will conceive during a menstrual cycle (monthly)
What is the definition of parity?
number of children born alive to a woman
What is the definition of gravidity?
number of pregnancies a woman has had
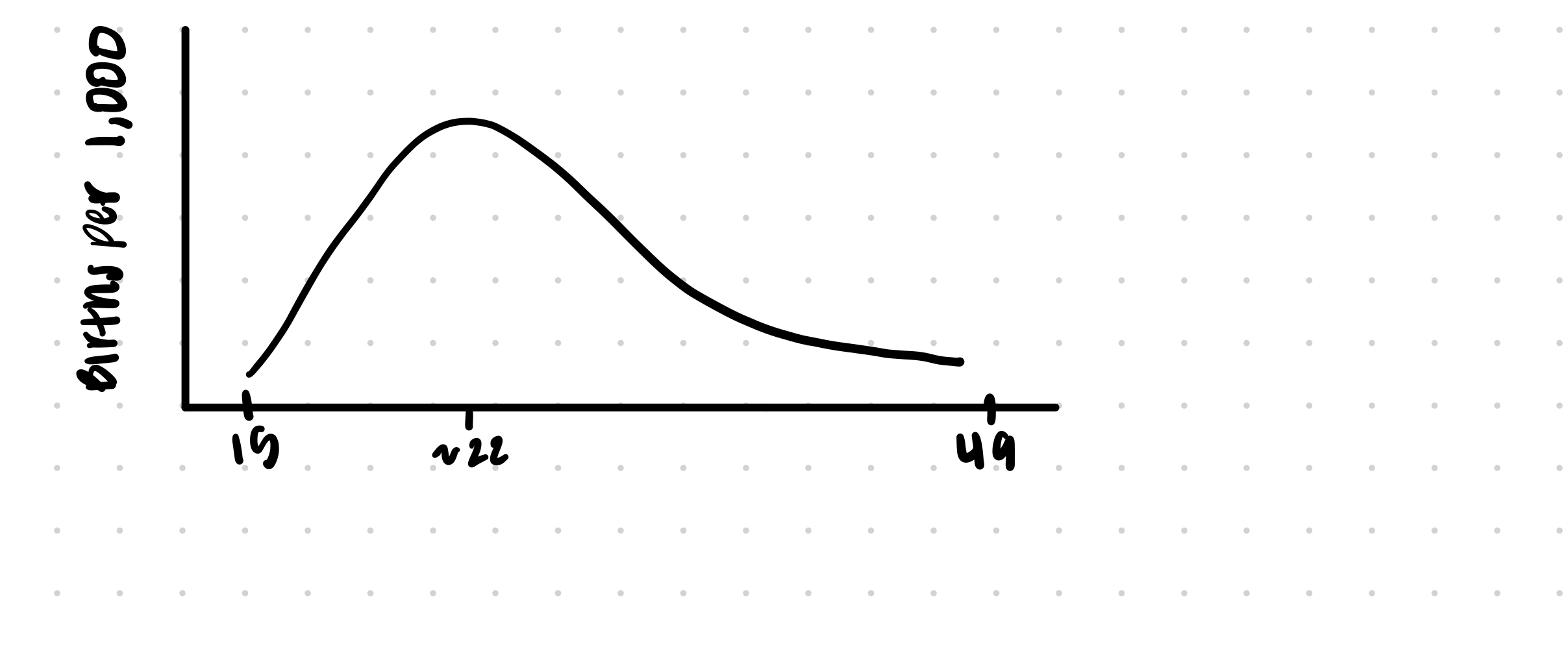
Sketch a typical pattern of age specific fertility
What is replacement fertility:
number of births per woman so the population exactly replaces itself in the long run (around 2)
Why is replacement level fertility (for TFR) about at least 2.1 births per woman instead of 2.0?
Ensures replace of a woman and her partner to counteract infant mortality and up to that child’s age of reproductive age
Name 3 of the intermediate fertility variables.
Married/in union, contraceptives, induced abortion
In what circumstances can a woman’s parity be higher than her gravidity?
Twin birth
Why/how does age at marriage affect TFR in a population?
younger marriage = early exposure to sexual intercourse = more pregnancies in their lifetime = higher total fertility rate
What are the two types of unintended births?
Mistimed (wanted pregnancy but later), unwanted (did not want another pregnancy)
What is the difference between a background or distal variable and an intermediate or proximate variable vis a vis fertility?
