DMS 209 Quiz 4(??) a work in progress
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What is quality assurance?
routine, periodic evaluation of an ultrasound system to guarantee optimal image quality
What are the 5 goals of quality assurance?
- proper system operation
- detection of gradual changes in image quality
- minimize downtime
- reduce number of non diagnostic exams
- reduce number of repeat exams
What is Schlieren imaging?
imaging system used to view a sound beam's shape within a medium
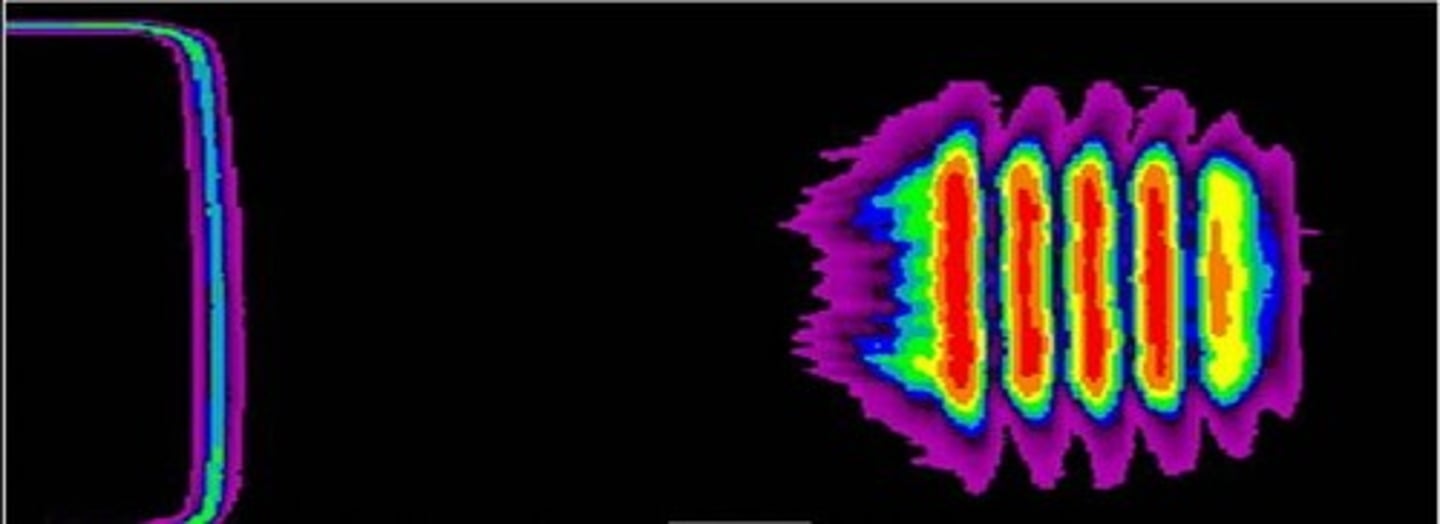
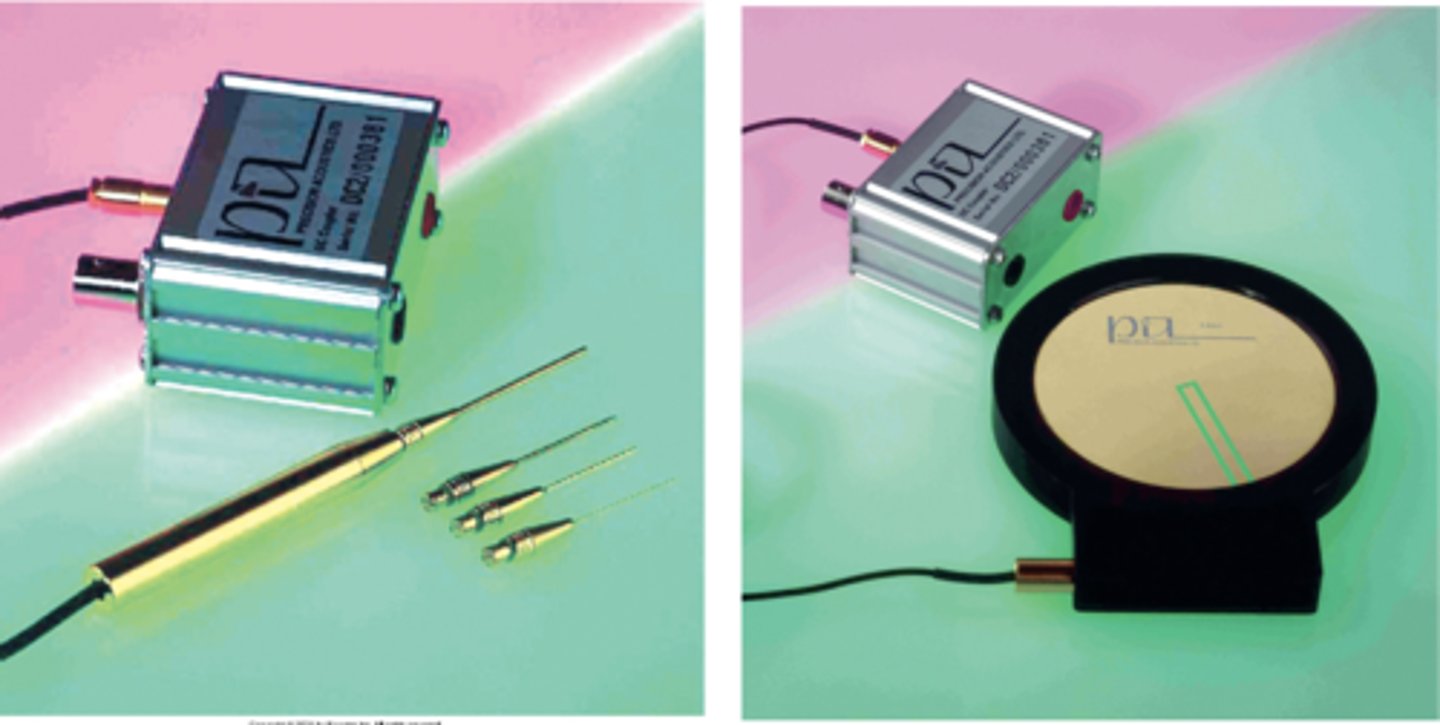
What is a hydrophone?
a small transducer and complementing device used to measure acoustic pressure or intensity at a specific location
- can also measure period, PRP, PRF, & PD
What is a calorimeter?
an instrument used to measure the total power in the entire sound beam through absorption
2 multiple choice options
What is a thermocouple?
an instrument that measures the power of a sound beam at a specific location
2 multiple choice options
What is liquid crystal?
a material used to indicate temperature changes represented through color changes
2 multiple choice options
What phantom(s) are used for quality assurance testing?
all of the above (tissue equivalent phantom, doppler phantom, & slice thickness beam profile phantom)
3 multiple choice options
What key things do phantoms test for?
- axial resolution
- lateral resolution
- depth calibration / vertical distance
- system sensitivity
- registration accuracy
- dead zone
What other things do phantoms test for?
- image uniformity / tissue texture
- lesion detection
- greyscale contrast resolution / dynamic range
- focal zone
- depth of penetration
What is normal sensitivity?
when measurements are tested with output power, amplification and TGC set at normal levels
What is maximum sensitivity?
when measurements are tested with output power, amplification and TGC set at maximum levels
What is the dead zone?
region from the transducer to the shallowest depth where images are inaccurate
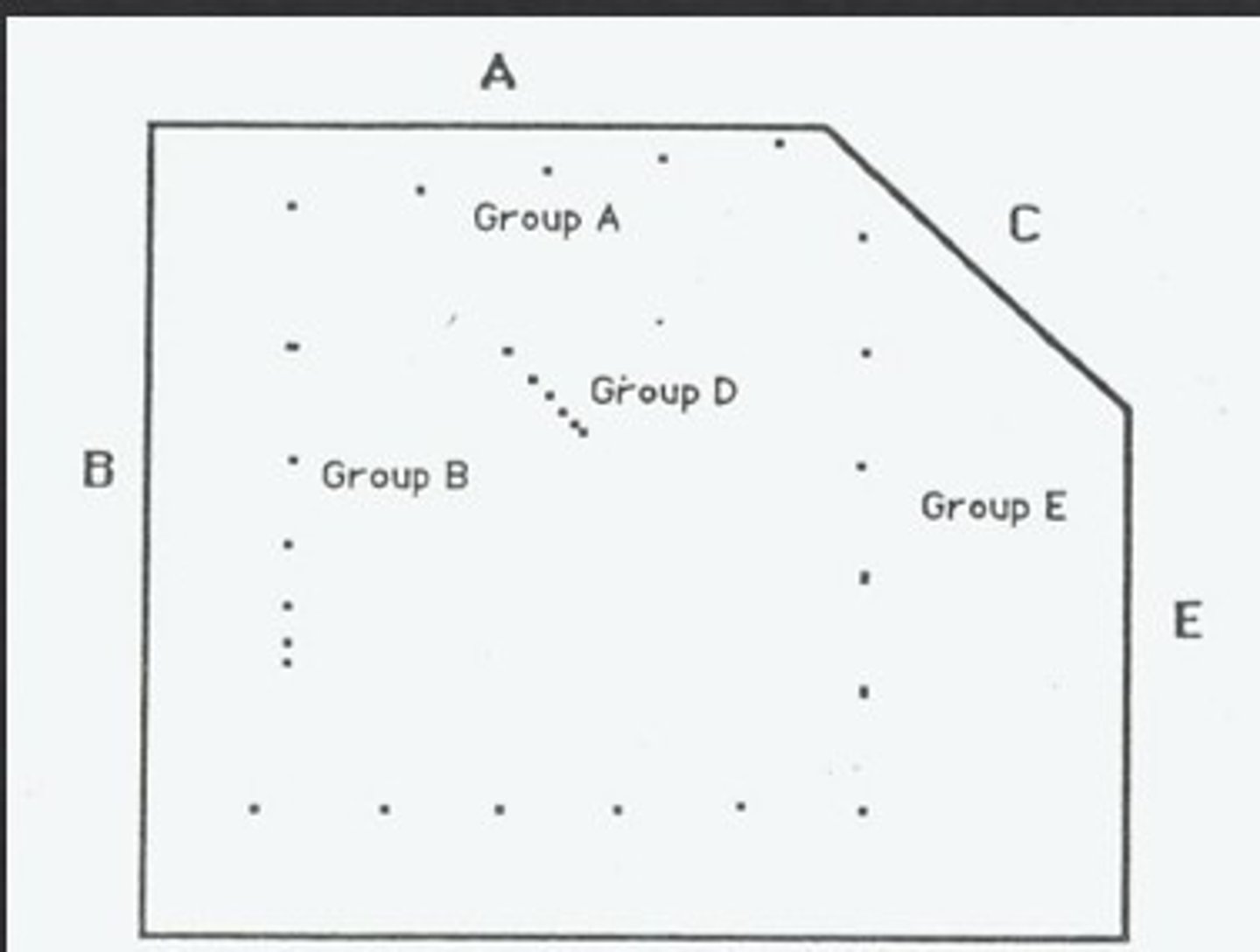
How is the dead zone thickness measured?
measure from 'A' to 'Group A' (see image)
True or False: Higher frequency transducers have a thinner dead zone than lower frequency transducers?