Distal (underlying) determinants of fertility result in changes in reproductive behaviors in populations (socioeconomic, cultural, health, and programmatic factors)
Proximate (intermediate) → the biological determinants of fertility
What is the most important intermediate determinant of fertility; distal determinant of fertility?
Immediate… use of contraceptives. Distal….education of women.
Why is the duration of postpartum amenorrhea associated with the duration of breastfeeding?
breastfeeding serves as a natural form of contraception → a woman cannot get pregnant if she is exclusively breastfeeding
How long is the potential reproductive life span of a woman (on average)?
15-49 years (~35years)
Without any contraception, what percentage of sexually active women will become pregnant in one year?
85%
Name two countries with below replacement fertility
China, Singapore
Name two countries with TFR above 5.0
Niger, Mali
What approximately is the global value of TFR in 2022 or 2023?
2.3 births per woman
Why in the plot of TFR vs contraceptive prevalence, do many countries lie off the fitted line?
Method mix is different, each country has a different failure rate..example Paraguay above line (Catholics Church does not approve)
What is the difference between primary and secondary sterility?
Primary sterility: never able to conceive or produce a live birth, Secondary: sterility after one or more children born
Name one hormone whose level spikes at midcycle and is a signal of impending ovulation
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Approximately how many sperm are there per ejaculate?
150-300 million sperm per ejaculate
At what time during the menstrual cycle is a woman fertile?
Ovulation
During which part of the menstrual cycle is progesterone high?
Luteal Phase
Briefly describe one of the fertility awareness methods
Standard Days method: identifies a 12-day fertile window during which women with regular menstrual cycles (26–32 days long) should abstain from sex or use a barrier method to prevent pregnancy.
Name one reason why fertility awareness methods have a high failure rate in typical use
Requires constant modification and attention, does not work with irregular cycles.
Name 2 advantages of male sterilization over female sterilization for couples who wish to have no more births
Safer, cheaper, and reversible in most cases
In what organ does sperm production begin?
Testes
Why is the withdrawal method not very effective?
Human error and pre-ejaculation can contain sperm
What does LARC stand for? What does it include?
Long acting reversible contraceptive, it includes the copper IUD and implant
From what organ does most of the fluid in the man’s ejaculate come from?
Seminal vesicles
Rank these contraceptive methods in order of effectiveness from low to high: IUD, condom, pill, and fertility awareness methods
Fertility awareness methods < condom < pill< IUD
How often is the DepoProvera shot given?
Every 3 months
In what region are infant and child mortality the highest?
Sub-saharan africa
In which sub-region is low birth weight the highest proportion of births?
Southern Asia
What is exclusive breastfeeding?
Feeding the baby only breast milk, not any other liquids including formula or water. (provides antibodies to the infant, promotes monding, has a contraceptive effect)
Name 2 interventions to prevent neonatal deaths
Skilled care at birth, postnatal care for mother and baby
Name 3 vaccines recommended by WHO for children 0-6 years of age.
DTaP, Rota, PCV, Hep A, Hep B
What is a treatment for bacterial pneumonia?
Antibiotics
What therapy saves children with diarrhea from dying?
Oral rehydration therapy
What are treated bed nets for?
malaria prevention.
What immunization is important for the mother to receive before or during pregnancy?
Tetanus Tdap
What is ORS?
Oral rehydration solution. Contains sugar, salt, and other minerals.
Name 2 preventive interventions for child mortality
Breastfeeding, vaccination, water and sanitation
Name 2 therapeutic interventions for child mortality
ORT and antibiotics
What is the definition of unmet need for contraception?
Women have unmet need if they are sexually active, do not want to have a child soon or at all, are not using any contraceptive methods, and are able to conceive.
Name one modern contraceptive method that also protects against sexually transmitted infections
Condoms
What is “dual protection”?
Use of methods that prevent both unwanted pregnancy and HIV/STDS during intercourse (ex. condom and pill)
In what region is contraceptive use the lowest?
Africa
Name 3 reproductive health components
Sexual behavior, infertility, contraception, STIs, breastfeeding, abortion
What is the rationale for the statement “development is the best contraceptive?”
Higher quality of education and income will decrease fertility rate. Countries developed had lower fertility.
Are neonatal deaths as a proportion of all under-five deaths increasing or decreasing? Why?
Increasing ….. Harder to prevent neonatal deaths