True
1 multiple choice option
How is lateral resolution tested in QA?
smallest distance at which two pins positioned side by side to the sound beam are displayed as two distinct echoes
1 multiple choice option
How is axial resolution tested in QA?
smallest distance at which two pins positioned parallel to the sound beam are displayed as two distinct echoes
2 multiple choice options
How is registration accuracy tested in QA?
testing the system to be able to place reflections in proper positions while imaging from different orientations
2 multiple choice options
What is a multipurpose tissue equivalent phantom?
a phantom comprised of materials able to transmit sound beams at 1540 m/s and attenuation at soft tissue rate, along with stainless steel pins and structures mimicking masses and cysts
2 multiple choice options
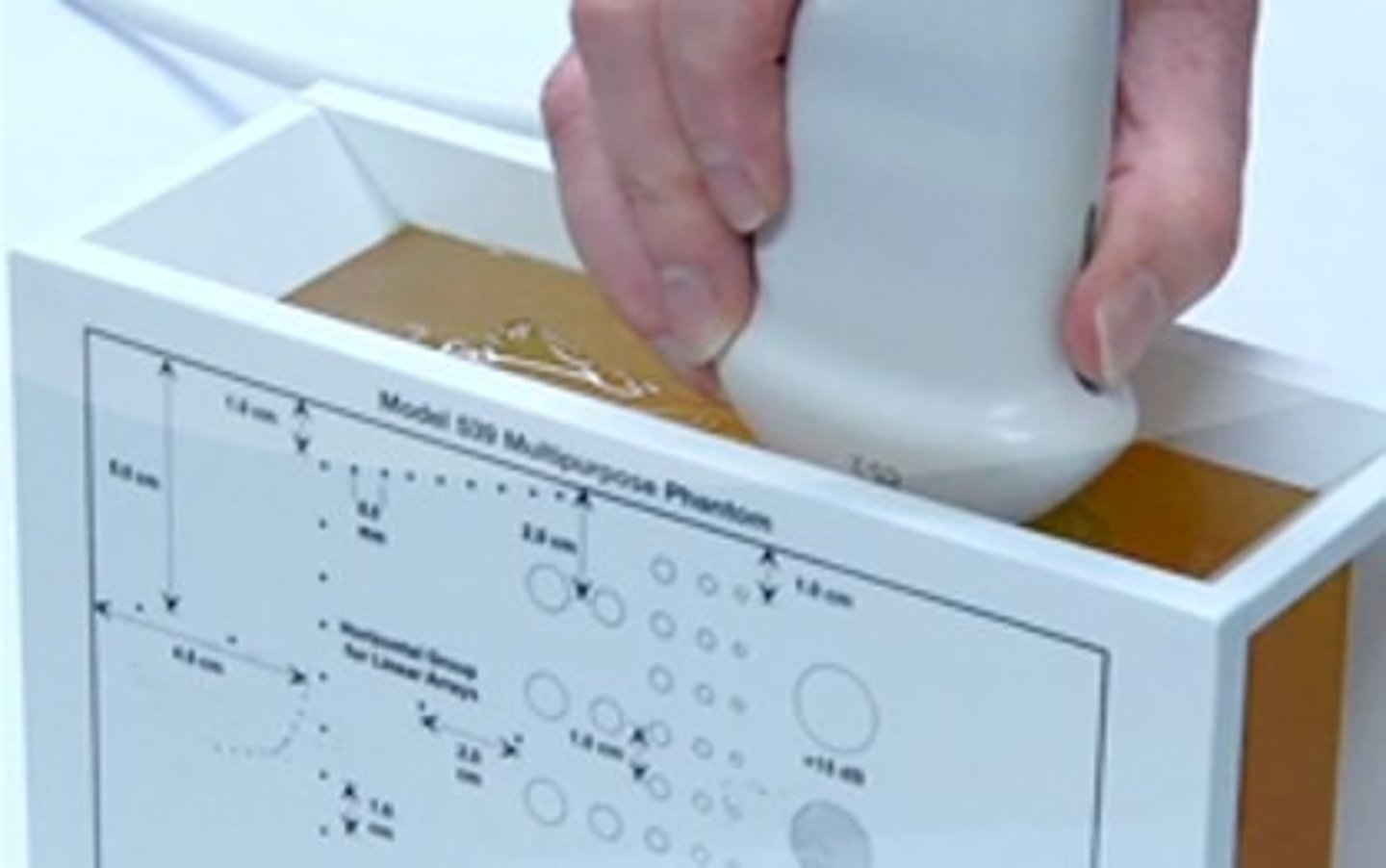

What is a slice thickness phantom?
the test object that evaluates the elevational resolution, or the thickness portion, of the sound beam perpendicular to the imaging plane
- a thinner plane equates to better spatial resolution
2 multiple choice options

What is a doppler phantom?
phantom use a physical moving structure, such as vibrating string, moving belt or a circulation pump to mimic blood flow in order to evaluate doppler properties
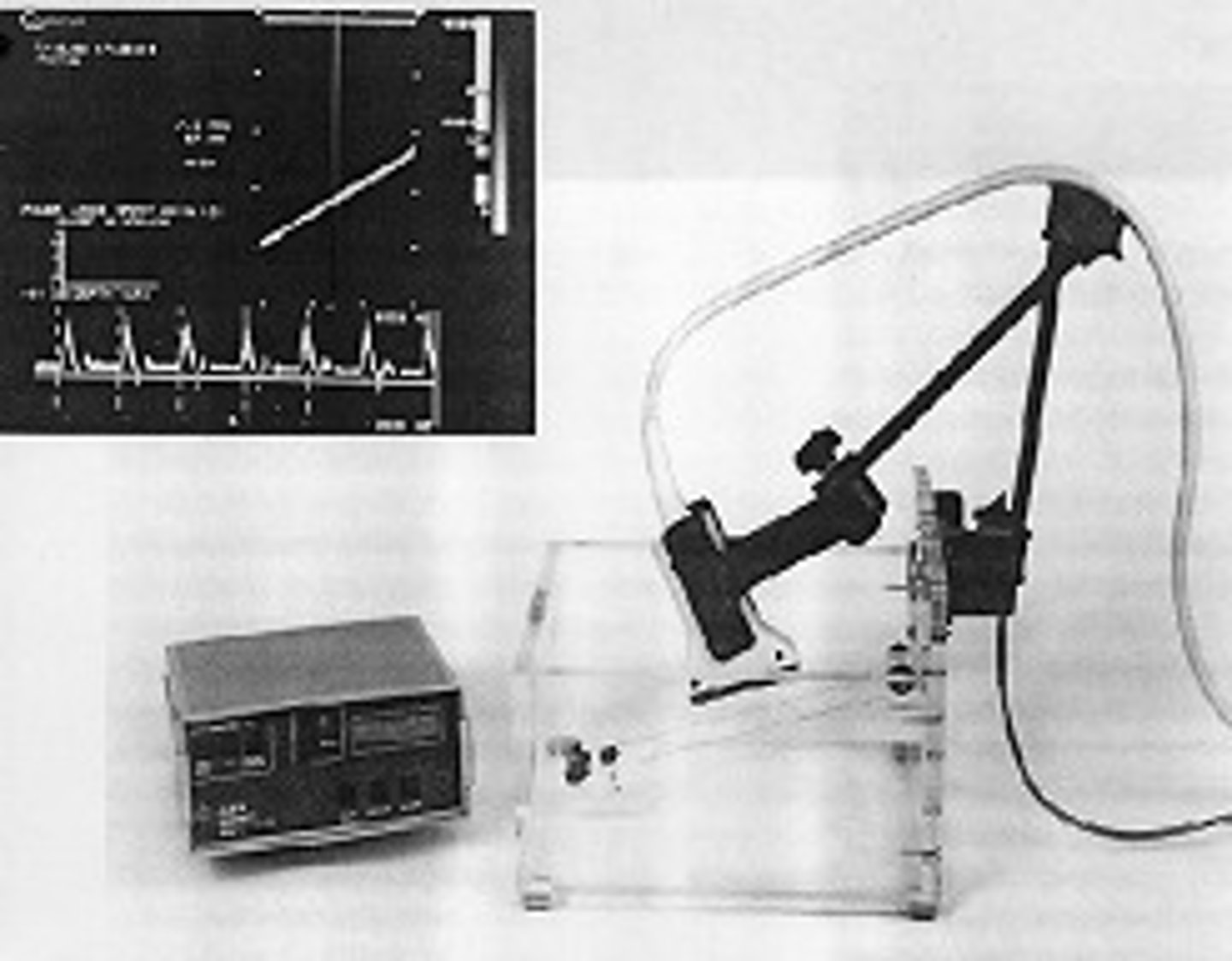

What does a doppler phantom test for?
all of the above (depth resolution, volume and velocity, & doppler angle)
3 multiple choice options
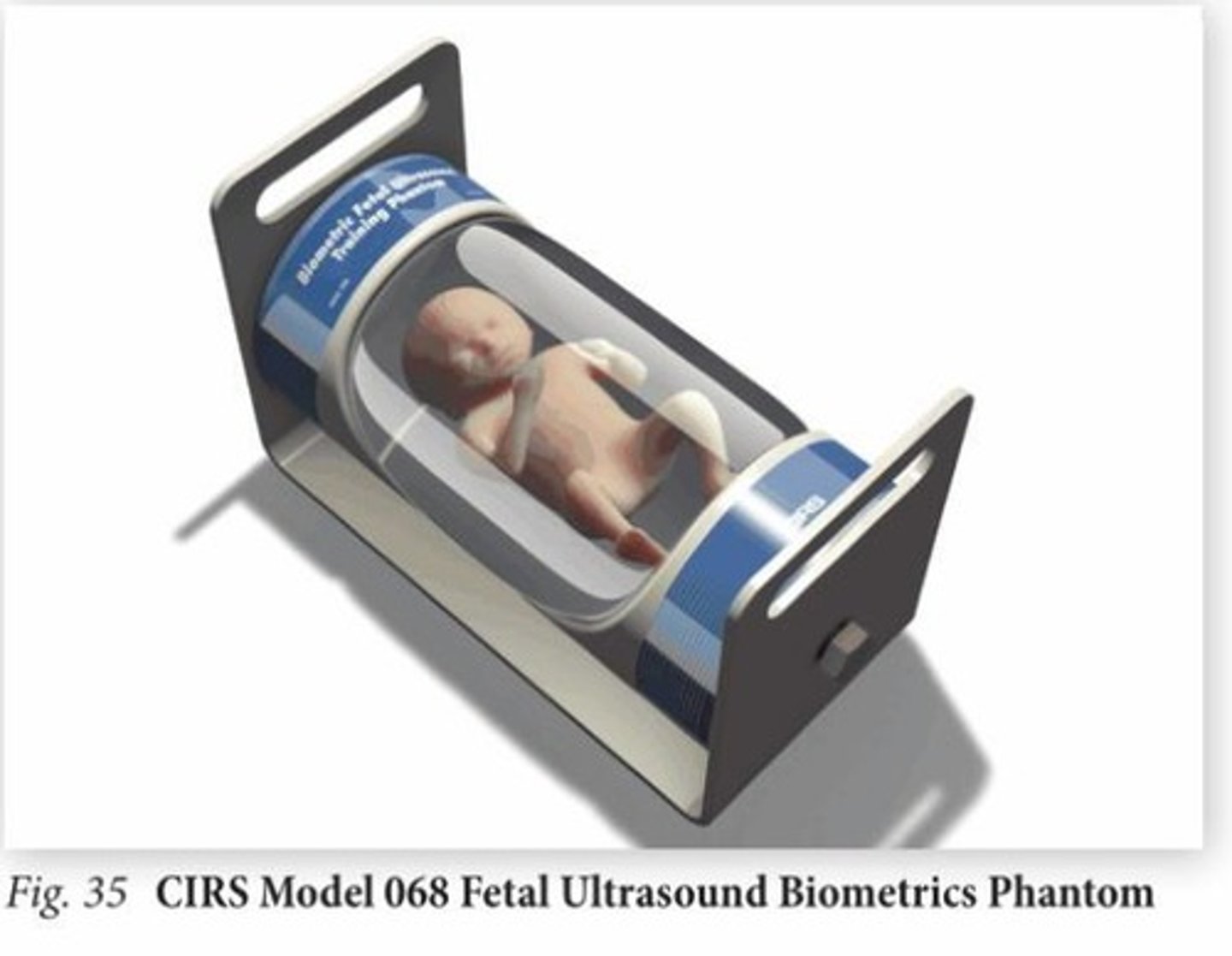
What is a fetal phantom?
phantom suspended in anechoic fluid allowing for simulated fetal assessment
- marked to 21 week gestational age for consistency
What is the 'gold standard' in QA?
the most accurate test for a particular study, assumed to be perfect
1 multiple choice option
How is a chi square used for QA?
ultrasound is compared with a gold standard test on a 2x2 table to determine true positive, false positive, true negative, or false negative
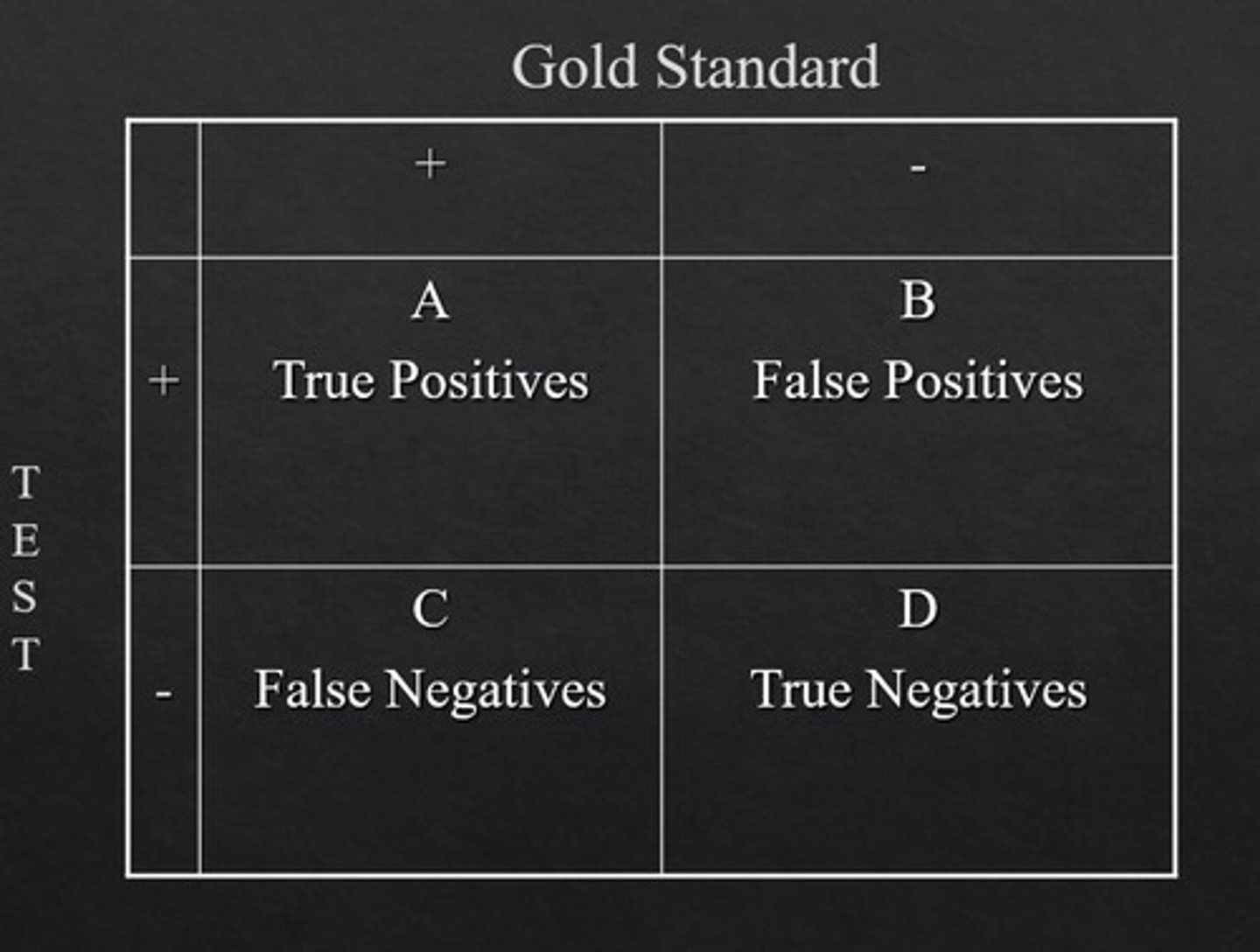
What is a true positive?
when both the test and the gold standard indicate a positive result (disease present)
3 multiple choice options
What is a true negative?
when both the test and the gold standard indicate a negative result (no disease present)
3 multiple choice options
What is a false positive?
when the test incorrectly indicates a disease present (positive) but the gold standard states it is negative
2 multiple choice options
What is a false negative?
when the test incorrectly indicates no disease (negative) but the gold standard indicates it is positive
3 multiple choice options
What is the positive predictive value?
Measures likelihood that a positive non-invasive exam is correct when disease is present (as a percentage)
3 multiple choice options
What is the negative predictive value?
Measures likelihood that a negative non-invasive exam is correct when no disease is present (as a percentage)
3 multiple choice options
What is accuracy?
How effective a test is at determining positive and negative results
3 multiple choice options
What is prevalence?
percentage of a population having a specific disease at a given time
3 multiple choice options
What is sensitivity?
the test's ability to find positive exams when there is a problem (TP/(TP +FP))
3 multiple choice options
What is specificity?
the tests ability in deciding an a normal exam (TN/(TN+FP))
3 multiple choice options
What speed do echoes return at with harmonics?
double the transmitted/fundamental/operating frequency of the transducer
3 multiple choice options
What is tissue harmonics?
harmonic signals from tissue particles
2 multiple choice options
What is contrast harmonics?
harmonic signals from microbubbles introduced into the body via a contrast agent
2 multiple choice options
What is contrast agent?
a liquid that is injected into the body intravenously and is used to enhance tissue echogenicity
Where is harmonics best utilized?
midfield
3 multiple choice options
What is pulse inversion?
When a second harmonic frequency is used instead of the starting harmonic frequency
- second harmonic frequency is double the initial frequency
True of false: harmonics is produced during reception, not transmission?
False
What is high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) and high intensity therapeutic ultrasound used for?
high powered ultrasound beams used to target specific areas of tissue
What is the effect of CW on targeted tissue in HIFU?
raised temperature, hyperthermia, thermal coagulation, and tissue necrosis
What is the effect of PW on targeted tissue in HIFU?
micro circulation, increased membrane permeability, and stable cavitation
Why is HIFU used?
all of the above (focal drug delivery, destroying tumor tissue, and destroying fat tissue)
3 multiple choice options
What are 3 specific uses for HIFU?
-uterine fibrosis
-liver cancer
-prostate cancer
True or false: Use of harmonics requires a narrow bandwith?
False
1 multiple choice option
Why is harmonics less effective in the farfield than the midfield?
the harmonic frequency attenuates faster than produced
What are some advantages of harmonic imaging?
- clutter reduced
- reverberation artifact reduced
- improved signal to noise ratio
- improved lateral resolution
What are some disadvantages of harmonic imaging?
- reduced axial resolution
True or false: The narrower the beam, the better the harmonics?
True
1 multiple choice option
How much does contrast increase blood tissue signal?
30 dB
3 multiple choice options
What are some uses for HIFU still under research?
- arthritis
- breast tumors
-glaucoma
-hyperparathyroidism
-neurological
What is static elastography?
tissue compression by ultrasound utilized to see the effects of pressure on the designated area
2 multiple choice options
What is dynamic elastography?
tracking of vibrating sound waves through tissue
2 multiple choice options
What is transient elastography?
tracking of a singular vibrating sound wave through a tissue
2 multiple choice options
What kind of elastography is best for breast ultrasound?
static elastography
2 multiple choice options
How is elastography evaluated in greyscale
soft tissues are brighter and harder tissues are darker